Biol 224 Lecture 23: Gas Exchange Partial Pressures
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
How are gases exchanged
By diffusion
across alveoli- capillary border
across capillary- interstitial fluid border
Diffusion in liquids
high concentration to low concentration
Diffusion in gases
high pressure to low pressure
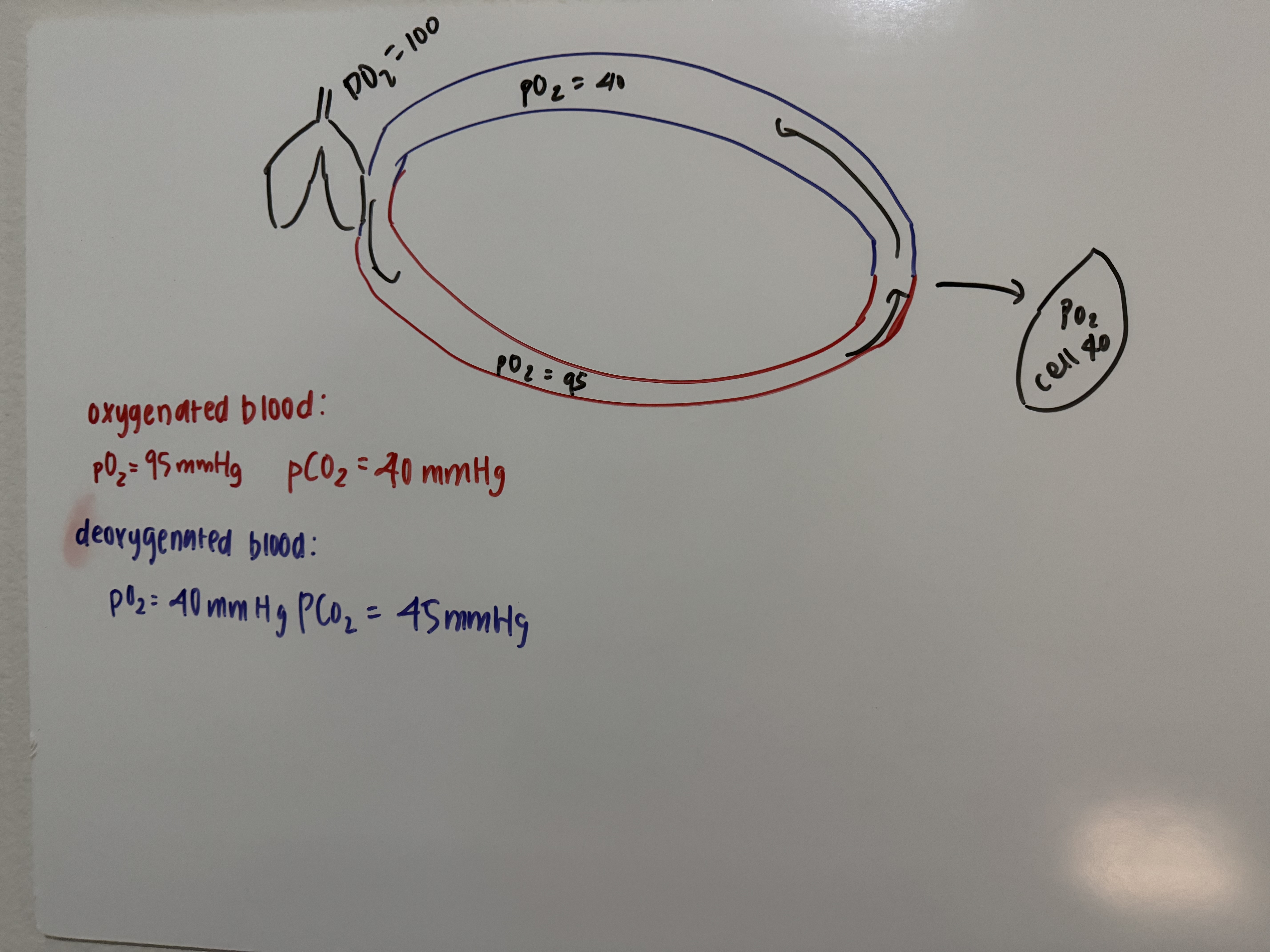
O2 diffusion path
lungs → blood → intersitial fluid → cells (always lowest in oxygen
CO2 diffusion path
cells → interstitial fluid → blood → lungs
Why dont we store o2?
Because we are constantly making ATP meaning we are constantly using oxygen
Reasons for efficient gas exchange?
Small diffusion distance
Large surface area of alveoli
differences in partial pressure across blood air barrier are substantial
o2 and co2 are lipid soluble
What can small diffusion distance be affected by?
Edema, pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis disease, etc
What can large surface area of all alveoli be affected by?
Emphysema
Efficiency of gas exchange
large differences in gas concentrations between air and blood
what can differences in gas concs between air and blood be affected by?
changes in concentraiton of o2 and co2 in the air
affected by changes in air pressure
high pressure causes more gas to go into blood and altitude affects air pressure
Daltons Law
Each gas contributes to total pressure in proportion to its relative abundance
Partial pressure
pressure contributed by a single gas in a mixture
In atomospheric (760 mm Hg) air what is Nitrogen
79% (doesnt change) 597 mmHg
In atmospheric air what is O2
21% 159 mm Hg
In atmospheric air what is H2O
.5% 3.7 mmh Hg
In atmospheric air what is Co2
0.04% 0.3mmHg
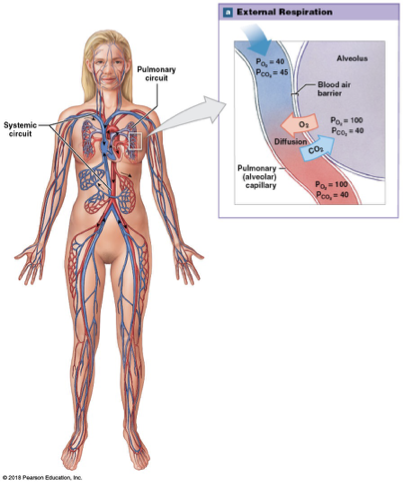
Alveolar gas levels
Po2 of 100 mmmHg and Pco2 of 40 mmHg
differs from air due to mixing of inhaled and residual air
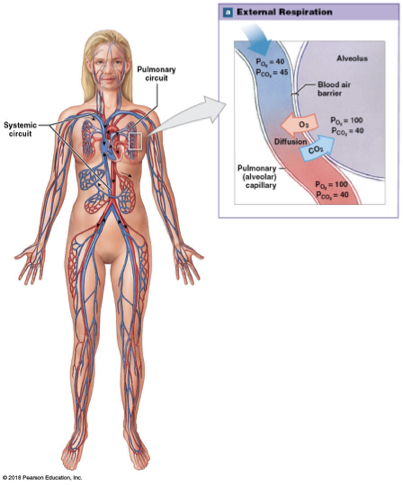
Arterial Blood Gasses
blood in systemic circuit arteries and arterioles carry blood to tissues
po2 of 95 mmHg and pco2 of 40 mmHg
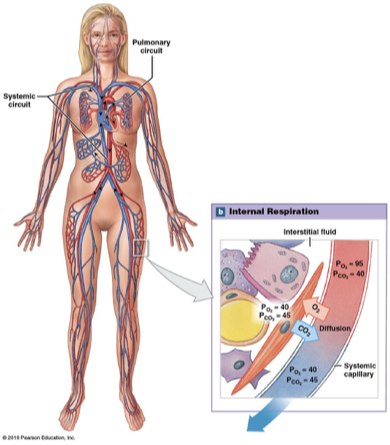
Tissue Interstitial fluid gas levels
Po2 of 40 mmHg and Pco2 of 45 mm Hg in inactive tissue (at rest)
Po2 of less than 20 mm Hg in active tissue
Venous blood gas levels
Blood in systematic circuit venules and veins returning blood from tissues
Po2 of 40 mm Hg and Pco2 of 45 mm Hg
Draw cycle of oxygen traveling/levels