Single Phase Motors
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the electrical safety limits for a gasfitter and typical skin resistance values?
Max: 100VA AC, 150VA DC
Dry skin resistance: 100k–600k ohms
Wet skin resistance: ~1k ohm
Shock thresholds:
15mA: painful
15–75mA: can’t let go, breathing may stop
100–200mA: heart skips, likely fatal
200mA: severe burns, heart may stop
What are the general characteristics of single phase motors?
Common where 3-phase not available (resi/commercial)
Efficiency: 60–68%
Sizes: up to 15HP, often fractional HP
Less efficient, heavier than 3-phase
How does a resistance split phase induction motor operate and what are its features?
Two stator windings (main and aux) with different R and L
Run winding: large conductors, more turns, bottom of stator
Aux (start): small conductors, fewer turns, 90° to run winding
Start winding disconnects at ~75% full speed
Start torque: 125–150% of running torque
Start current: 5–6× running
Phase angle: ~30°
Constant speed (typically 1750 RPM, 4-pole)
Reversible (at standstill), Reversing (while running)
Used for: washers, sump pumps, fans (low inertia loads)
What is a capacitor start induction motor and how does it compare to a resistance start motor?
Adds capacitor to aux winding for phase shift
Nearly 90° phase angle
Same number of turns in run and aux windings → more startup flux
Lower current draw (~30% less)
Higher starting torque
Canister-mounted capacitor
After start, operates like resistance split phase motor
What is a permanent split capacitor (PSC) motor and its pros/cons?
Aux winding and capacitor stay in circuit continuously
Advantages:
Quiet, 2-phase-like operation
Good power factor, efficiency
No centrifugal switch
Can reverse while running
Disadvantage:
Uses large, costly oil-filled capacitor
Types:
Single Voltage Non-Reversible
Dual Voltage Reversible
Single Voltage Reversible
2-Speed Single Voltage
What is a two value capacitor motor and what makes it unique?
Combines PSC and capacitor start motor features
Uses 2 capacitors:
Start capacitor: high capacitance, electrolytic
Run capacitor: continuous rated, oil-filled
Uses cutout switch
Provides both strong starting and running performance
Reversible by swapping start winding leads
What is a shaded pole motor and what are its limitations?
Aux winding: 1-turn copper ring around each pole
No centrifugal switch
Phase shift from shading creates rotation
Very inefficient (5–35%)
Low starting torque
Reversing requires mechanical changes or shaded ring circuiting
Variable speed by adjusting applied voltage
Used in low HP applications
How are single and dual voltage motor leads typically configured?
May have 2 to 9 leads (for reversing, thermal, capacitor, etc.)
"T" labels for leads common
NEMA rotation: CCW viewed opposite shaft end
IEC rotation: CW viewed from shaft end
Both result in same actual direction
What is important about thermal protection in single phase motors?
Leads labeled "P"
One lead is current sensing (has resistance), one is breaking (0 ohms)
In dual voltage motors:
2 main coils in parallel (low voltage), in series (high voltage)
Start coil remains in parallel with one main coil
What are basic maintenance steps for a single phase motor?
Lubricate
Check stator and bearing temps
Check shaft for bearing wear
Check insulation with megger
Replace rather than repair in most cases
What are the key nameplate specs to interpret on a single phase motor?
Service Factor: how much overloading allowed without overheating
Insulation Classes:
A: 105°C
B: 130°C
C: 155°C
D: 180°C
Enclosure: TEFC (Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled = most common)
Frame: standard for motor size and mounting pattern
How do you calculate motor current draw and power loss?
Motor HP = mechanical power
current draw = electrical input
1 HP = 746 Watts
Efficiency losses:
Electrical: iron loss (core), copper loss (resistance)
Mechanical: friction in bearings, windage (air resistance)
How do you calculate current draw from nameplate values?
Given: 1.5 HP, 115V, 75.5% eff, 73% power factor
1.5 × 746 = 1119W
1119 / 0.755 = 1482W (real power)
1482 / 0.73 = 2030W (apparent power)
2030W / 115V = 17.7 Amps
What are the four main components of a resistance split phase motor?
Frame
Centrifugal switch
Stator
Rotor
What is the typical HP range for resistance split phase motors?
1/6 to 3/4 HP
Is a resistance split phase motor reversible?
Yes, if start winding leads are brought out to the terminal box
What distinguishes aux windings in PSC vs resistance start motors?
PSC: aux coil rated for continuous duty
Resistance split phase: aux coil only used for start
What component does a capacitor start motor have that a PSC motor doesn’t?
Cutoff switch (to remove start cap after startup)
How does capacitance differ between capacitor start and PSC motors?
Start motor: higher capacitance, oil-filled, continuous duty rated
What extra components does a two value capacitor motor have?
Cutout switch
Start capacitor (higher capacitance than run cap)
Is a two value capacitor motor reversible?
Yes
How do you reverse a shaded pole motor?
Reverse armature or change field winding connection
Motor Types Chart
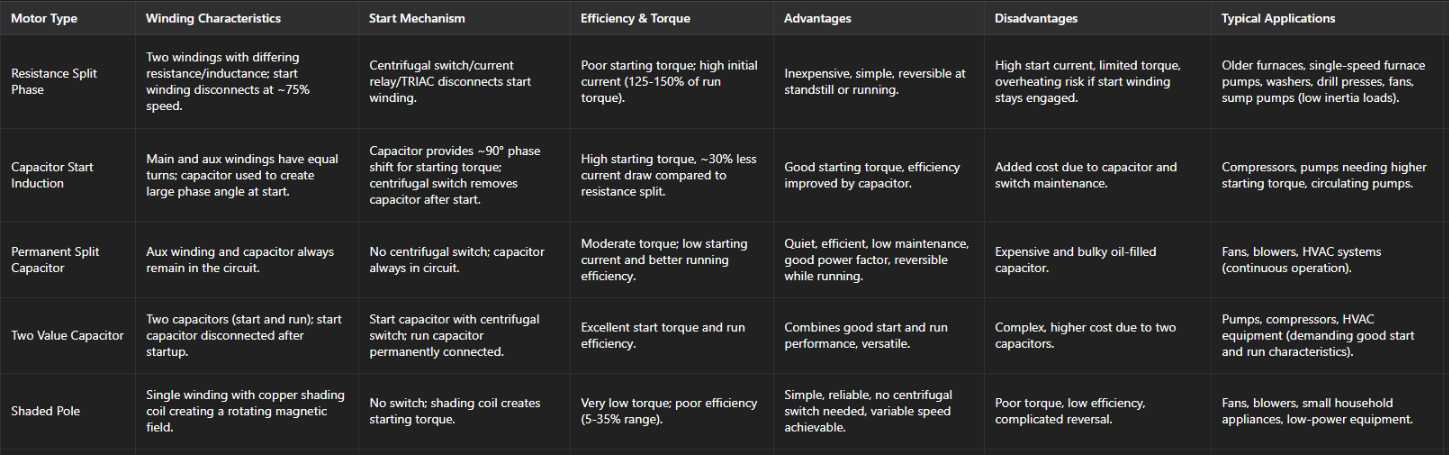
Single Phase motor wiring diagrams