The Social Self (Chapter 3)
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Textbook + Lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is the self concept?
sum of total beliefs that people have about themselves
made up of “cognitive molecules” called self schemas
self-concept consists of multitude of schemas
What is the paint & mirrors trick to show self-concept?
magpie with dot on neck placed in front of mirror
realizes is looking at mirror realizes reflection and attempts to take off dot
some primates: humans (but not young kids ~6), bonobos, chimps, and orangutans all do as well
some evidence for dolphins, orcas, asian elephants, magpies
trickier with animals with diff minds/bodies
What are self-schemas?
templates or ideas we have for understanding the self
ex: liberal/conservative, masculine/feminine, introverted/extroverted
self schemas are to self concept like what books are to library
How might people identifying with 2 different cultures have different self concepts?
people who identify with two cultures might have "double consciousness” abt who they are
How is self-relevant info processed differently? (brain scans)
through brain imaging, areas of the brain become more active when lab participants see self relevant info than when they see other ppl/words/etc.
cocktail party effect → hearing name among crowd of people
How did Gordon Gallup test self-recognition? (how can self-recognition be tested)
placed diff animals in front of mirror to test self-recognition
only great apes (chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans), seemed capable of self-recognition
later tested further by adding a red dot and great apes tried to pick it off
What 2 important steps/factors/whatever make the self concept?
seeing self as distinct self (knowing there is a self)
social factors
What is the looking glass self?
other ppl serve as a mirror for us to view ourselves
we think of ourselves based on what we imagine others to think of us and incorporating it into self-concept
Are we good at introspection?
we’re bad at introspection → leads us astray on road to self-knowledge
affective forecasting + impact bais
What is affective forecasting?
predicting future emotions/affect/states
predicting how people would feel in response to emotional events
we’re shit at it → impact bias
study:
asked participants to predict how they would feel after diff positive/negative life events + compared predictions to ppl who actually experienced them
What is impact bais?
people overestimate the strength and duration of emotional reactions
makes people have difficulty predicting how they would feel in response to future emotional events
What is self-perception theory?
when internal states are weak, people infer what they think or how they feel by observing their own behavior + the situation in which that behavior takes place.
occurs only w/ ambiguous internal states
takes situation and environment into account
when ppl are led to say or do things when they’re unsure of how they feel, they can internalize it and define themselves as such
e.g. if someone has ambiguous internal state and they are coaxed into nodding up/down they might believe they agree with whatever message
How is self-perception a form of introspection/learning about self?
observing our behaviours is a method people employ to learn about ourselves and develop a concept of “self”
more likely to happen for attitudes we don’t already have a strong opinion about, then once formed, opinions about ourselves are harder to change
What is the Self-Other-Knowledge-Asymmetry Model? (SOKA)
we know ourselves better when it comes to traits that are internal and hard to observe (anxious, optimistic, etc.)
there is no self-other difference when it comes to traits that are “external” and easy to observe (quiet, sociable, messy, etc.)
others may know us better than ourselves when it comes to observable traits that can be touchy for self-esteem (smart, creative, rude)
we have motivated blind-spots to protect self-esteem
What is the facial feedback hypothesis?
hypothesis that changes in facial expression can lead to corresponding changes in emotion.
part of self-perception theory
e.g. using a machine to contract facial muscles to make a smile/frown can cause corresponding feelings (happy/sad) to ambiguous stimuli
What is the overjustification effect?
intrinsic motivation decreases when being associated with a reward or other extrinsic factors (e.g. paid to do a job you love)
What is distinctiveness theory?
to avoid informational overload, we tend to selectively notice aspects of the self what makes us distinctive in relation to others
tend to describe ourselves in ways that distinguish us from one another
Other people help us to define ourselves
has informational value → we can’t share everything about everything
What is the social comparison theory?
The theory that people evaluate their own abilities and opinions by comparing themselves to others
end to describe ourselves in ways that distinguish us from one another
Other people help us to define ourselves
When do you engage in upward social comparison?
comparing self to someone judged to be better than self
engage when goal is to improve
When do you engage in downward social comparison?
comparing self to someone judged to be worse than self
engage when goal is to make selves feel better (/enhance self esteem)
What is lateral social comparison?
comparing oneself with another who is considered to be more or less equal (similar to us)
engage in lateral social comparisons when our goal is to get an accurate comparison of our abilities
What is the two-factor theory of emotion?
experience of emotion is based on 2 factors:
physiological arousal
cognitive interpretation OF arousal
increased HR + standing in front of bear → “i must be scared” → fear
What are autobiographical memories?
memories of one's own experiences, including one's thoughts and emotions
“observing ourselves via memory”
we don’t remember all memory equally or objectively
memory is very porous → when we retrieve memory it is malleable and open to alteration
remember recent info better
2 exceptions tho
What is the recency effect?
we remember recent things more easily
2 exceptions to the recency effect:
“reminiscence bump” of memories from adolescence when we’re old
transitional “firsts”
e.g. first kiss, first few days of school, etc.
What are flashbulb memories?
enduring, detailed, high-resolution memories
speculated for “survival purposes”
not necessarily accurate or consistent over time but still feel special
How does culture affect self-concept?
individualism vs collectivist countries form diff self concepts
culture made up of 4 I’s → culture cycle
ideas
institutions
interactions
individuals
What is dialectism?
An Eastern system of thought that accepts the coexistence of contradictory characteristics within a single person
characterized by acceptance of contradictions through compromise
opposite characteristics can be in one person
What is self-esteem?
An affective component of the self, consisting of a person’s positive and negative self-evaluations
self esteem differs in both amount and stability
self esteem typically stays roughly the same from childhood into adulthood
stays stable relative to others
What is sociometer theory?
theory that self-esteem is a gauge monitoring our social interactions
sends us signals as to whether our behavior is acceptable to others.
increased activity in rejection-related brain regions associated w/ lower self esteem
What is terror-management theory?
humans biologically programmed for life and self-preservation
humans cope with the fear of their own death by constructing worldviews that help to preserve their self-esteem
What is self-discrepancy theory?
there are 3 selves: actual, ought, and ideal
actual self - self concept
ought/ideal - self guides
discrepancies from actual and ought/ideal selves decrease self esteem
3 selves predict self esteem and wellbeing
self discrepancies generally stay stable over time
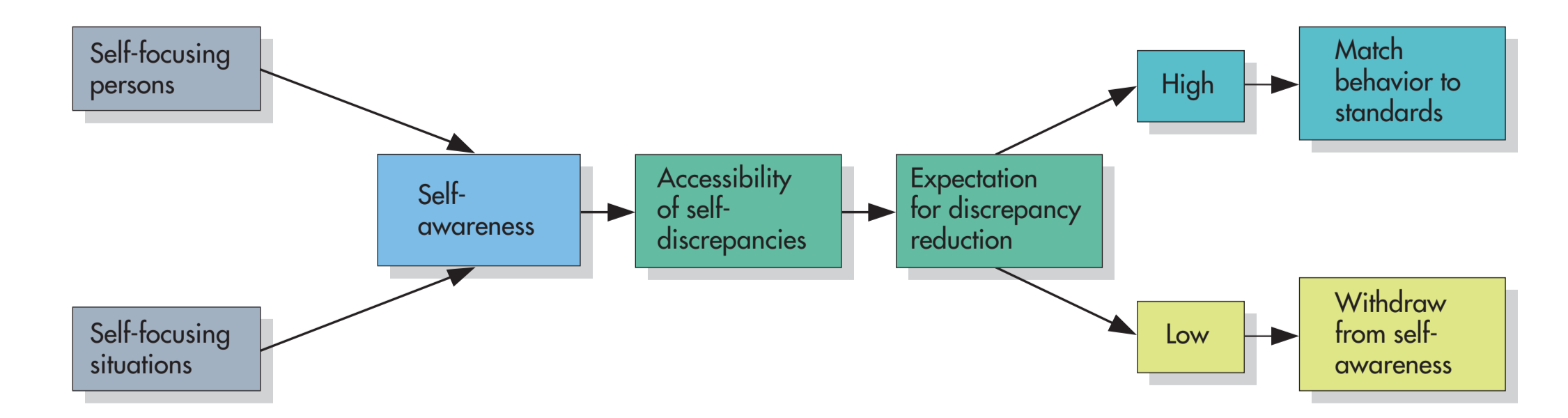
What is self-awareness theory?
the mroe attention is focused on leads people to notice self-discrepancies → motivating either escape from self-awareness or a change in behavior?
What are the two ways of coping when with discomfort from self-discrepancies?
shape up → fix self, reduce discrepancy
ship out → stop thinking about self
withdraw from self awareness, distract self, etc.
can often cause substance abuse as means to stop thinking abt it
What determines which coping mechanism is used for self-discrepancies?
they think they can fix the discrepancy
and whether they are satisfied w/ progress once they tried
What is private self-consciousness?
personality characteristic of individuals who are introspective
often attending to their own inner states.
tendency introspect about inner thoughts and feelings
What is public self-consciousness?
personality characteristic of individuals who focus on themselves as social objects, as seen by others.
tendency to focus on our outer public image
What is the Dunning-Kruger effect?
everyone tends to overestimate own abilities → some do it more than others
those w/ lowest scores on logic, humour, and grammar most likely to overestimate own abilities
[experts underestimate ability… maybe]
What is self-regulation?
process by which people control their thoughts, feelings, or behavior in order to achieve a personal or social goal.
ego depletion: willpower = finite resource
some say glucose as the resource but very unlikely
What are ironic processes?
harder you try to inhibit a thought, feeling, or behaviour → less likely you are to succeed
What are some different mechanisms of self-enhancement?
better than average effect
implicit egotism
self-serving cognitions/beliefs
self-handicapping
BIRGing
downward social comparisons
What is the better-than-average effect?
people see positive traits as more self-descriptive than negative traits
most ppl think they’re above average on various personality trait and ability dimensions
What is implicit egotism?
unconscious and subtle expression of self-esteem
ppl quicker to associate “self” words with positive traits than negative ones
What are self-serving cognitions/beliefs?
take credit for success and distance self from failures to protect self esteem
intrinsic explanations for successes
(IM BUILT DIFFERENT)
extrinsic explanations for failures
(this prof is tryna get me bro)
unrealistic positivity about future (illusion of control)
What is self-handicapping?
making excuse for future performance in anticipation of failure
behaviours that sabotage performance provide an excuse for failure (and therefore protect the self)
effectively protects SE but increased risks of failures
What is BIRG/basking in reflected glory?
sibling = CORF
cutting off reflected failure
we identify w/ groups when they experience success (BIRG) and distance with failure (CORF)
e.g. school sweatshirts following wins vs losses
How are downward social comparisons used for self-enhancement?
aren't objective in who we compare ourselves to
often do it downward
53% downward in hospital
the more often these comparisons were made downward, the better they felt
can't always avoid going downward
two approaches are to be happy and BIRG, or jealousy and social distance occurs
seems to be related to whether its OUR thing.
if not, its cool, if so, jealousy
What is positive illusion and how may it be adaptive?
To the extent we are deceiving ourselves, may act more confident, and experience more success
Depressed individuals are actually more accurate
About their future probabilities, their own abilities, how others perceive them
people who harbor positive illusions of themselves are likely to enjoy the benefits and achievements of high self-esteem and social influence
What is the spotlight effect?
tendency to believe that more people are paying attention to you than they actually are
especially when embarrassing situation
What is self-presentation?
process by which we try to shape:
what other people think of us
what we think of ourselves
What is strategic self-presentation?
our efforts to shape others’ impressions in specific ways in order to gain influence, power, sympathy, or approval
2 goals:
integration - get along
self promotion - get ahead
What is self verification?
the desire to have others perceive us the way we perceive ourselves
when described as how you perceive yourself → take it at face value
when described as not how you perceive yourself → try to act more like how self perceives
e.g. described as submissive → act more assertive
desire for self verification stronger than desire for flattery/self-enhancement
ppl w/ low SE prefer to have ppl admit their shortcomings
What is self-monitoring?
tendency to regulate one’s own behavior to meet the demands of social situations.
personality trait that determines if people prefer strategic self-presentation or self verification