Collin College Bio 1407 Lab Practical #2
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Alternation of Generations
Two distinct generations give rise to one another. The haploid gametophyte generation is characterized by the production of male ad female gametes through mitosis. The male and female gametes fuse during fertilization, forming the diploid sporophyte.
Sporophyte
Dominant generation in vascular seedless and seed plants. diploid result of meiosis of gametophytes
Gametophyte
Dominant generation in non-vascular seedless; haploid result of mitosis of the sporophyte
Gametangium
Term for the structure where gametes form
Sporangium
structure where spores are produced (dominant in moss, ferns, and fungi)
Zygote
Fertilized ovum
Spores
single-celled reproductive units in non-flowering plants
Antheridia
Male gametangium; chamber where male gametes form in Seedless plants
Archegonia
Female Gametangium; chamber where female gametes form in seedless plants
Heterosporous
A plant that bears two types of spores, microspores and megaspores. The resulting gametophyte is dioecious
Homosporous
A plant that bears a spore-producing body that produces only 1 type of spore that contains both male and female parts.
Gametophyte = monoecious
Phylum Hepatophyta
Non-Vascular Seedless
Liverworts
ex. Marchantia - reproduces asexually by gemma cups, and sexually by alternation of genrations ( needs water to move sperm)
Phylum Anthocerophta
Non-Vascular Seedless
Hornworts
Phylum Bryophyta
Non-Vascular Seedless
True Mosses
Asexual repro through fragmentation
Sexual repro through aog
gametophyte stage consists of small spirally arranged leaf-like structures surrounding a central axis. The gametophytes are monoecious.
ex. polytrichum
Heterosporous
Thalloid Liverworts
flat, leaf-like lobed bodies known as thalli and are commonly found along creek banks or on moist soil
Non-Vascular Seedless Characteristics
- No seeds, flowers, or fruits
- No vascular tissues
- Multicellular w/ cellulose cell wall
- No true roots, stems, or leaves
-Depend on water for reproduction
-Small; live in dark, damp places
- Transport water and other nutrients though
cell-to-cell osmosis
- Gametophyte Gen dominant (n)
Xylem
water
Phloem
nutrients
Cuticle
Waxy covering on the surface of plant organs
Stomata
a tiny spore in a leaf plant surrounded by a pair of guard cells that regulate its opening and closure, and serves as the site for gas exchange
Sporophyll
Specialized leaf that bears the sporangia
Strobilus
cone-shaped structure that sits at the tip of the lycophytes and contains spores
Microsporangium
the sporangium that produces the male spores that result in male gametophytes.
Megasporangium
the sporangium that produces the female spores that result in the female gametophytes
Microspores
spores that develop into male gametophytes
Megaspores
Spores that develop into female gametophytes
Phylum Lycophyta
Seedless Vascular Plants
club mosses, quillworts, spike mosses
ex. lycopodium (homosporous)
Selaginella (heterosporous)
sporophyte gen dominant
most ancient group of seedless vascular plants
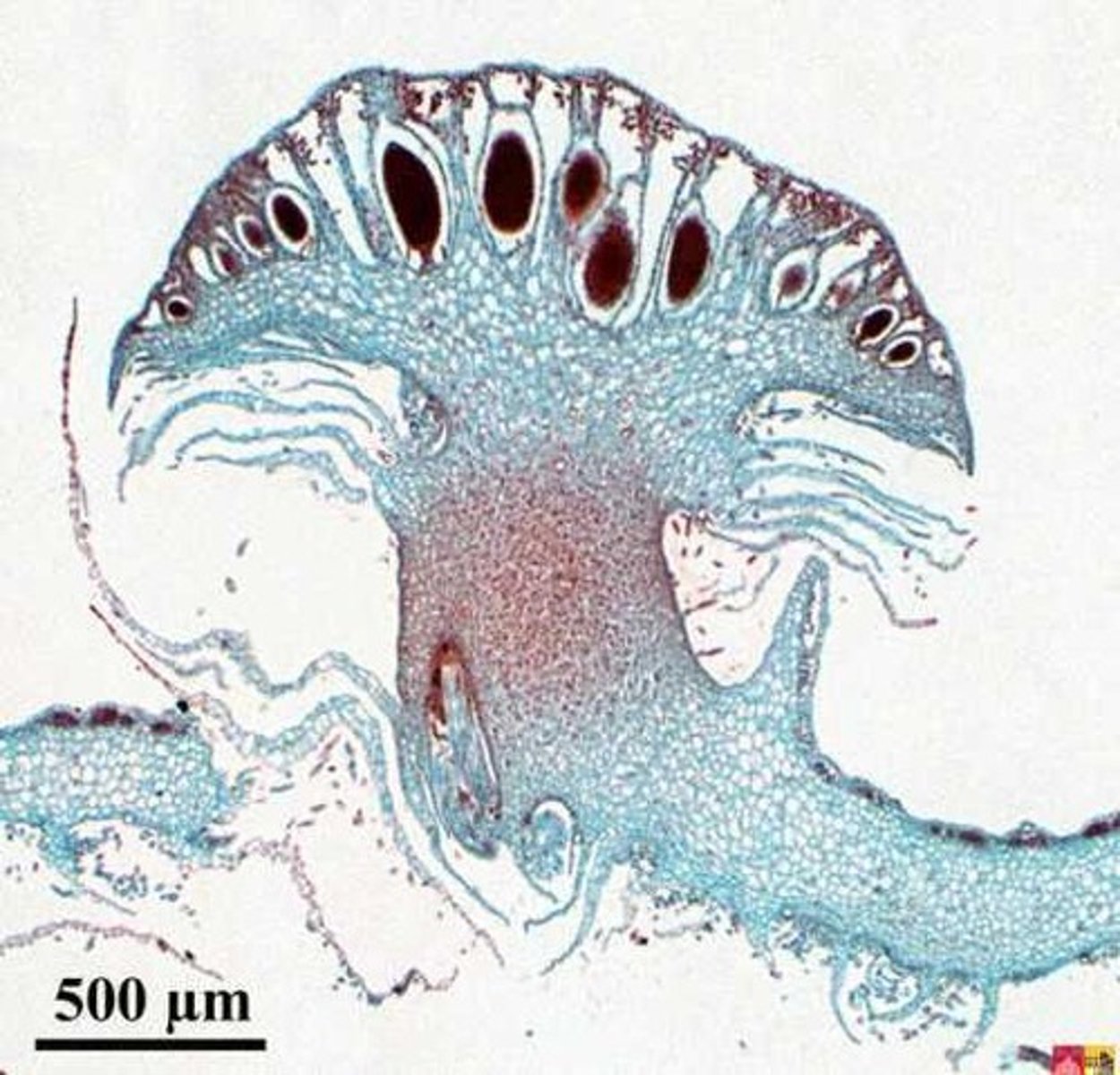
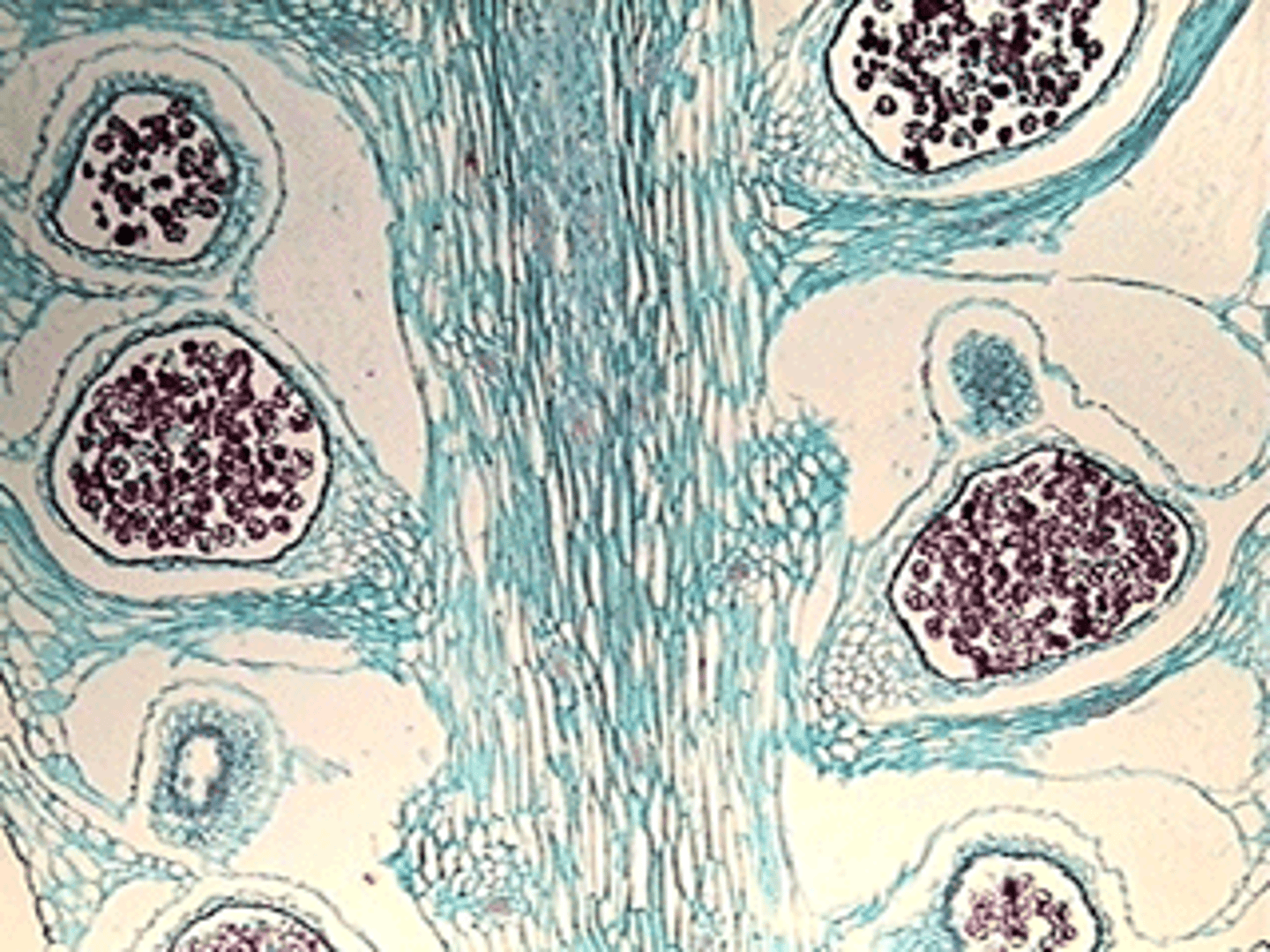
Lycopodium Strobilus
Seedless Vascular
Phylum Lycophyta
homosporous
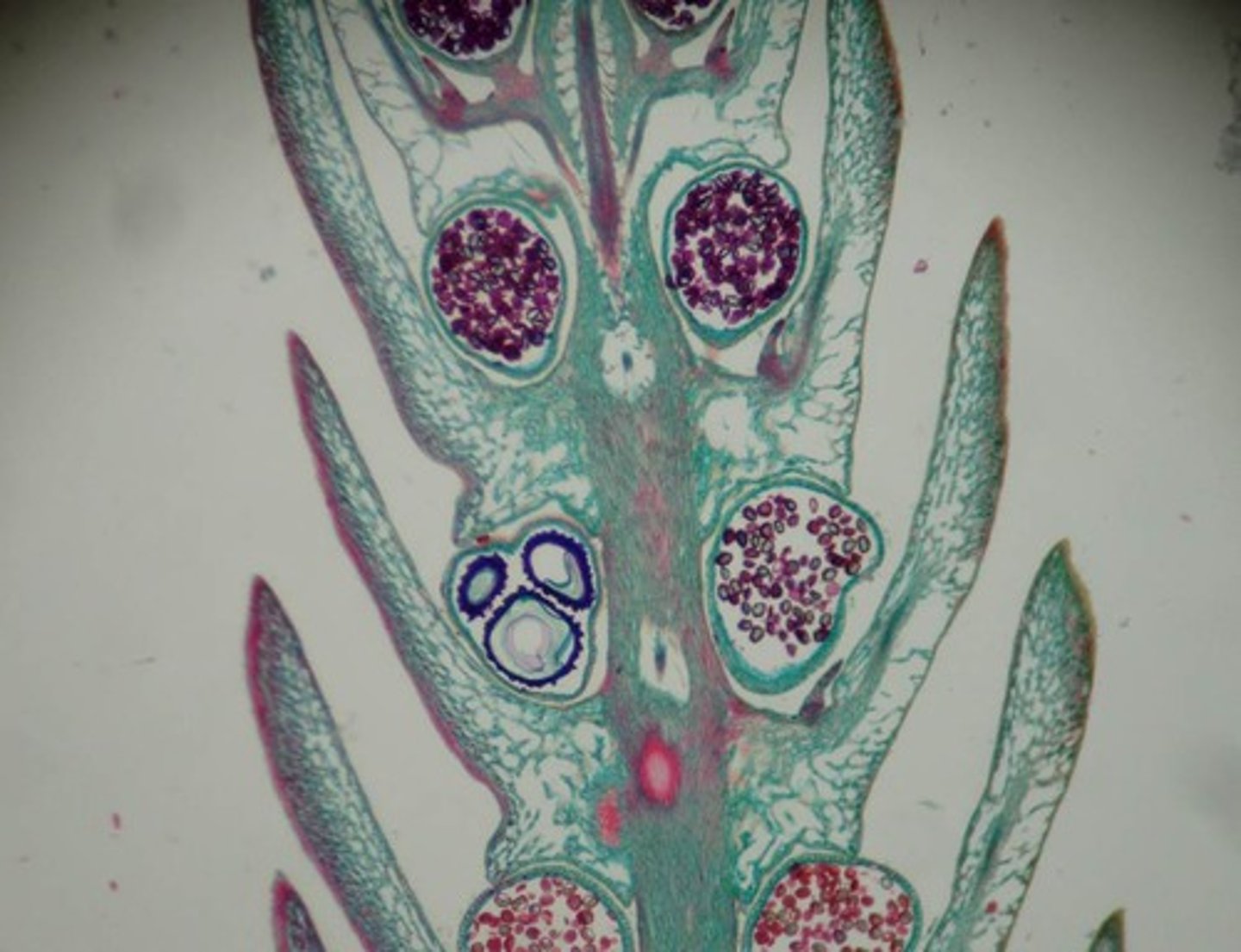
Selaginella Strobilus
Seedless Vascular
Phylum Lycophyta
heterosporous
Phylum Psilophyta
Seedless Vascular
Whisk Ferns
Phylum Sphenophyta
Seedless Vascular
Horsetail
ex. equistem
Horsetail sporophytes produce strobili at the tip of the stem composed of scale-like sporangiophores.
Phylum Pterophyta
Seedless Vascular
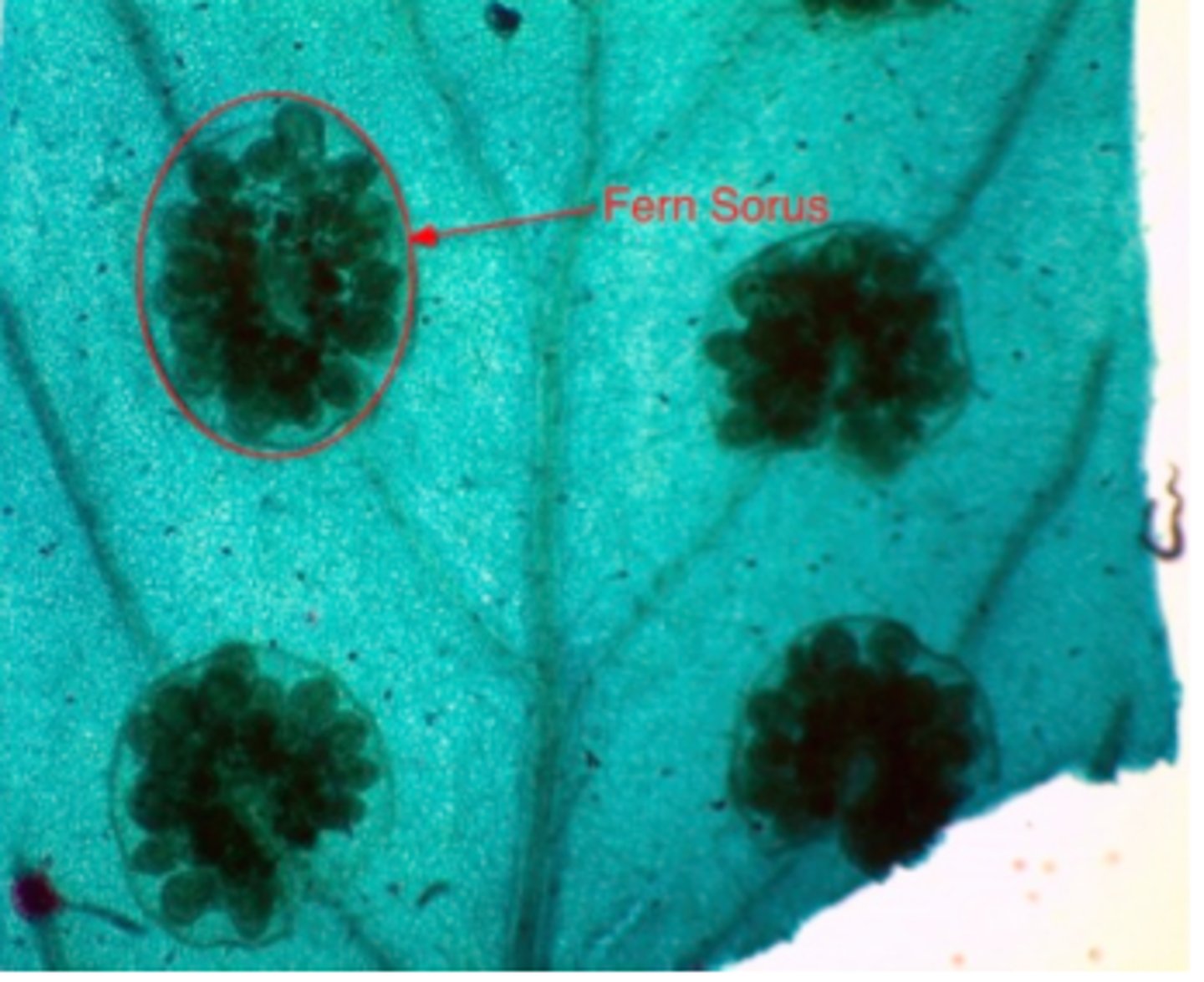
Ferns
sporophyte stage is dominant in ferns with most being homosporous.
Spores known as sori found on the underside of fronds
gametophyte generation is heart-shaped and known as prothallus
Gymnosperm
cone-bearing plants with naked seeds, not enclosed in an ovule
Angiosperm
flowering plants, most diverse and numerous plants on Earth
Ovulate Seed Cone
female cone; megasporangium that produces female gametophytes
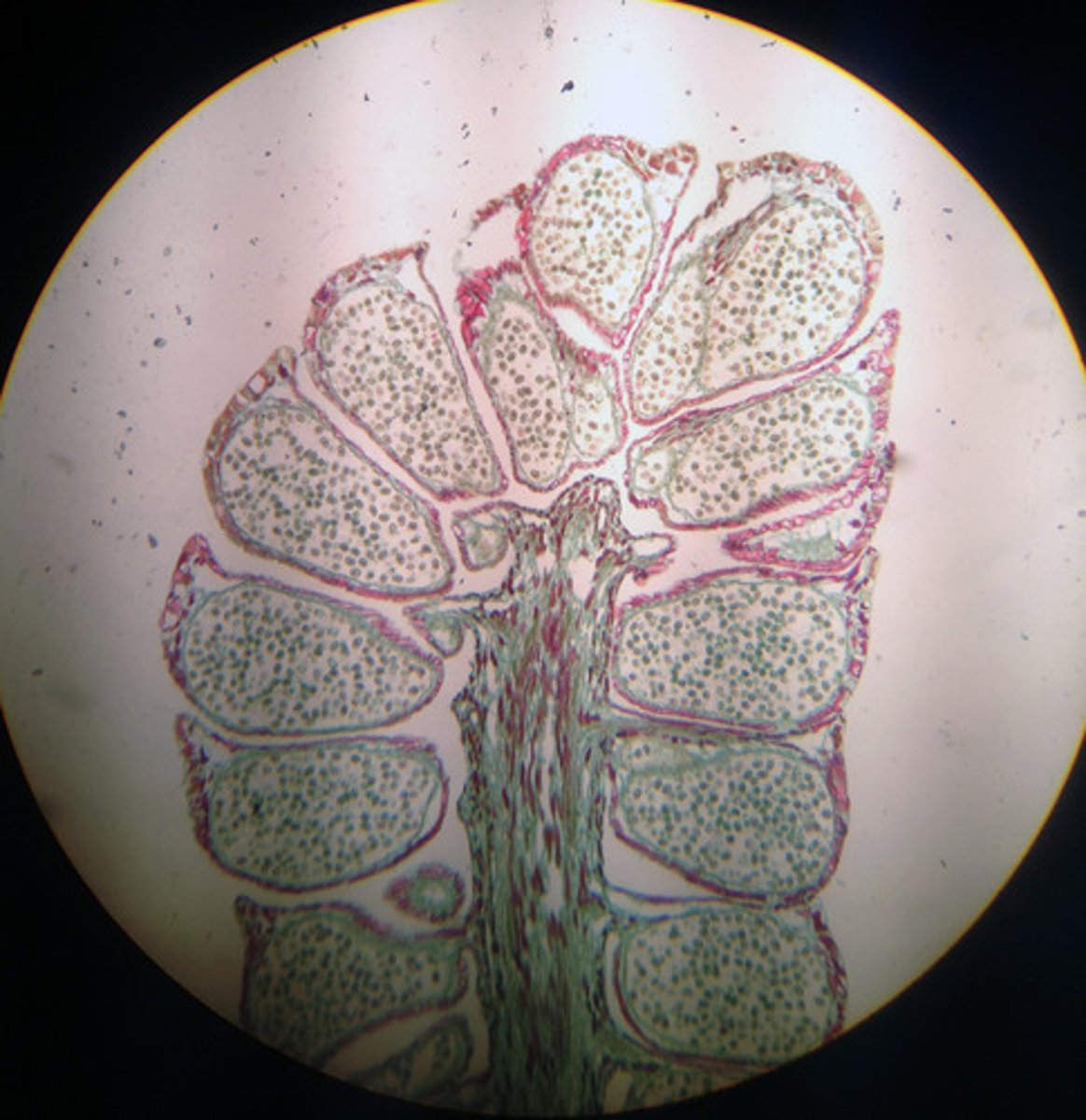
Pollen Cone
male cone; microsporangium that produces male gametophytes
Integument
outermost layer of an ovule
Dioecious
contain male and female reproductive parts on different plants
Monoecious
contain both male and female reproductive parts on the same plant
Phylum Cycadophyta
Gymnosperm
ex. Cycads, Sago Palms
Phylum Ginkgophyta
Gymnosperm
ex. ginkgo biloba
Phylum Gnetophyta
Gymnosperm
ex. Ephedra, Welwitschia, Gnetum
Phylum Coniferophyta
Gymnosperm
dioecious
ex. conifers
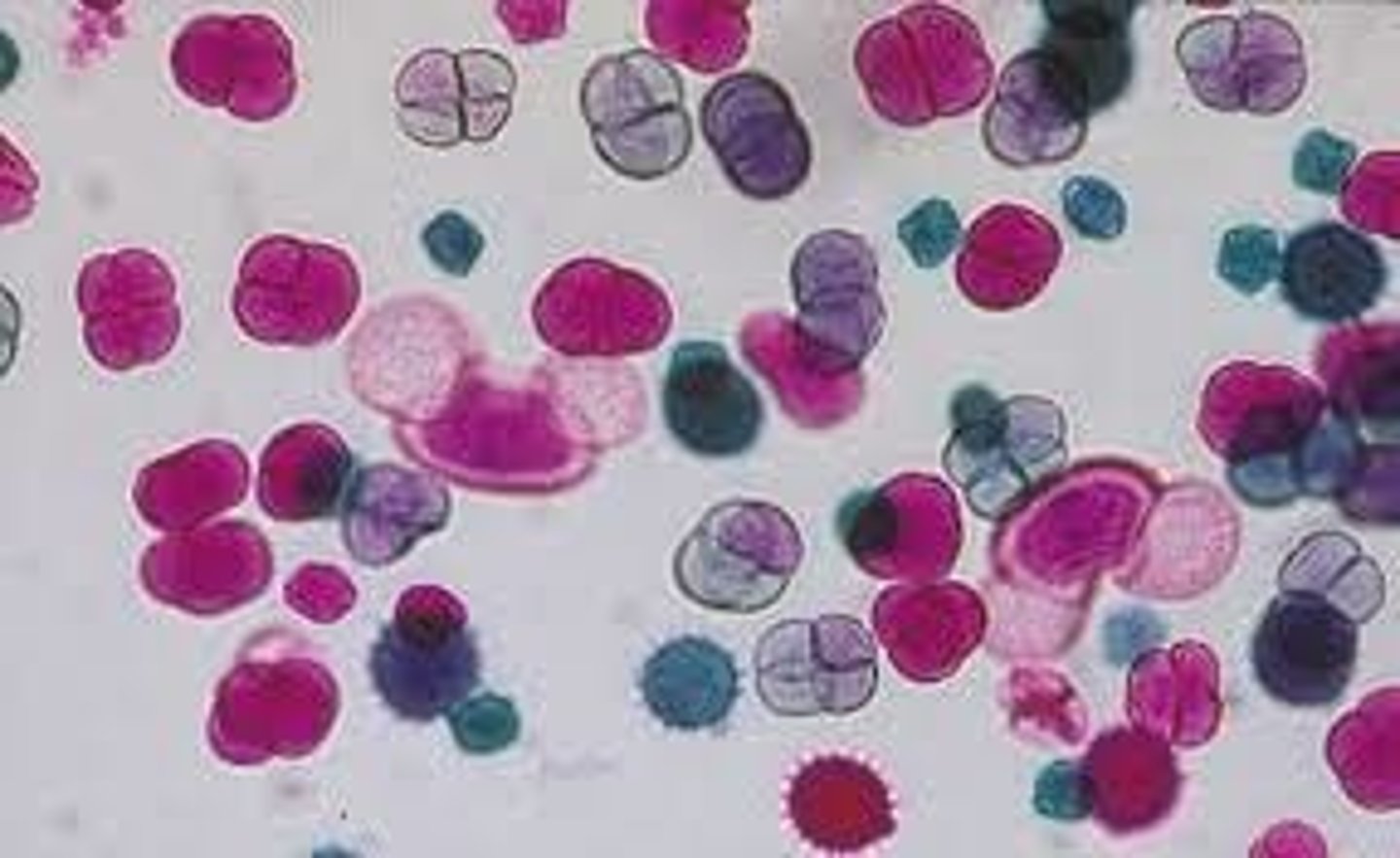
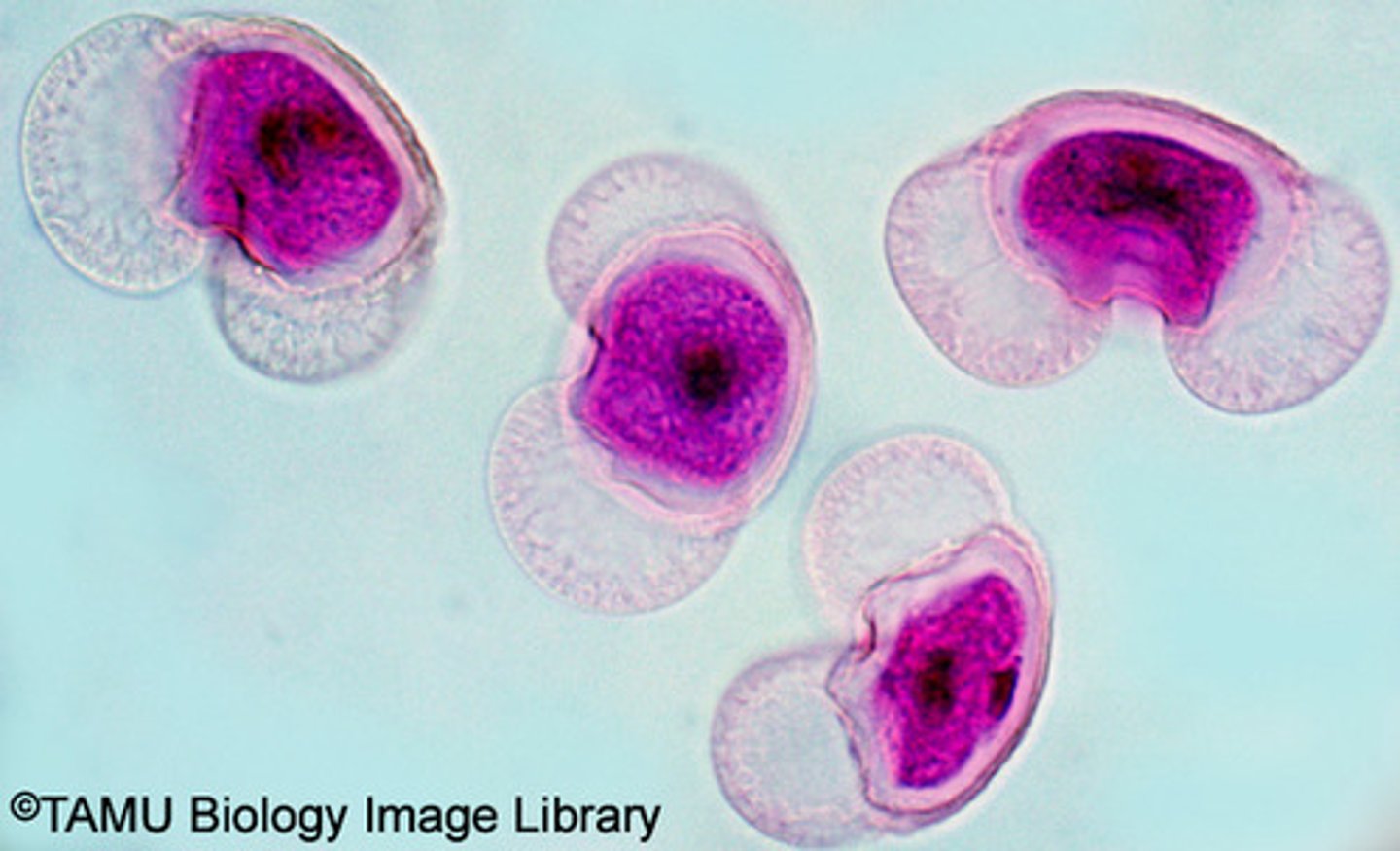
Pine Pollen Grains
Pinus Staminate Cone
Cotyledon
a seed leaf that nourishes the developing embryonic plant
Eudicot
the presence of pollen grains having three, long, grooved openings & 2 cotyledons
Dicot
a seed that contains two cotyledons; pollen grains have one grooved opening
Monocot
seed that has only 1 cotyledon ; pollen grains have one grooved opening
Radicle
embryonic root at the lower end of the hypocotyl
Hypocotyl
the stem-like portion beneath the cotyledon
Epicotyl
stem-like portion above the cotyledon
Coleoptile
the sheath-like protective structure that encloses the young shoot tip of a monocot.
Flower
reproductive structure of all angiosperms
May be solitary or an inflorescence, actinomorphic (radially symmetrical), zygomorphic (bilaterally symmetrical), or have a superior or inferior ovary.
Fruit
-seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that forms from the ovary
-may be simple (formed from a single ovary) or compound (formed from multiple ovaries that have fused together)
Herbaceous Tissue
plants that have no persistent woody stem above ground
Woody Tissue
a plant with woody parts, especially stems
Complete Flower
flower that contains sepals, stamen, pistils, and petals
Incomplete Flower
flower that lacks one or more sepals, petals, stamen, or pistils
Perfect Flower
possess both stamens and pistils
Imperfect Flower
possesses one sex; lacks either stamens or pistils
Ripened Ovary
Fruit
Dicots Petals
4&5 petals
Monocot Petals
3&6 petals
Phylum Magnoliophyta
All Angiosperms
Sporophyte Generation Dominant
Double Fertilization
the fertilization process characteristic of flowering plants, in which one sperm cell of a pollen grain fertilizes an egg cell while a second fuses with two polar nuclei to produce a triploid body that gives rise to the endosperm
Meristematic Tissue
growth tissue, located in stems and roots of plants
Ground Tissue
plant cells tissues that are neither dermal or vascular: 3 types
Parenchyma Tissue
photosynthesis, storage, support, movement of water and food
Collenchyma Tissue
support young plants, leaves and flowers. Makes up the strings in celery.
Sclerenchyma Tissue
provide support for the plant. Dead at maturity.
Epidermis
the outermost layer of cells in plant structures. Helps prevent water loss and protects plant from pathogens.
Symbiosis
a close long-term relationship between two or more species
Mutualism
relationship between two species, where both organisms benefits
Commensalism
relationship between two species, where one species benefits and one is not impacted
Parasitism
relationship between two species, where one species benefits and the other is harmed
Apical Mertistem
growth tissue at the tip of roots and stems that causes them to increase in length
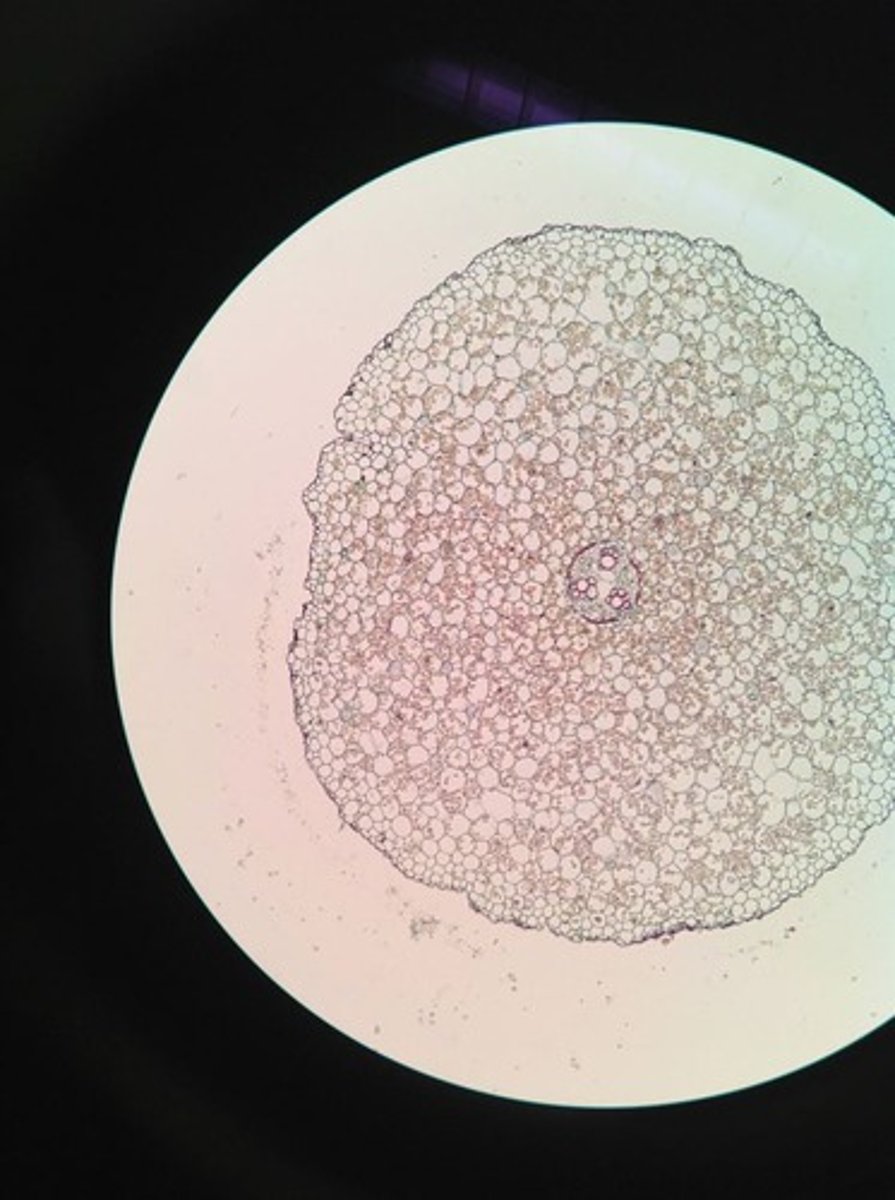
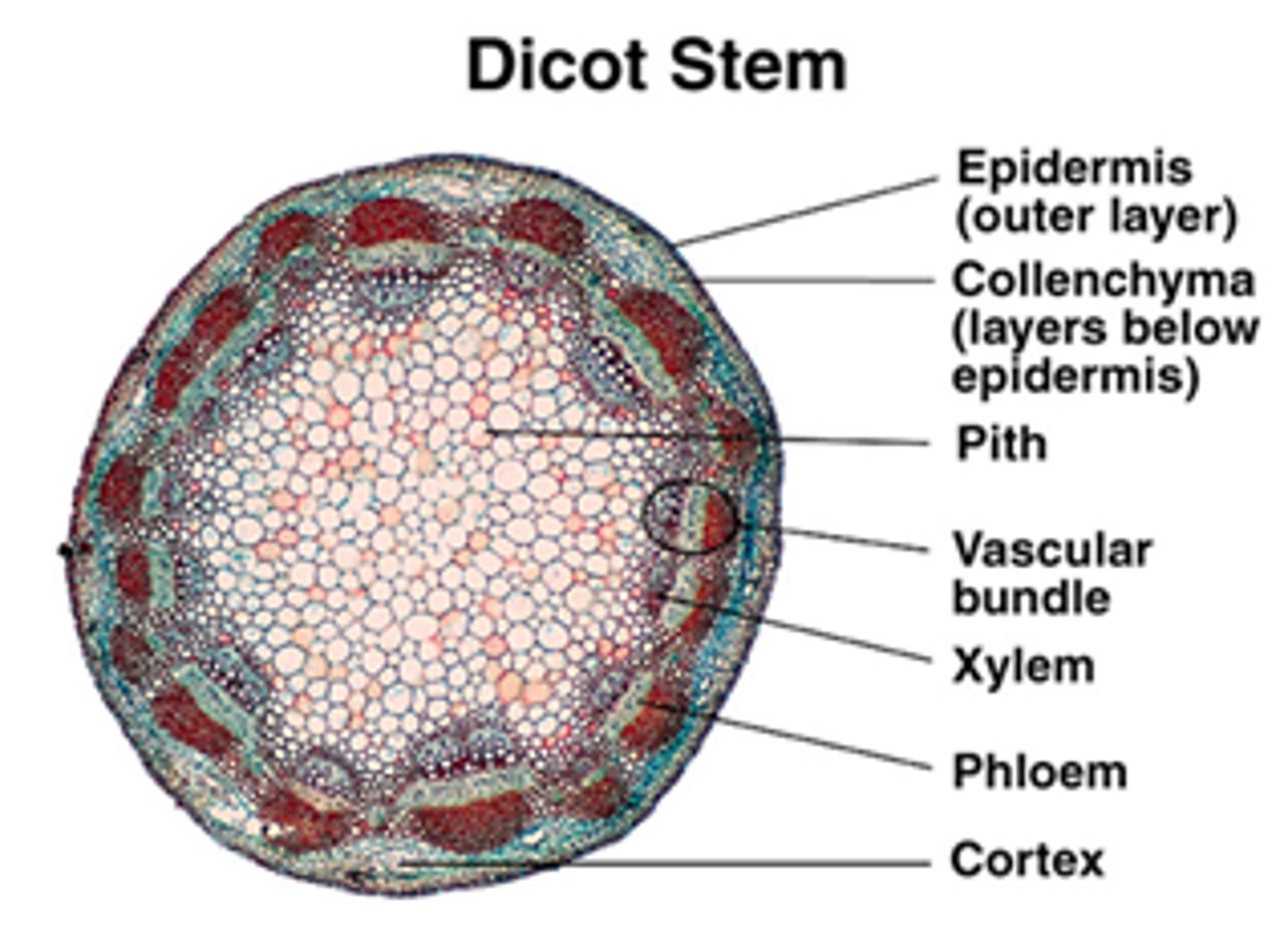
Eudicot and Dicot roots
-the xylem is star-shaped with several radiating arms
-The phloem is located between the radiating arms.
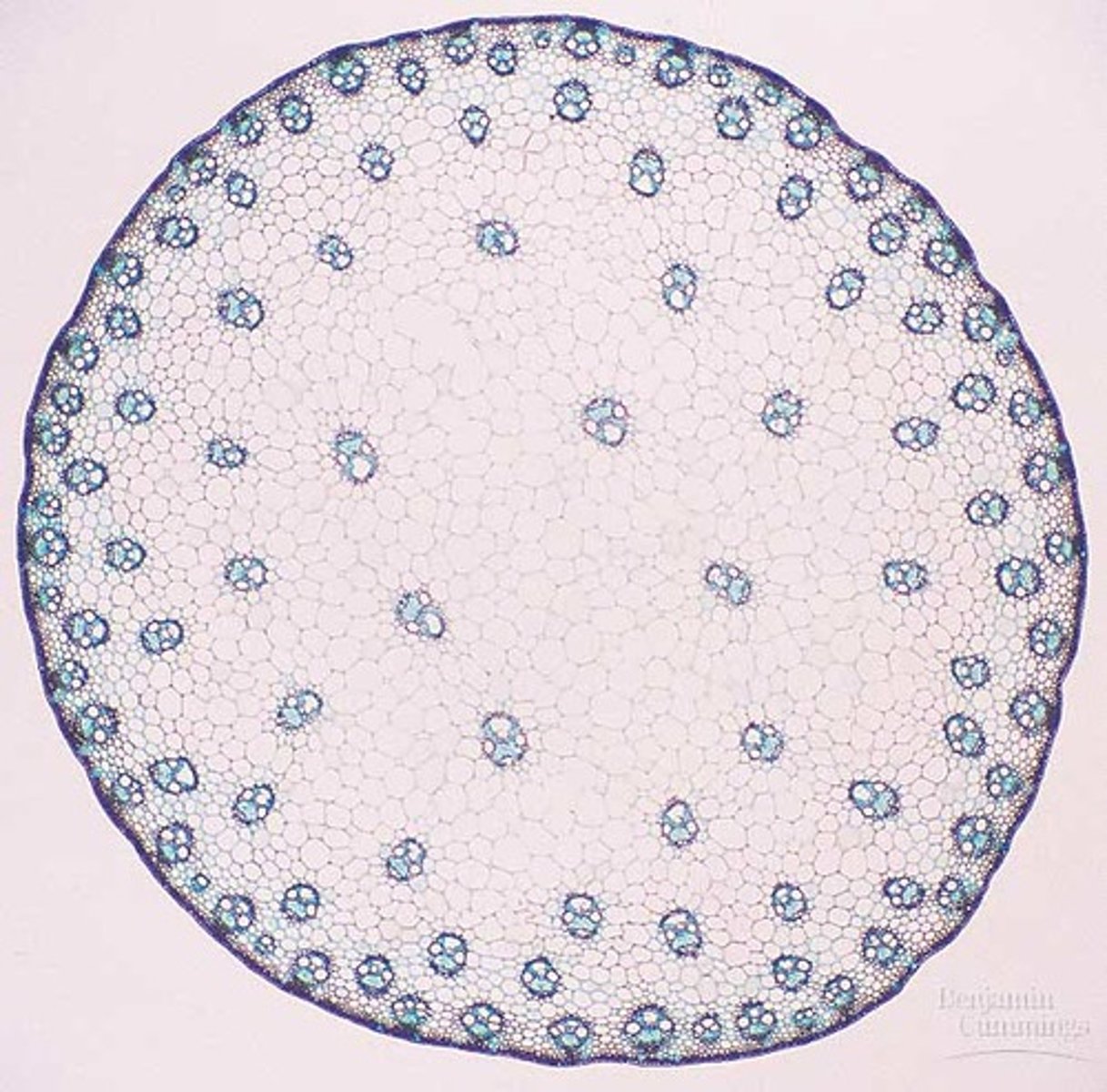
Monocot Roots
-ground tissue
-pith
Vascular tissue is located in bundles in a ring surrounding the pith, with the xylem oriented exteriorly and the phloem oriented interiorly.
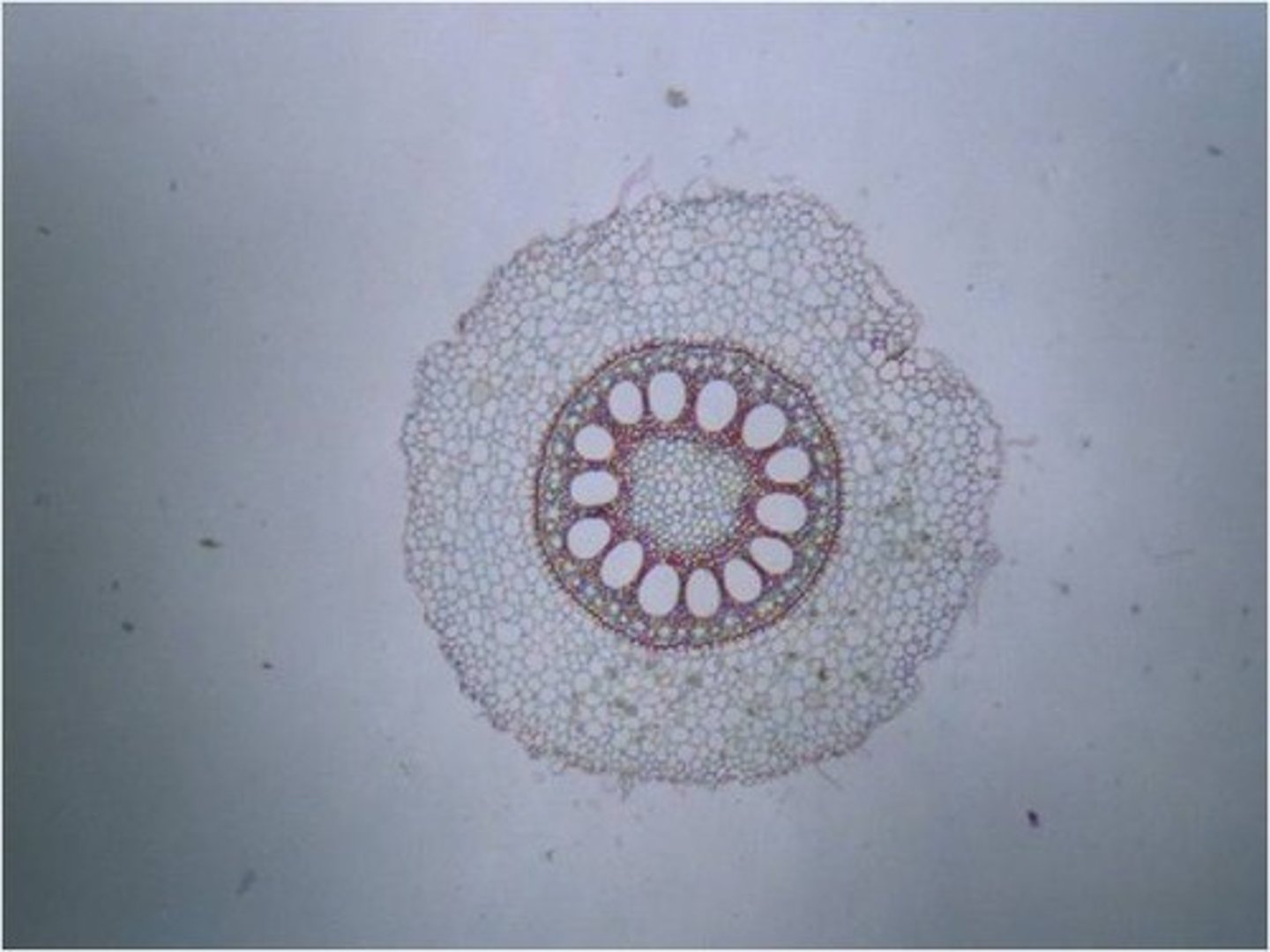
Eudicot and Dicot Stems
Monocot Stem
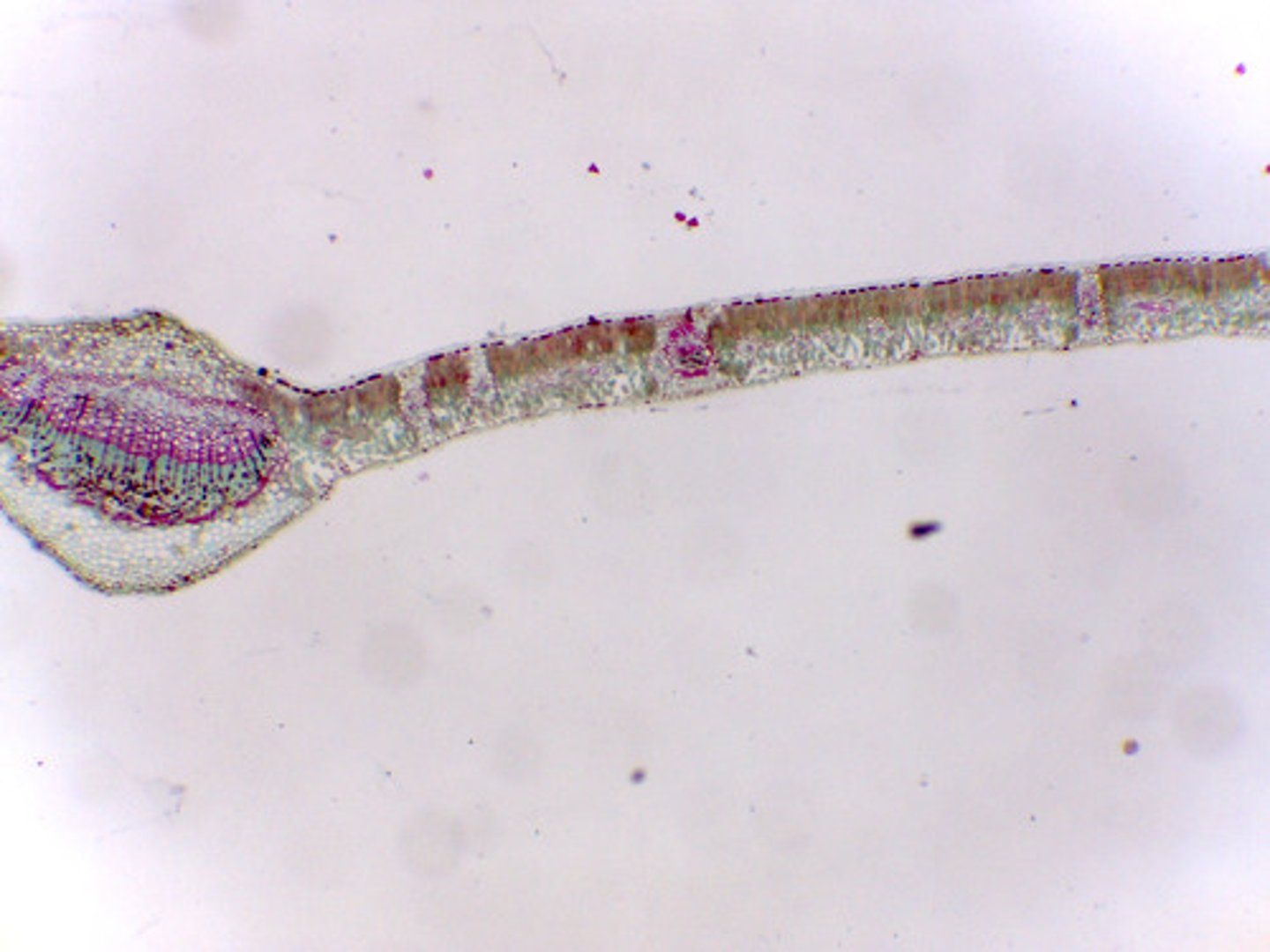
Eudicot and Dicot Leaves
branching veins
Monocot Leaves
parallel veins
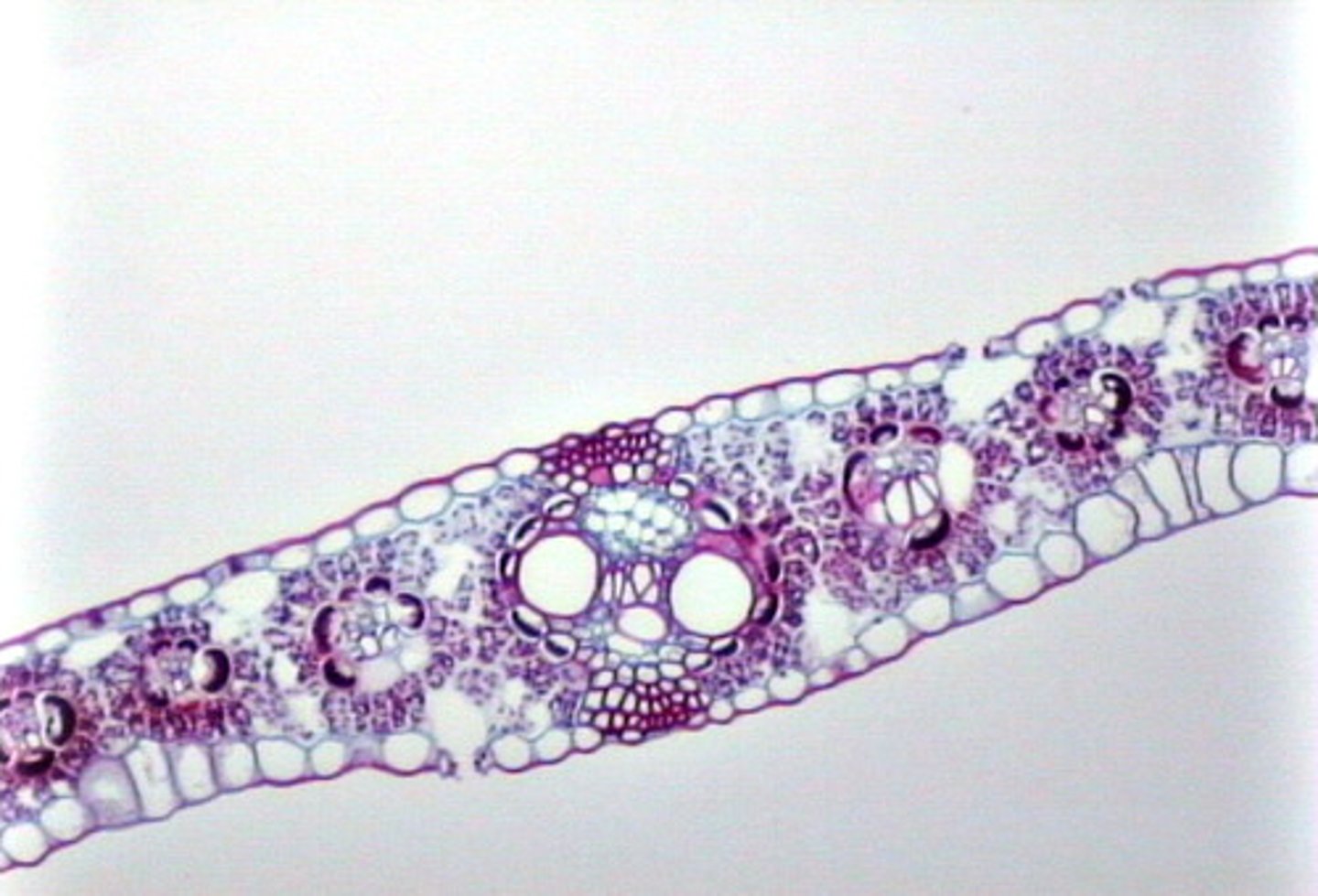
Mesophyll
The tissues of a leaf that are located in between the layers of epidermis and carry on photosynthesis, consisting of the palisade layer and the spongy parenchyma - photosynthesis takes place in the palisade layer
Hyphae
numerous small filaments that make up the body of a mushroom
Mycelium
hyphae that's been grouped into a mass
Rhizoid
modified hyphae that anchor the fungi to a substrate
Gametangia
the area of the hyphae where the gametes are produced
Phylum Chytridiomycota
-Unicellular organisms
-Cell walls are composed of chitin
-They display flagellated spores and gametes
-Chytrids cause a fungal infection called chytridiomycosis in amphibians
Phylum Zygomycota
Rhizopus stolonifer (the common black bread mold) contains three types of hyphae:
-rhizoid
-stolons
-sporangiophores
reproduce by cojugation
Phylum Ascomycota
These fungi are commonly found in symbiotic conditions with green algae forming lichens
ex. Peziza apothecium, Morchella, Penicillium, and Aspergillus , yeast species: Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Phylum Glomeromycota
Fungi known as mycorrhizae that live in a mutualistic relationship primarily on the roots of terrestrial plants
Phylum Basidiomycota
Fungi in this phylum include mushrooms, puffballs, rusts, and stinkhorns, and earth stars
Crustose
brightly colored patches of crust on rock or tree bark
Foliose
have a leaf-like thalli that overlap, forming a scaly lobed body
Capsella Mature Embyros
2 cotyledon
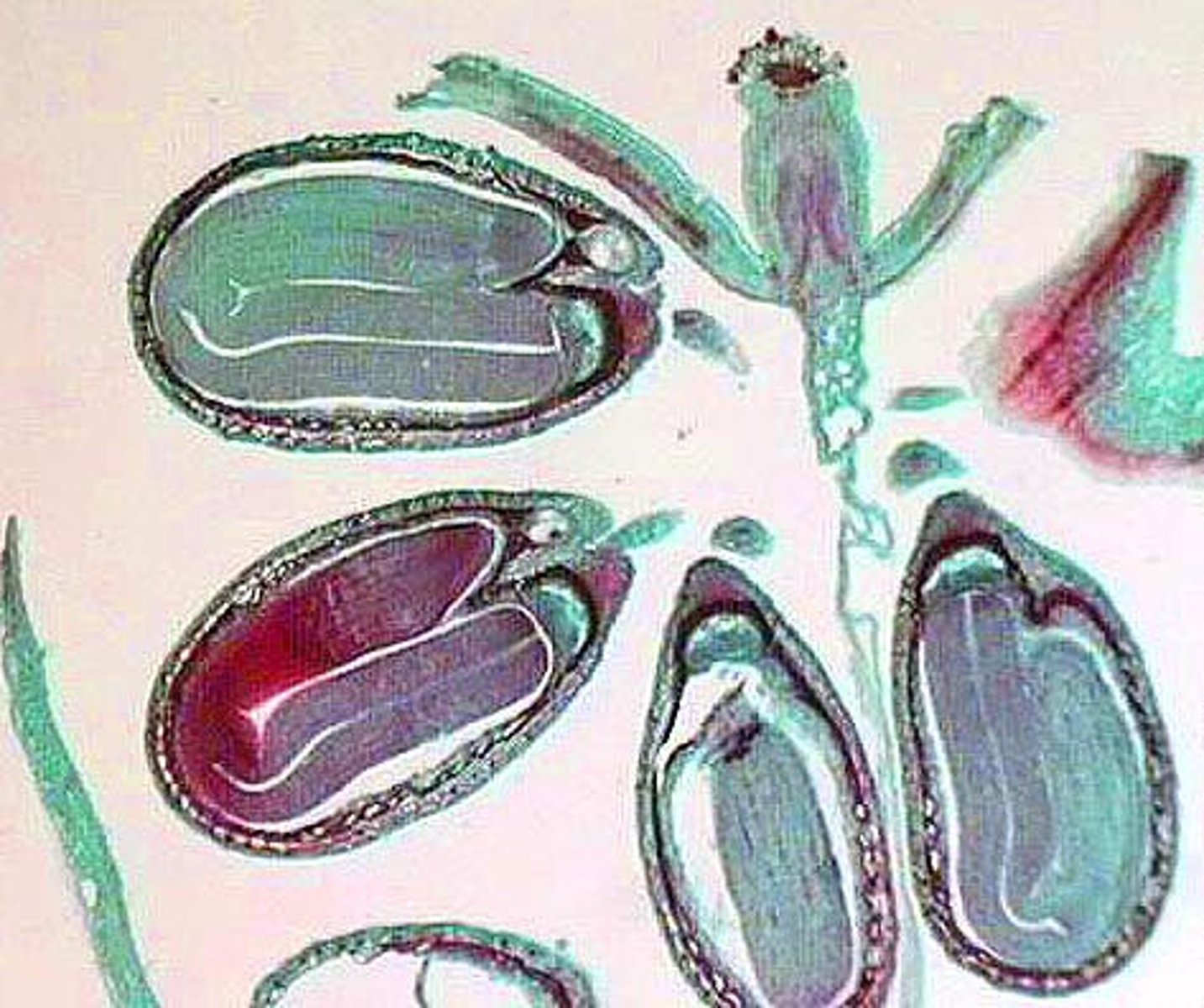
Capsella Embryo
heart-ish shaped
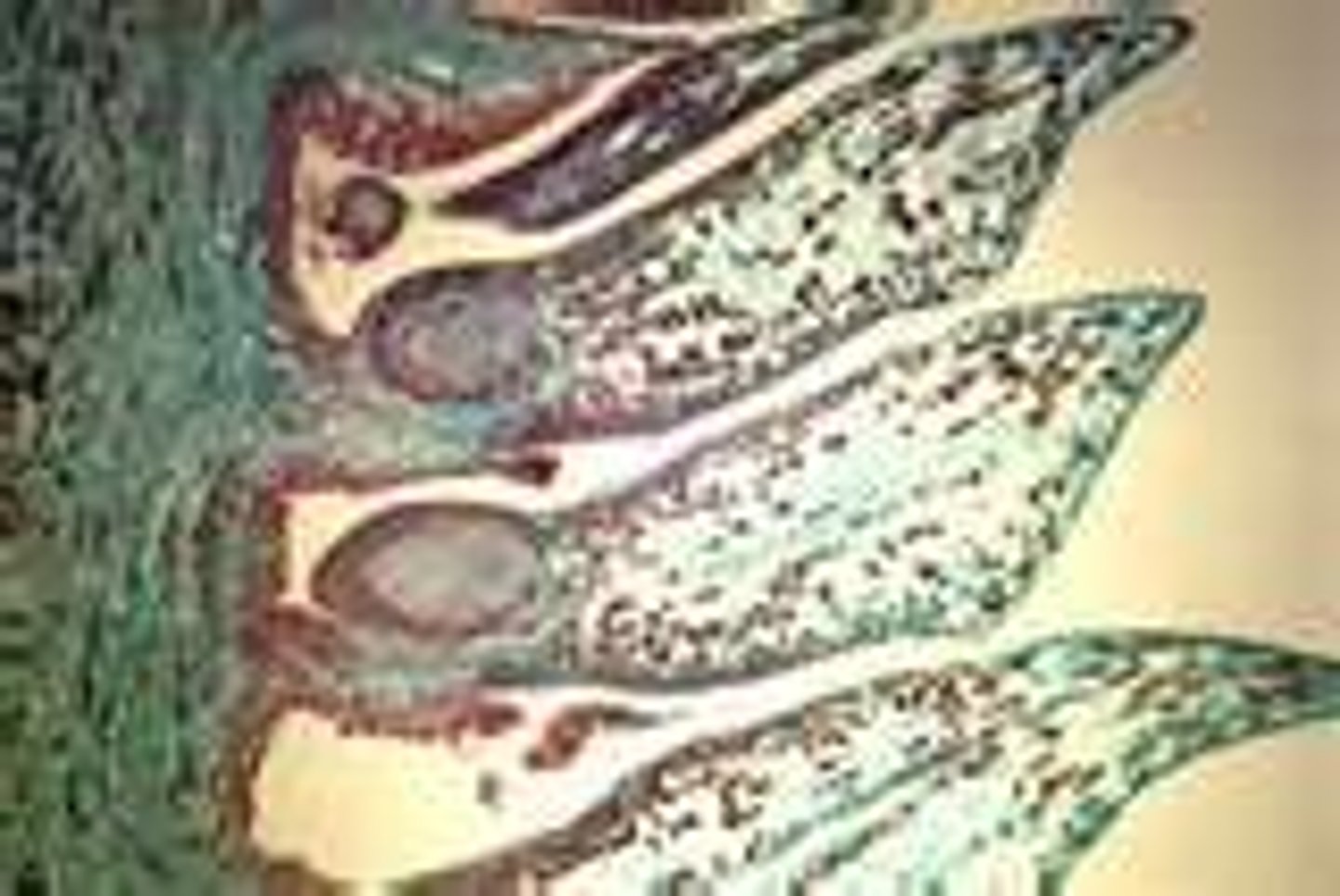
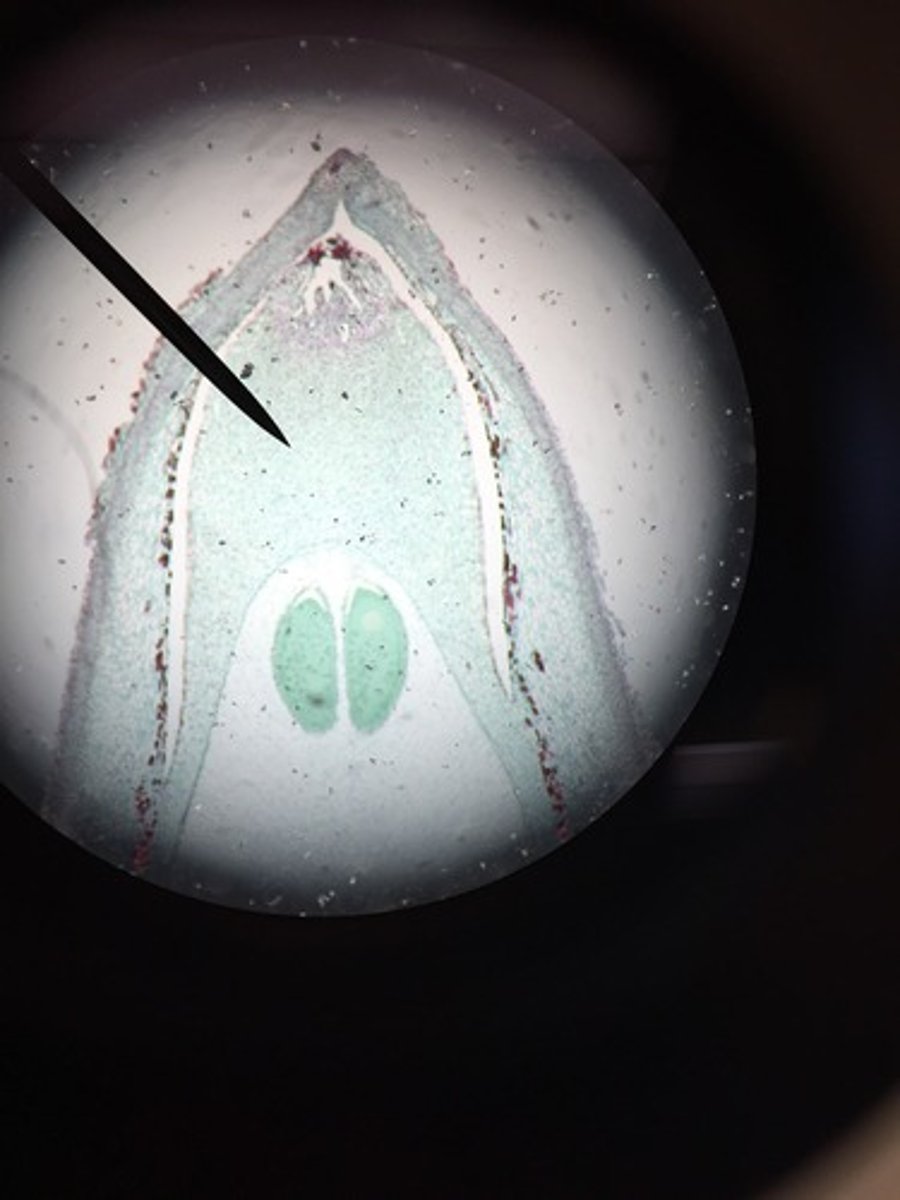
Pinus Ovulate Cone

Pinus Ovule Mature
Mixed Pollen