SLHS 580 Unit 3 Test(final)
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
Three parts of the WHO model(world health organization)
impairment, disability, handicap
impairment
a problem with structure (function) of the body
disability
functional limitation with regard to an activity
handicap
an environmental factor preventing living of normal life
What does the ICIDH Model stand for?
International classification of impairment ,disability, and handicap
Three parts of the ICIDH model
structure/function
activity
participation
ICIDH model: Structure/function
functioning at the level of the body
ICIDH model: activity
functioning at the level of the individual, activity limitations they experience
ICIDH model: participation
functioning of a person as a member of society; involvement of people in all areas of life, and participation restrictions they experience
Developmental disorder
begins in childhood, lifelong impairments
Acquired disorder
develops after birth from external factors
Acute acquired disorder
sudden onset, recovery is possible with rehab
Degenerative acquired disorder
gradual onset, progressive decline
Left hemisphere
responsible for language usage, processing auditory stimuli, detail oriented and analytical
Right hemisphere
visuospatial processing, attention, pragmatics; used for slow integration of information; holistic and big picture oriented
Frontal lobe lesion
Non-fluent speech (telegraphic)
Omission errors Concomitant motor deficits
Relatively good comprehension
Temporal lobe lesion
Fluent speech maintained
Problems with open class words (nouns, verbs)/ semantic errors
Substitution errors (e.g., dog for cat)
Typically no motor deficits/but auditory deficits
Poor comprehension
What are some examples of developmental disorders?
autism, cerebral palsy, down syndrome
Accelerated aging
people with Down syndrome experience symptoms of aging at a much faster rate than people w/o Down syndrome • Symptoms begin by 40-50 years old
High prevalence of ________ in Down syndrome at earlier age
Alzheimers
30% of people with Down syndrome who are in their 50s
50% of people with Down syndrome in their 60s have Alzheimer's dementia
Developmental language disorders
can have a significant impact on participation and activity in adulthood, but limited research is available
Autism spectrum disorders
A more variable genetic basis and less available research makes it more challenging to predict patterns of aging
The first individuals were labeled with ASD in the 1940s - elders with this diagnosis are now present in the population
An estimated 1% prevalence across the lifespan
It is likely that as the elder population identified as autistic grows, more knowledge will become available.
ADHD
lifespan disorder, meaning that it does not go away, however some people do not get diagnosed until adulthood
Mild cognitive impairment
a stage between expected age-related cognitive decline and the pathological decline associated with dementia; includes issues with memory, language, thinking, and/or judgement o ADLs are not affected
Characteristics of MCI
Plaques and tangles
Small strokes or TIA
Shrinkage/atrophy of hippocampus
Enlargement of ventricles
What percent of individuals with MCI develop dementia each year?
10-15%
Pragmatics study
older adults with MCI show increased non-verbal communication strategies (e.g., pointing, gestures, increased eye contact, head nodding)
What is the greatest risk factor for dementia?
aging
Alzheimer's disease
most common form of dementia
Pathology - presence of plaques and tangles
key symptom is memory loss, also poor judgement/decision-making, planning, reasoning, changes in personality or behaviors
Vascular dementia
often co-occurs with other types of dementia
Pathology - stroke / cardiovascular disease
Dementia with Lewy bodies
Pathology - presence of Lewy bodies
Parkinson's Disease Dementia
Pathology - presence of Lewy bodies specifically in substantia nigra
Mixed dementia
more than one type of dementia pathology is present
Incidence
number of new cases in the population over a certain period of time
Increases with age
Prevalence
number of current cases at a certain point in time
Higher prevalence of women
Whole brain effects for Alzheimers disease
Cortex shrinks • Expanded ventricles • Weight decrease
Neuronal effects for Alzheimers disease
Plaques - deposit of amyloid in spaces between neurons. Interferes with neuron communication at synapses
Tangles - deposits from cell components within the neuron. Interferes with microtubules in the cell, preventing individual neuron communication and resulting in cell death
Microglia - immune cells that work to clear up plaques and tangles; can cause inflammation which exacerbates presence of plaques and tangles
Progression of Alzheimer's Disease
1) entorhinal cortex
2) hippocampus
3) inferior temporal regions, temporal pole
Braak Stages
based on brain symptoms at autopsy; tracks the development of tangles across the brain
Braak stages I and II
tangles in the entorhinal cortex
Braak stages III and IV
tangles spread to hippocampus
Braak stages V and VI
tangles spread to neocortex
Brain reserve theory
no direct relationship between amount of Alzheimer's pathology in the brain and the extent of behavioral symptoms
Plasticity
the brain's flexibility in adjusting to injury
Neurological brain reserve hypothesis
the size and structure of the brain allows some to absorb more injury before cognitive function is affected
Behavioral/cognitive brain reserve hypothesis
complex cognitive ability increases neural plasticity and ability to work around pathology
Diagnosis of Dementia: Three behavioral symptoms must be present
1) impairment in short term memory
2) impairment in another area of cognition
3) impairment in social/daily living
Diagnostic tools for diagnosing Dementia
Neuroimaging - PET Scan
Cerebrospinal fluid testing
Blood-based biomarkers
Clinical stages of Dementia
Stage 1 - no symptoms; subclinical stage
Stage 2 - encoding and storage of new memories affected; short-term memory loss; mood-related changes
Stage 3 - onset of mild dementia; difficulty with word retrieval, comprehension, recognizing people/faces; may wander and forget where they were going/get lost
Stage 4-5 - onset of moderate dementia; misinterpretation of events; paranoia/paranoid delusions
Stage 6 - onset of severe dementia; visual deficits; major changes in sleep, bladder/bowel control, personality
Stage 7 - very severe dementia; impairment of basic functions; aspiration pneumonia more likely; bedridden
Biomarkers of Dementia
Structural imaging-changes clear - no norms though!
Functional imaging- reduced glucose metabolism in memory areas - no norms though!
Molecular imaging - PET scan, PiB
Pittsburgh compound B (PiB)
radiotracer that binds to amyloid plaques, can only be observed through molecular imaging techniques like PET scan
Stroke is also known as ...
cerebrovascular accidents (CVA)
Risk factors for stroke
Men more at risk than women
Mexican Americans more at risk than non-Hispanic White Americans
Black Americans more at risk than White Americans
Ischemic stroke
blood clot blocks or plugs a blood vessel in the brain
Embolic stroke is a type of ...
ischemic stroke
Thrombotic stroke is a type of ...
ischemic stroke
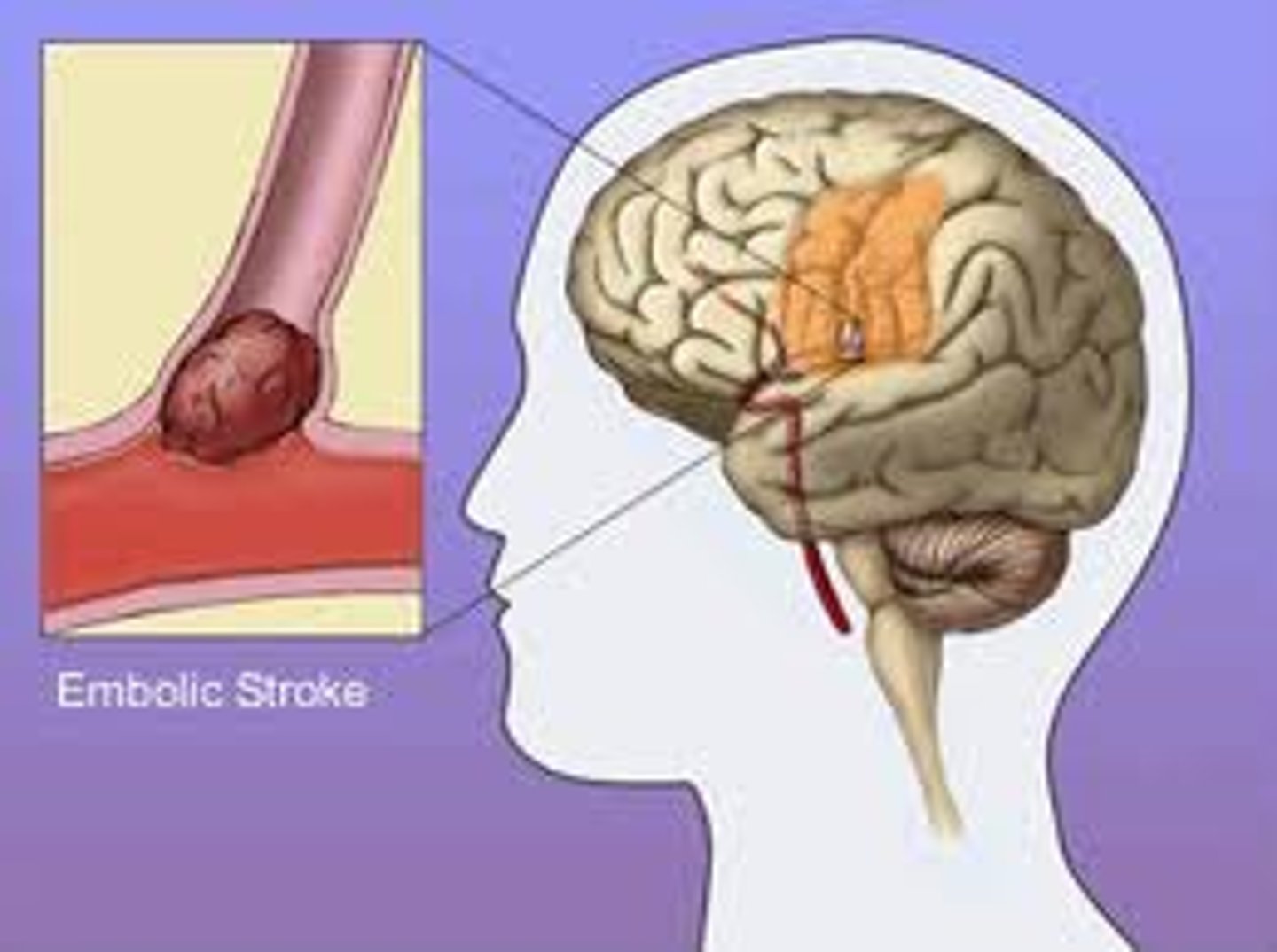
Embolic stroke
blood clot forms and travels through the bloodstream to the brain, the clot eventually lodges in a blood vessel and blocks the blood flow
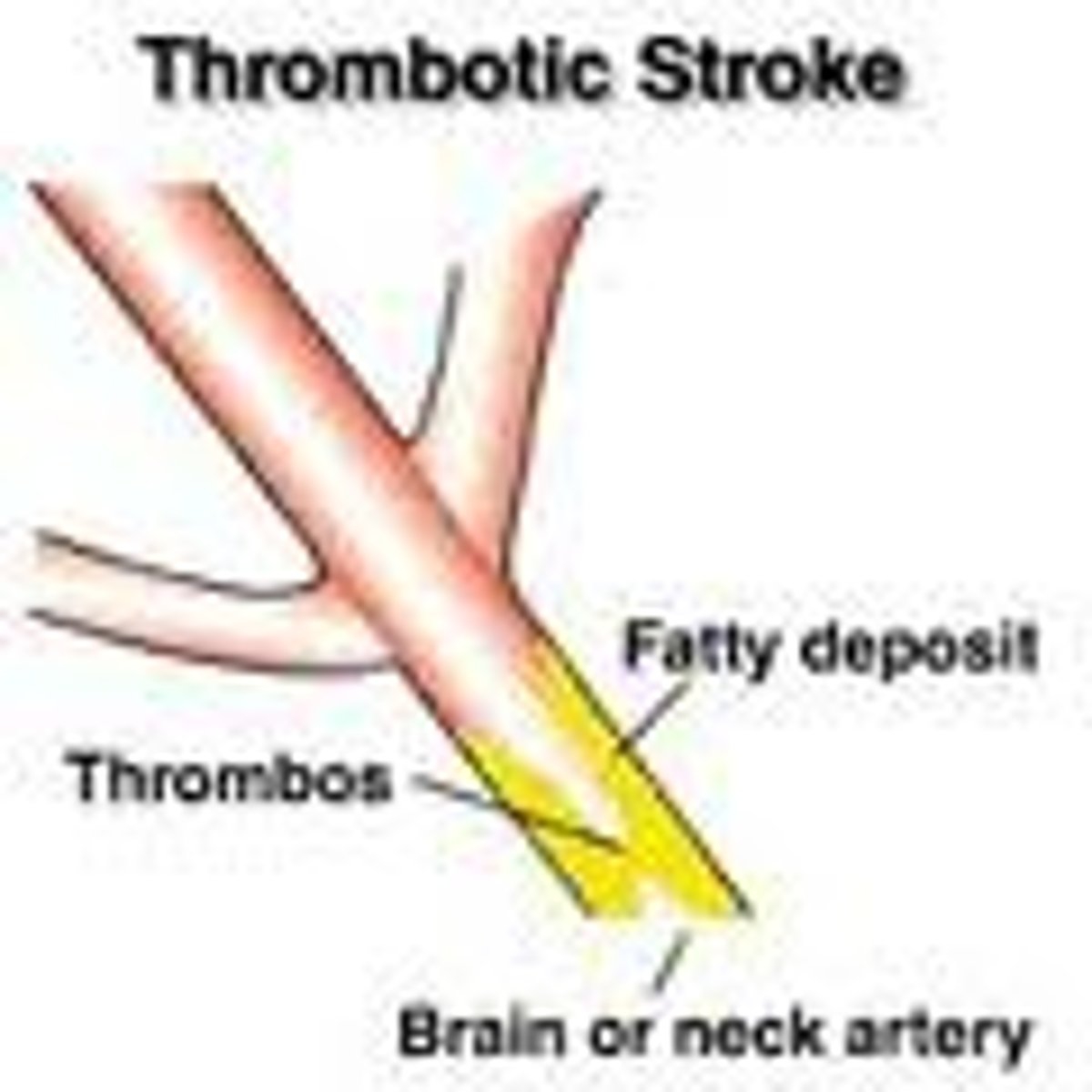
Thrombotic stroke
buildup of fatty deposits on the cell wall of the artery, impeding blood flow
Hemorrhagic stroke
a blood vessel in the brain breaks or ruptures
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
temporary ischemia that quickly resolves
Symptoms last less than 24 hours
Potential warning sign of impending stroke
Higher likelihood of having another TIA or stroke
Symptoms of stroke
Numbness/weakness on one side of the body
Confusion
Trouble speaking and/or understanding
Sudden vision problems
Dizziness or loss of balance
Severe unexplained headache
BE FAST acronym for stroke
B = balance
E = eyes
F = face
A = arms
S = speech
T = time
Experiential / phenomenological accounts
understanding the experience of living with a disorder
Atherosclerosis
fatty deposits form on the walls of blood vessels, restricting the blood flow to the brain
Puts pressure on the heart to increase the blood pressure
Arteries widen over time, thinning the walls and increasing the risk of rupture
Can lead to thrombosis
Can cause vascular dementia
High blood pressure / hypertension
Heart works harder to pump blood faster
Related to stress, hormones, diet
Increased force of blood on the artery wall over time Increased risk of heart attack
Stroke recovery stages
acute, subacute, chronic
Acute phase: stroke recovery
(hours and days post-stroke) frequent and rapid improvement, reduction in edema, reperfusion, neural plasticity
Subacute phase: stroke recovery
(weeks after stroke) neural re-organization is occurring
Chronic phase: stroke recovery
compensatory reorganization
What is an important factor in the likelihood of stroke recovery?
age
Aphasia
Language, but not intellect, is affected
Ischemic stroke is the highest cause of aphasia
Broca's Aphasia
NONFLUENT
Production
-Slow speech rate, lots of pausing
-Omits function words, mostly produces content words (telegraphic speech), content is still relatively meaningful -----Impaired naming, writing
Comprehension
-Intact for single words and simple sentences
-Impaired for complex sentences
Repetition
-Impaired, but better than production
Wernicke's Aphasia
FLUENT
Production
-Abnormally fluent speech, word salad
Intact grammar, but semantics is impaired
Speech contains paraphasias
Comprehension
-Impaired, also may not be aware that it's impaired
Repetition
-Impaired for words and sentences
Conduction Aphasia
Production
-Speech is fluent but contains articulation errors (e.g., transpositions)
Comprehension
-Auditory comprehension is spared
-Oral reading is poor
Repetition
-Impaired ability to repeat words, especially nonwords
Anomic aphasia
Production
-Usually fluent and grammatical correct, except for word retrieval problems (tip of the tongue)
Comprehension
-Good
Repetition
-Good
What are paraphasias?
speech errors
Phonemic paraphasias
substitution of one phoneme for another
Neologistic paraphasias
substitution of a nonword that is phonetically and semantically unrelated to the target word
Semantic paraphasia
substitution of one word for another
Primary progressive aphasia
a type of dementia that affects language networks initially
Socioemotional selectivity theory
the perception of time plays a fundamental role in the selection and pursuit of social goals
Knowledge-related goals
when time feels open-ended, more likely to plan for longterm goals
Emotion-related goals
when time feels short-term, more likely to make choices to feel good in the present
Positivity effect
older adults prefer positive information over negative information in tests of memory, attention, cognitive control, etc
Self regulation
the ability to identify, plan ahead, and avoid situations that may elevate negative affect, and stress
Older adults with better self-regulation skills show healthier aging process
Increased stress long term is associated with...
greater cognitive and physical health decline
Mayo Clinic study
looked at survival rates in people classified as optimists or pessimists; optimists showed a higher survival rate than pessimists
Nun study
sisters who showed higher positive emotional content in their autobiographies showed lower mortality in late life
Social isolation is linked to...
higher mortality rates, cardiovascular disease, depression/anxiety
Open family system
bigger social network and access to resources
Closed family system
more isolated social network and fewer connections to community; tend to be more vulnerable when significant health events occur
Is depression a normal part of aging?
NO, , but the most prevalent mental health issue in older adults
Older adults with PTSD often perform _______ on tests of processing speed, learning, memory, and executive function
worse
Do older adults with PTSG have a higher or lower rate of developing dementia than non PTSD?
higher
Post-pandemic resilience
Older adults showed lower rates of anxiety and depression during the pandemic than middle/younger adults
Older adults may be more resilient due to crystallized experience/perspective
Stages of chronicity
1. Shock
2. Realization
3. Denial
4. Mourning
5. Adaptation
What are the three models of counseling?
behavioral, humanistic, existential
Behavioral model
focuses on how past experiences influence present actions; uses positive reinforcement to support attainment of goals
Humanistic model
focuses on supporting feelings here and now, providing safe space to help individual express themselves
Existential model
focuses on supporting individual through understanding four concepts of life: death, responsibility (freedom), isolation/loneliness, and meaning of life