neuroglia
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
neuroglia
cells that function is to support neurons
maintain ECM
protection
able to divide
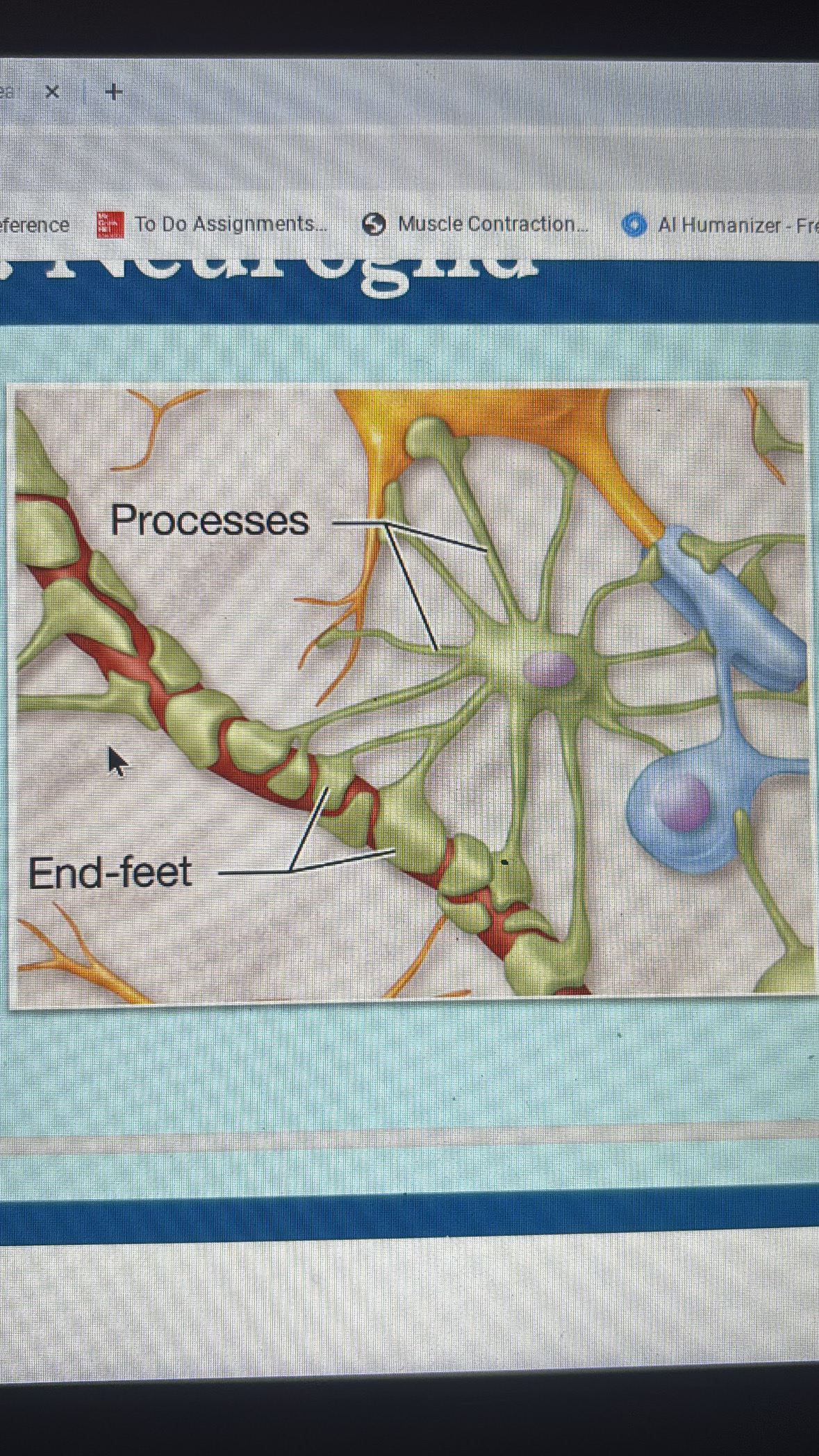
astrocytes
CNS
largest and most numerous
anchor neurons and blood vessels
form blood brain barrier
repair damage brain tissue
Oligodendrocytes
myelinate certain CNS axons in the CNS
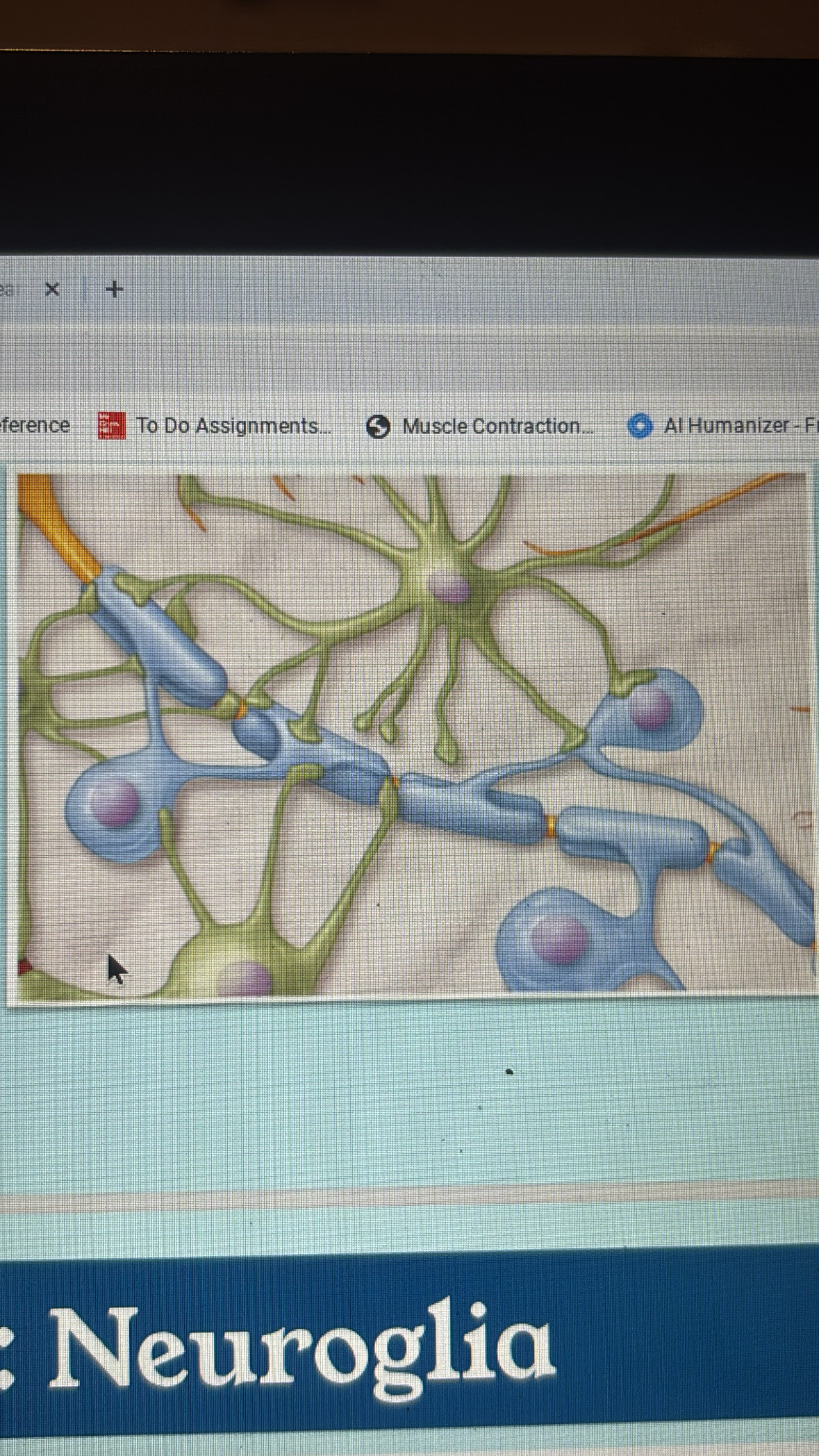
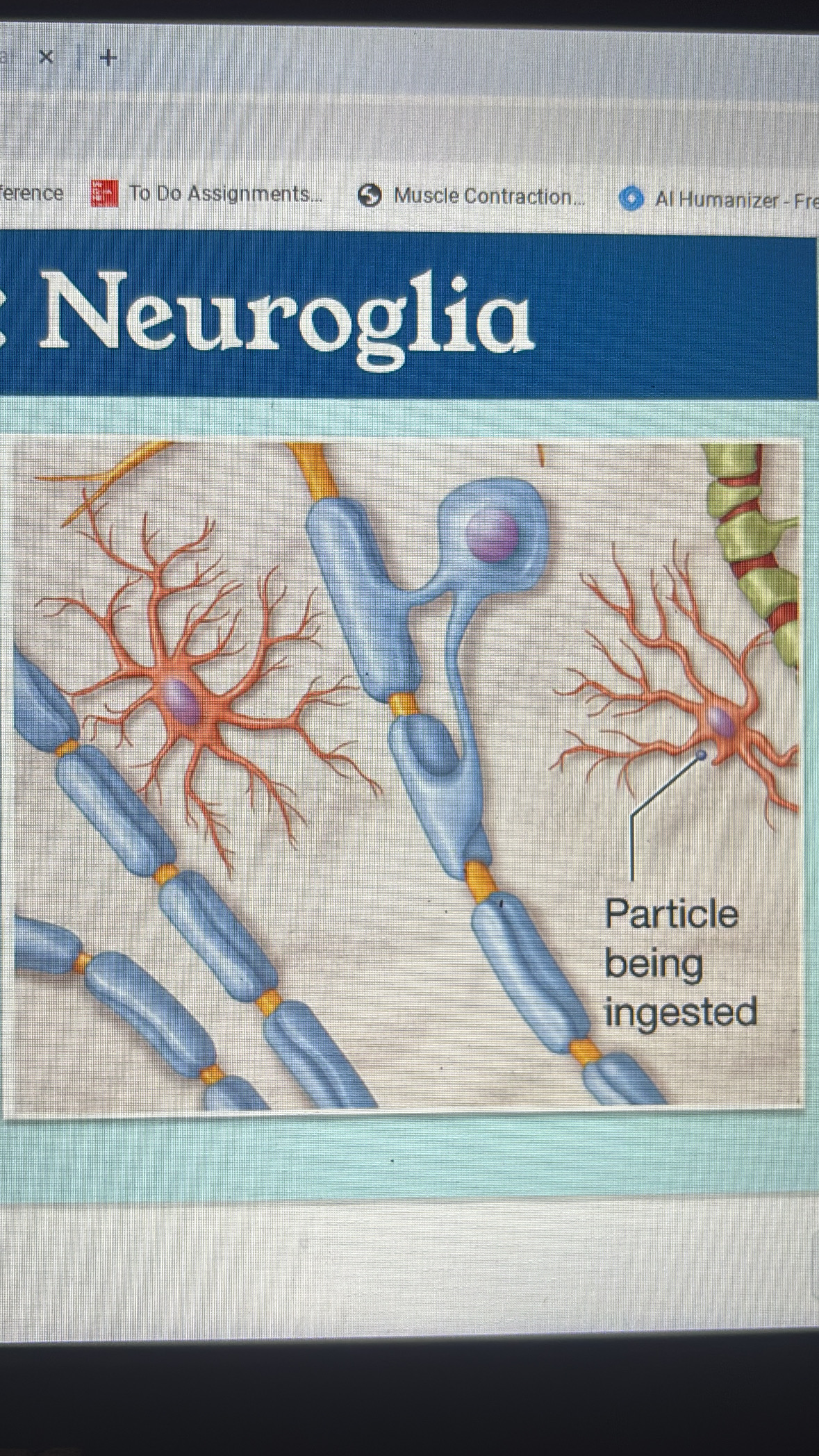
microglia
CNS
activated by injury
removes cells and debris by phagocytosis
stimulate inflammation
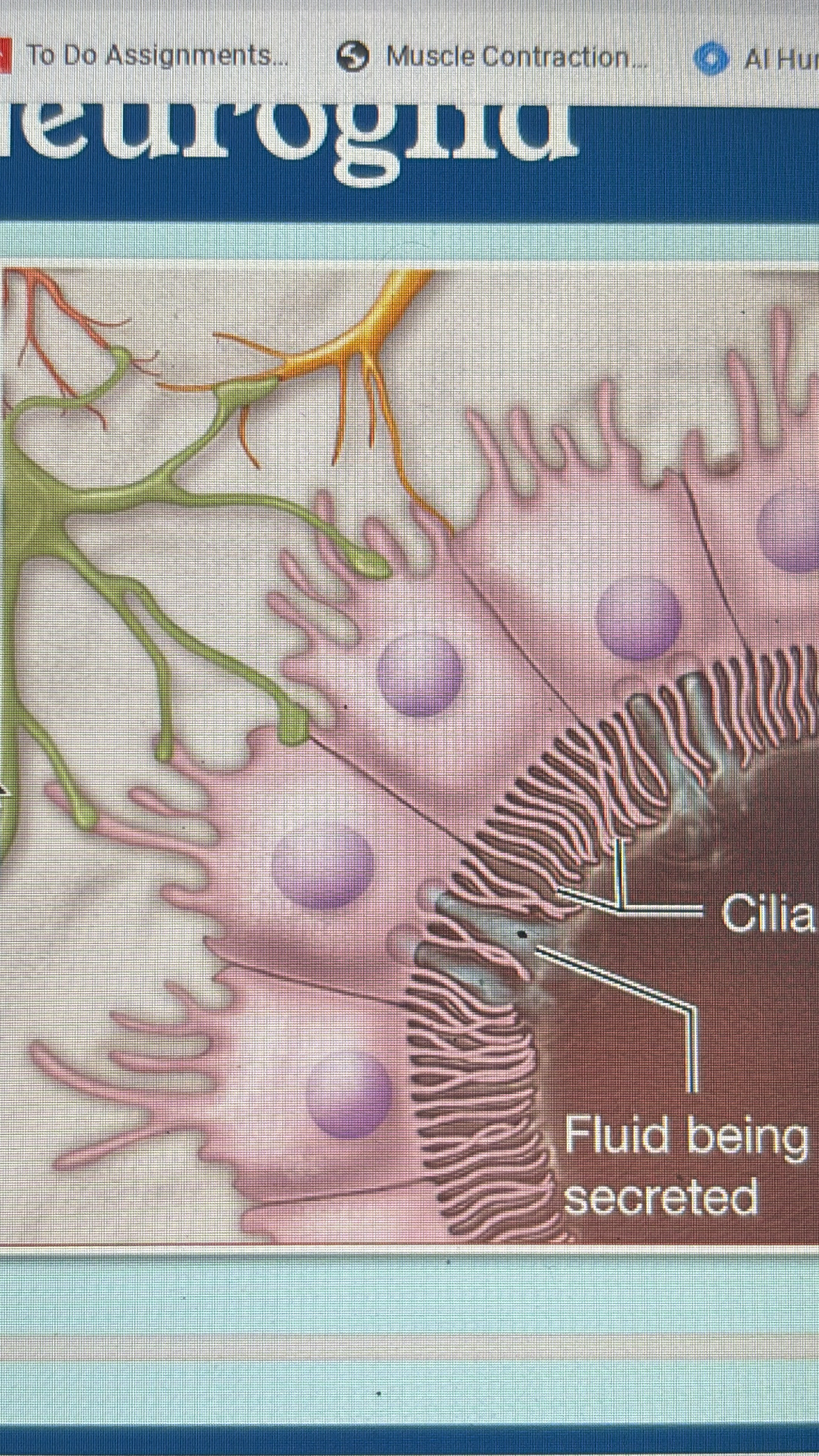
ependymal cells
CNS
line cavities
circulated cerebrospinal fluid
produces cebrospinal fluid
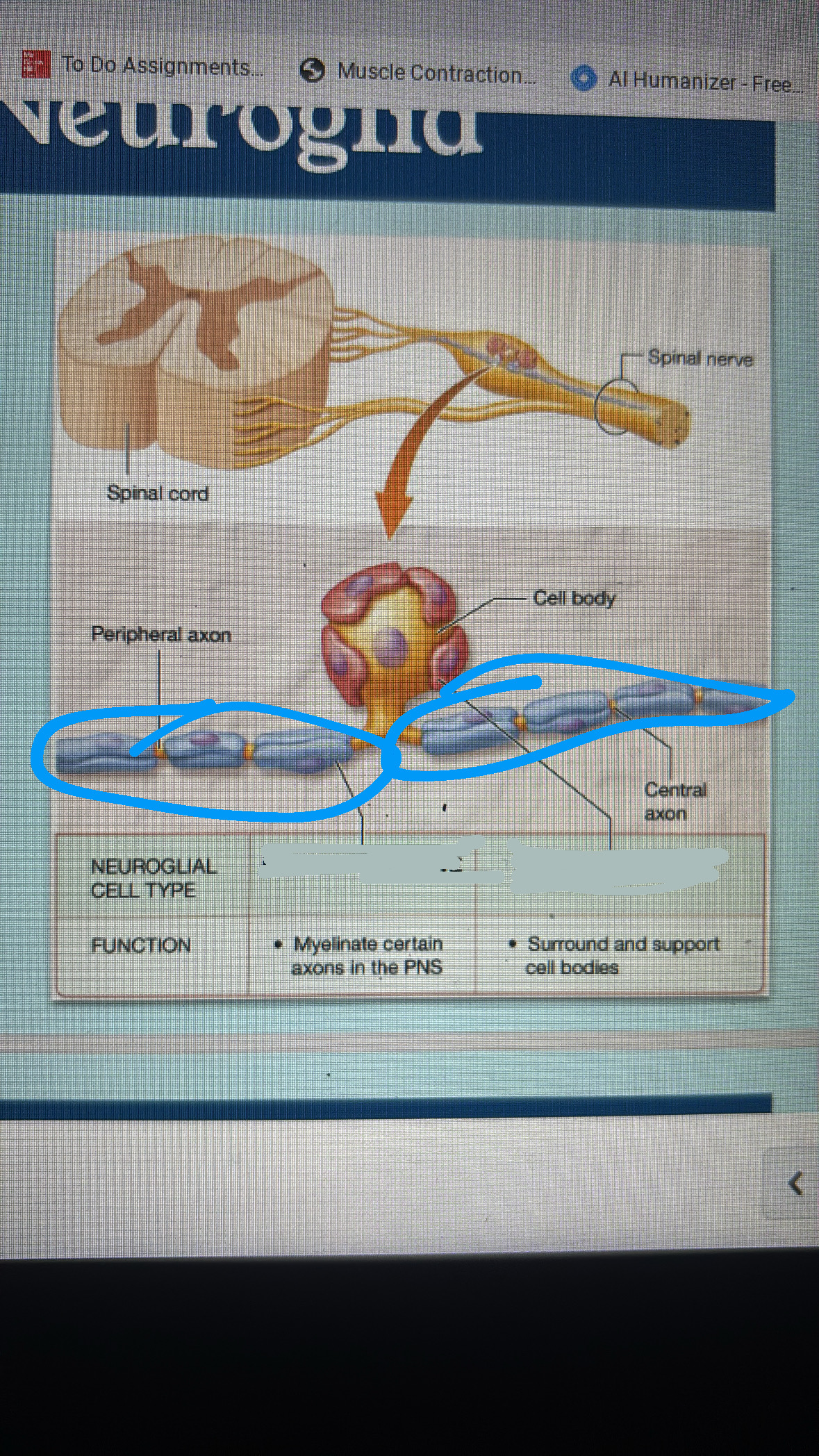
neurolemmocytes
PNS
repair damaged axons
aka Schwann cells(protective myelin sheath)
repair damaged axons
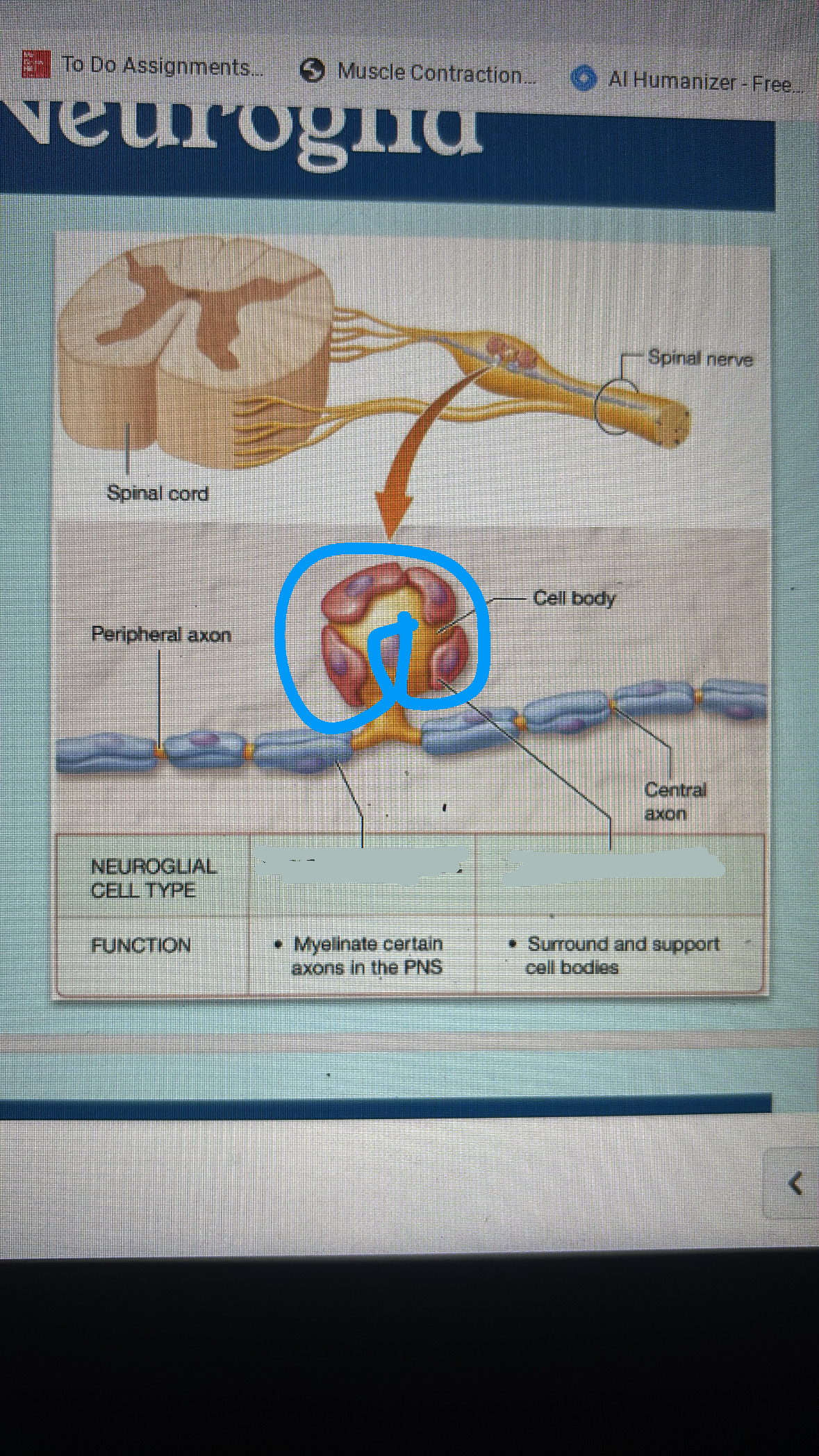
satellite cells
poorly understood
supports cell bodies
links to other cells
maintain ECM
myelinated axons
conducts action potentials 12-150x faster than axons w/o
membrane potential
electrical gradient across the plasma membrane, resting is -70mV and polarized
“all or nothing”
local potentials
only travel short distances potential
reversible
neurons
excitable cells that send/receive signals in the form of action potential
directly responsible for nervous tissue function
generally amitotic
ventricles
continuous cavities within the brain and spinal cord
lines with ependymal cells
filled with cerebrospinal fluid
cerebrospinal fluid
cushions and insulated the brain
removes waste from the brain re