Unit 1 Vocabulary
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Absolute Direction
the exact direction a person is heading
Absolute Distance
the exact distance between 2 places or objects
Absolute Location
the exact location of an object, usually expressed in coordinates of longitude and latitude
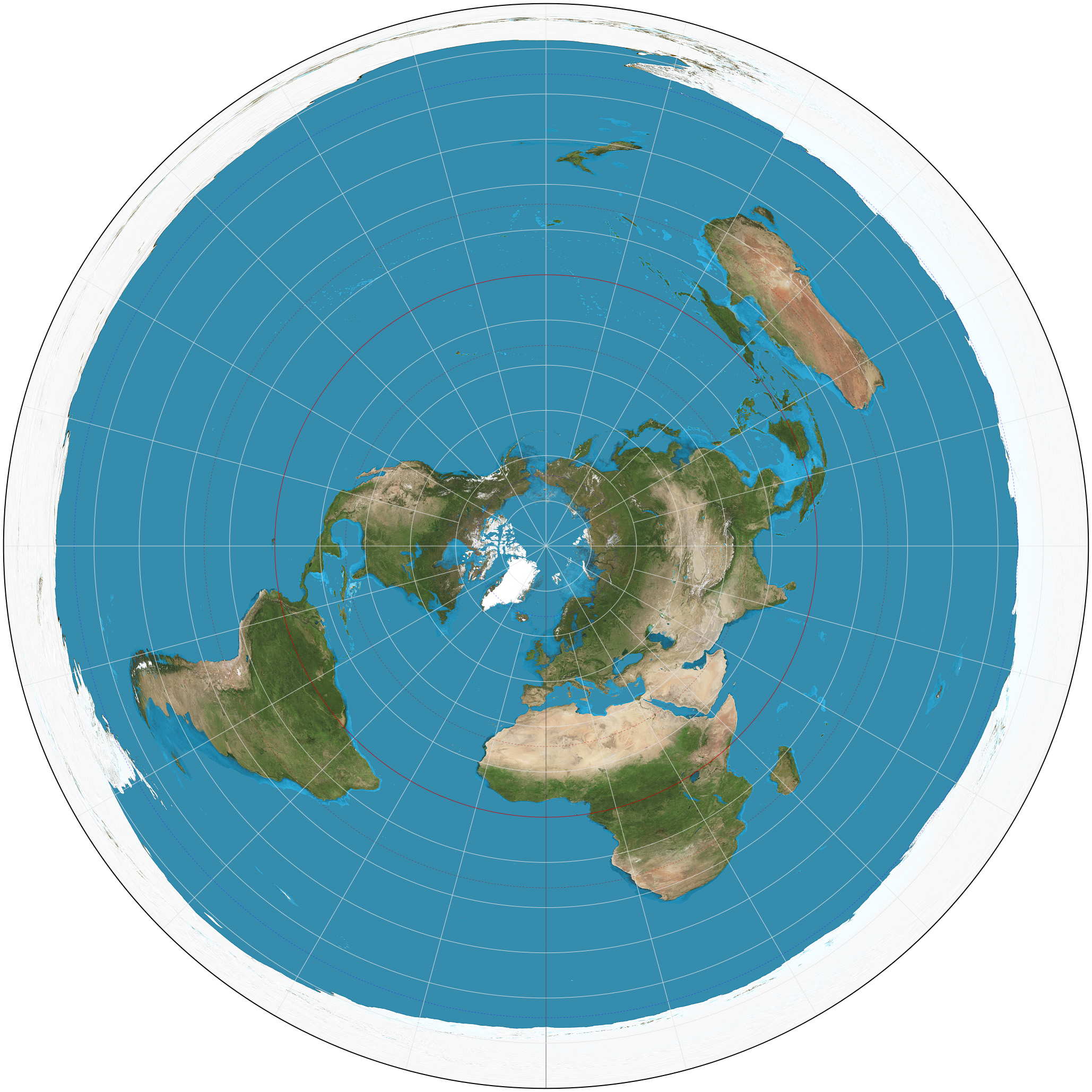
Azimuthal Projection
Can see polar areas with less projection
Advantage: true distance
Disadvantage: only see part of Earth at 1 time
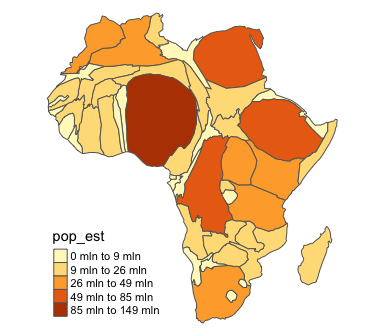
Cartogram
Show relative size of an area based on a particular attribute
Census
and official count of the number of people in a defined area, such as a state
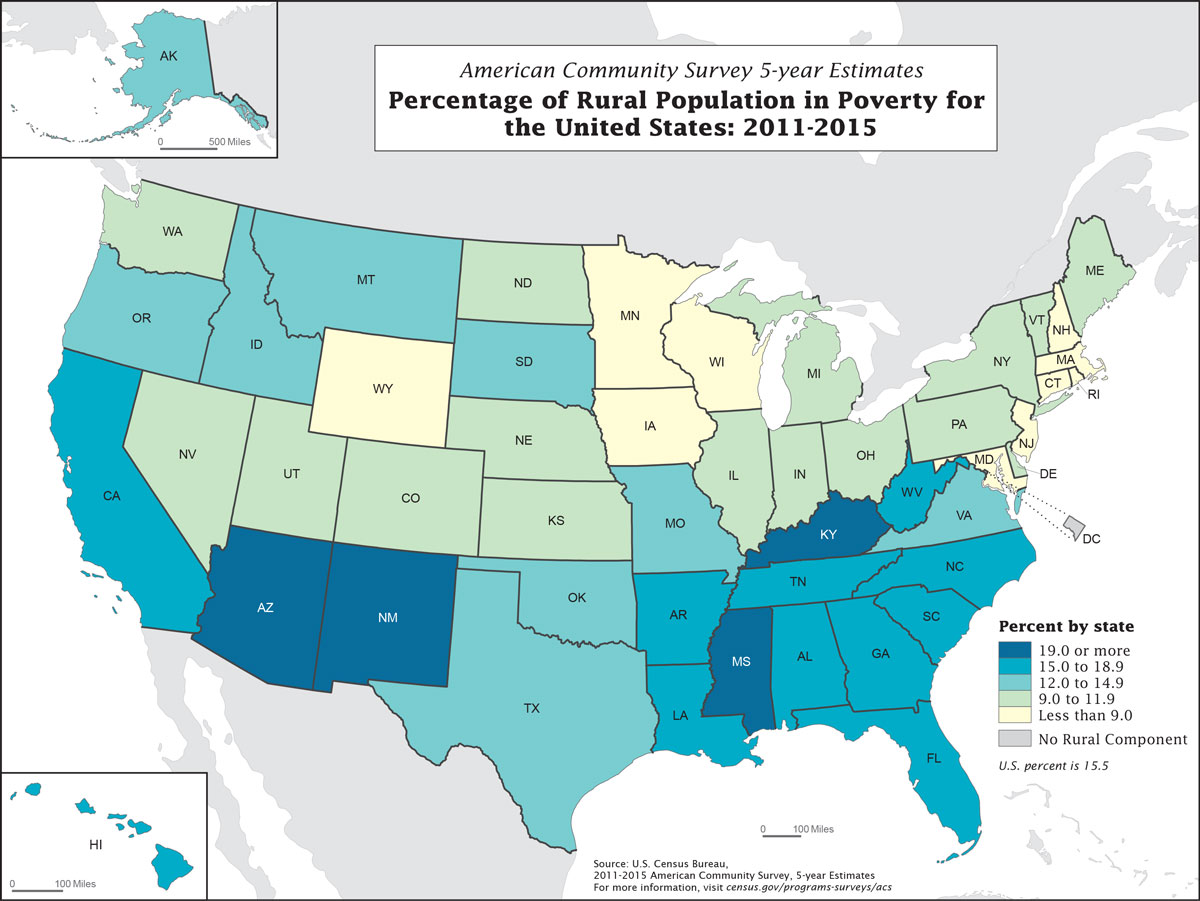
Choropleth Map
Uses colors or shading to represent categories of data
Clustered
close together

Dispersed
spread out

Distance Decay
the farther away one thing is from another, the less interaction the two things will have
Dot Map
dots are used to show location of specific observations or events.
Environmental Determinism
Human behavior is largely controlled by the physical environment.
COMPLETELY determines your culture
Flows
a movement of people, goods, or information that has economic, social political, or cultural effects on societies
Formal (Uniform) Region
defined boundaries and NOT up for debate
countries boarders
states/provinces
culture/languages
Functional (Node) Region
An area organized by its function around a focal point (node)
pizza delivery area, water tower, cell phone coverage
Perceptual (Vernacular) Region
type of region that reflects people's feelings about a place, up for debate
Geographic Information System (GIS)
a computer system that can collect, analyze, and display geographic data
Global Positioning System (GPS)
a network of satellites that are used to determine the location of something on the Earth’s surface
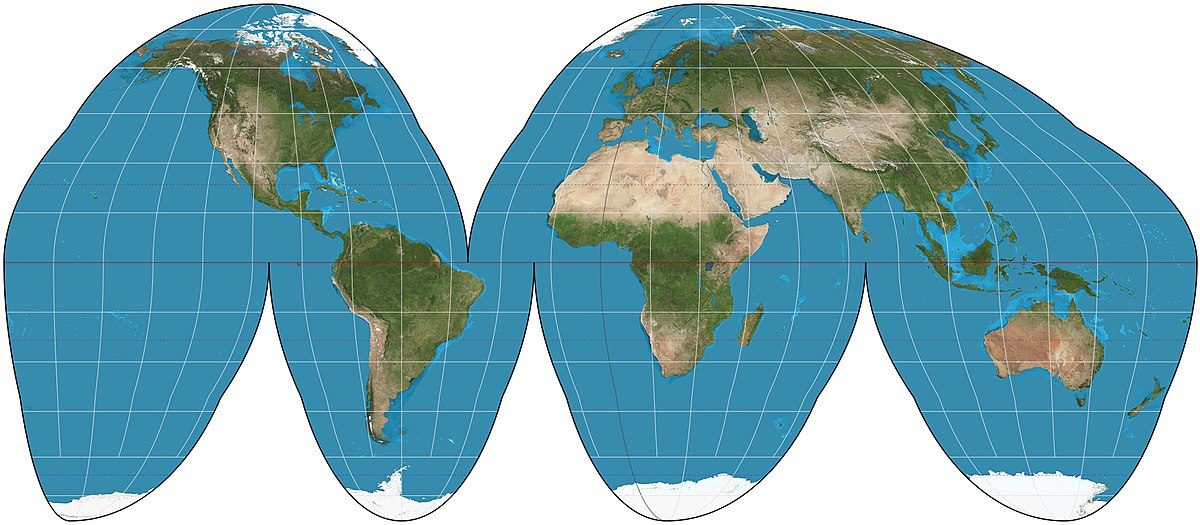
Goode-Homolosine Projection
Avoids shape distortion and the restrictions of a rectangular map
Creates “interruptions”
Advantages: shape & size
Disadvantages: distance
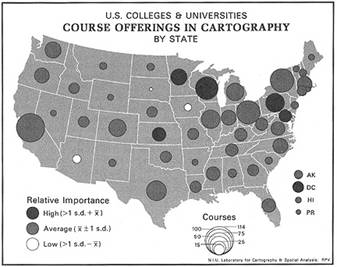
Graduated Symbol Map
Differently sized symbols are used to represent quantitative data
Grid Pattern
intersecting lines of latitude and longitude, typically used to describe road layout
Human Geography
the study of the processes that have shaped how humans understand, use, and alter Earth
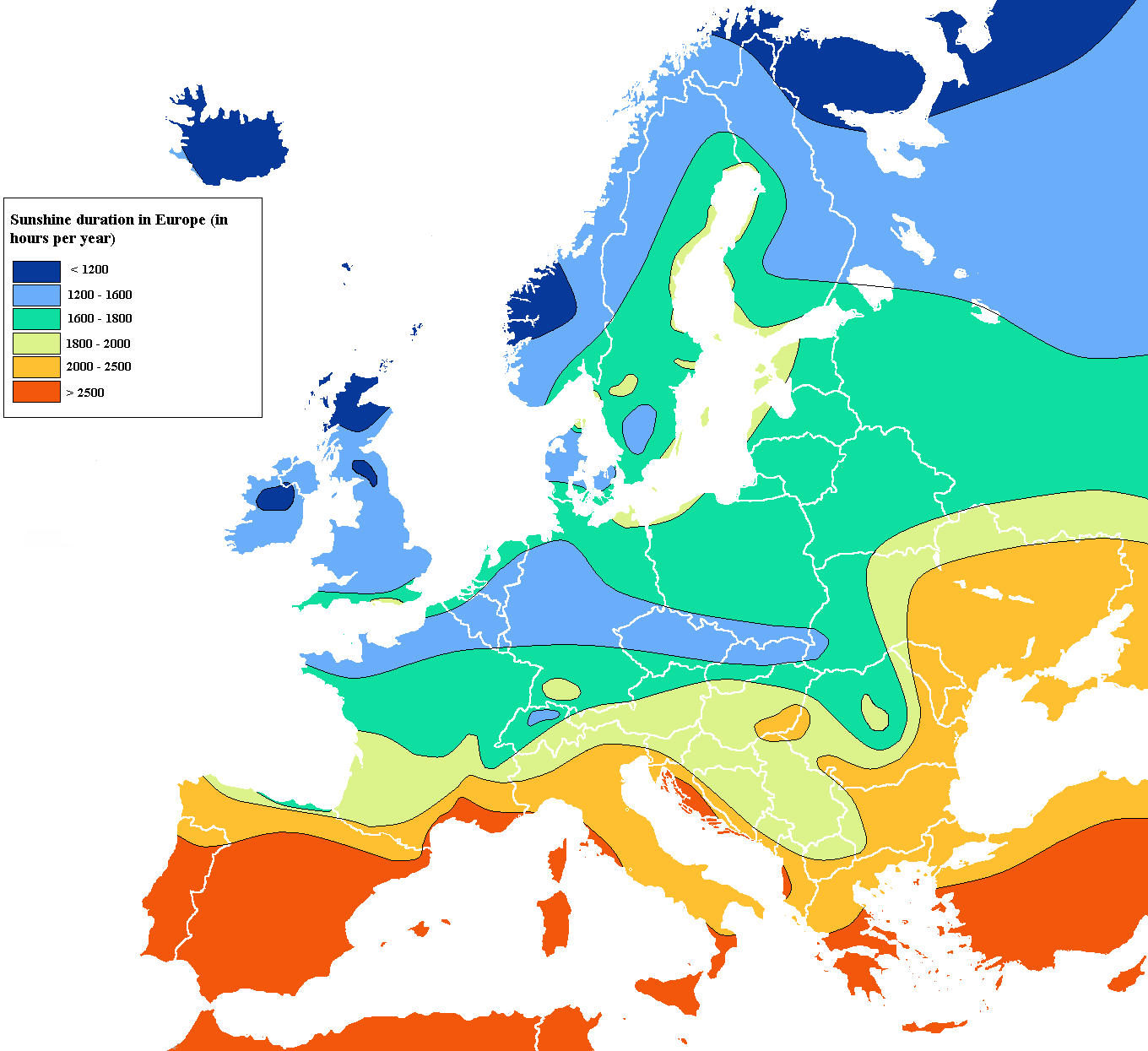
Isoline Map
Lines connect data points of the same value. Isoline maps are used to show particular characteristics of an area.
Linear Pattern
homes are clustered in a line, typically along a road or a river
Mercator Projection
Advantage: Direction
Disadvantage: land size (especially near the poles)
Purpose: for navigation across the ocean
*Massive Greenland, Massive Antarctica
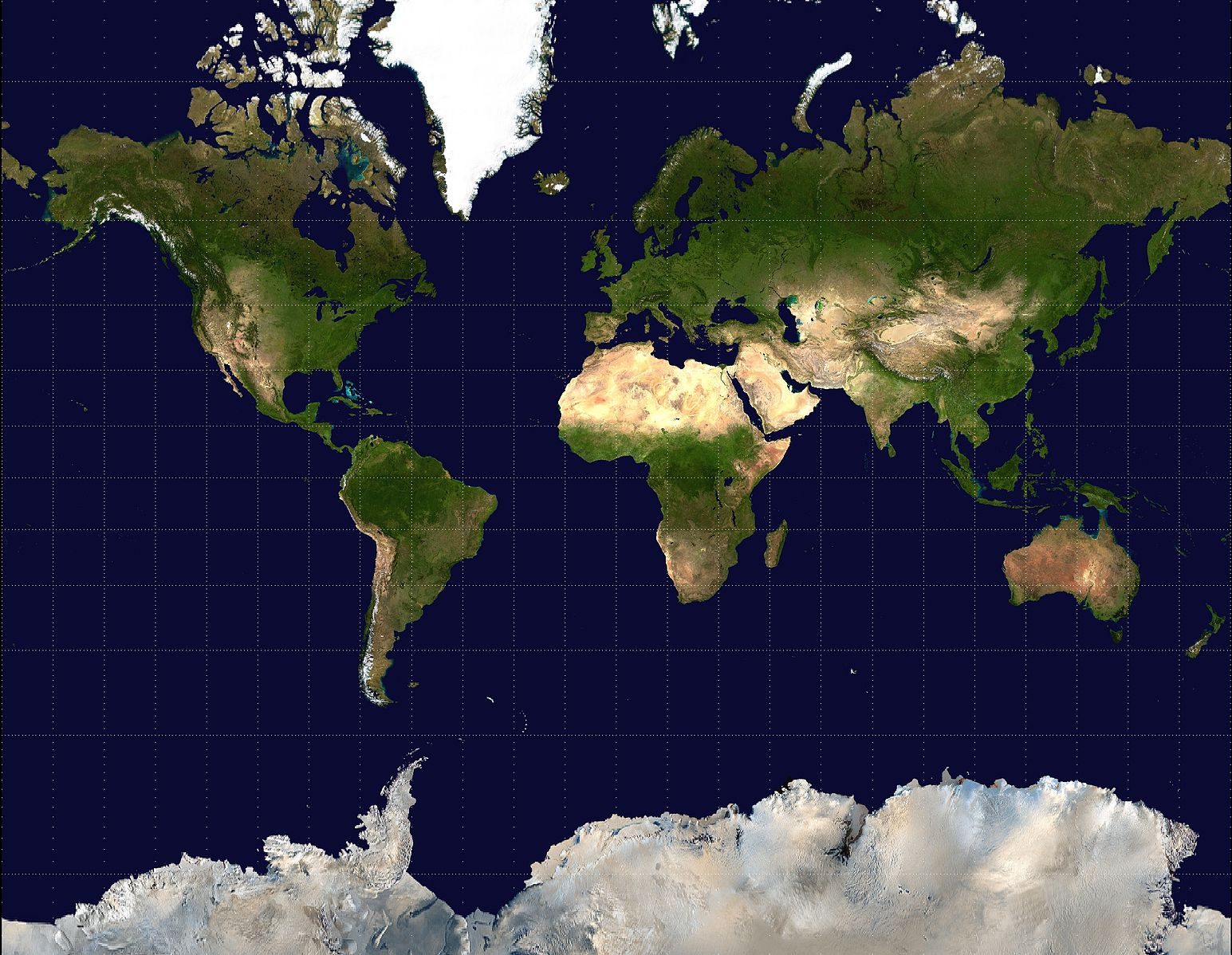
Peters Projection
Advantage: relative size/area
Disadvantage: shape (stretched and squished)
Wanted to correct Mercator’s mistakes
Place
a location on Earth that is distinguished by its physical and human characteristics; a unique location
Possibilism
The environment places some limitations on human activity, but societies have a range of options on how to live in said environment.
SOMEWHAT determines your culture
Qualitative Data
information that is often in word form, and is up for interpretation, debate, and discussion
Quantitative Data
information that is in number form, and is objective and not up for debate
Reference Map
an informational map that shows boundaries, names of places, and geographic features of an area
Region
an area of Earth's surface with certain characteristics that make it cohesive yet distinct from other areas
Relative Direction
the direction given in relation to another object’s current location
Pier 39 is located to the left of Chinatown
Relative Distance
the approximate measurement between 2 places
ex: The distance from Miami to Orlando is around 200 miles
Relative Location
a description of where a place is in relation to other places or features
ex: 50 miles west of Miami, Florida
Remote Sensing
a process of collecting information about the Earth’s surface from satellites orbiting the earth
Robinson Projection
Advantage: since all distortions are present, none of them are too bad
Disadvantage: all 4 distortions are present, so nothing is correct
Used in schools, because it is easiest on the eyes
Scale of Analysis
observation of data at the global, regional, national, or local
Site
its physical characteristics, such as landforms, climate, and resources
Situation
location of a place in relation to other places or its surrounding features
Spatial Analysis
the process of analyzing patterns and relationships within an area or geographic data
Thematic Map
a map that displays spatial patterns of places and uses quantitative data to display specific topics
Time-Space Compression
the reduction of time it takes for something or someone to get from one place to another
Large Scale Map
LARGE amount of DETAIL
ex: maps of your school, local town/city, a county
Small Scale Map
SMALL amount of DETAIL
ex: maps of the world, continents, large states