A&P: Visual pathway
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Optic chiasm
Flattened structure behind the optic nerve
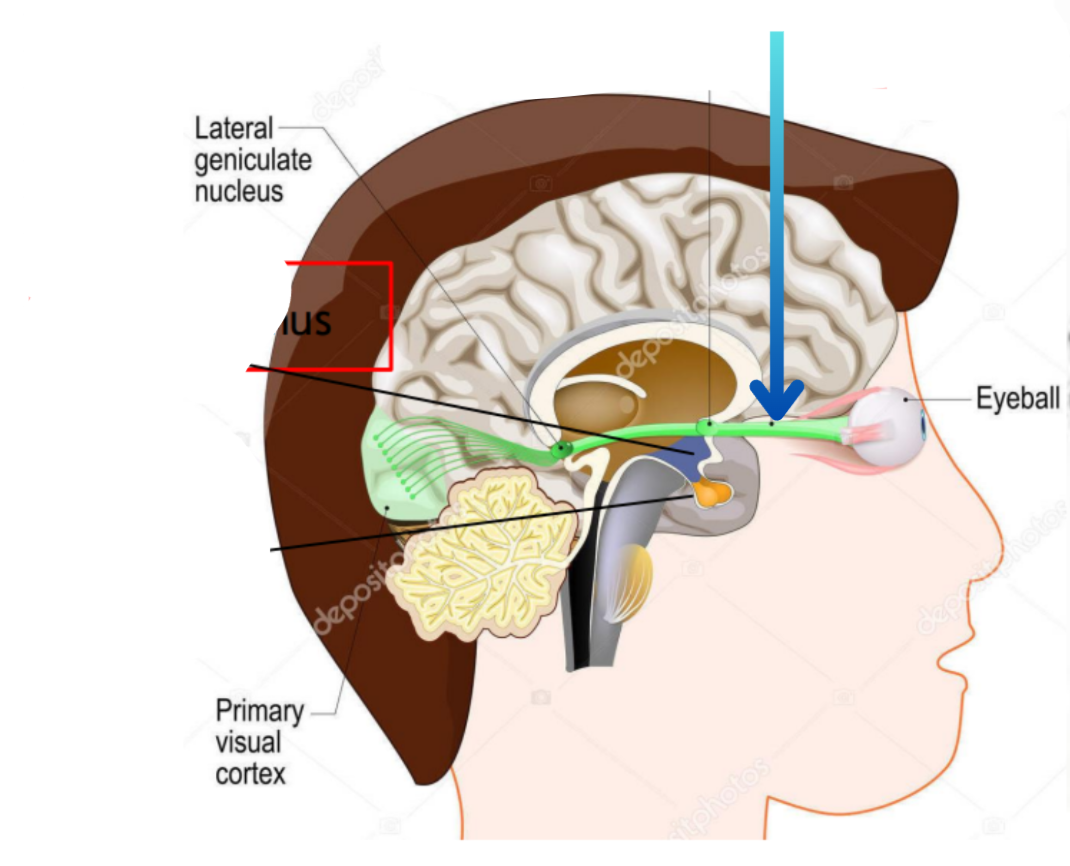
Optic nerve
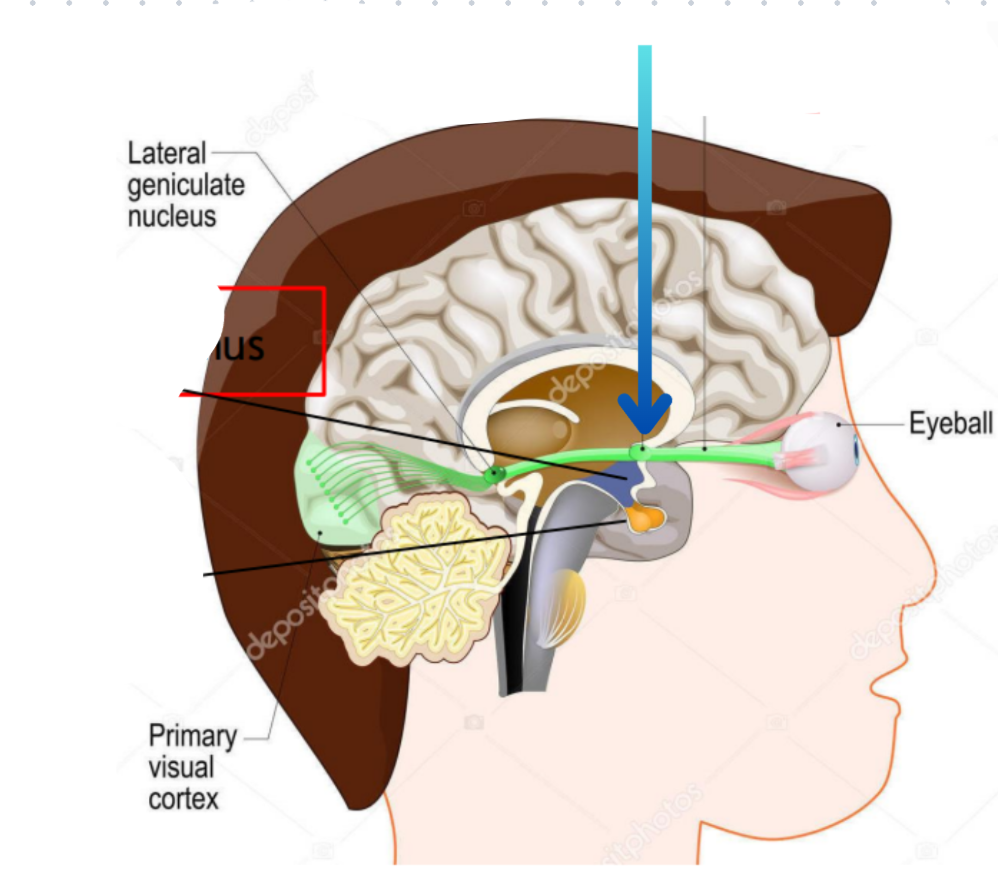
Optic chiasm
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
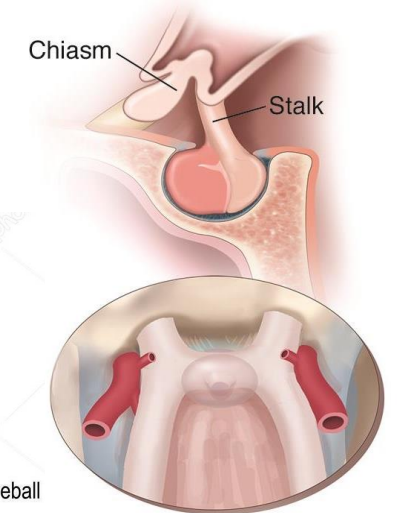
Prefixed optic chiasma
Lies more anteriorly over tuberculum sellae, pituitary tumor involves optic tract first.
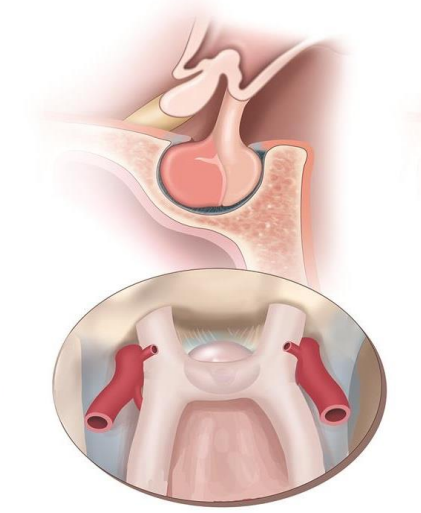
Normal optic chiasma
Chiasm lies directly over sella
Expanding pituitary tumor involves chiasm first
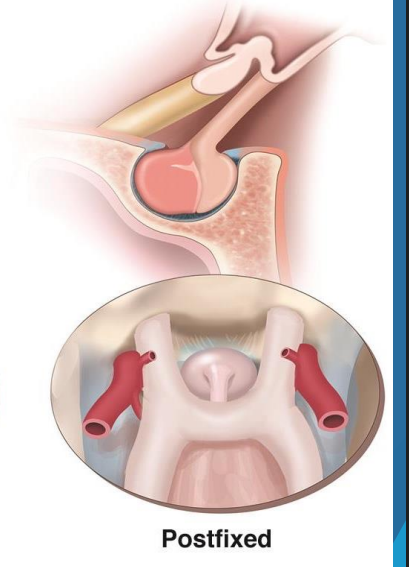
Post fixed optic chiasm
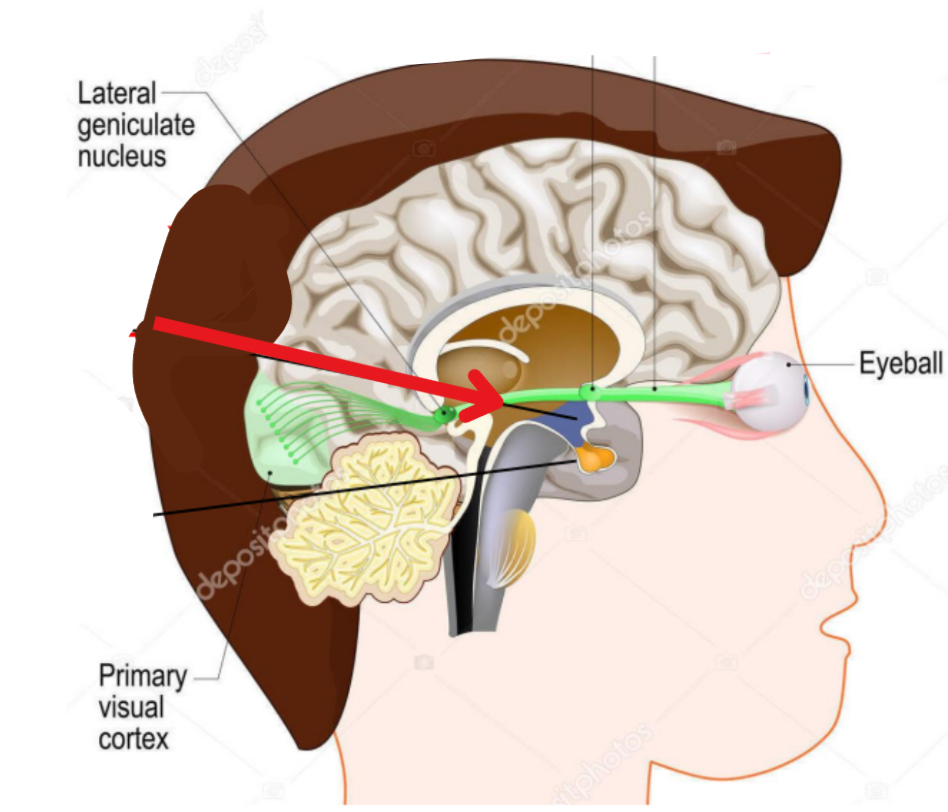
Optic tracts
Cylindrical bundles of nerve fibres
Crosses nerve fibers
Nasal fibers of OD and OS
End at lamina 1,4, and 6 of LGN
Uncrossed nerve fibers
Temporal fibers of OD and OS
End at lamina 2,3, and 5 of LGN
Magnocellular layers
Layers 1 and 2 of LGN
Contains large cells
Carry signals for detection of movement and flicker
Parvocellular pathways
Layers 3-6 of LGN
Contains small cells
Accurate point spatial information for texture, shape, and fine depth vision
Koniocellular pathway
Function still not understood
Thought to be involved with color vision
Short-wavelength sensitive cone cells in retina
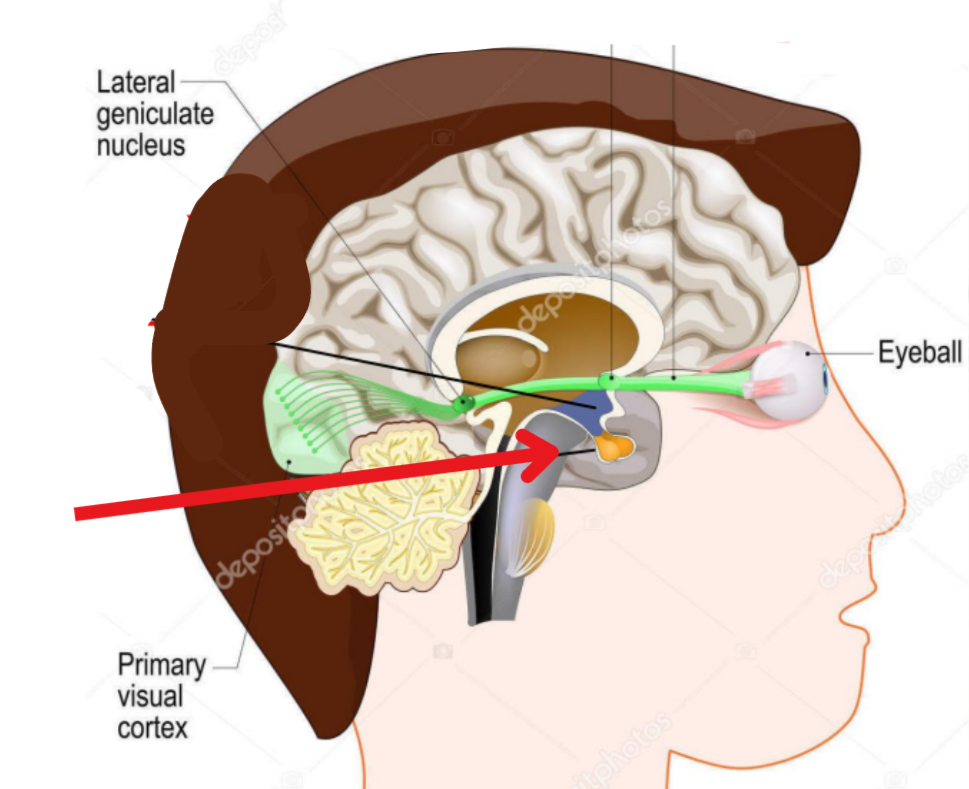
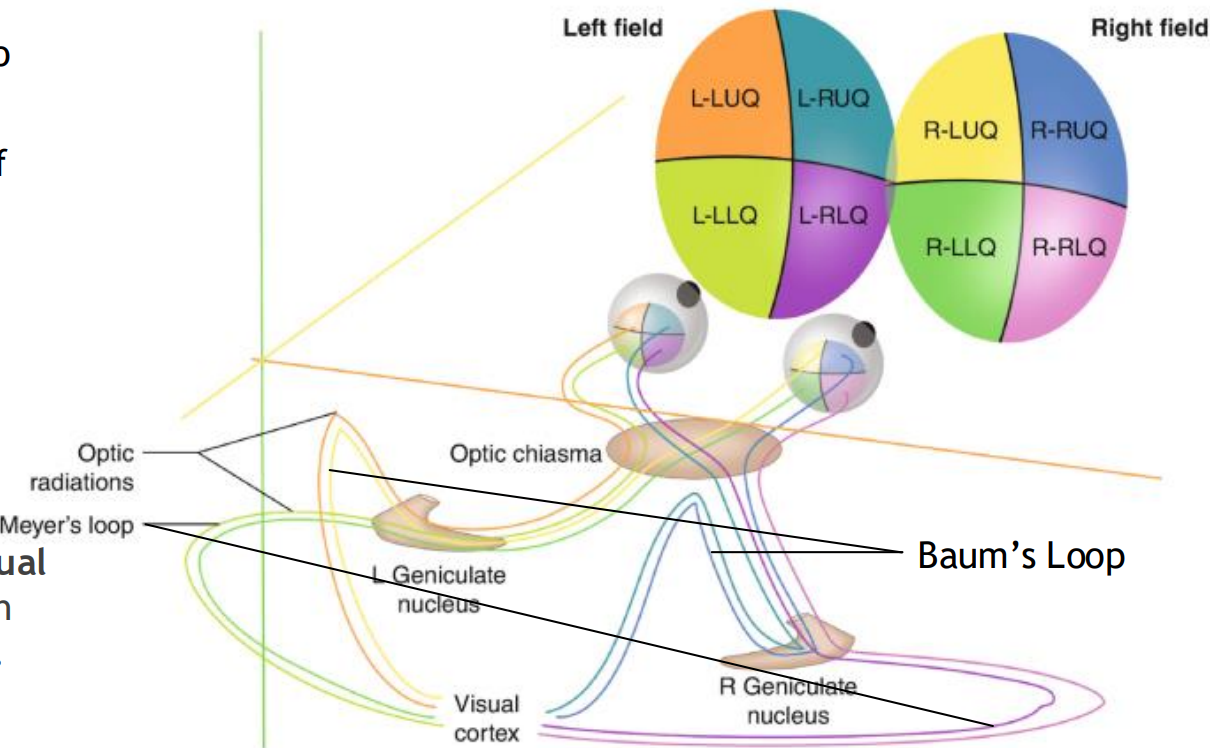
Optic radiations
Neurons of the LGB send their axons to the occipital corte
Baums loop
Made up of superior fibers of the retina (Process inferior visual field)
As they pass through parietal lobe, they form baums loop
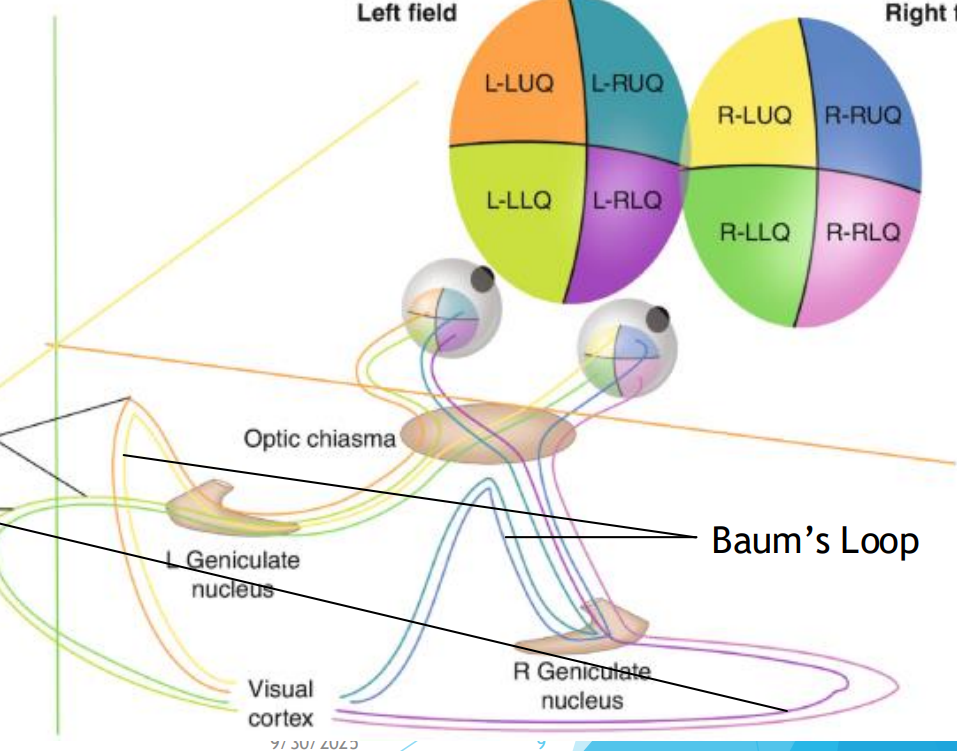
Meyers loop
Made up of inferior fibers of the retina (Process superior visual field)
As they pass through the temporal lobe, they form meyers loop
Occipito temporal (Ventral) pathway
Begins at V1 of LGN (Foveal vision)
“What pathway”
Occipitoparietal (Dorsal) pathway
“Where” pathway
Movement, spatial awareness, locating objects