Unit 6 & 7 - Supply, Disposal and Recycling Strategies
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Global Supply Chain Management
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are “residues”, where and why do they appear and how to deal with them?
Residues are substances that are inevitably generated in a production process, but which are never the goal of production or consumption. Residues that flow back into production or consumption, in whole or in part, are known as “recyclable materials” or “waste for recycling”. Residues that are not reused are known as “waste for elimination”.
“Residues from consumption processes” are materials or products that can no longer be used by the customer, or packaging material that is no longer fit for use.
“Residues from production processes” are any work materials, raw materials, auxiliary materials, operating materials, or emissions of air, water, or soil that are no longer usable and can be attributed to the production process.
Why does quality assurance matter and which fundamental options exist when dealing with quality?How does the Quality Function Deployment work?
What are the key Fields of Decision for Supply Strategies?
Make or buy
Market research
Scope of supply
Supplier responsibilities
Briefly describe disposal logistics
Core services
transport
transshipment
storage
Additional services
collection
separation
Information services
What is re-use?
Using an item for its original purpose (e.g. 2nd hand clothing)
What is re-utalization?
Using something for an alternative purpose (e.g. using old t-shirts as cleaning cloths)
What is recovery?
Material yield is used for same purpose as original material (scrap glass containers, e.g.)
What is reclamation?
Material is used for different purpose as original (shopping bags from plastic bottles, e.g.)
Explain the correlation between quality assurance and competitive pressure
Due to globalization, technological progress and social developments, businesses are under competitive pressure. The competitive pressure affects companies and supply chains and foster formation of supply chains.
Globalisation: global production to achieve lower unit costs, global sales to increase revenue.
Technological progress: shorter product life cycles and a need for innovative activities.
Social developments: increasing consumer expectations, legislative initiatives.
Explain the correlation between quality assurance and cooperation along the supply chain
Cooperation along the supply chain is helpful for various reasons. Value creation split among partners, collaborative innovative efforts and need to create synergies, leads to pressure to seamlessly integrate partners into the production network.
Name some methods within quality management
ISO standards, Quality function deployment (QFD), Total quality management (TQM), EFQM and Six sigma.
What are the motives for introducing quality management systems in organisations?
Companies use quality management systems for a few reasons:
Quality matters when people buy services.
They want to be better than their competitors.
They want consistent quality and checks from neutral organizations.
This is important in a globalized market with more outsourcing.
What does QFD mean and what main factors does it take into account?
QFD means Quality Function Deployment and is a subarea of Total Quality Management in which the factors of flexibility, cost, and time rank as priorities alongside the key variable of quality.
Which QFD tools are you familiar with? Describe one of these tools in detail.
A frequently used as a planning and analysis tool in the context of QFD. This tool is a matrix that takes into account six different areas in product development and is reminiscent of a house due to the relative positions of the various elements.
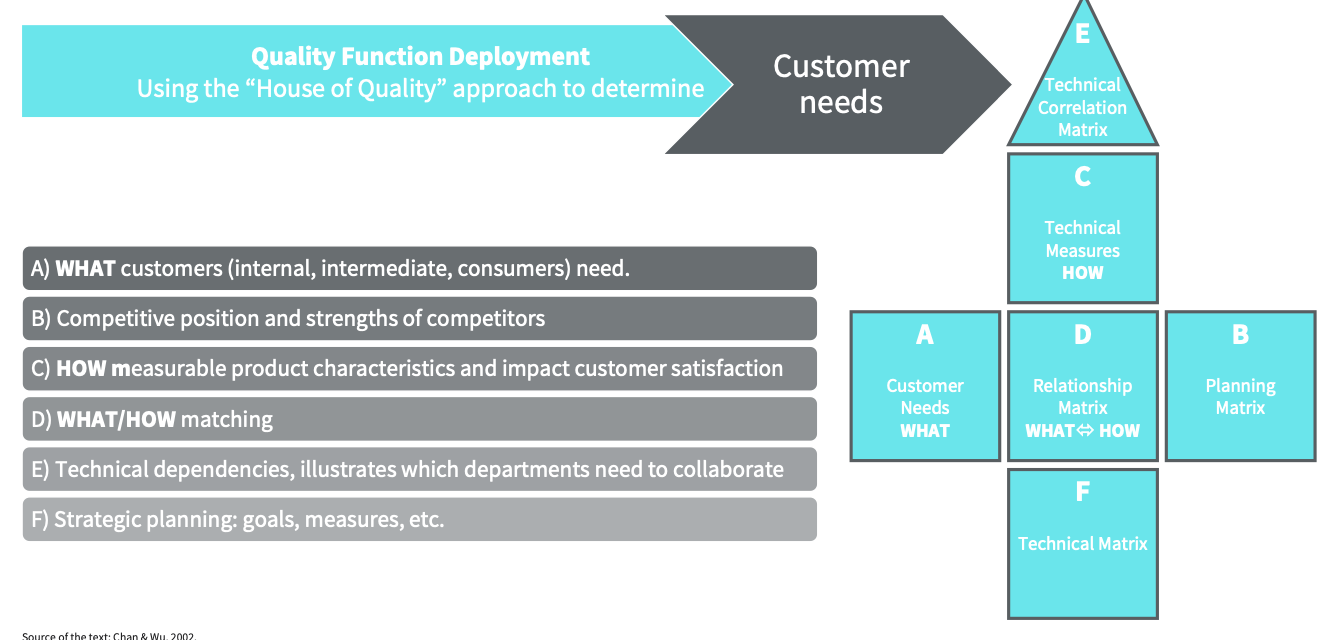
What are the four phases of QFD?
Customer needs
Technical measures
Planning process
Process operations