Urban Growth Models
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts related to models of urban growth and organization discussed in the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
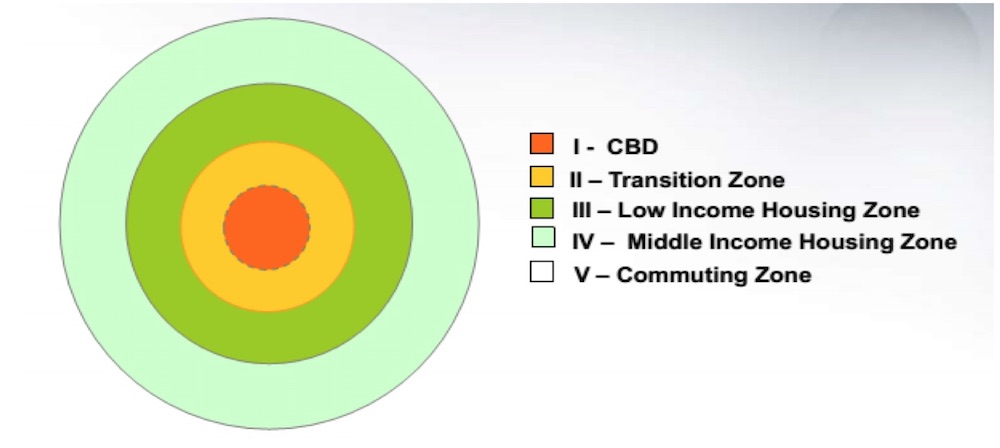
Concentric Zone Model
Also known as the Burgess model, it describes urban land use as a series of concentric rings radiating from the Central Business District (CBD), with different socioeconomic characteristics.
Central Business District (CBD)
The commercial and business center of a city, typically characterized by high land values and density of economic activities.
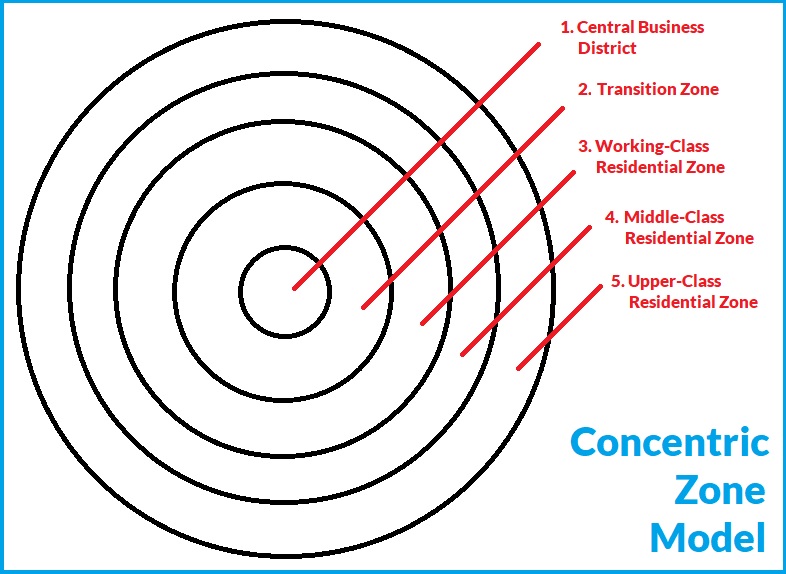
Zone of Transition
The area surrounding the CBD, often featuring poor-quality housing, light industry, and a mix of lower-income populations.
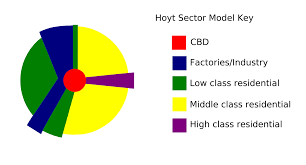
Sector Model
Developed by Homer Hoyt, it suggests that urban areas develop in sectors or wedges based on transportation routes and types of economic activities.
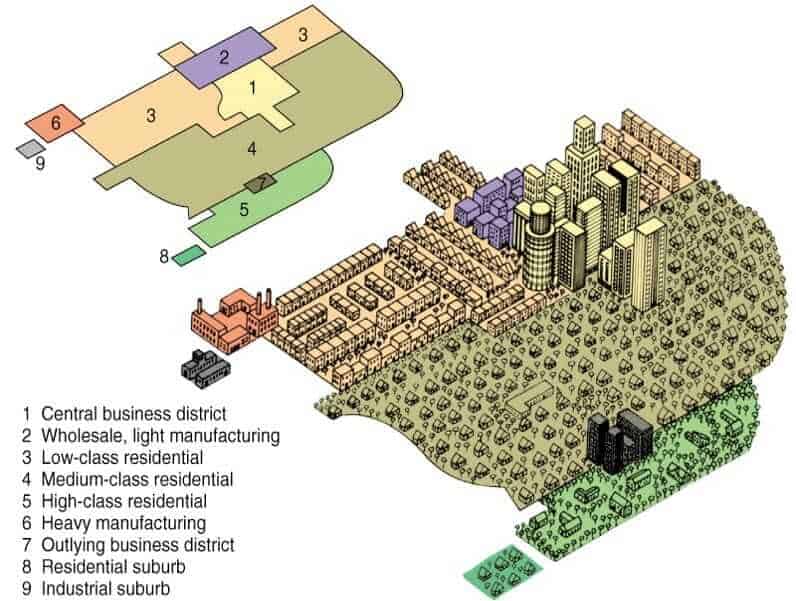
Multiple Nuclei Model
A model that posits cities have multiple centers of development, such as business districts and industrial parks, rather than a single dominant center.
Urban Sprawl
The uncontrolled expansion of urban areas into the surrounding rural land, often leading to increased commute times and reliance on automobiles.
Economic Activity
The variety of operations that occur within a city, impacting land use patterns and residential distribution.
Residential Areas
Zones within a city primarily composed of housing, which can vary by socioeconomic status, typically categorized as low, middle, or upper class.
Transportation Access
The ability for different areas of a city to connect with transportation networks, shaping land use and residential patterns.
Edge Cities
Suburban areas that develop around major intersections or transportation corridors, characterized by a concentration of commercial and retail spaces.