Chapter 25 - Seedless Plants
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What do Chlorophytes, Charophytes, and Plants have in common?
Multicellular
cell walls made of cellulose
Chloroplasts with same pigments(chlorophyll)
Storage molecule is starch
Why did algae move from oceans to shallow lakes?
More resources and less competition
What was an important adaptation that green algae was subjected to?
Periodic dehydration(when lakes dried out)
What were advantages of land(for algae)?
CO2 higher, light intensity is higher, more minerals, no “herbivores”, no competition
What was a constant danger for algae when they moved from water to land?
Desiccation(drying out)
Both gametes and zygotes must be protected from desiccation
What are derived characteristics from plants?
Alternation of generations(1n and 2n are multicellular)
Walled haploid spores
Apical Meristem-where most of growth happens
Evolution of waxy cuticle to resist desiccation(keeps from drying out)
Mycorrhizae
Cell walls with Lignin(unique to plants)
Walled haploid spores
dispersal through air: sporopollenin protects (made within multicellular sporangium
Multicellular gametangia
protects sperm within antheridium(male)
Eggs protected within Archegonium
fertilization here: forms zygote(female)
Apical meristems have continuously dividing cells
True
in the apical meristem of the root it shoots towards sunlight and grows towards resources
True
What is the function of the waxy cuticle?
The waxy coat stops dissecation
How do the pores in the plant allow for the CO2 and O2 exchange?
The stomata controls in most plants
What are secondary metabolites?
chemicals that deter, repel or poison competitors,
herbivores, & parasites
Mycorrhizae
mutualism with fungi; helps water & mineral absorption
• dates back to first land plants (before true roots)!
What are Bryophytes?
seedless nonvascular plants
What do bryophytes require for reproduction?
Water
What do bryophytes have instead of true roots?
Rhizoids(attachment)
How many Phyla are in Bryophytes?
3
What Phyla belong to Bryophytes
Liverworts
Hornworts
Mosses
What is the scientific name for Liverworts?
Marchantiophyta
What is the scientific name for Hornworts?
Anthocerotophyta
What is the scientific name for Mosses?
Bryophyta
What ploidy is dominant for the gametophyte generation in bryophyte?
Haploid
What does dominant mean?
Longest lasting or largest
What in Bryophytes make/release haploid spores?
Sporangium
What does the bryophyte gametophyte make?
eggs and flagellated sperm
Where does the diploid sporophyte grow?
Grows within the Archegonium of the gametophyte
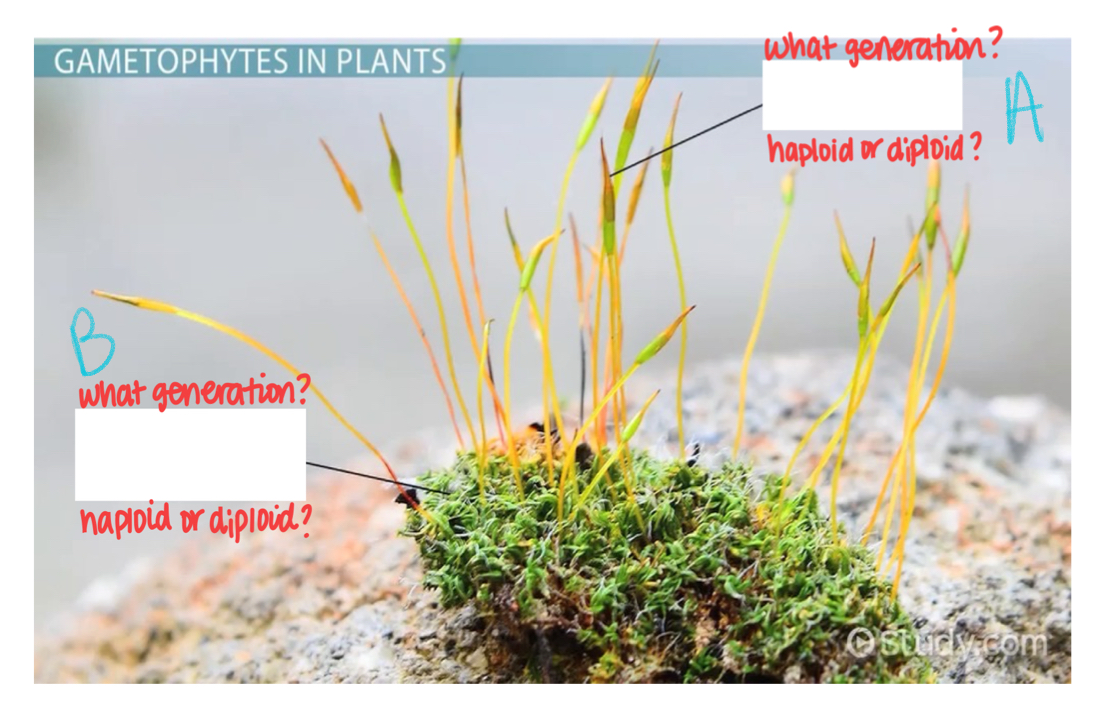
What generation is A?
Sporophyte
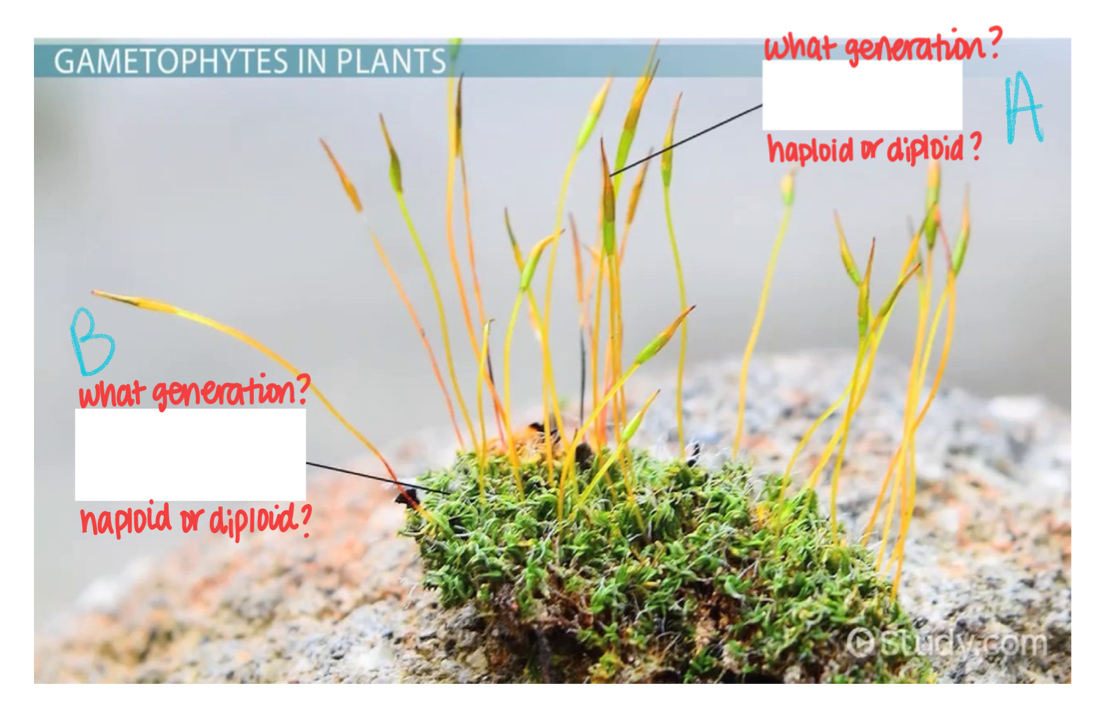
What ploidy is generation A?
Diploid
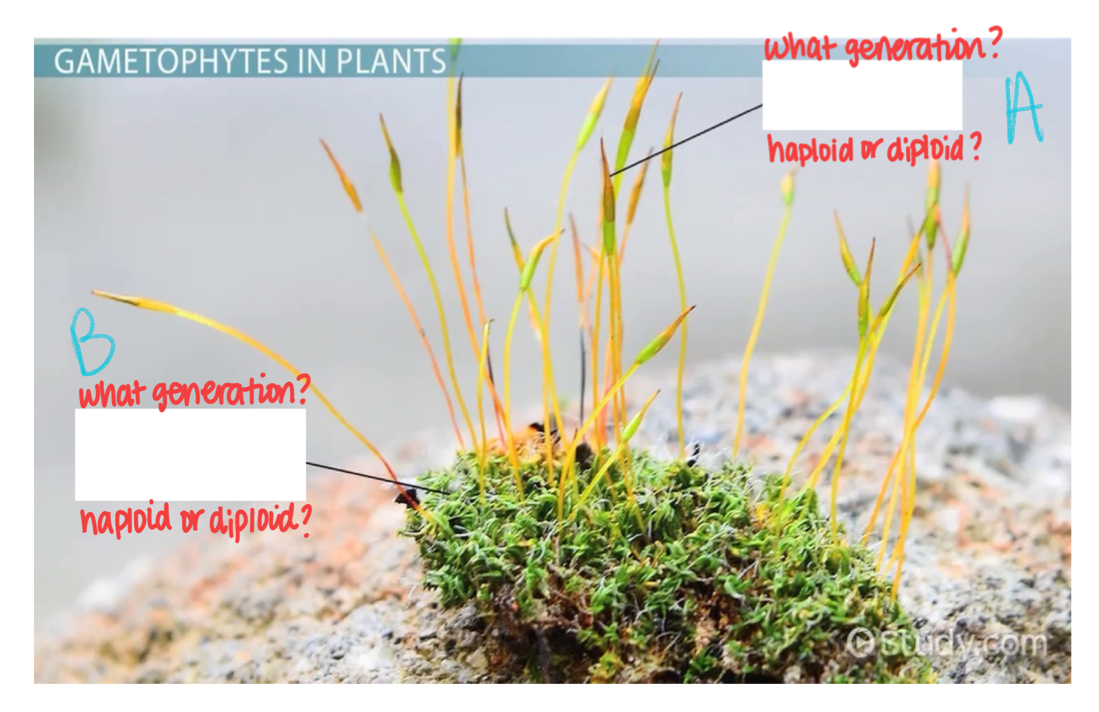
What generation is B?
Gametophyte
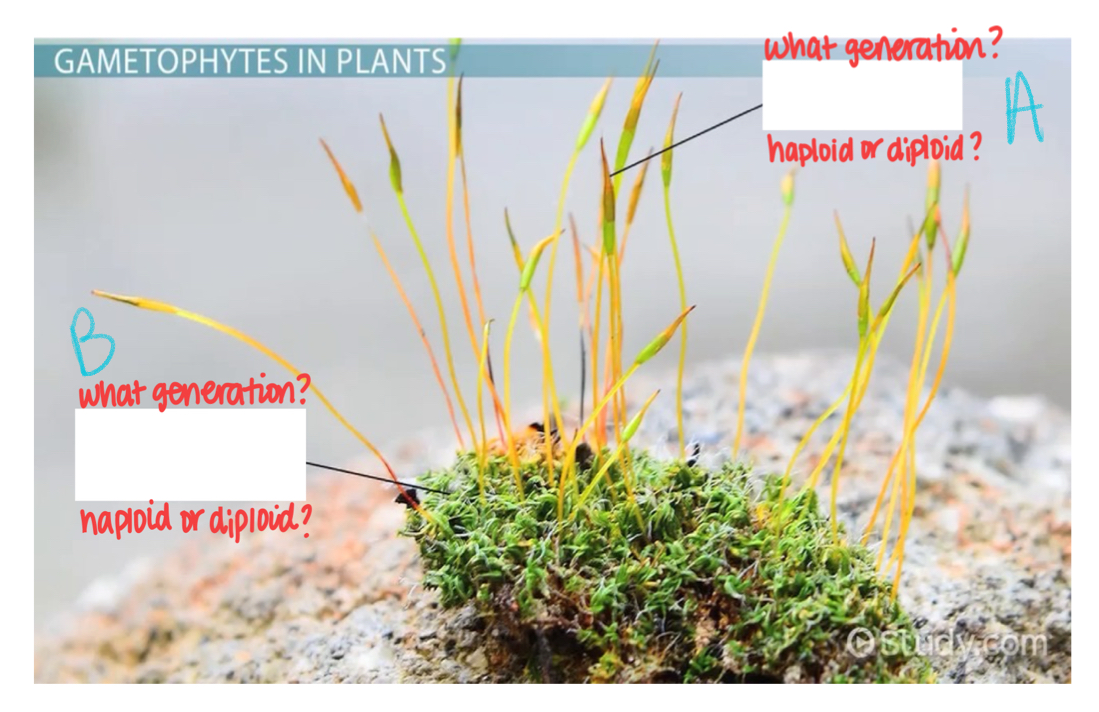
What ploidy is B?
Haploid
What is Sphagnum “peat moss” bogs used for?
harvested for fuel; important for wetlands
How old is the oldest seedless vascular plant fossil?
450 Million years old
Xylem
cells specialized to move water and minerals
Phloem
cells specialized to move sugars, amino acids, other organic products
What only contains Microphyll
Lycophytes
What are microphylls
Small, spine-shaped leaves supported by a single
strand of vascular tissue
Are microphyll leaves unbranched or branched vascular tissue
unbranched vascular tissue
Almost all other vascular plants have megaphylls
True
Which have greater photosynthetic productivity(more surface area) microphylls or megaphylls
Megaphylls
What are Sporophylls?
Leaves modified to bear sporangia
Fern sporophylls look like normal leaves but have
sori that generate spores on underside
True
What are Strobilus
Lycophyte sporophylls that are modified into a cone-like structure
Lycophytes
Club mosses(spike moss and quillwort)
Monilophytes
Whisk ferns, horsetails, ferns
Whisk ferns
have vascular tissue, no true leaves or true roots, homosporous, and dichotomous branching.
Horsetails
Contain Strobilus, homosporous, photosynthesis occur in the stem, and jointed stems with tiny leaves
Ferns
Most widespread and diverse monilophytes, large megaphylls, sori on underside of sporophylls, and can be epiphytes.
What are epiphytes?
grows on the surface of a plant
What are Seedless Vascular Plant characteristics?
Branched sporophytes that are
independent of gametophyte for nutrition
Diploid sporophyte dominates life cycle
Transport in Xylem and Phloem (vascular
system)
Xylem: cells specialized to move water
and minerals
Phloem: cells specialized to move
sugars, amino acids, other organic
products
Evolution of true roots
Evolution of true leaves