L24 The Vestibular System (Imported from Quizlet)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Which way is up? and where am I going?
What 2 questions does the vestibular system answer?
Keeping our eyes still as we move, maintaining our upright posture, our ability to perceive our own movement within space
What does the vestibular system contribute to?
Inner
Which part of the ear is the vestibular system?
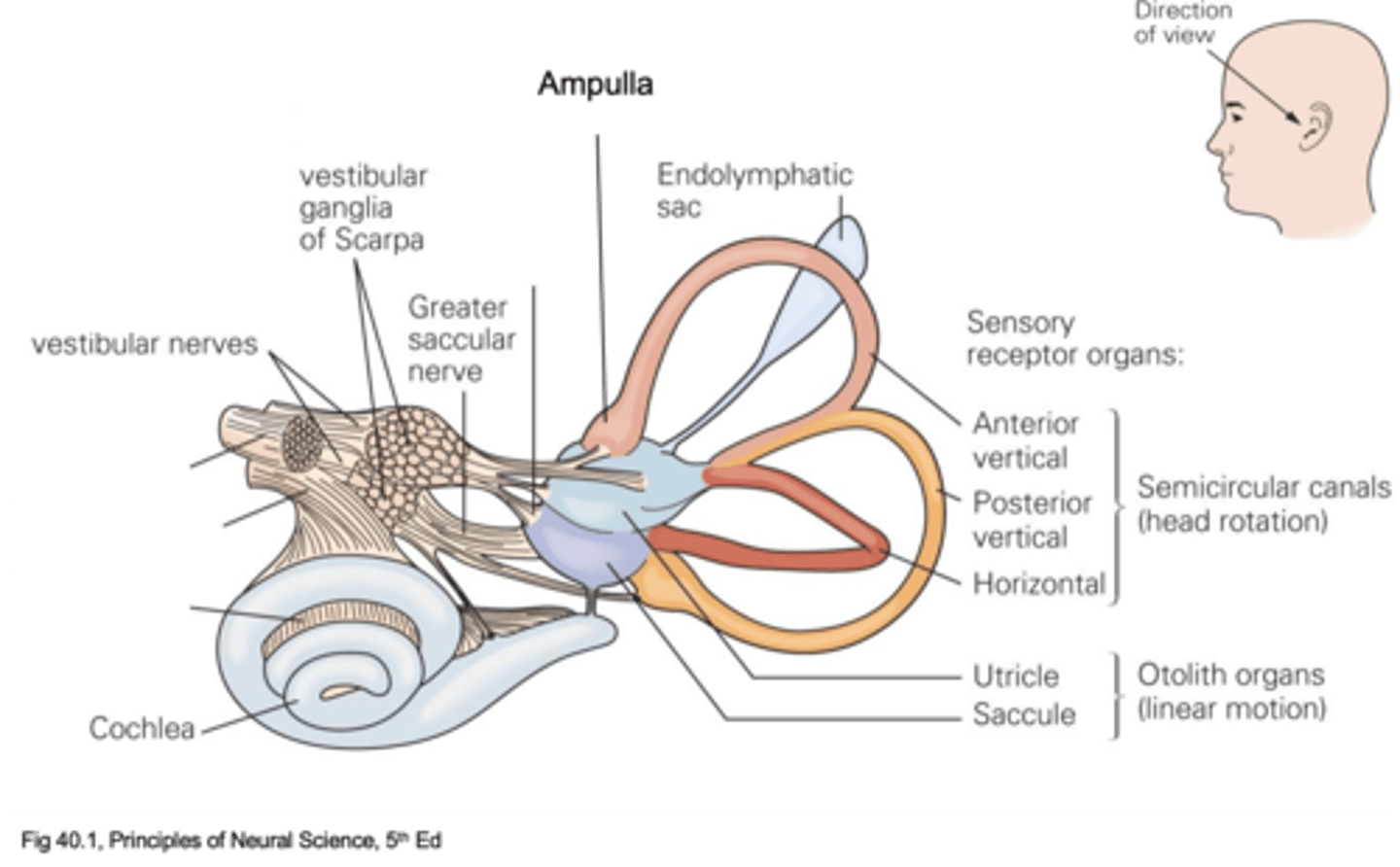
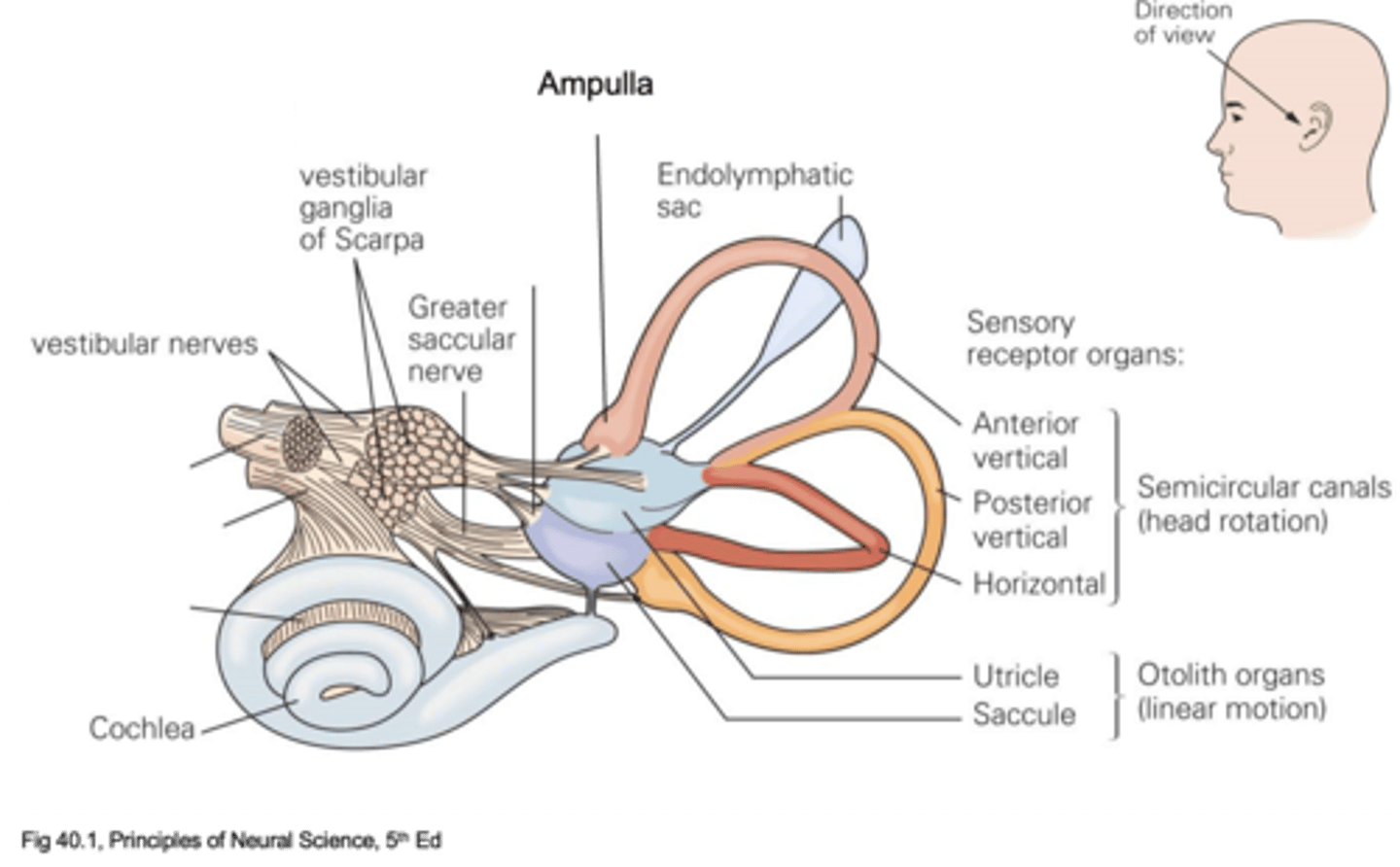
Semicircular canals and otolith organs
What are the 2 main anatomical structures of the vestibular system?
Head rotation
What do semicircular canals detect?
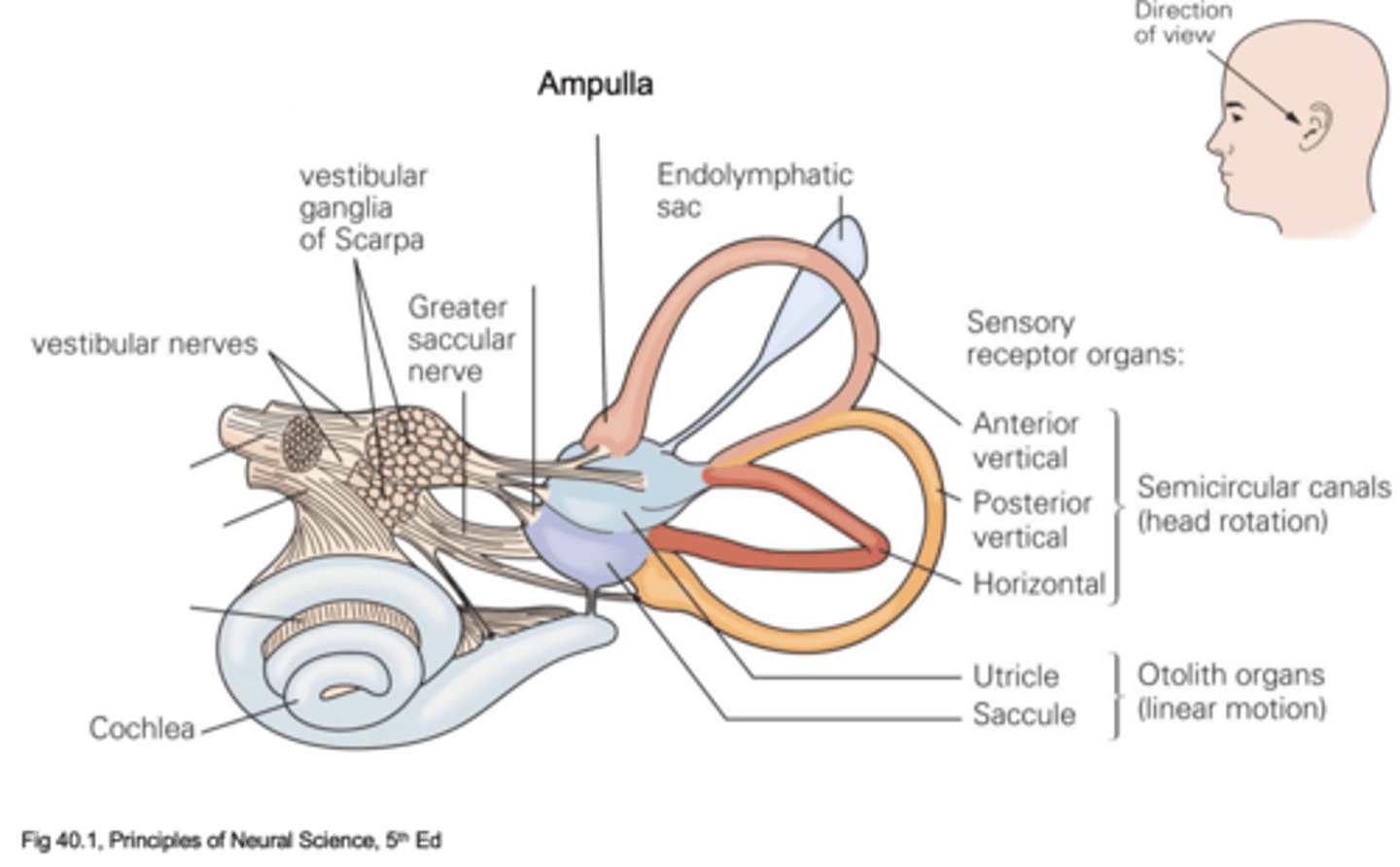
Anterior vertical, posterior vertical and horizontal - all for different types of rotation
What are the different types of semicircular canal and what do they do?
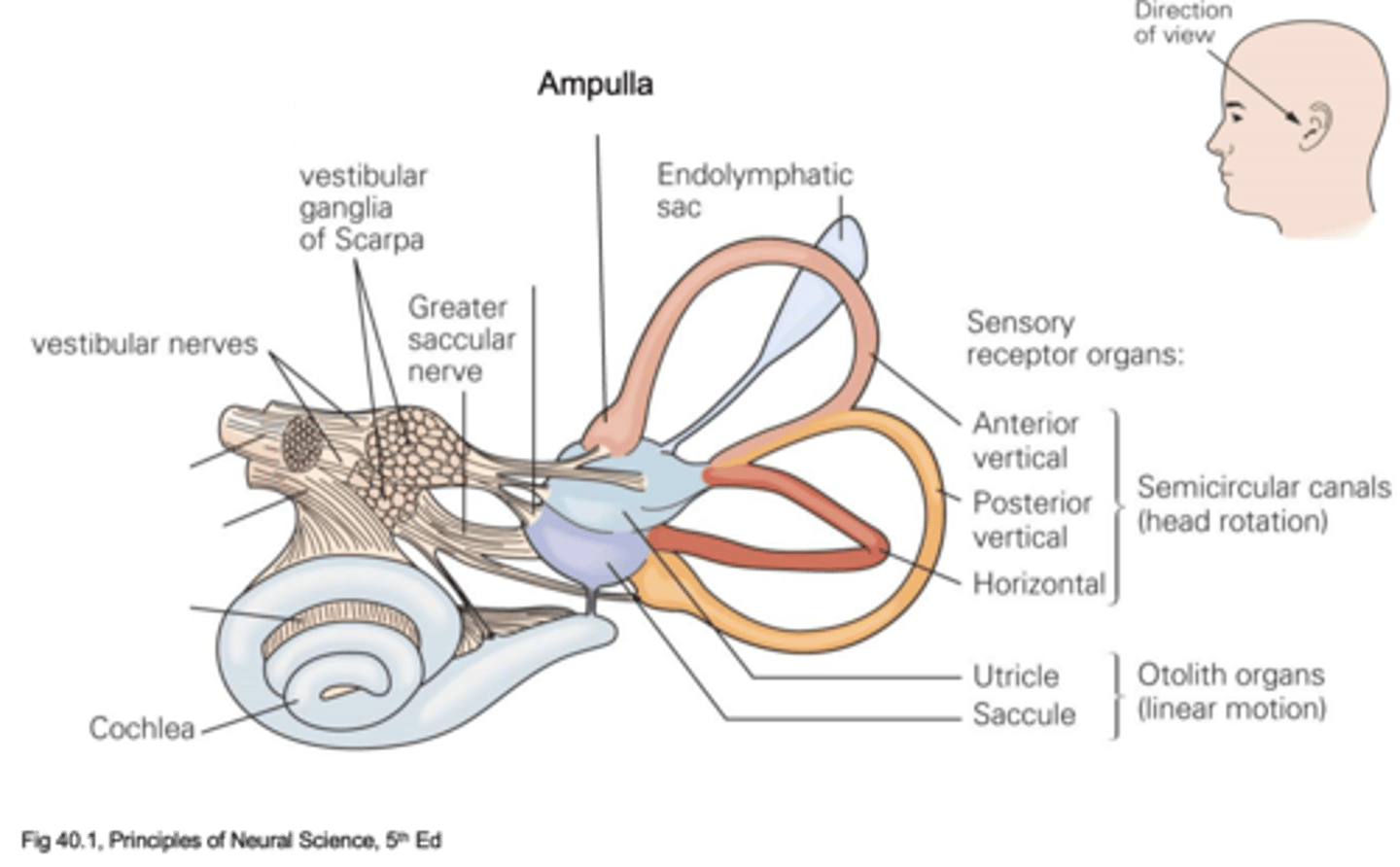
Wide openings called ampulla
What is at the ends of the semicircular canals (where mechanotransduction machinery is found, hair cells)
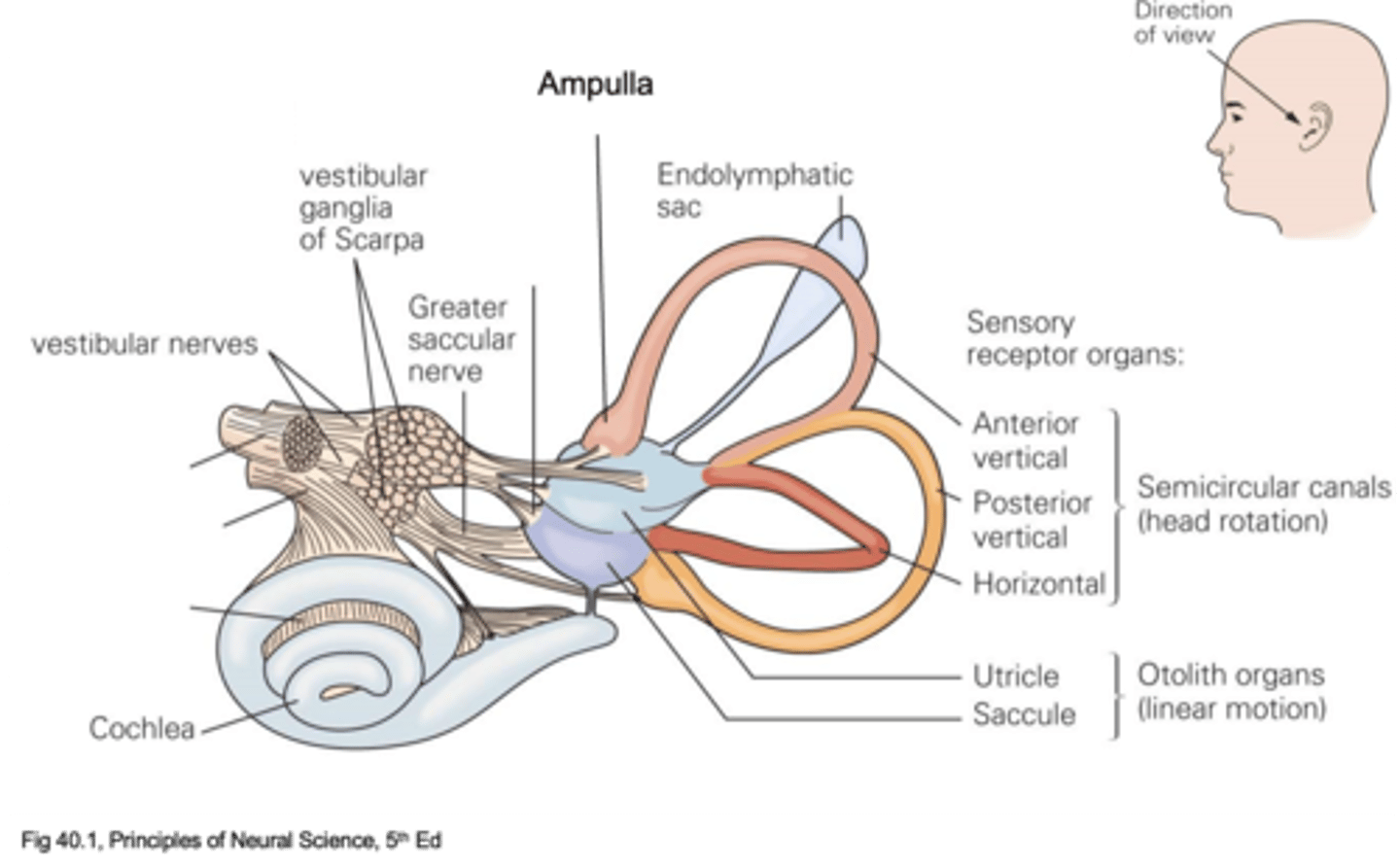
Linear motion
What do otolith organs detect?
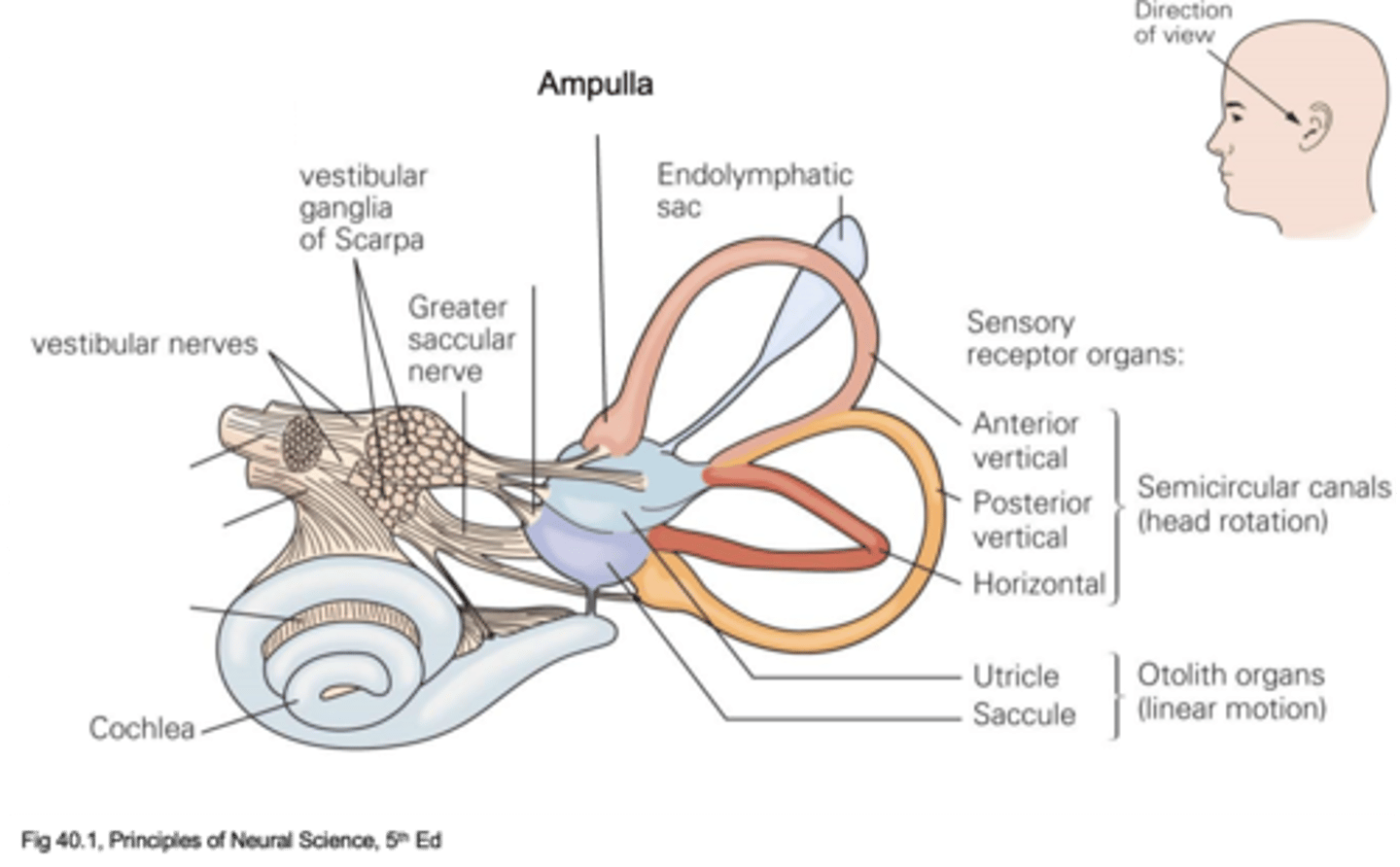
Utricle and saccule
What are the 2 parts of the otolith organs?
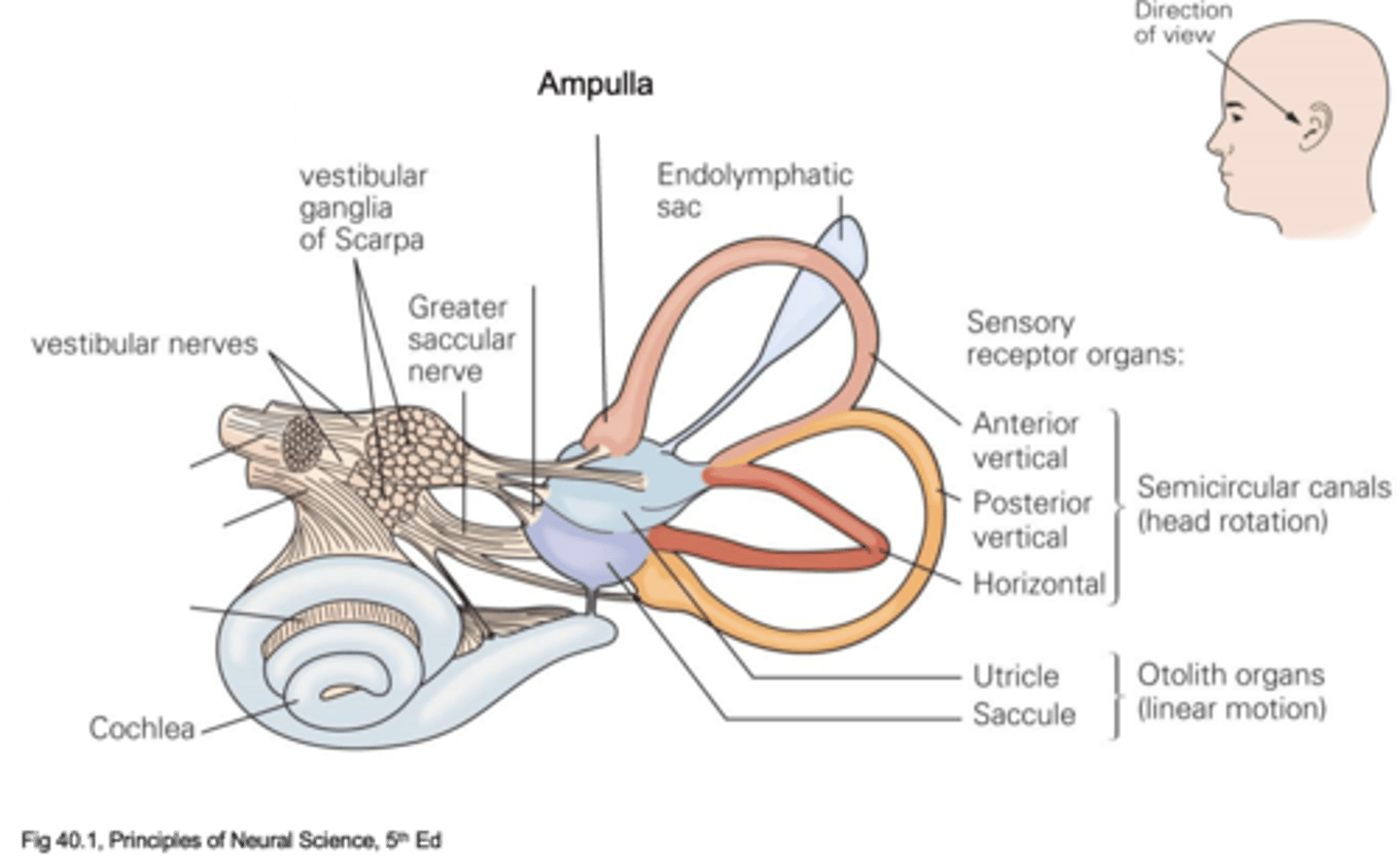
Movement up and down
What does the saccule detect?
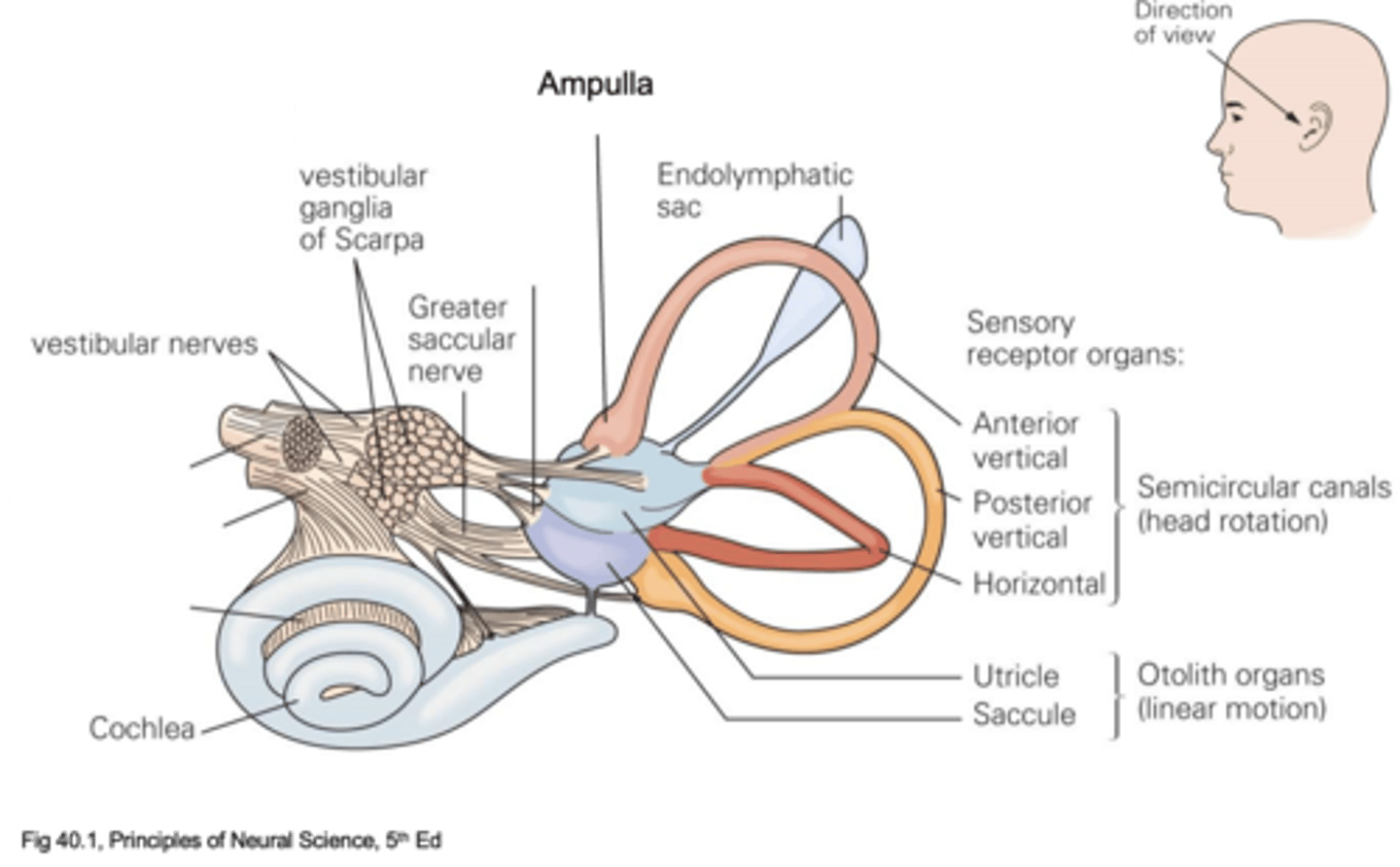
Movement forward and backwards
What does the utricle detect?
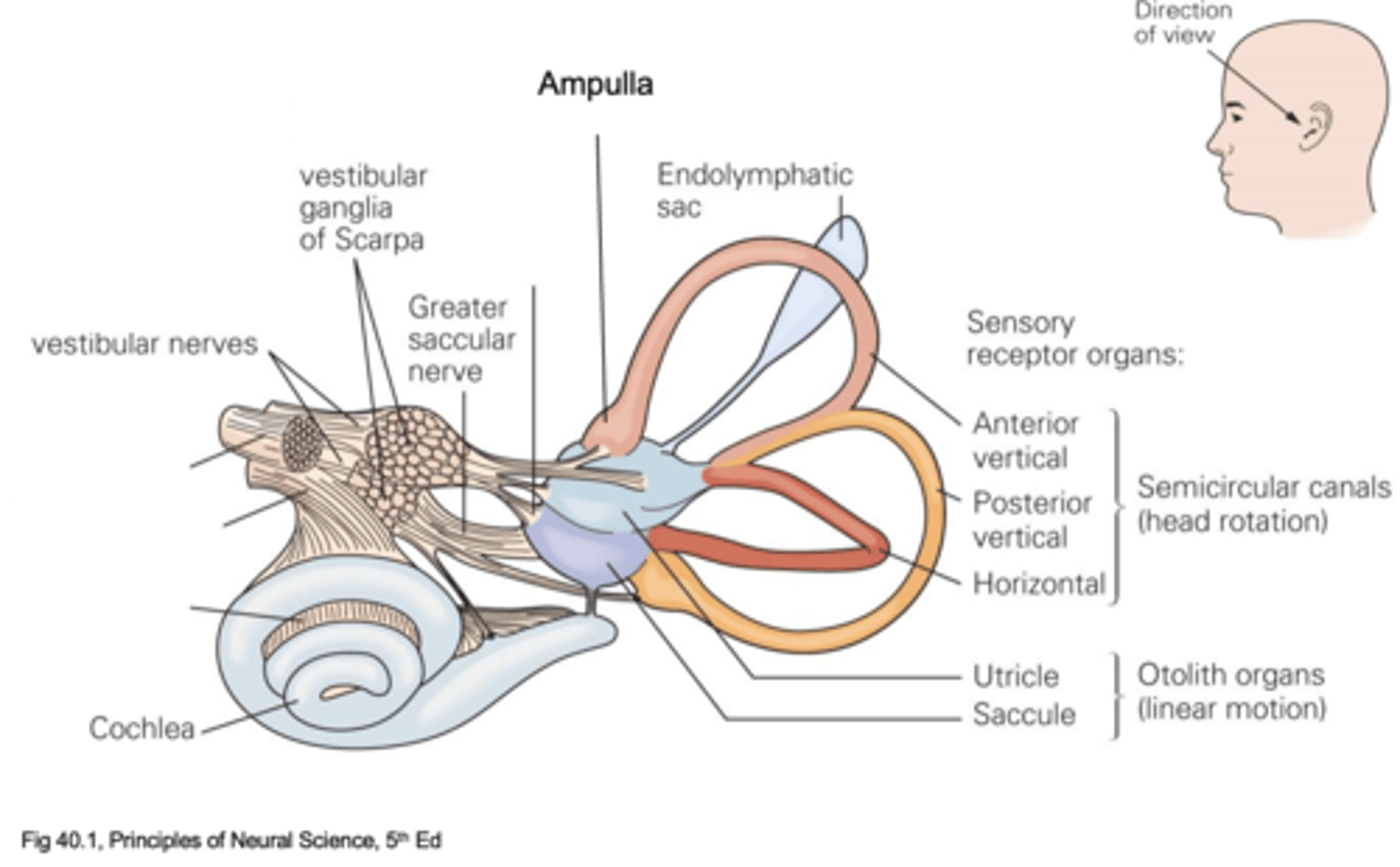
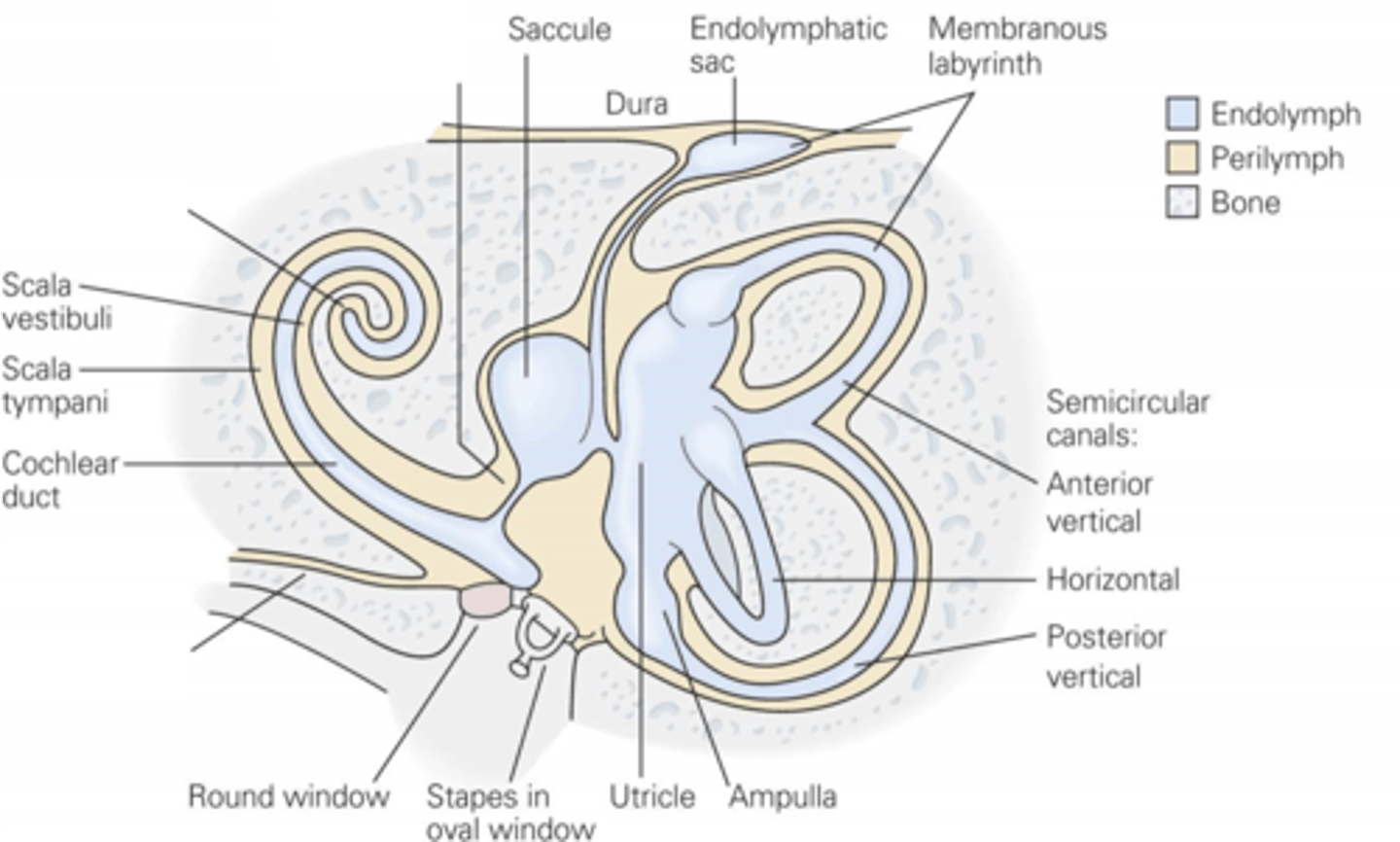
Endolymph
What are the utricle and saccule filled with?
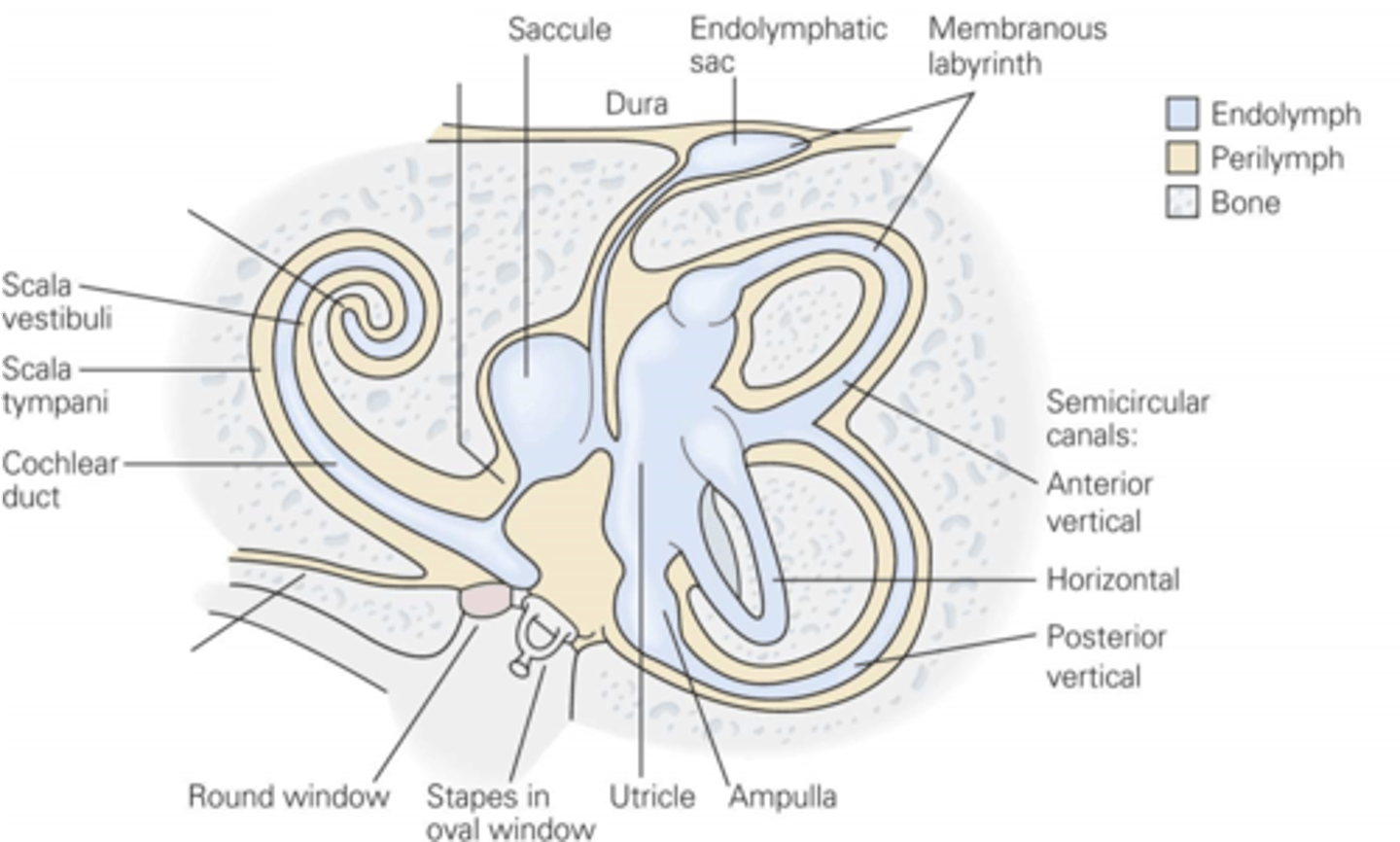
Endolymph, perilymph
In the semicircular canals, the middle bit is filled with ____________ and the chambers either side are filled with ___________
Sensory receptors of the vestibular system
What are hair cells?
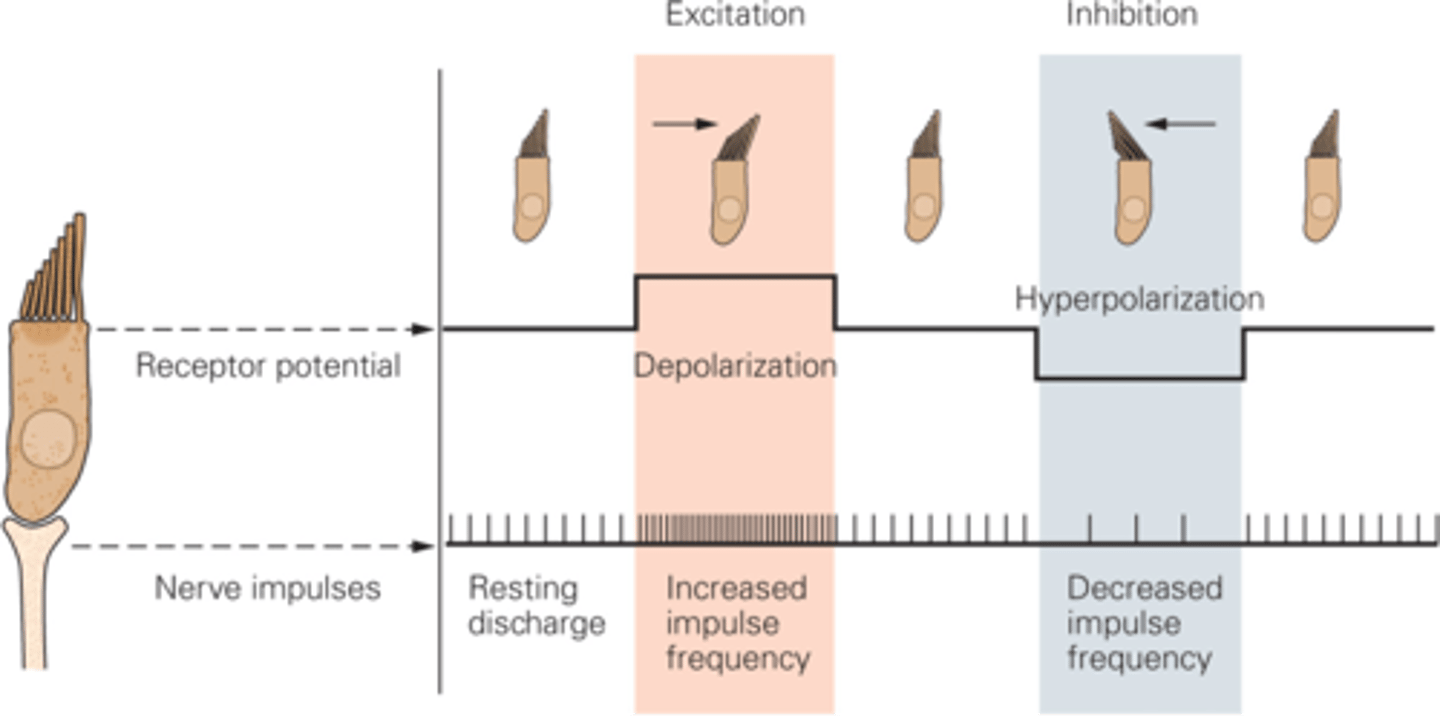
Lower, 0, 20
Hair cells of the vestibular system have the same principle as hair cells of the auditory system but they respond to ________ frequencies (_ to ~__Hz)
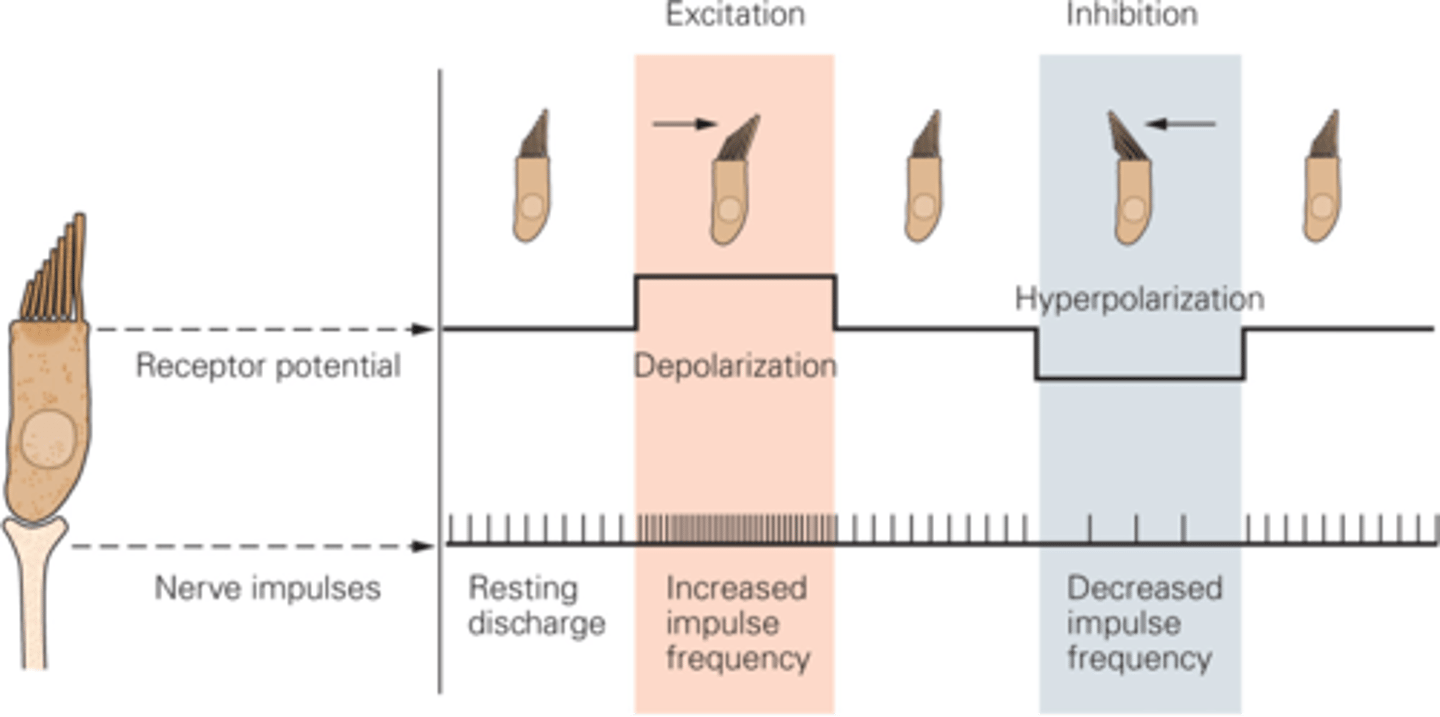
Stereocilia, hair bundle
Each individual strand is a _____________ but the entire structure that sits on top of hair cells is known as _____ __________
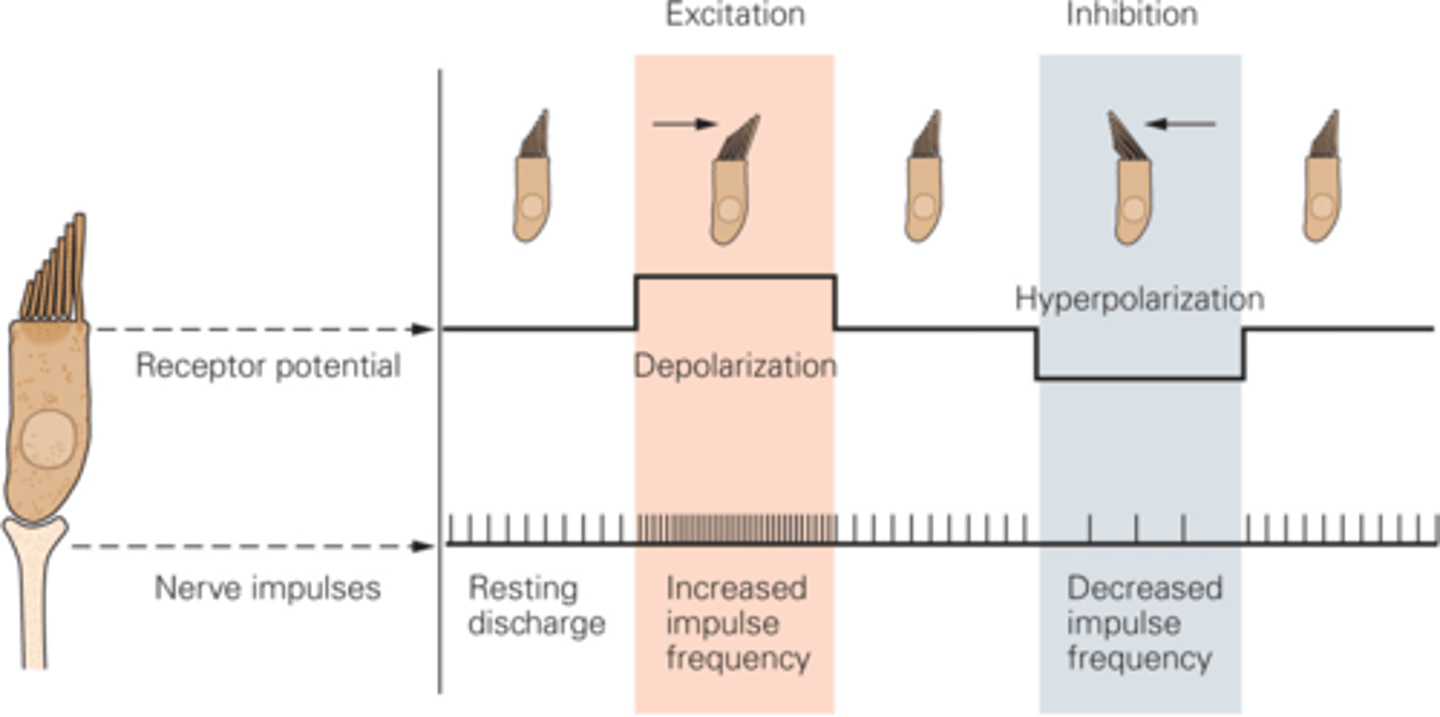
Upright
If there's no stimulus/movement then the hair bundle stands ___________
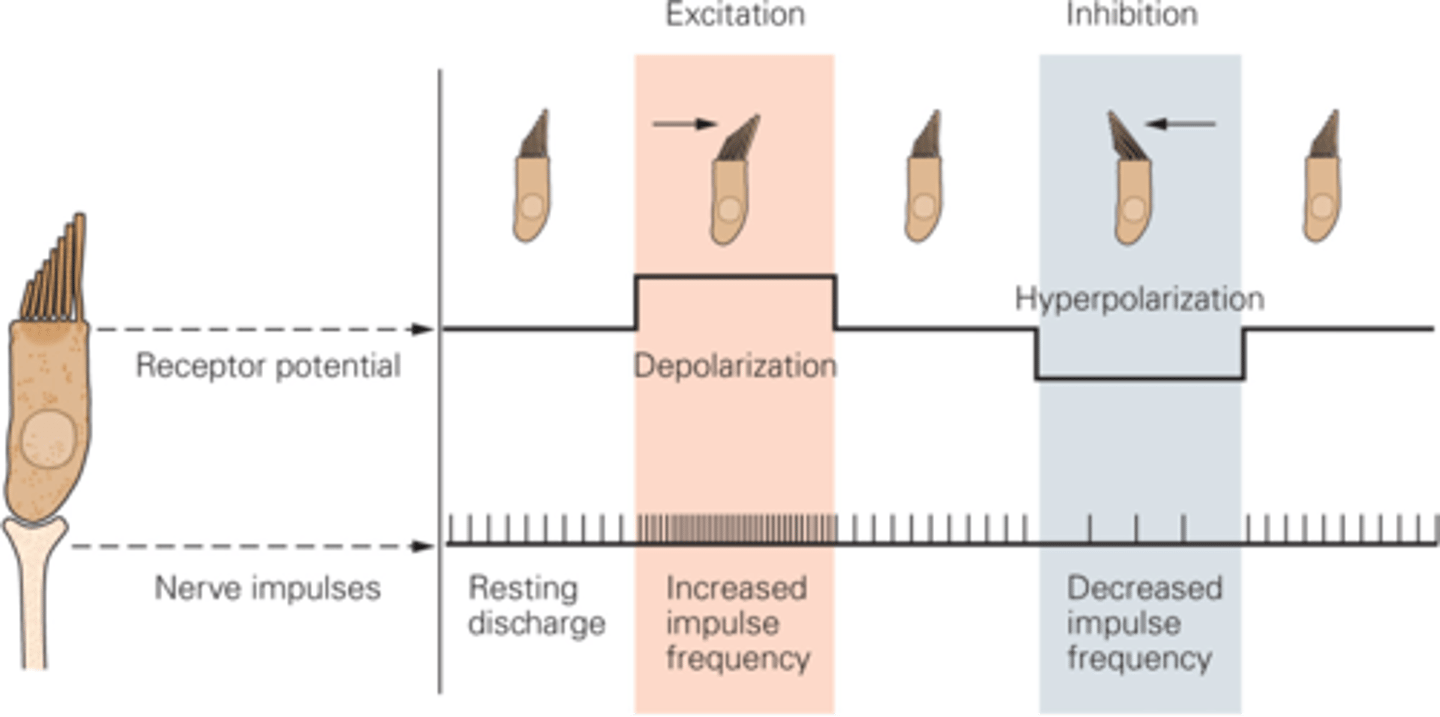
Tip links are stretched, MET channels open and potassium moves in causing graded potential from the top to the base (depolarisation) causing voltage-gated calcium channels to open and calcium comes in and this causes release of glutamate which activates glutamate receptors in the afferent fibres of the vestibular system and general EPSPs and this can stimulate to become action potentials if the EPSPs are big enough
What happens if the hair bundle moves towards the taller stereo cilia?
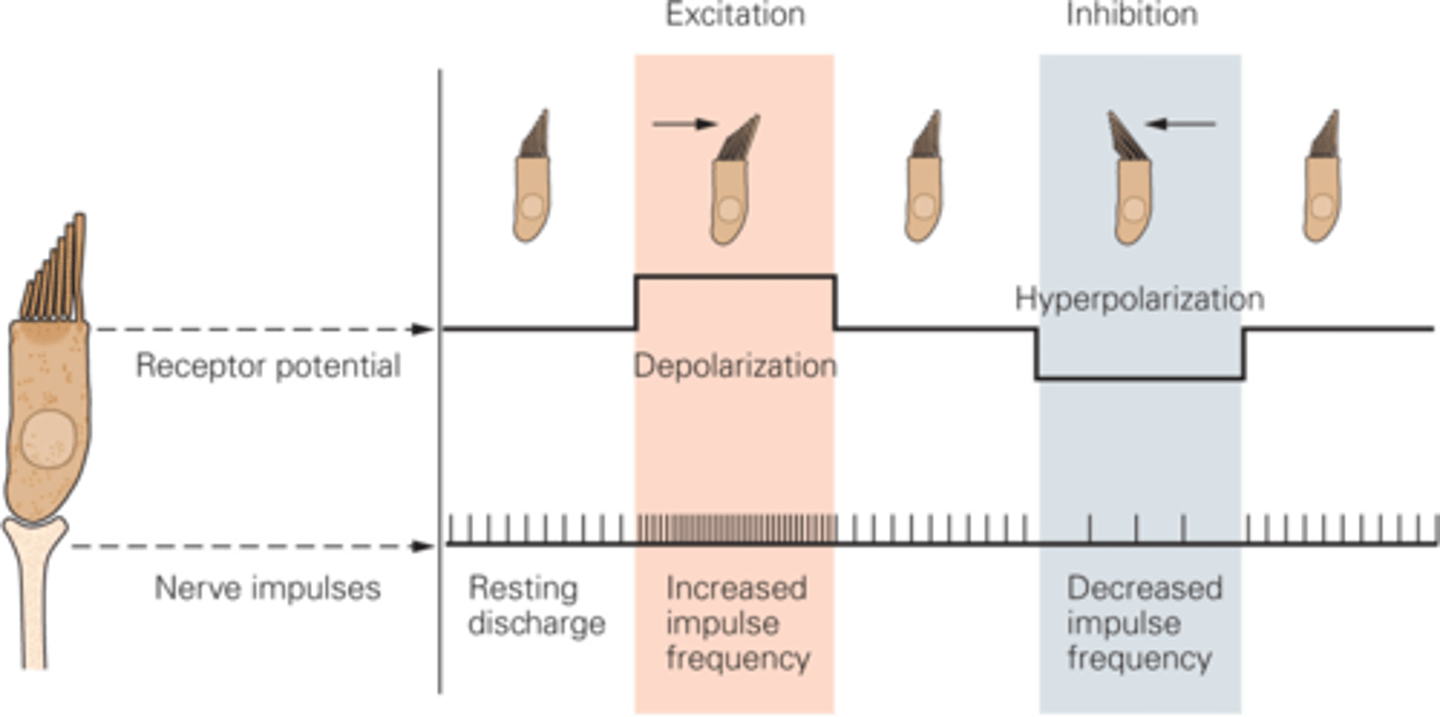
Tip links become slackened, the channels shut, potassium cannot come in so the hair cell will hyperpolarise, decreasing in frequency of nerve impulses
If the hair cells are moved towards the shorter stereo cilia, what happens?
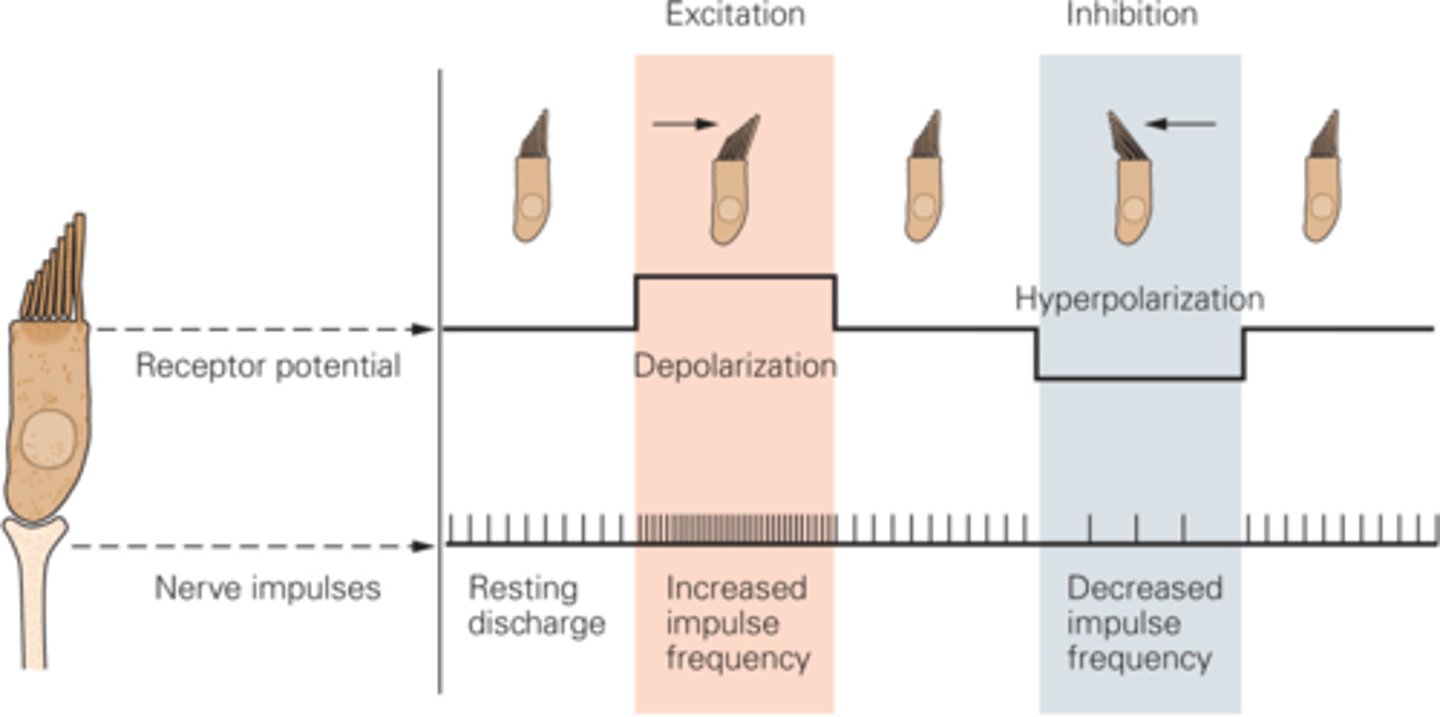
Tension
Both in the auditory and vestibular system there is some _________ on the hair cell at rest

Kinocilium
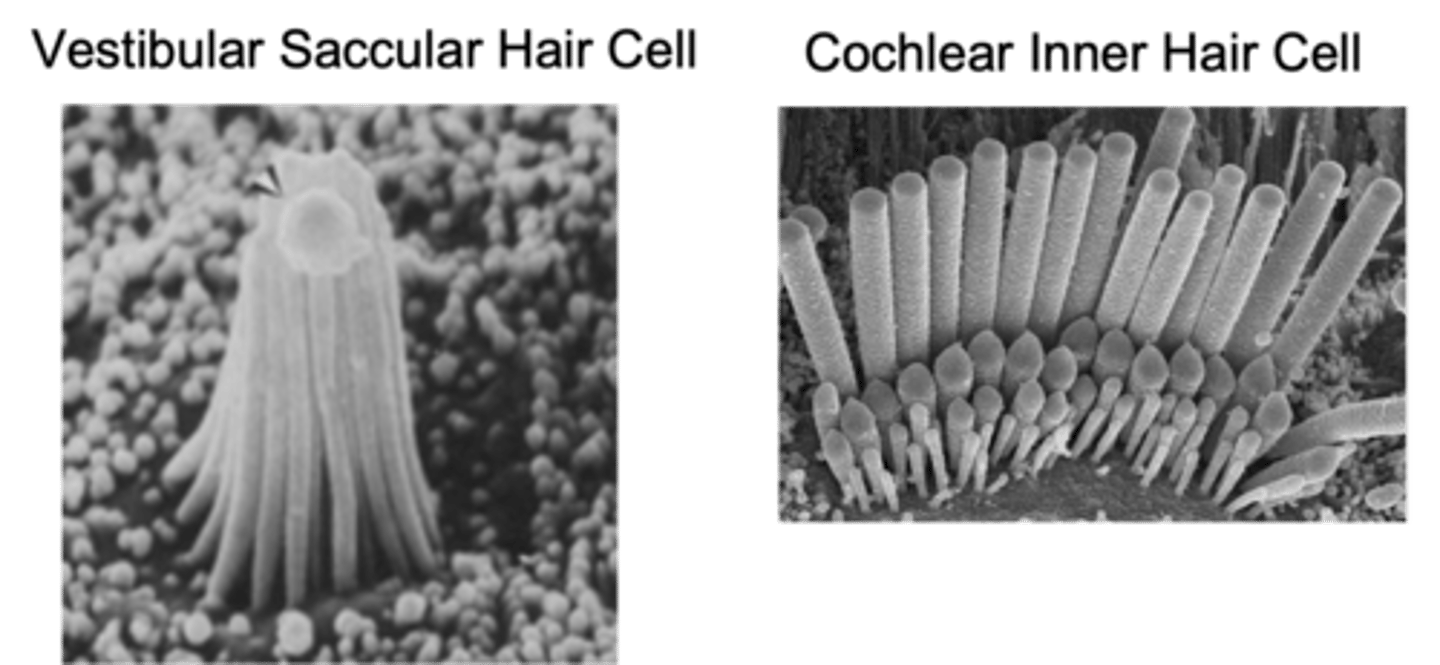
What do vestibular hair cells keep throughout life that cochlear hair cells don't?
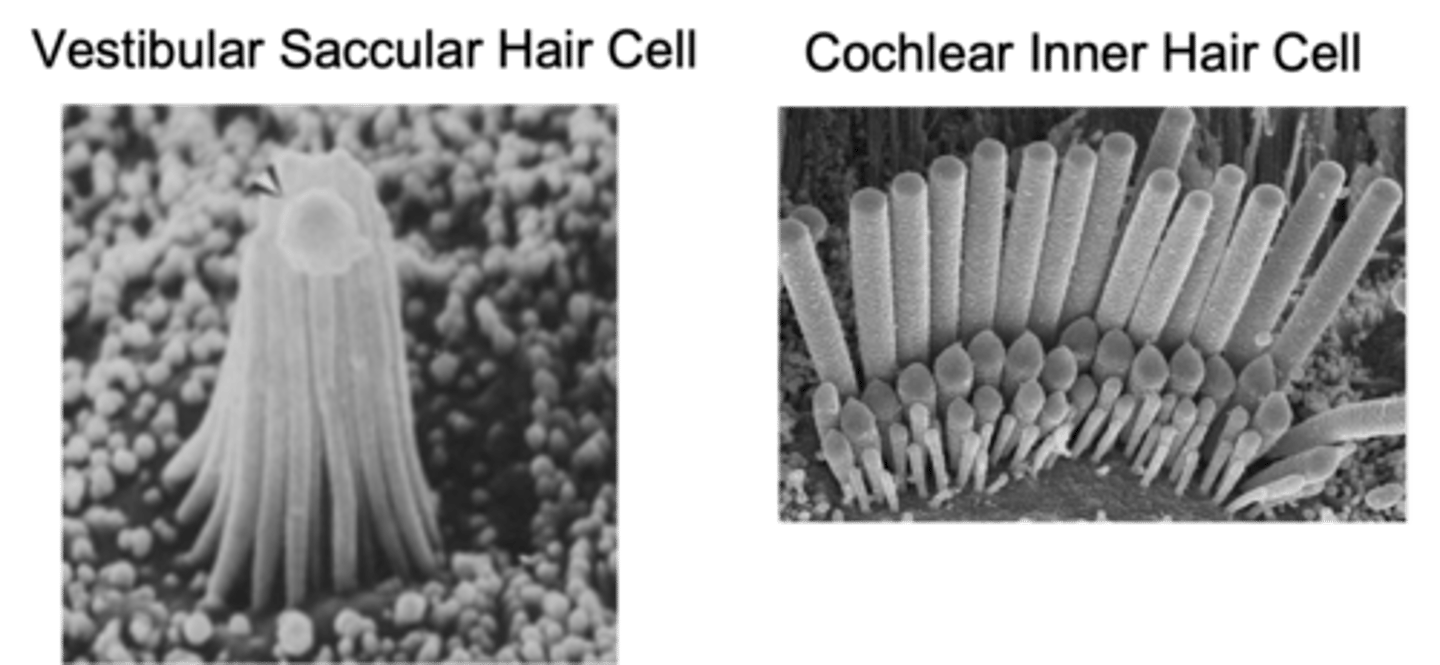
Clumpy, rows, lower
Vestibular hair cells are more _______ but retain the staircase structure but have more _______ - this is due to the _________ frequencies stimulating it
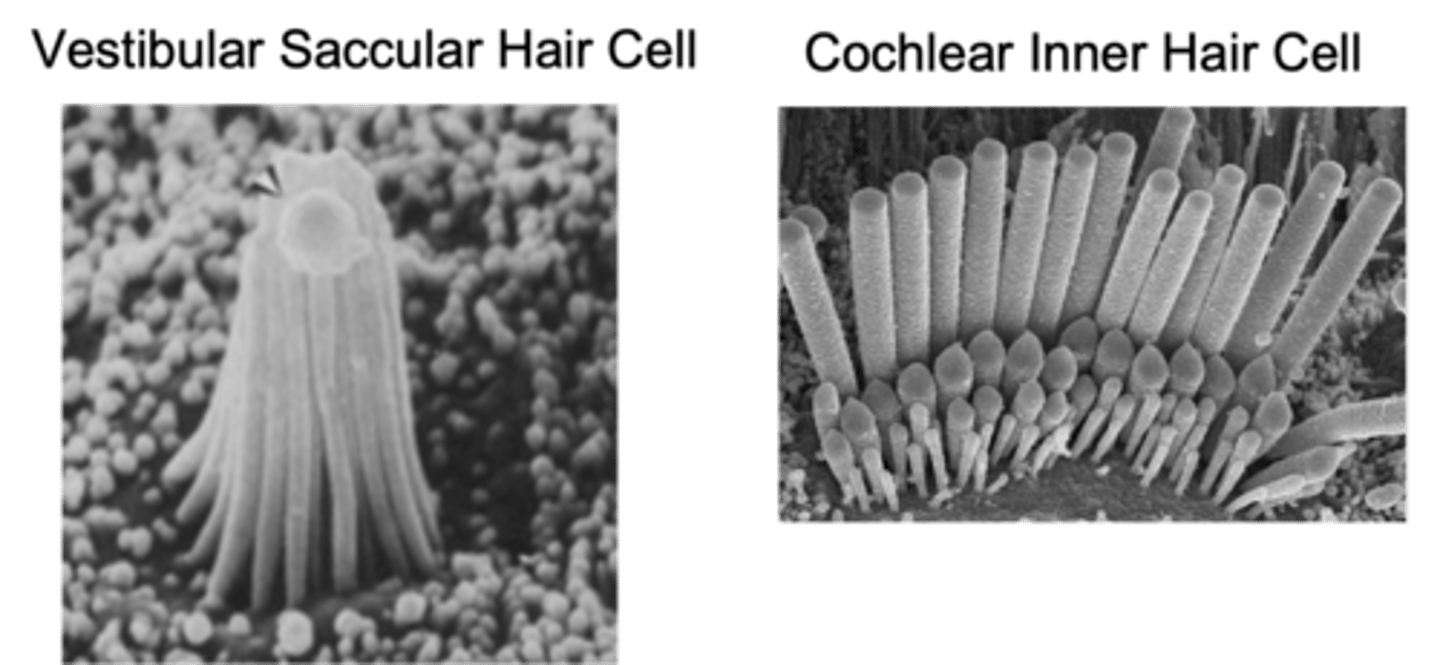
3
How many rows of stereo cilia do cochlear hair cells have?
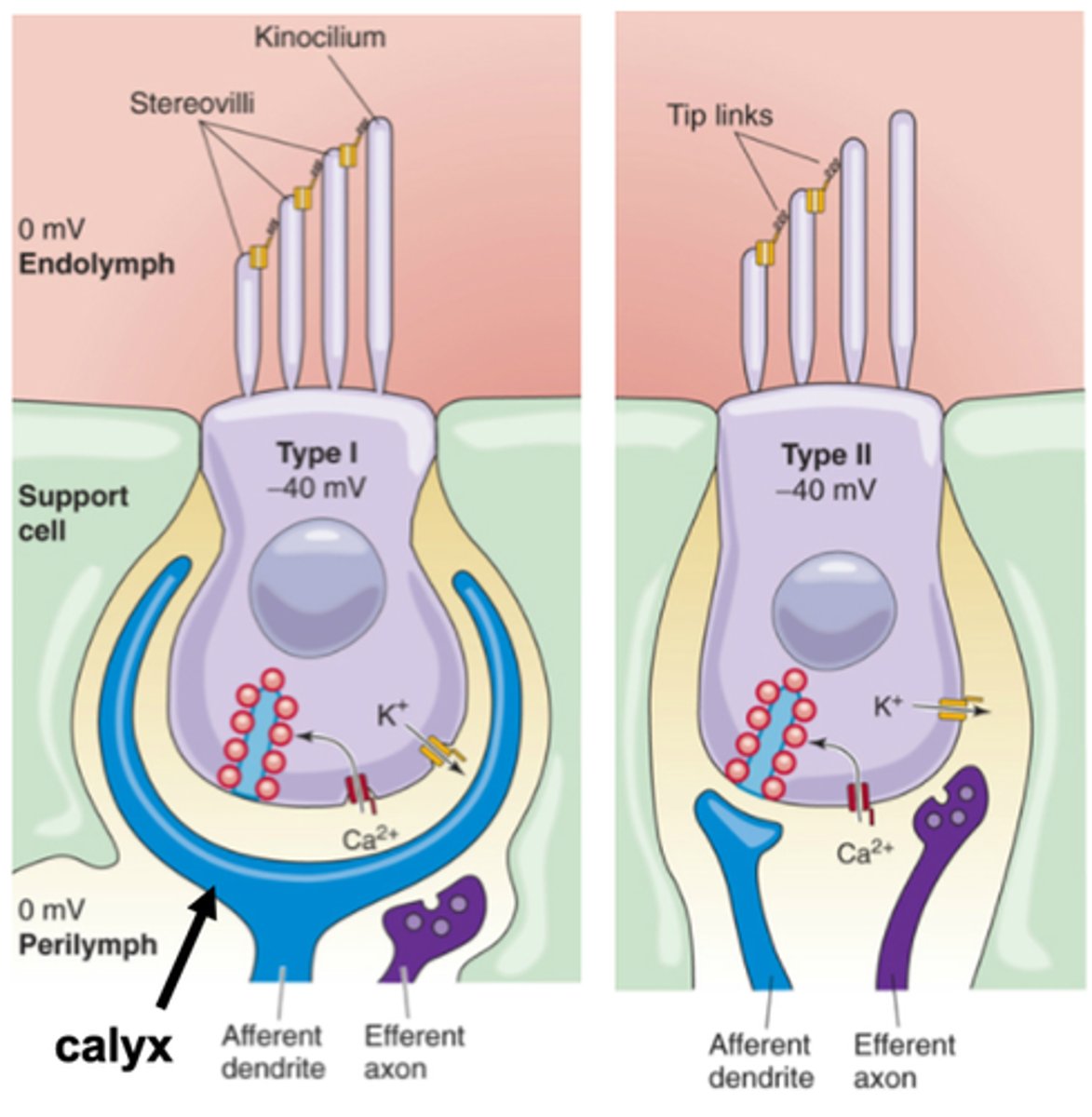
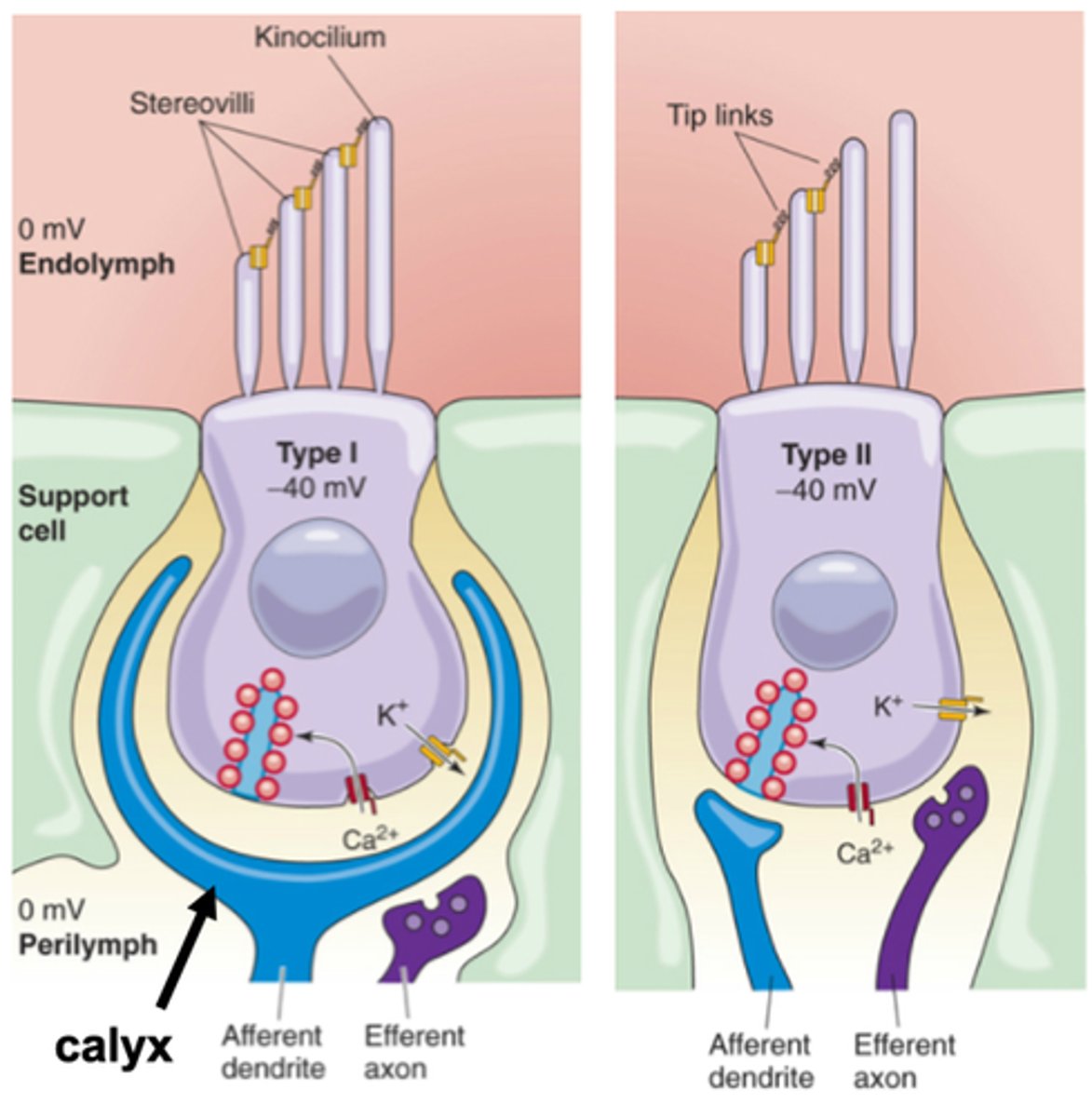
Type I and Type II
What are the two types of vestibular hair cells?
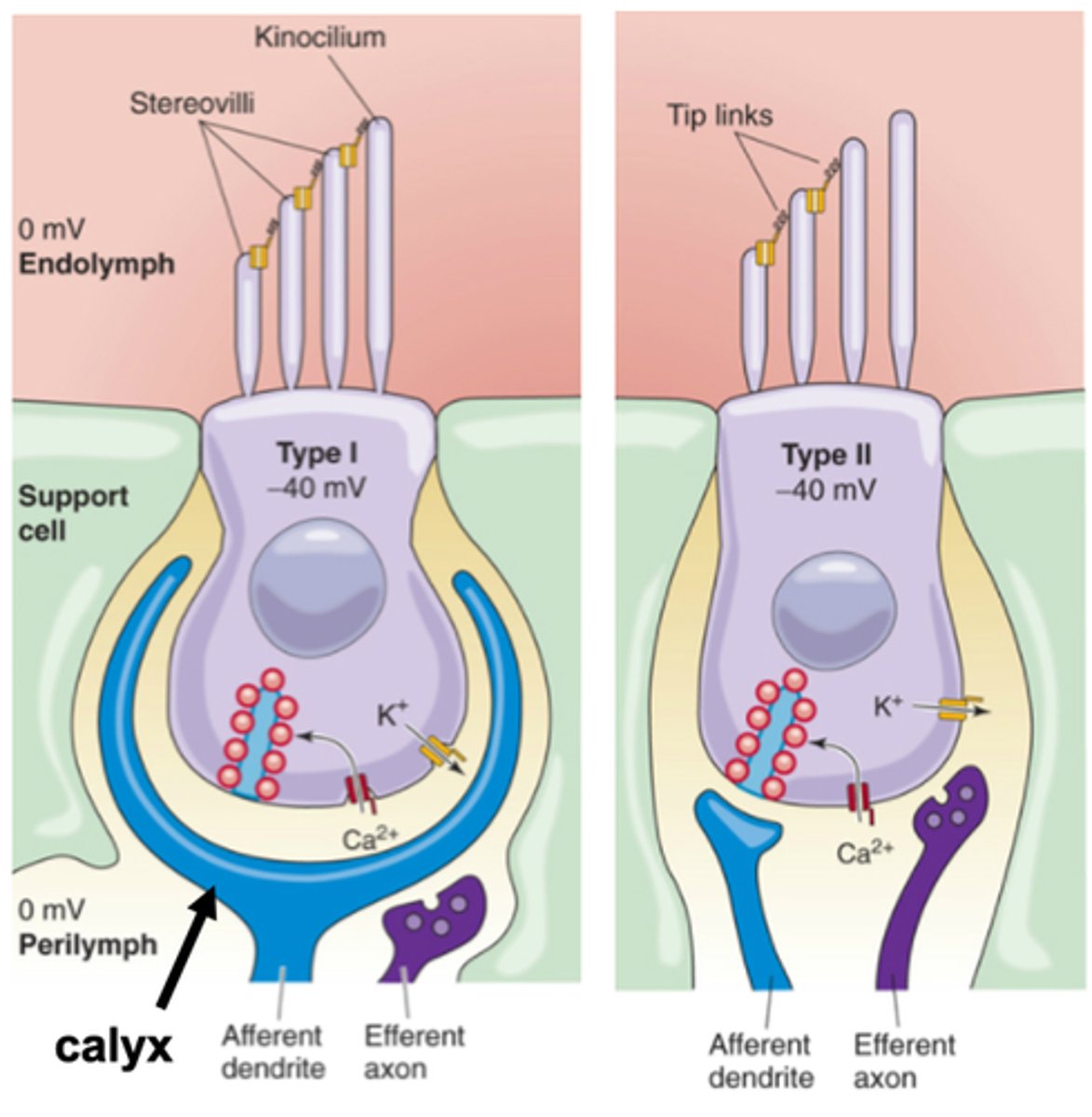
How they communicate with the afferent fibre
What is the major difference between Type I and Type II hair cells?
Typical neurone to neurone contact
What communication with the afferent fibre do Type II hair cells have?
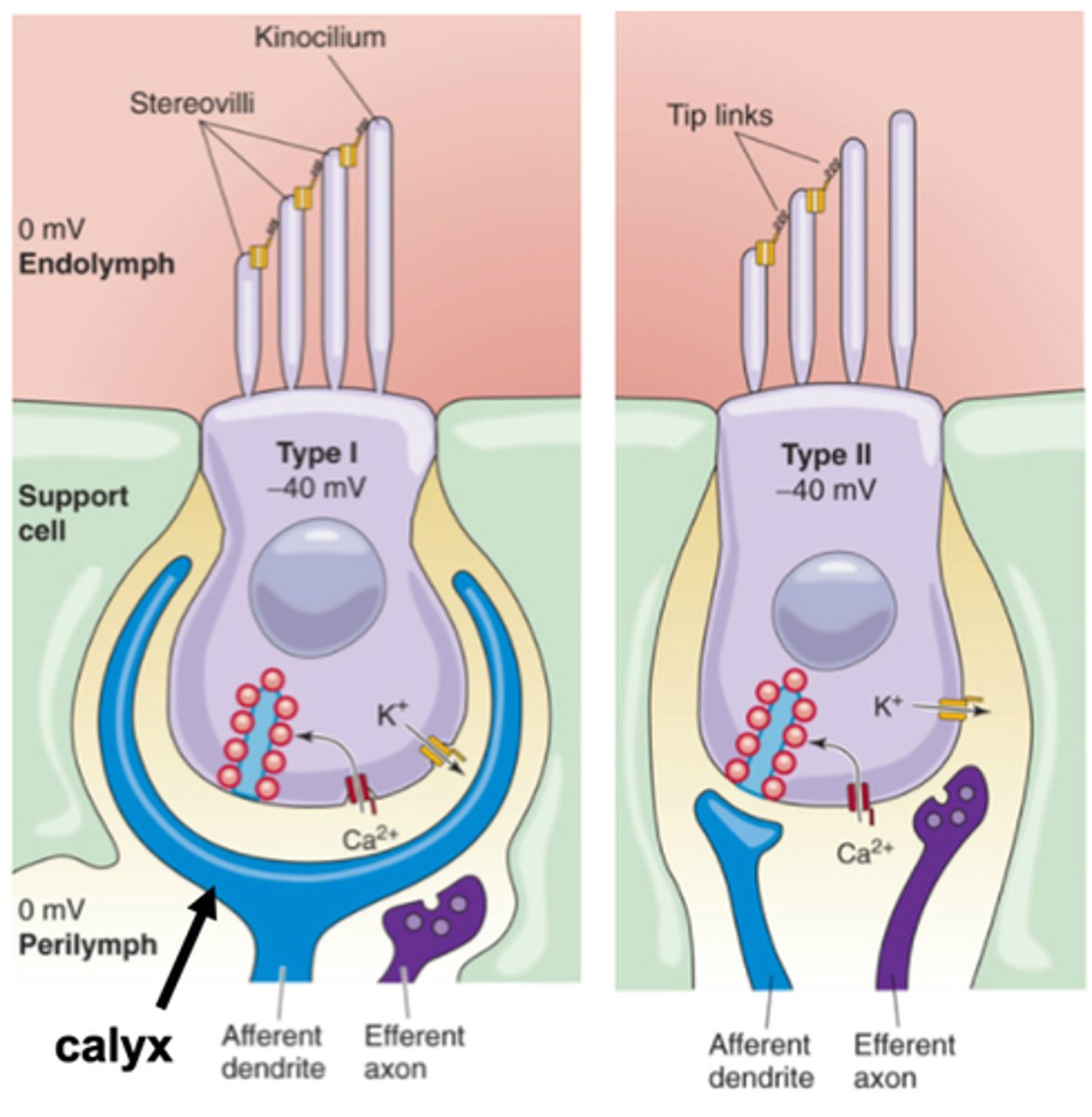
Calyx
In Type I there is a massive __________ which is a postsynaptic region massively expanded to enclose the bottom of the Type I hair cell
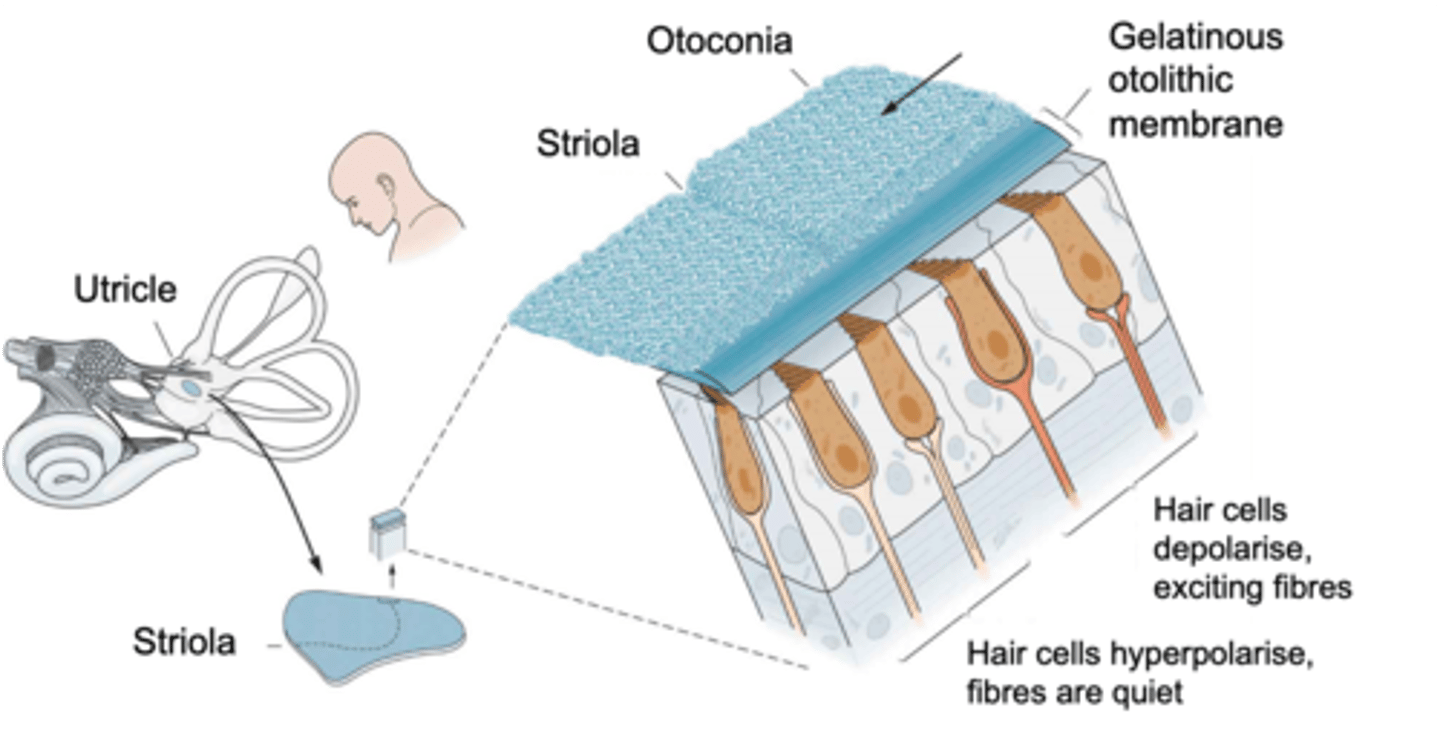
Head tilt, linear acceleration
The saccule and the utricle detect ______ _______ and _________ ______________
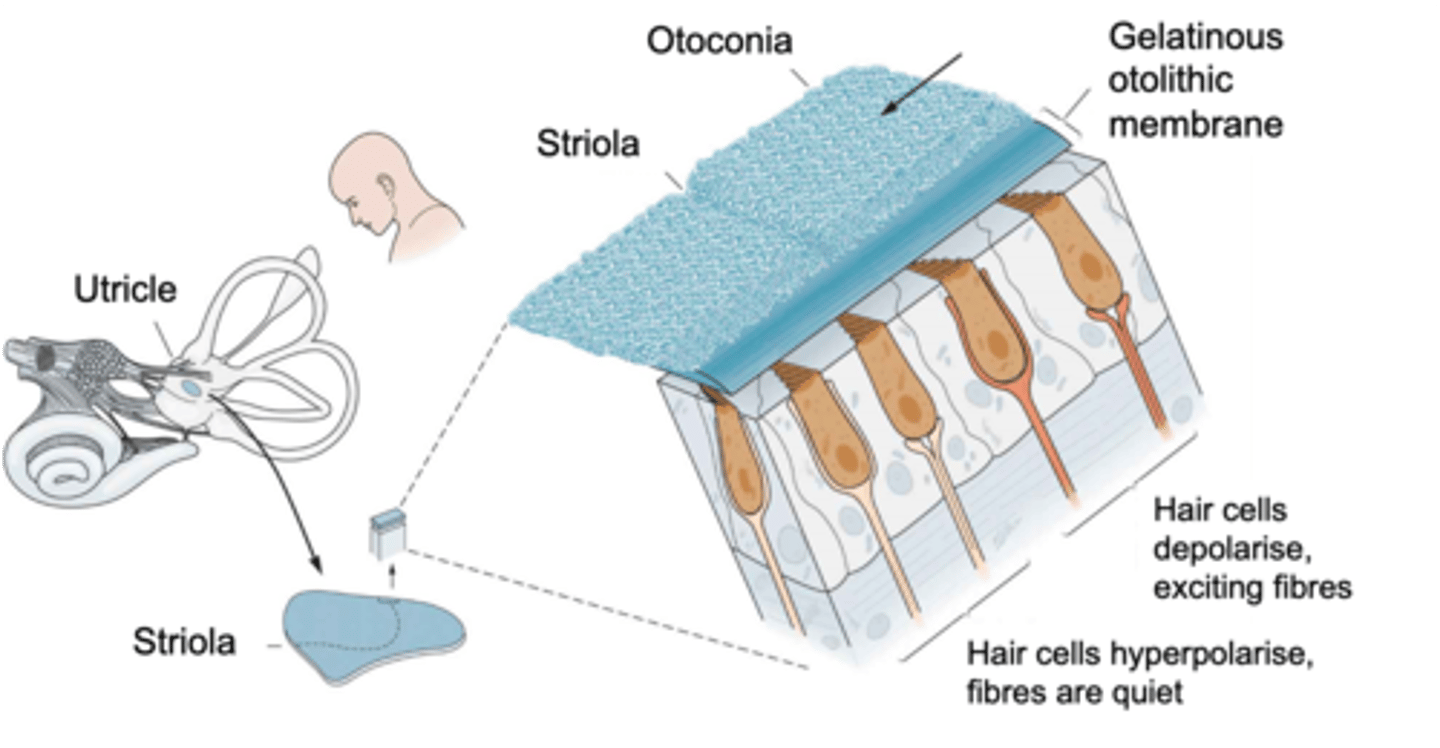
Macula
Hair cells are found in a sensory patch called the ...?
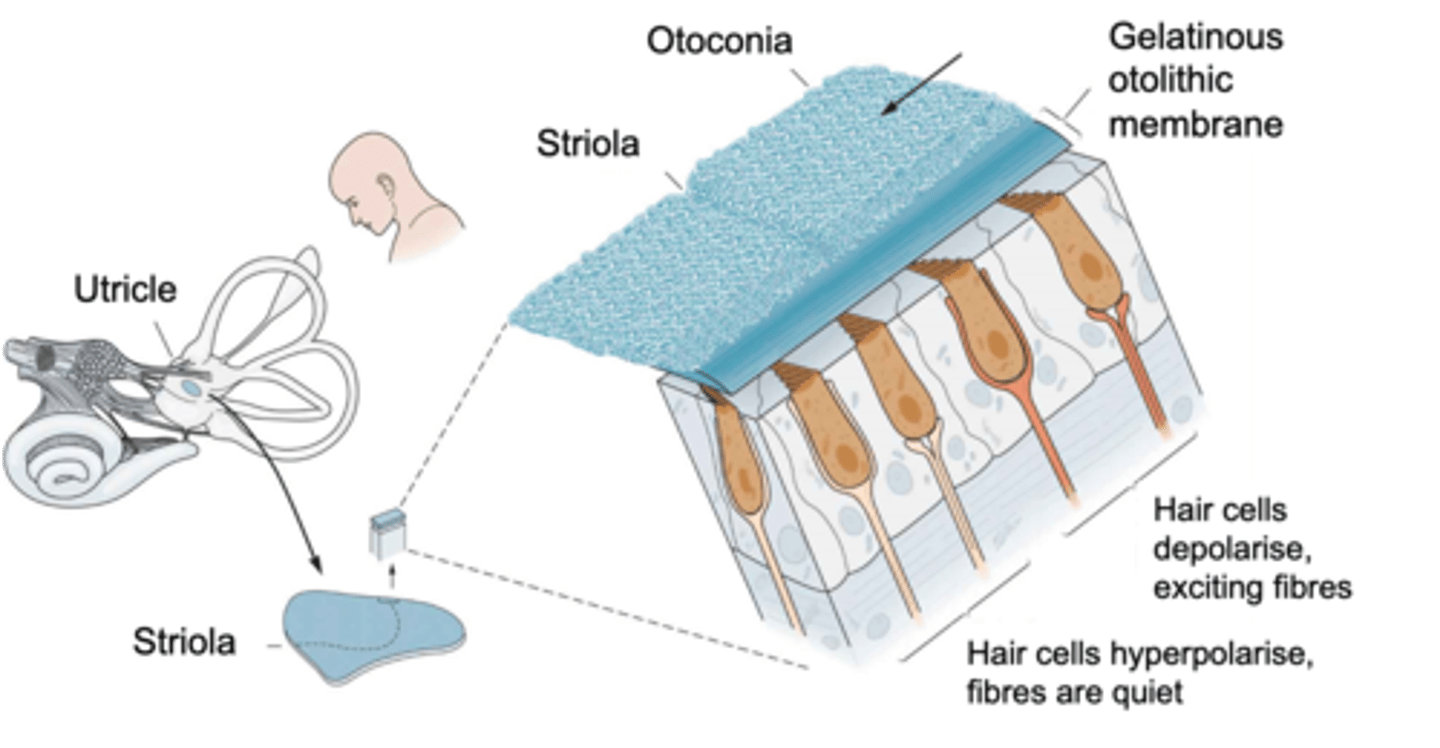
Striola, opposite
Inside the macula there is a wobbly line known as the ________ where on one side hair cells are orientated in one direction (taller hair cells pointed towards it) and on the other side the hair cells are the ___________ way
Gives a dual response - as one is activated the other is inhibited
What does the orientation of the hair cells within the macula do?
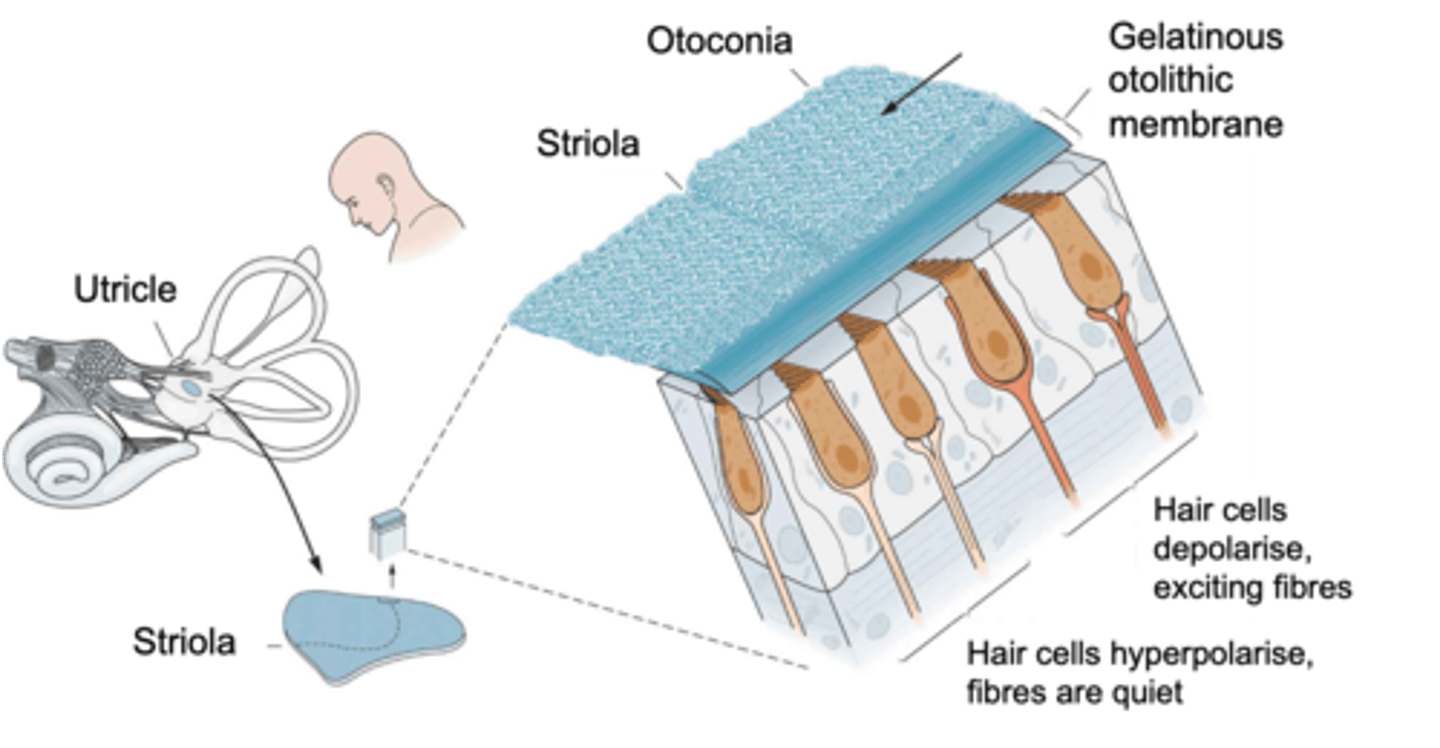
Jelly, calcium crystals
Otolithic membrane is ______ like and otoconia are ___________ __________
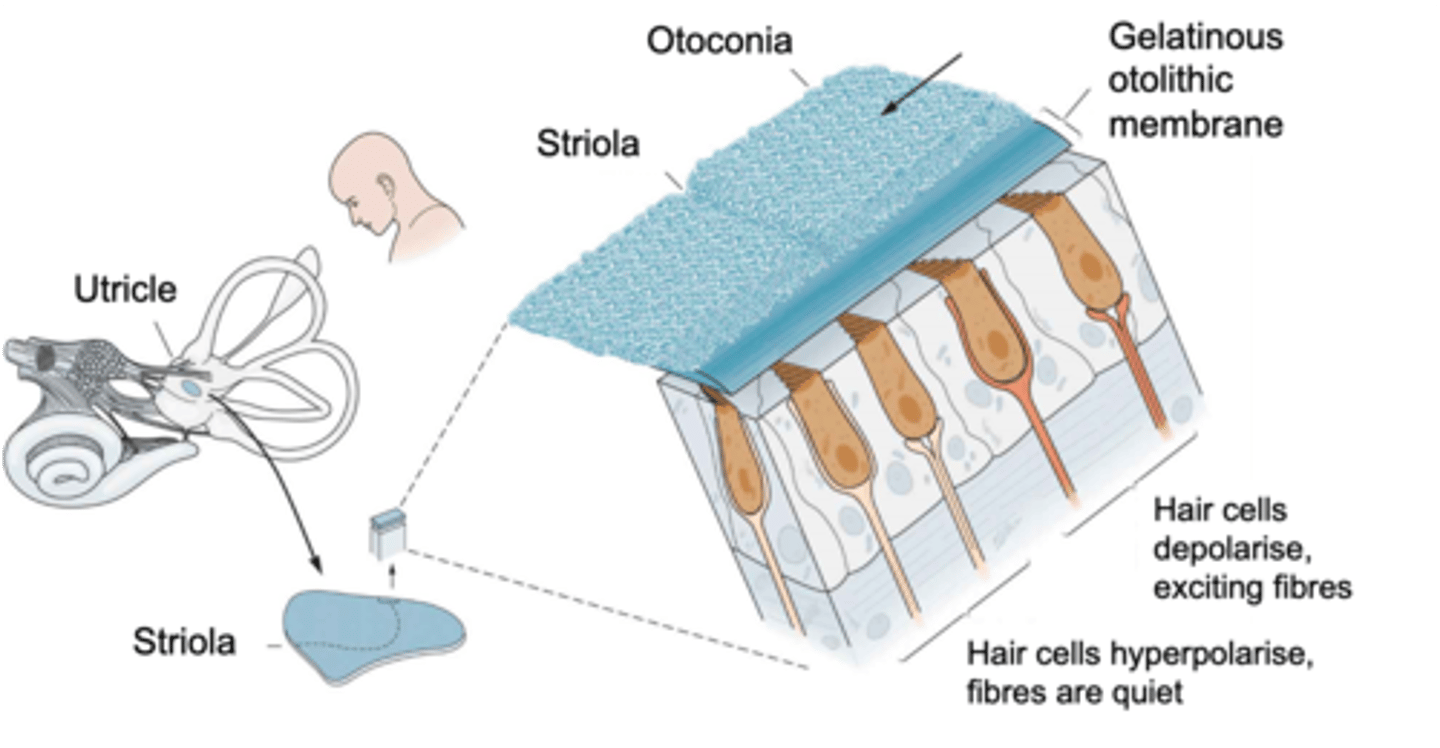
Gravity, hair cells
If you move, the otoconia moves due to _________ and pulls the otolithic membrane which in turn pulls the ______ _______ with it

All the CNS is hearing is that the nerve fibres have been activated but it does not know how it has been activated
Vestibular input to the CNS can be ambiguous, why?
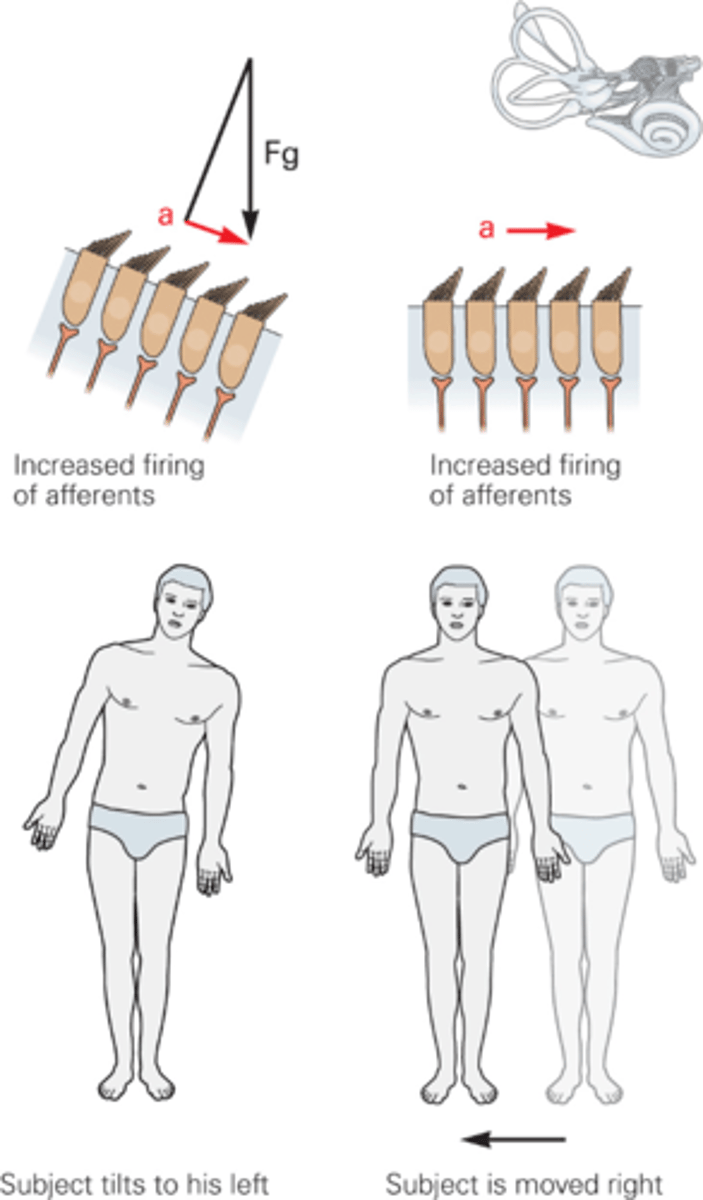
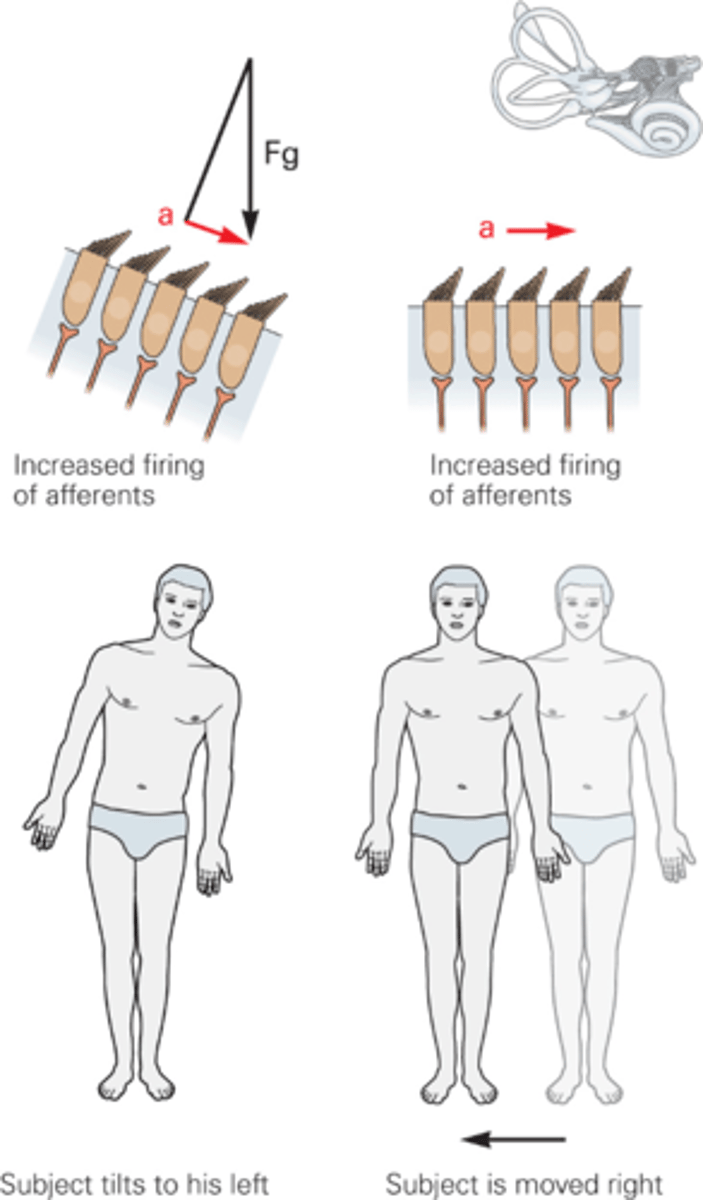
Endolymph, otoconia
______________ and ___________ are heavier, they won't move as quickly as the rest of the body so they drag the hair bundles in that direction
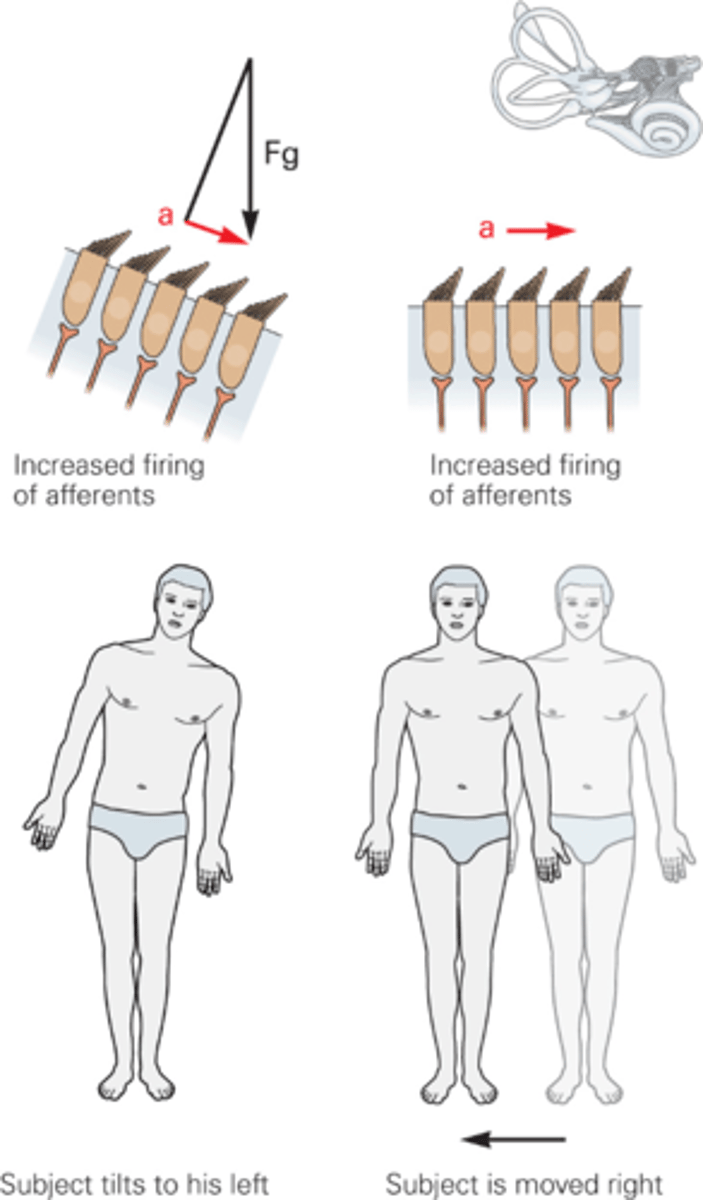
Force of gravity
What does Fg stand for?
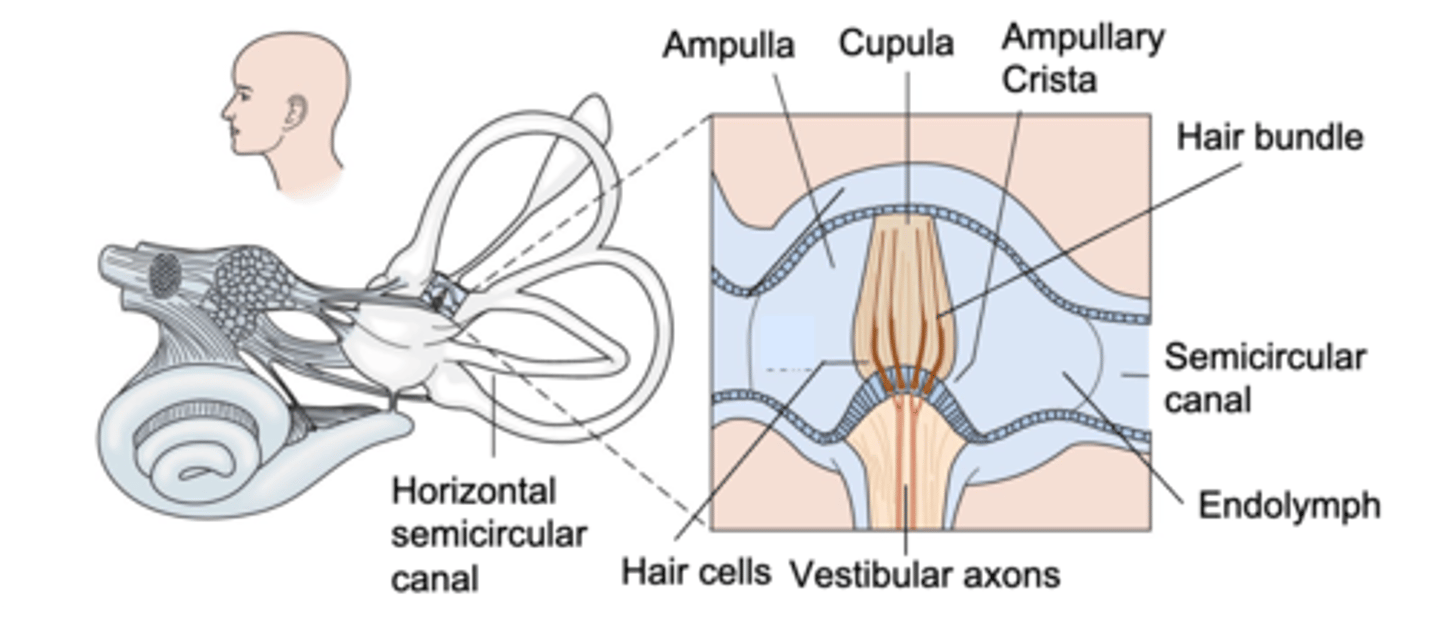
Cupula
What is the name of the gelatinous structure penetrated by hair bundles?
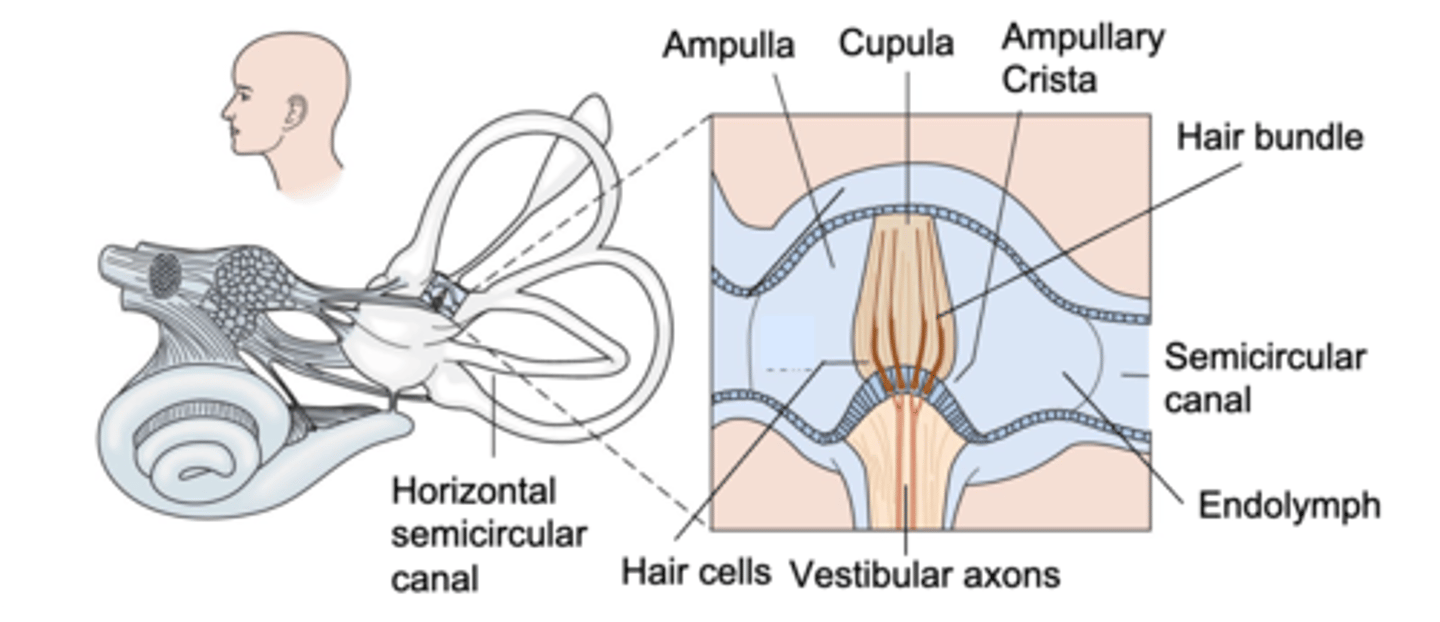
It forces them to move
If the cupula moves, what happens to the hair bundles?
Angular acceleration
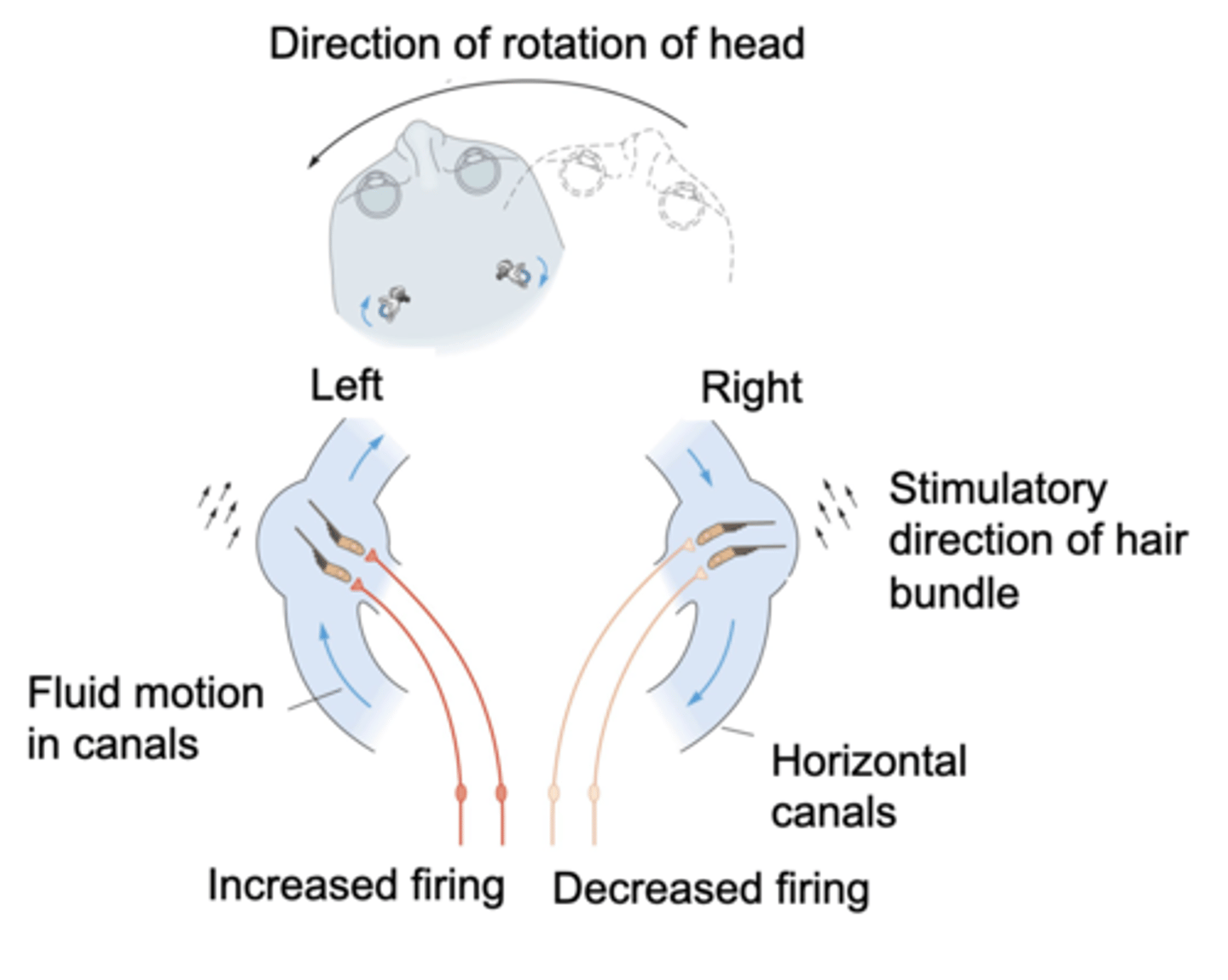
The semicircular canals detect _________ _____________ (rotation)
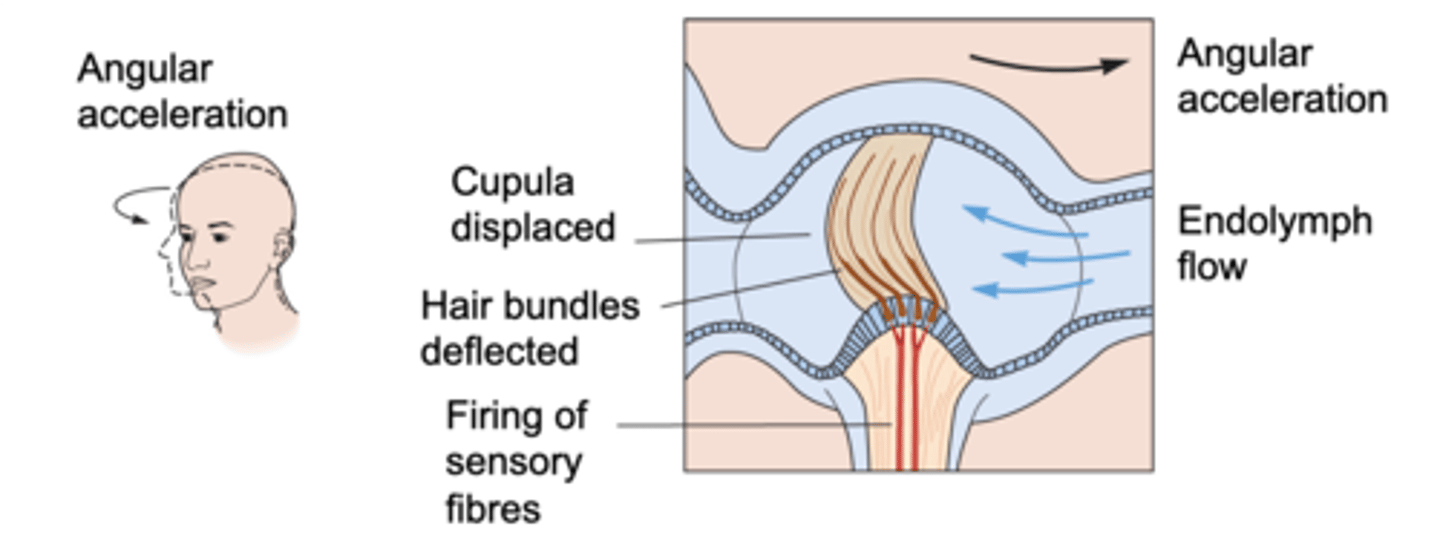
Inertia, displaces
The _________ of endolymph during rotation __________ the cupula
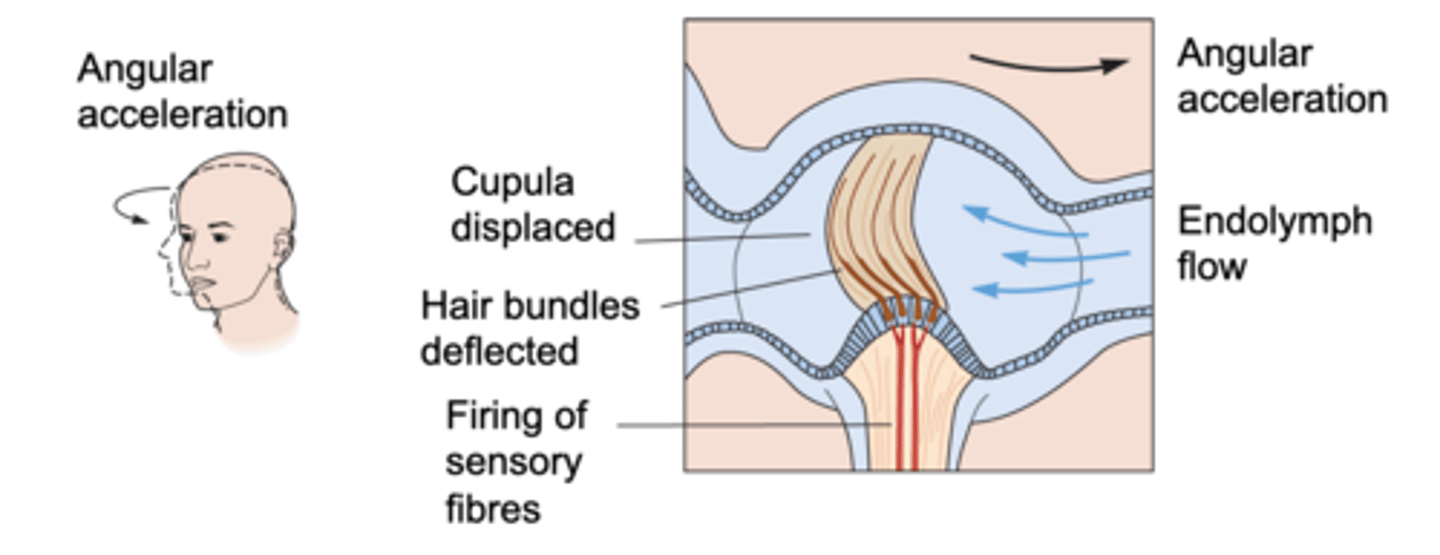
Pushing, right, hair bundles
Endolymph takes a while to move so even though you rotate to the left the endolymph won't catch up, so because of that if you move it appears the endolymph is turning to the right therefore __________ the cupula to the _______ and with it the ______ __________
Pairs
Semicircular canals on either side of the head work in ...?
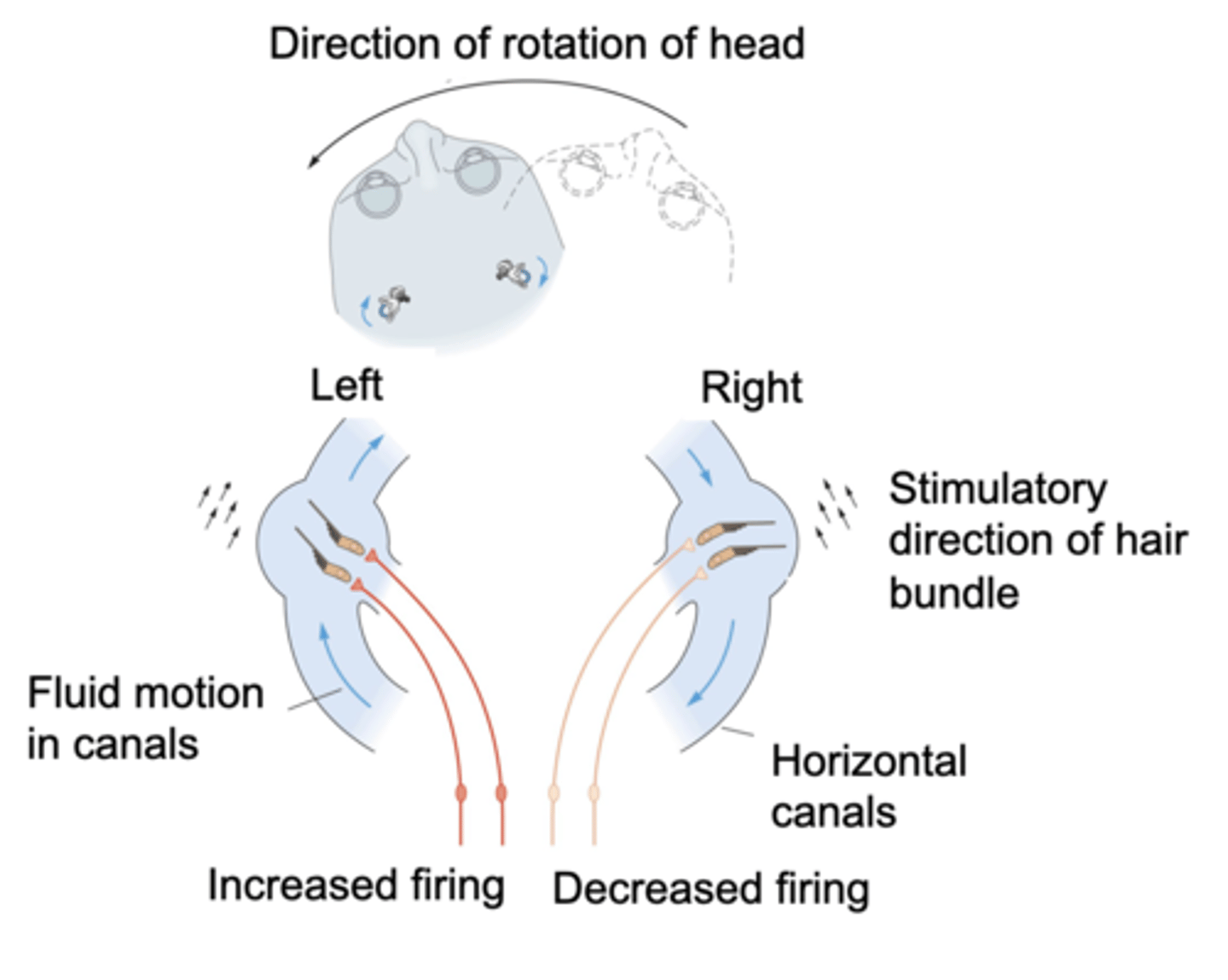
Right, activation, inhibition
As we turn to the left, the endolymph turns to the _______ in both semicircular canals, this causes _____________ on one side of the head and _____________ on the other side due to the rotation of the hair bundles
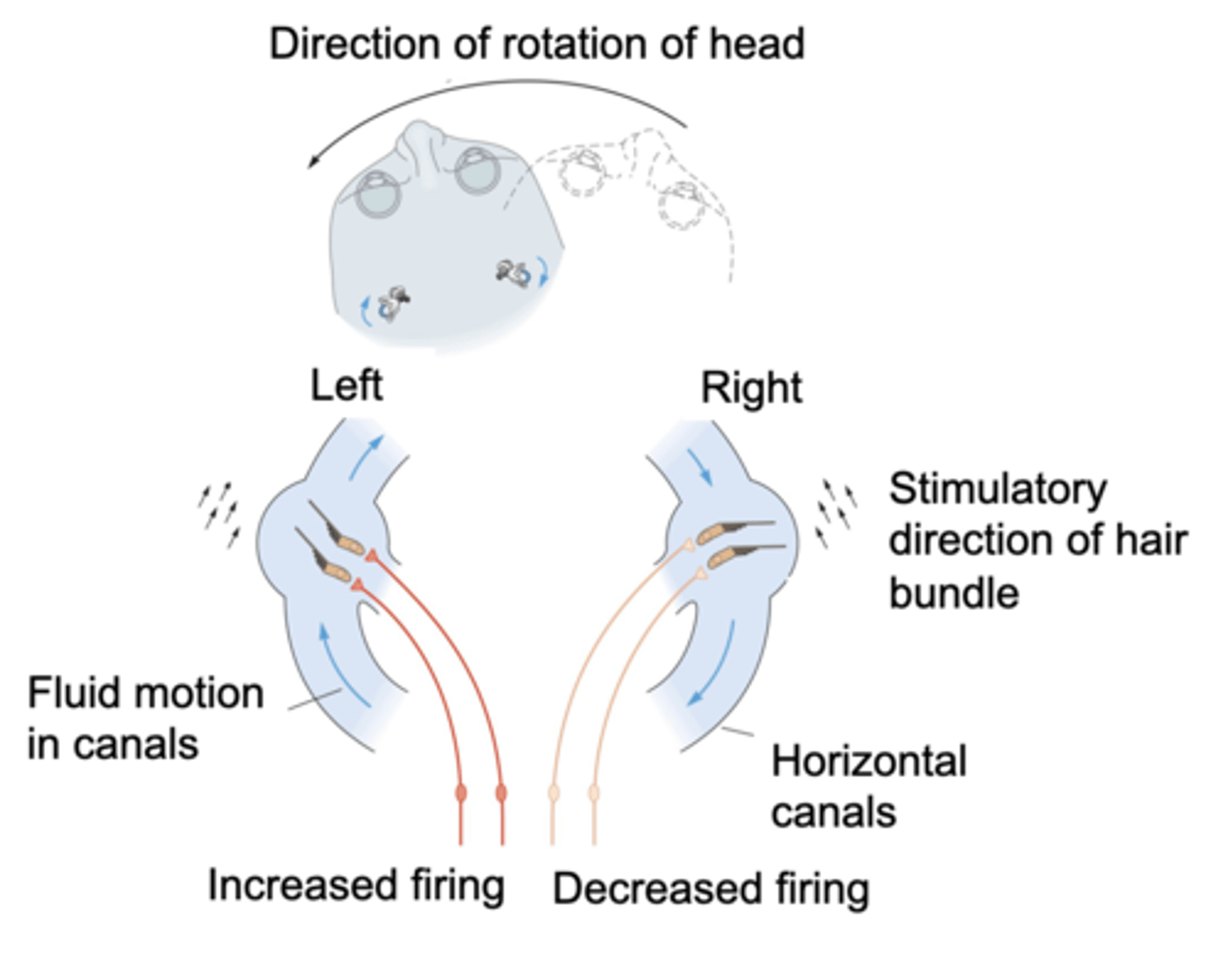
Same plane, functional pair
Horizontal canals on both sides lie in roughly the ______ _______ so can act as a _____________ ______
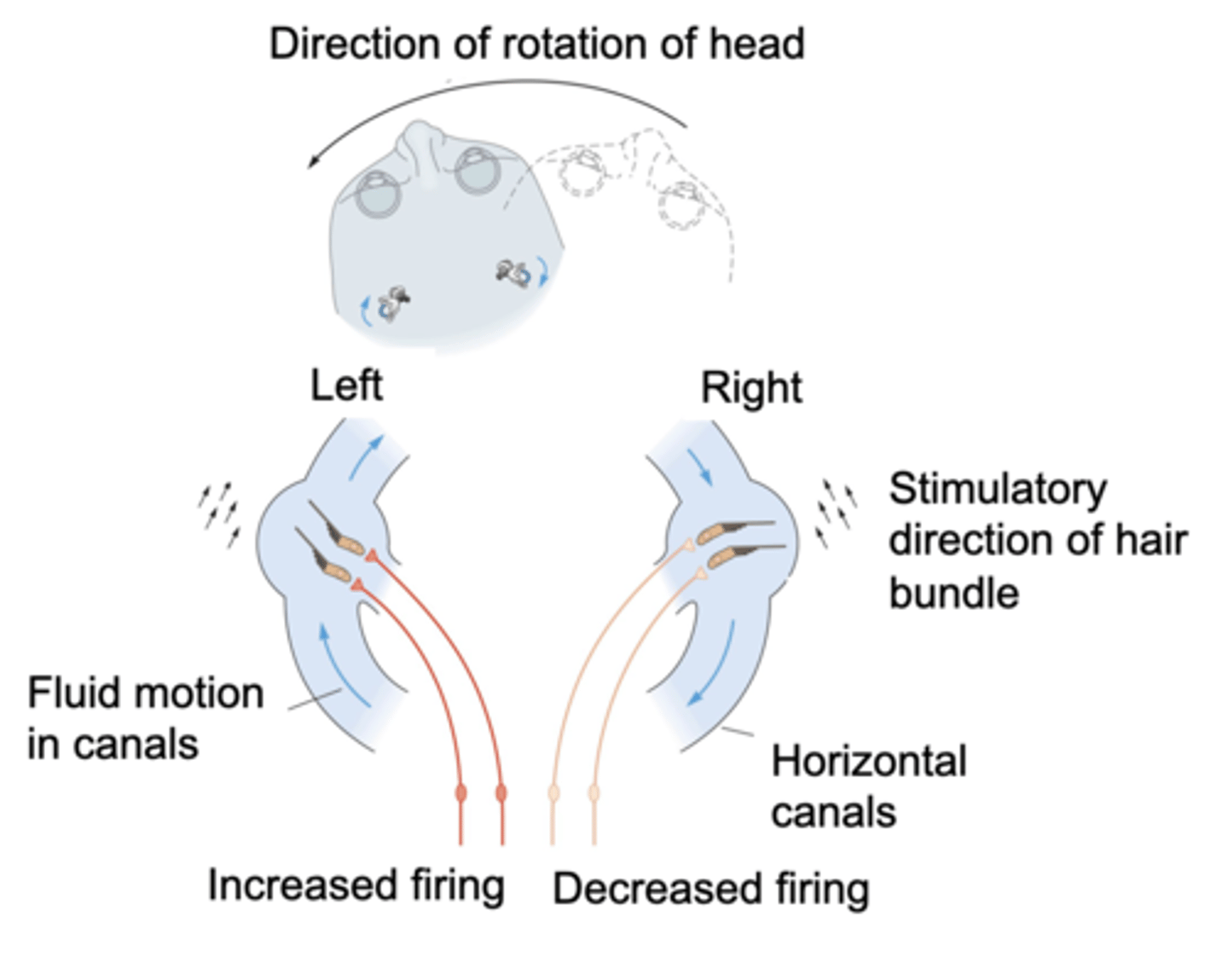
Parallel, functional pair
The anterior canal on one side lies in __________ with the posterior canal on the other side so acts as a _______________ ______
Vestibular nuclei (in the brain stem)
Where is the first place the vestibular organs input into?
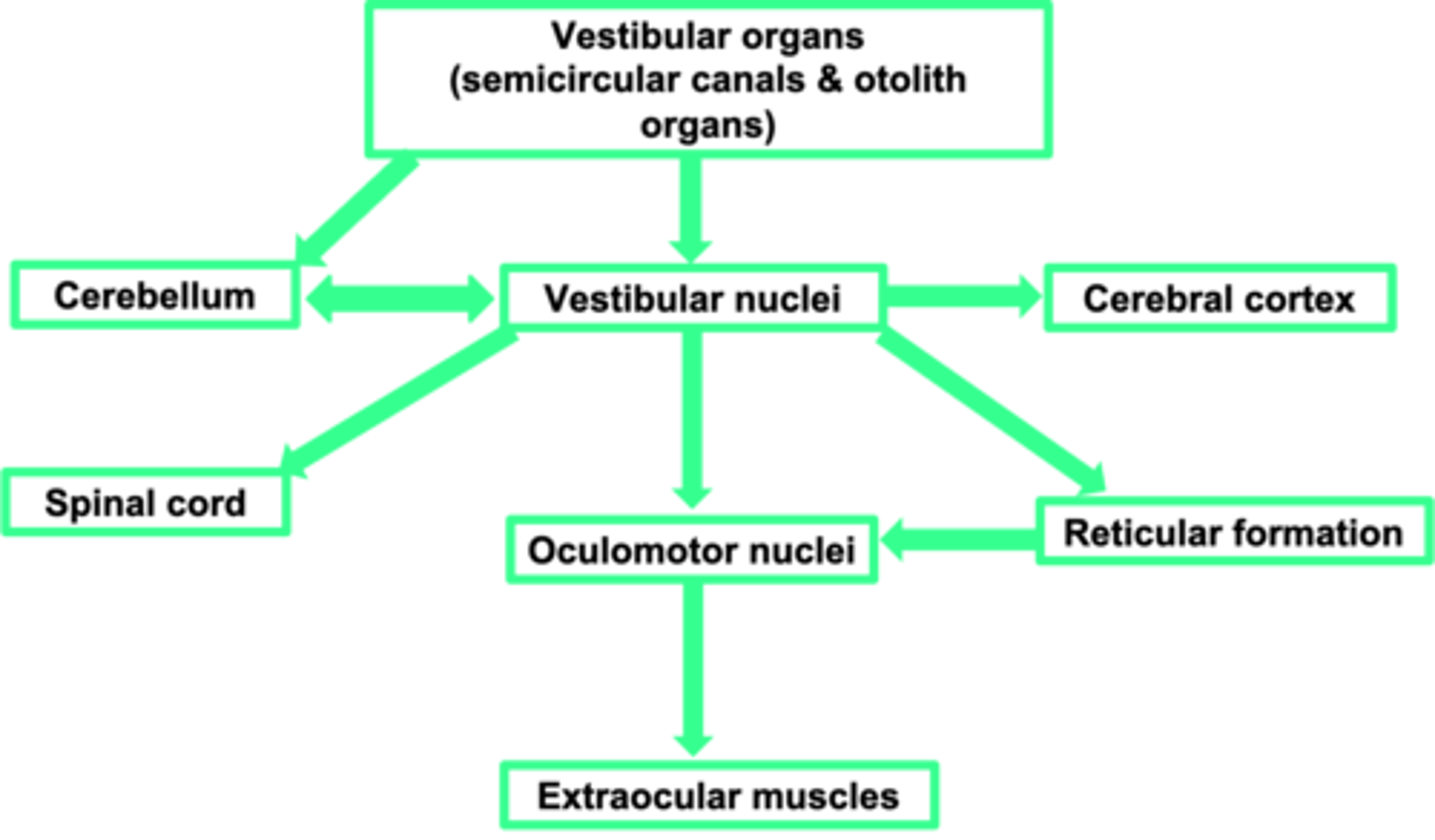
Perception
What does the cerebral cortex allow?
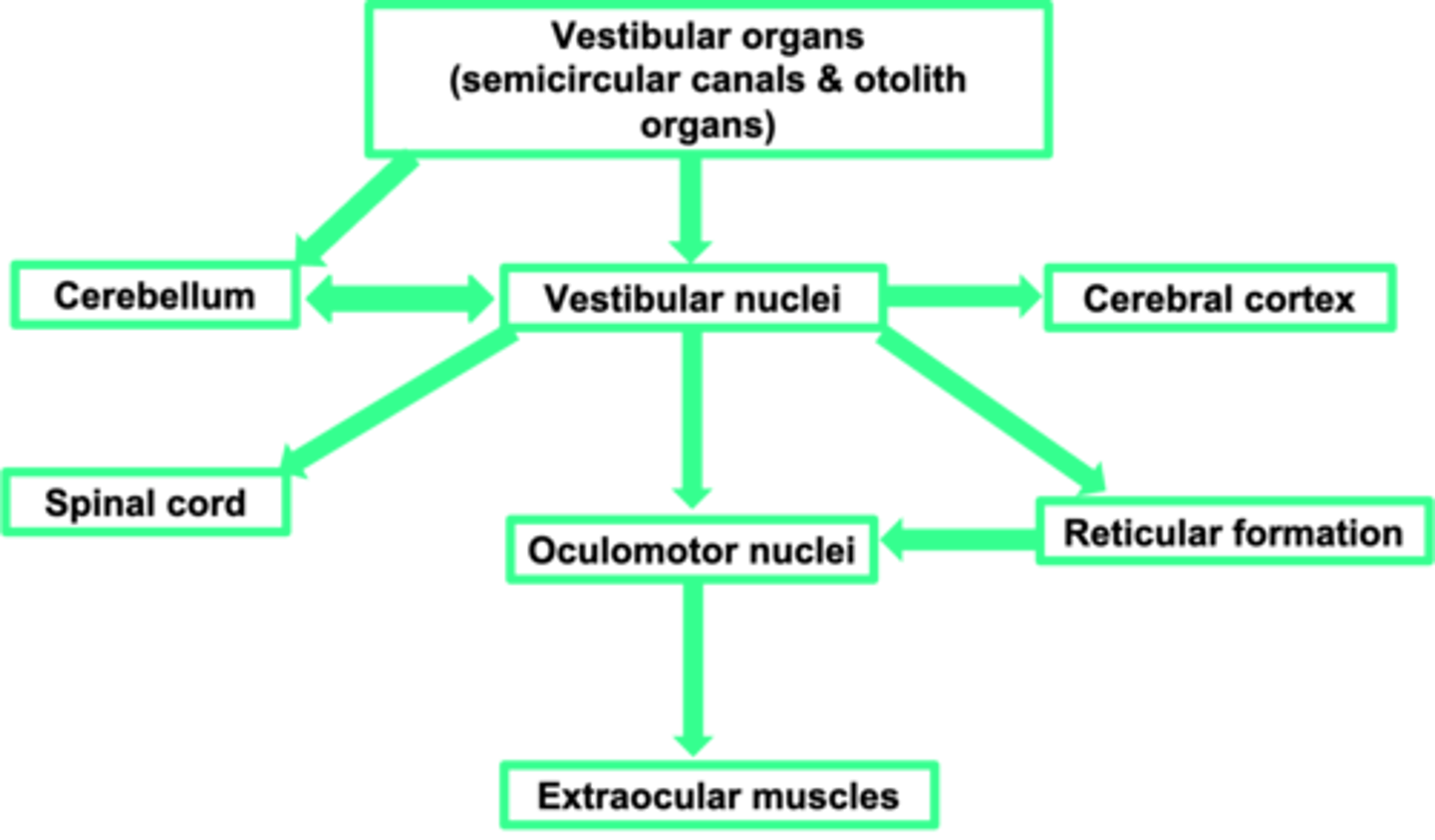
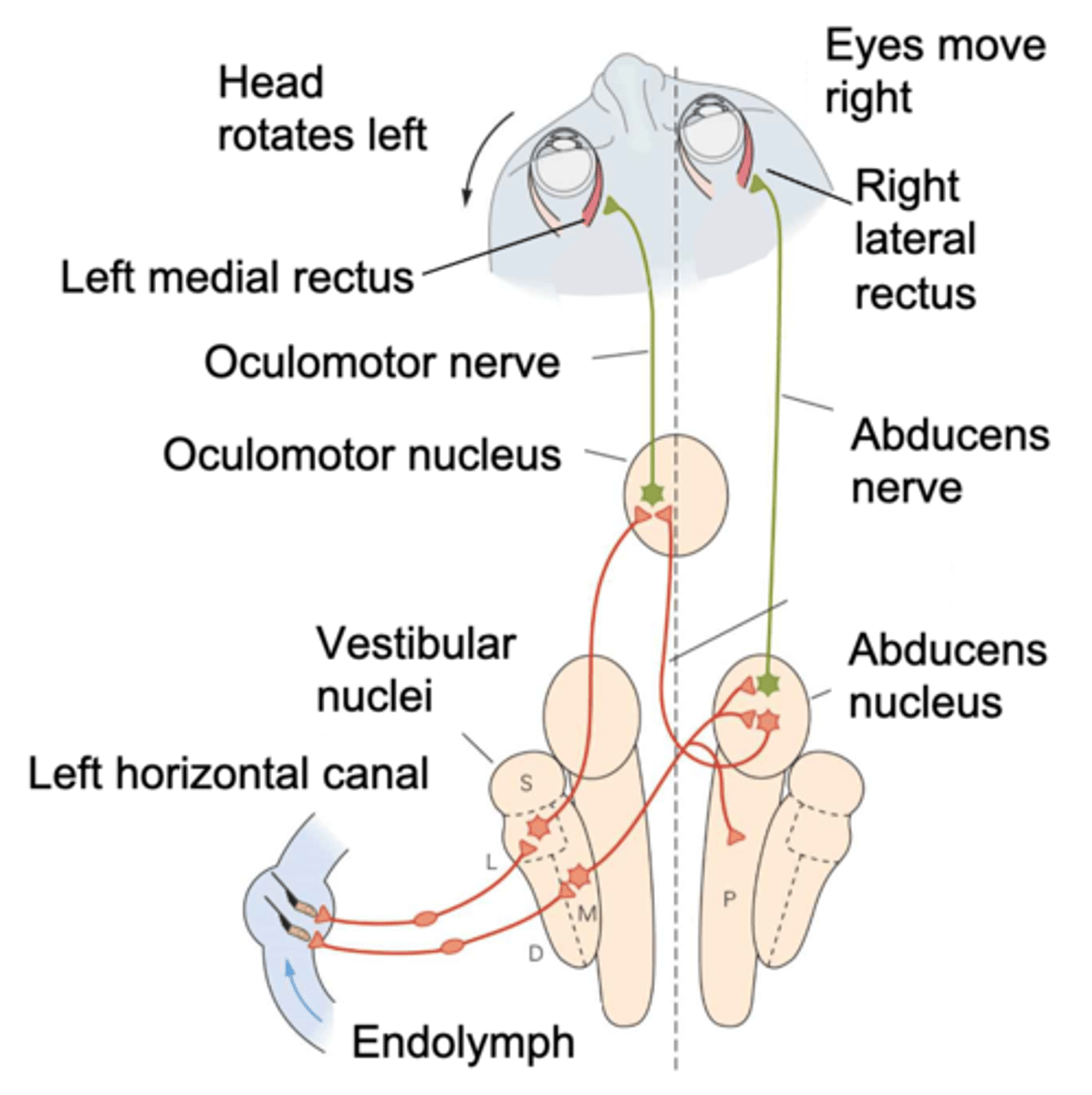
Sends information to the muscles of the eye (ocular = eye, motor = muscles) - adjusts the eye muscles
What does the oculomotor nuclei do?
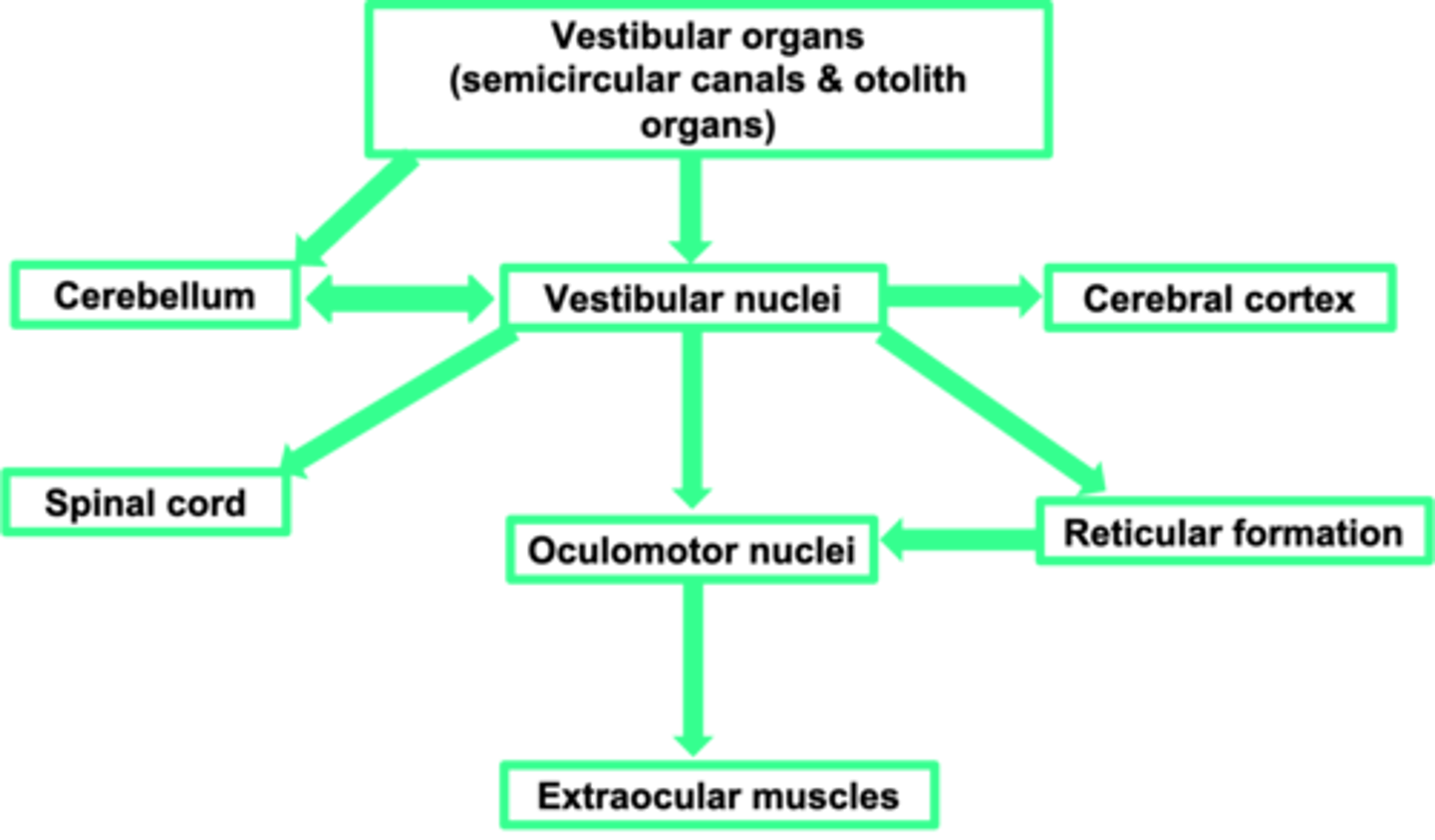
Change in movement
What does the spinal cord allow?
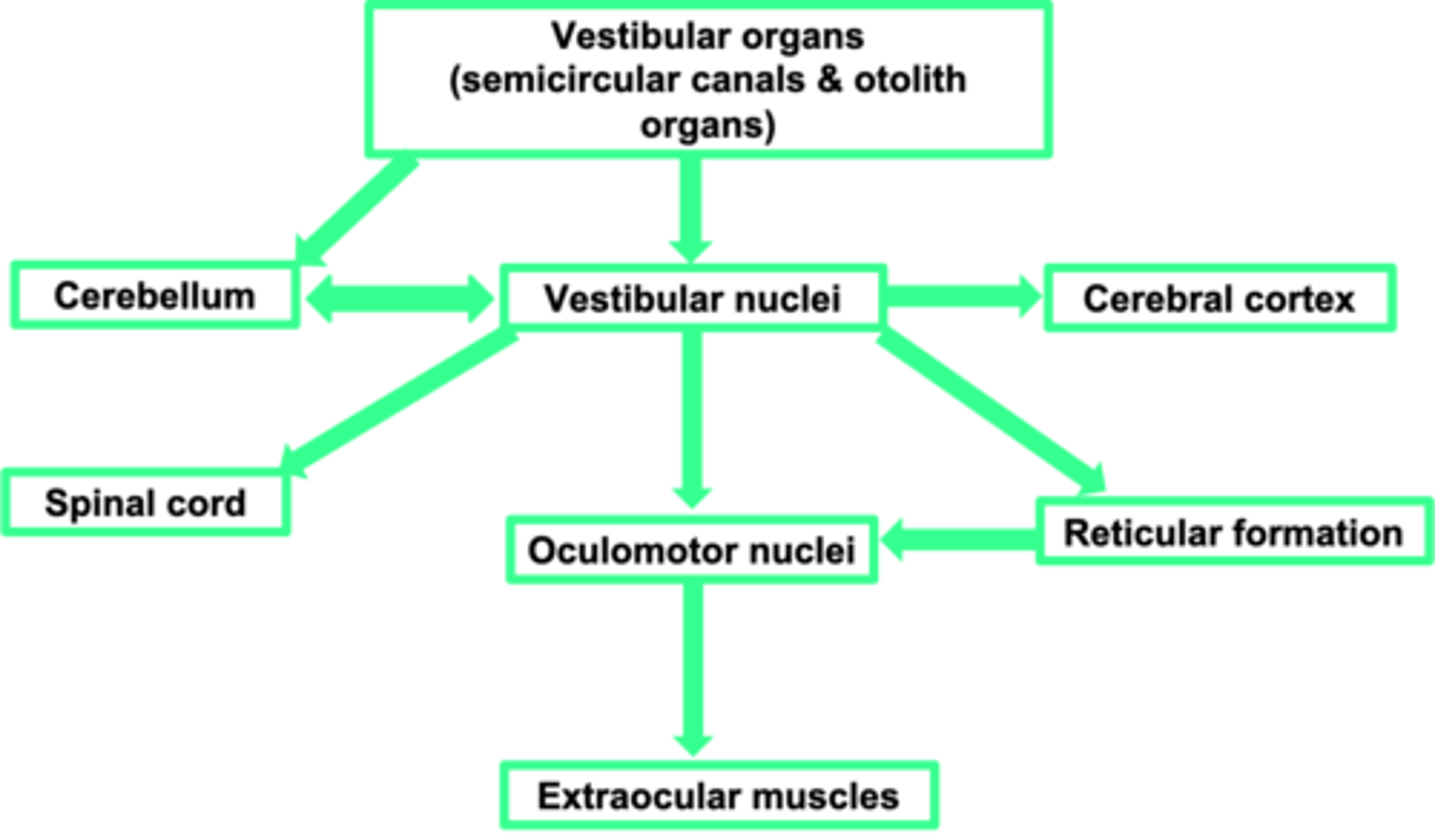
Motor coordination
What is the cerebellum important in?
Cerebellum
The vestibular system needs a strong link to the ...?
Brain stem, oculomotor nucleus, abducens nucleus
When shaking your head you activate your vestibular system and hair cells, allows communication into ________ _______ and allows connection with _______________ _________ and ____________ __________ which pulls your eyes back in the right direction
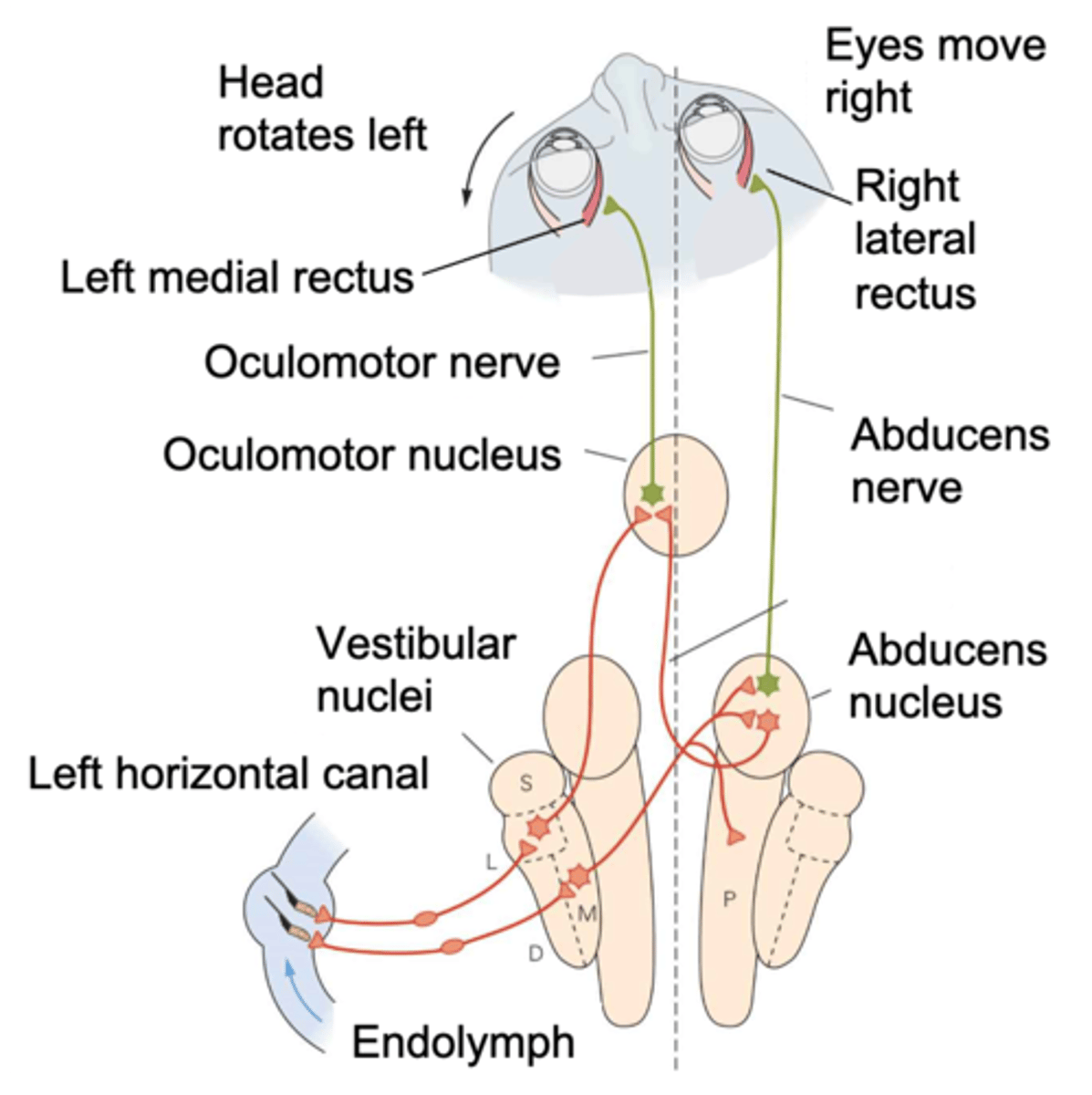
Pull your eyes to the right
If you move your head to the left and you want to remain focused, what must your eye muscles on your right do?
The resetting of eye position during sustained head rotation
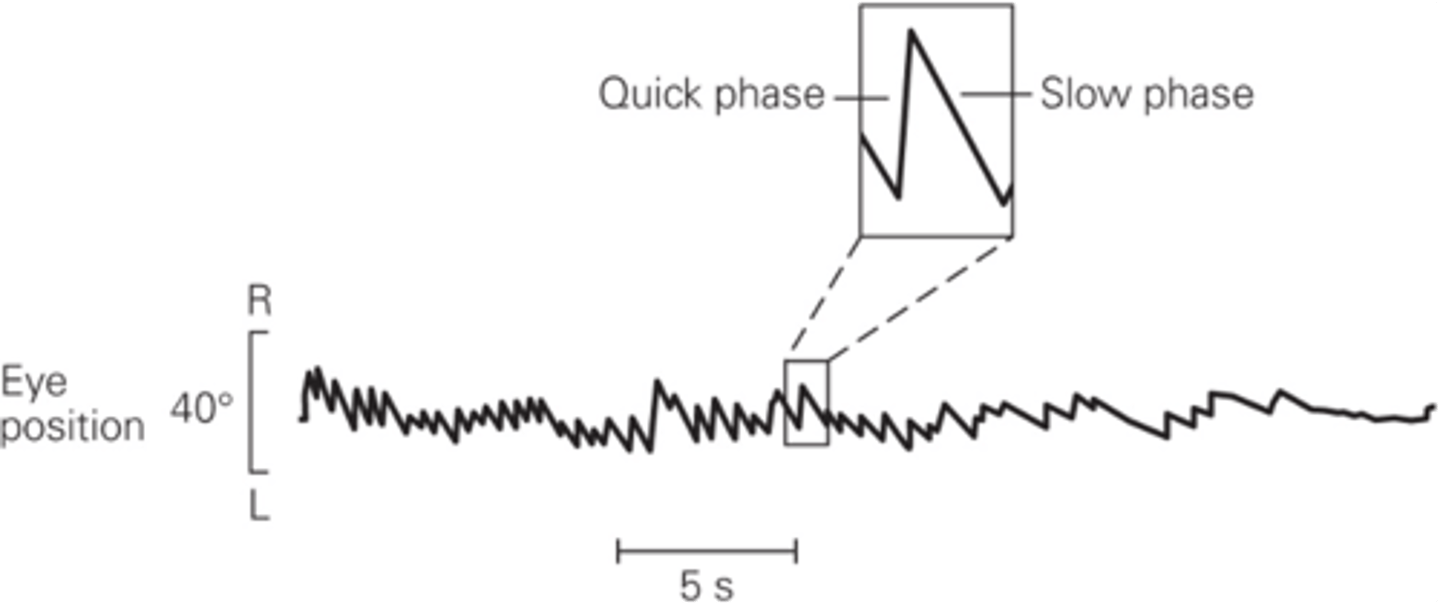
What does vestibular nystagmus enable?
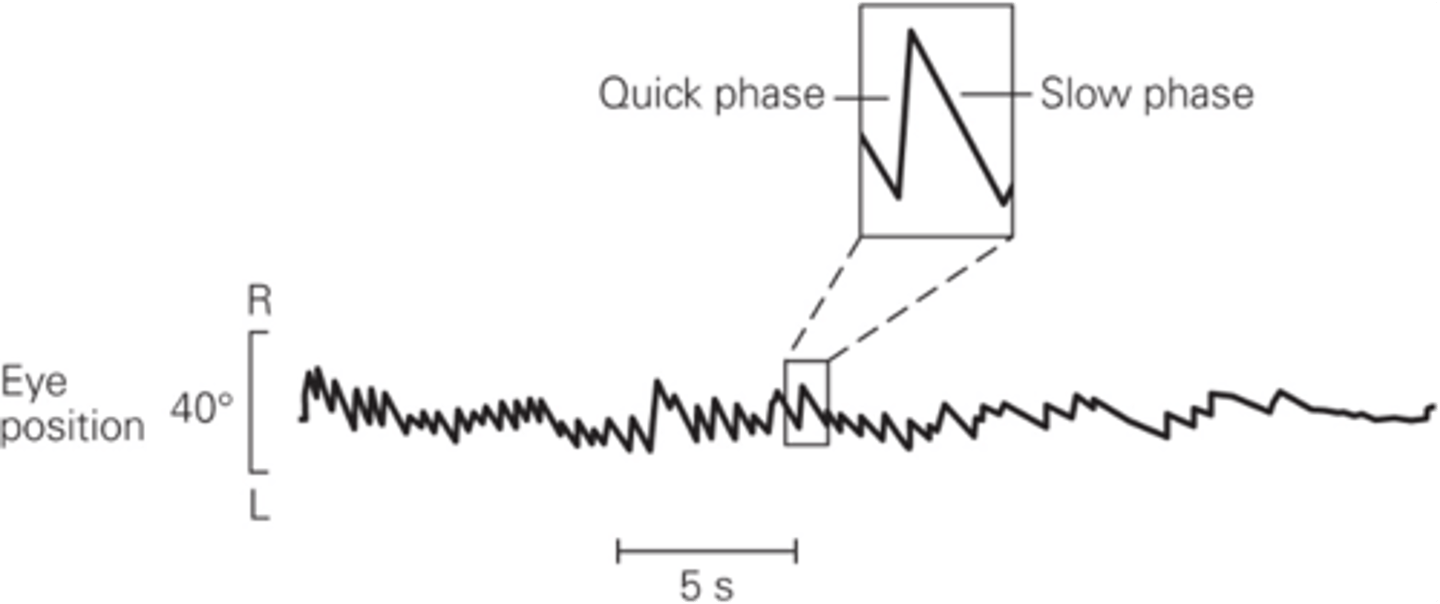
Eyes rotate in the opposite direction to head movement
What is slow phase?
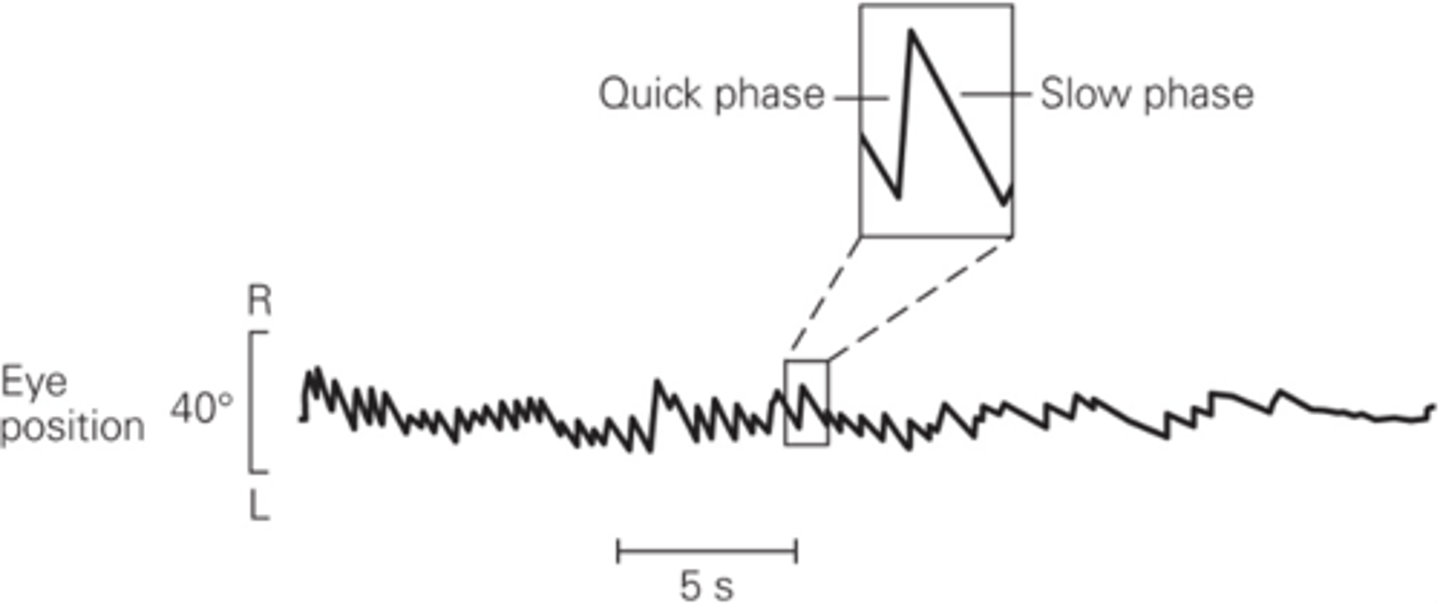
Rapid resetting movement back to the centre of the gaze
What is quick phase?
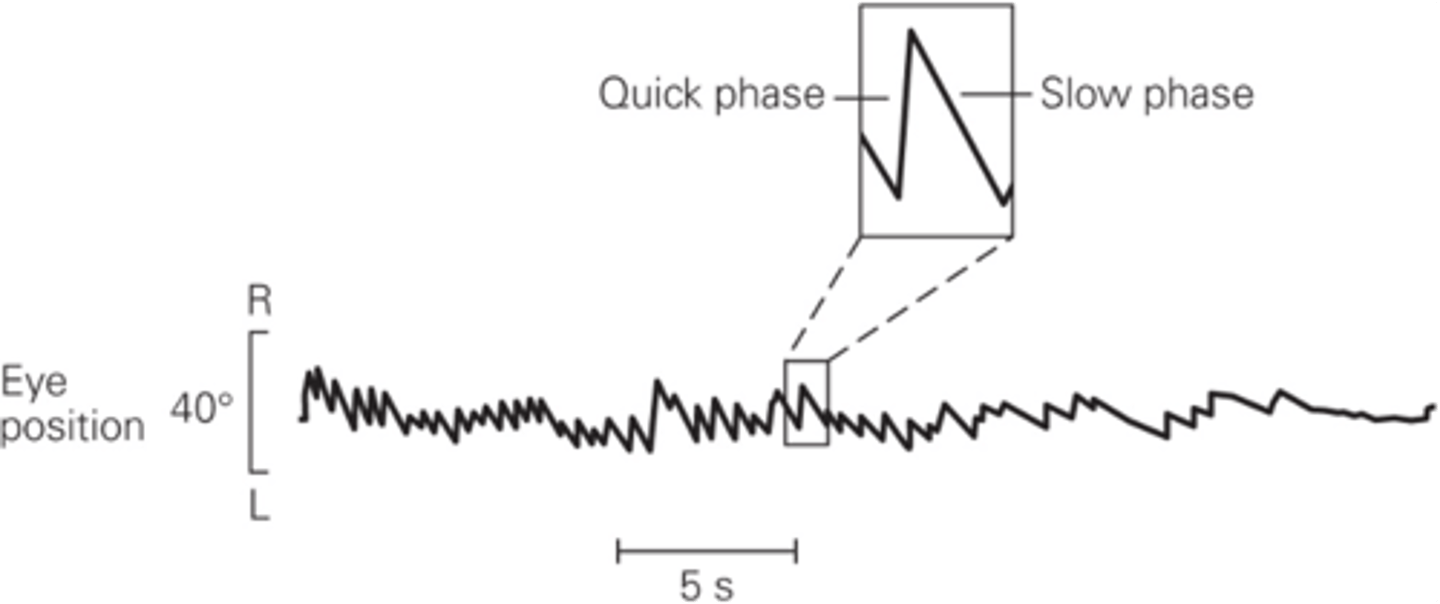
Right beating nystagmus
Right quick phase movement = ?