Cell Membrane and Transport / Transport in Humans (Biology H)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Cell membrane/ Plasma Membrane
a lipid bilayer made up of phospholipids
A phospholipid is made up of ______ heads and ____ tails.
hydrophillic, hydrophobic
Cell membrane’s function is to _____ what enters and leaves the cells, while ___ and ___ the cell.
regulate, protecting, supporting
What are examples of what the cell membrane lets in vs. what it lets out?
food in water goes in, waste goes out
The cell membrane is vital to helping maintain _____.
homeostasis
Homeostasis is having a relatively constant internal ___ and ____ conditions (happy and balanced)
physical, chemical
The cell membrane is _______, meaning that some substances can pass and others cannot,
selectively permeable
Example of cell membrane being selectively permeable? (particles that can enter, others that cannot)
**Small molecules (water, O2, CO2) can pass through freely but large charged particles such as proteins, sugars, and ions cannot
Membrane has ______ embbeded and ___ sometimes attached. These can move or float within the membrane, so the membrane is said to be a __________.
proteins, carbohydrates, fluid mosaic model
What does Fluid Mosaic Model mean? Proteins embbeded in the __________ move around and “float” among the lipids - _____. Many different kinds of ____ make up the cell membrane - ____.
lipid bilayer, fluid, molecules, mosaic
___ will help some ____ or ___ molecules pass through the membrane.
proteins, larger, charge
Integral proteins: __________ proteins; some function in ____ (facilitated diffusion or active transport), or ____ like ATP synthase, receptors, or cell to cell contact/communication like forming ____ and ______.
transmembrane, transport, enzymes, tissues, organs
Peripheral proteins:____ the membrane at the surface - often ____, some play a role in cell ____.
bind, enzymes, shape
Glycoproteins: sugars attached to ____ in ____. Some are ____, or cell to cell communication.
proteins, membranes, receptors
Carbohydrates act as ____________ - help cells identify each other
chemical identification cards
Cholesterol (lipid) is used to keep the membrane ____ - ***at some temperatures, the fatty acids of the phospholipid can __________, so the cholesterol prevents them from packing too tightly so molecules can still ____.
fluid, pack together, pass
Glycolipids: sugar molecules attached to _________ - usually _______ -signaling other cells, or ___________ like cholesterol.
phospholipids, outer surface, chemical messengers
Molecules need to be _________ in and out of the cell
transported
Passive transport: molecules that can pass ____ through the _____ from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration
freely, membrane
Concentration is the amount of solute vs solvent
High concentration = more ____
Low concentration = less _____
solute
____ IS REQUIRED in passive transport - just ____
NO ENERGY, happens
3 types of passive transport
___, _______, ______
Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, Osmosis
Diffusion: process by which particles move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration, ____ needed. Once particles reach _______, particles will move in ______.
NO ENERGY, equilibrium, BOTH directions
_________ forms when there are ____ amounts of molecules on either side of a membrane
Concentration gradient, differing
In a mixture, molecules move _____________ towards equilibrium
down its own gradient
A Larger gradient = _____ diffusion!
Creates ____________
___________ can form when ions diffuse (like nerve impulses!)
faster, potential energy, electrical energy
Facilitated Diffusion: diffusion in which __________ molecules need assistance from a _________ to move down its concentration gradient. HIGH TO LOW, ________ NEEDED. ***Still passive transport, molecules move from an area of high concentration to low concentration, but they need some assistance to pass the selective cell membrane
large or charged, protein channel, NO ENERGY,
Osmosis: movement of_____ across a membrane by _________ (uses protein aquaporin)
water, facilitated diffusion
Osmosis is moving ____, not _____
water, solute
Osmosis: _____ NEEDED (still _____transport!)
no energy, passive
Hypertonic solution: many ____, little ____ (Cell SHRIVELS/SHRINKS)
solutes, water
Hypotonic solution: little ___, lots of ____ (Cell SWELLS (can burst))
solutes, water
Osmosis: Water will move from a _____solution to _____ solution
Water moves from a greater concentration, to where there is a lesser concentration
HYPOtonic, HYPERtonic
Isotonic solution: equal concentration of __ and _ on both sides of the membrane (— of osmosis!!!)
water, solutes, end goal
Water moves in the direction where there is ___ (salt, sugar), and therefore a _____ amount of water. A simple rule to remember: SALT SUCKS!!
solute, lesser
Salt is a _____, so when it is _____ inside or outside the cell, it will draw the water in its direction – i.e. “suck” the water in or out. This is also why you get thirsty after eating something salty.
solute, concentrated,
Pressure is exerted on the _______ side of the solution (___ solute)
hypertonic, more
Cells are filled with salts, sugars, proteins, so it will be ____ to freshwater
hypertonic
When a cell is placed into water (_____ solution), water moves into the cell and could cause it to ___ (cytolysis)
hypotonic, burst
When the cell is placed into a ______ solution, water leaves the cell and it will ____ (plasmolysis)
hypertonic, shrivel
Plant cells have ____ to prevent ______
cell walls, plasmolysis
Active transport: movement of substance ____ its concentration gradient. Moving from an area of LOW concentration to HIGH concentration. REQUIRES ______. Usually need the help of a _____ or a ______ to cross the membrane
against, ENERGY, transport protein, protein pump
Naturally, our cells contain ___ concentrations of sodium and ____ concentrations of potassium
low, high
Sodium-Potassium Pump moves sodium ______ cell and takes _____ into the cell
out of the, potassium
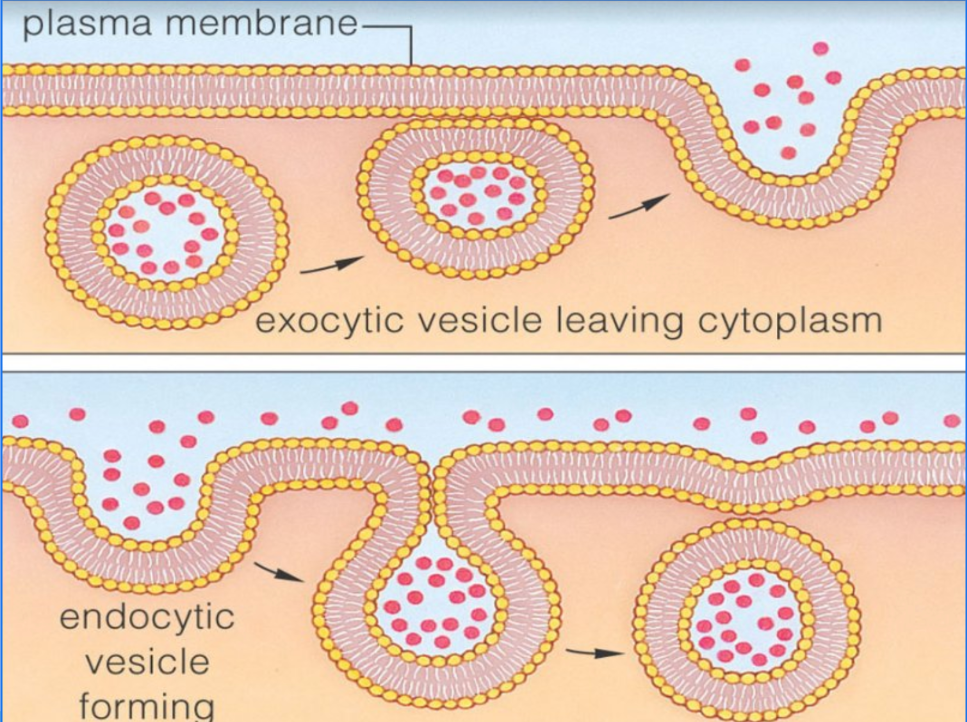
Endocytosis:
process of taking materials into the cell through infoldings, or pockets, in the cell membrane
Endocytosis: Cells _______ to do this - ____ transport!
USE ENERGY, active
How does Endocytosis occur in cells? The pocket will _____ inside the cell and _________.
break free, form a vacuole/vesicle
Phagocytosis
cell engulfs large solid particles and pinches into cell forming food vacuole (CELL EATING)
Pinocytosis
tiny pockets form along the cell membrane, fill with liquid, and pinch off to form vacuoles filled with liquid (CELL DRINKING)
Exocytosis
release of large amounts of material out of the cell
Exocytosis: Cells _______ to do this - ____ transport!
USE ENERGY, active
Exocytosis: How does it occur in cells?
The membrane of a vesicle/vacuole will fuse with the cell membrane and release its contents outside of the cell.
Diffusion occurs in many places in the body: Some examples are diffusion of ____ in ______ system and diffusion of ____ from ___ to _____ in digestive system
gases, respiratory
nutrients, intestines, bloodstream