the limbic system
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is the limbic system?
region of the brain believed to be responsible for emotions
where is the limbic system found?
border between the brainstem and the cerebrum
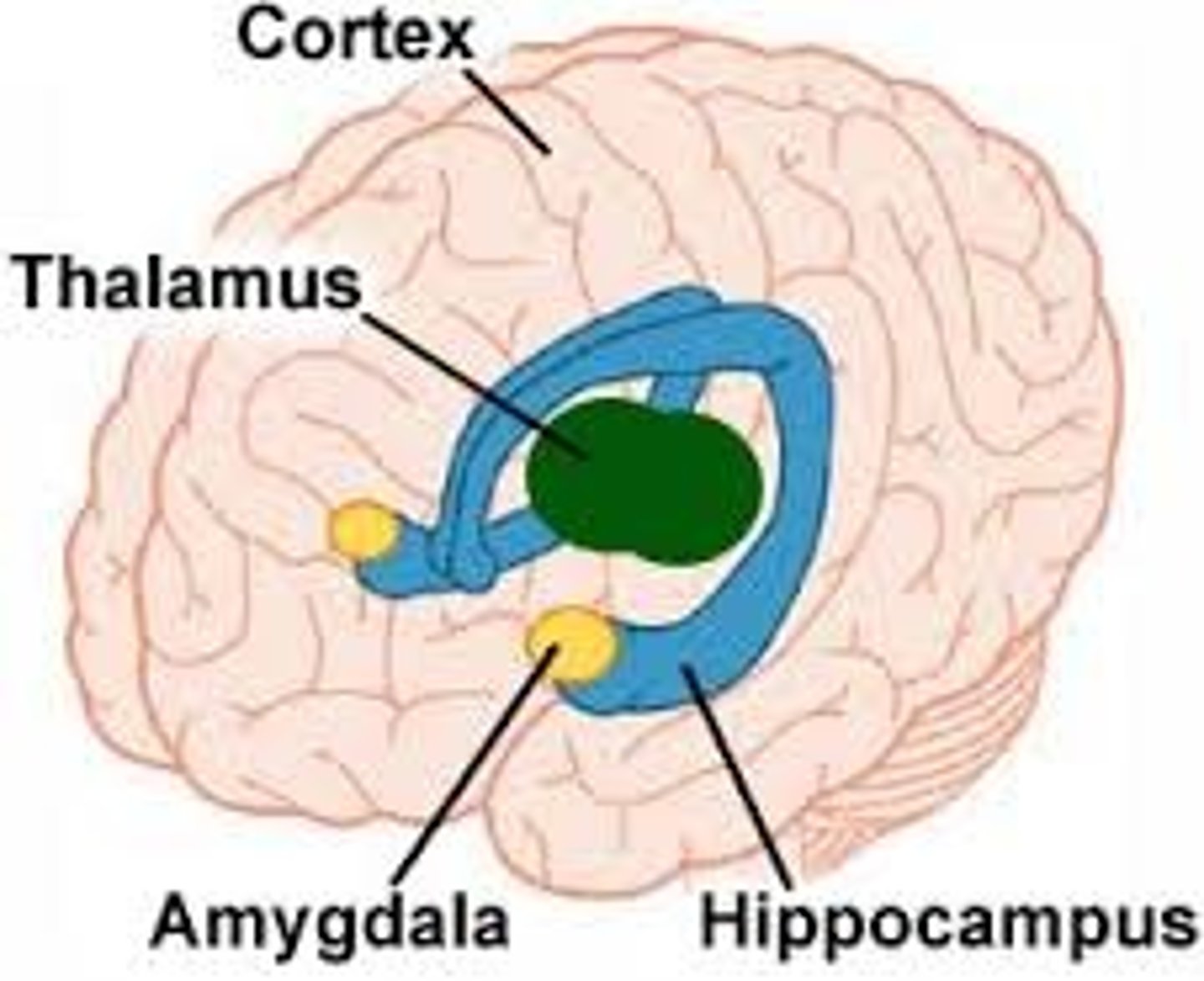
what is a way to remember the functions of the limbic system?
5 F's
Feeding - satiety and hunger
Forgetting - memory
Fighting - emotional response
Family - sexual reproduction and maternal instincts
Fornicating - sexual arousal
what are the two sections of components of the limbic system?
- cortical components aka limbic lobe
- subcortical components
what are the cortical components? (5)
- pre-frontal cortex
- insular cortex
- hippocampus
- cingulate gyrus
- parahippocampal gyrus
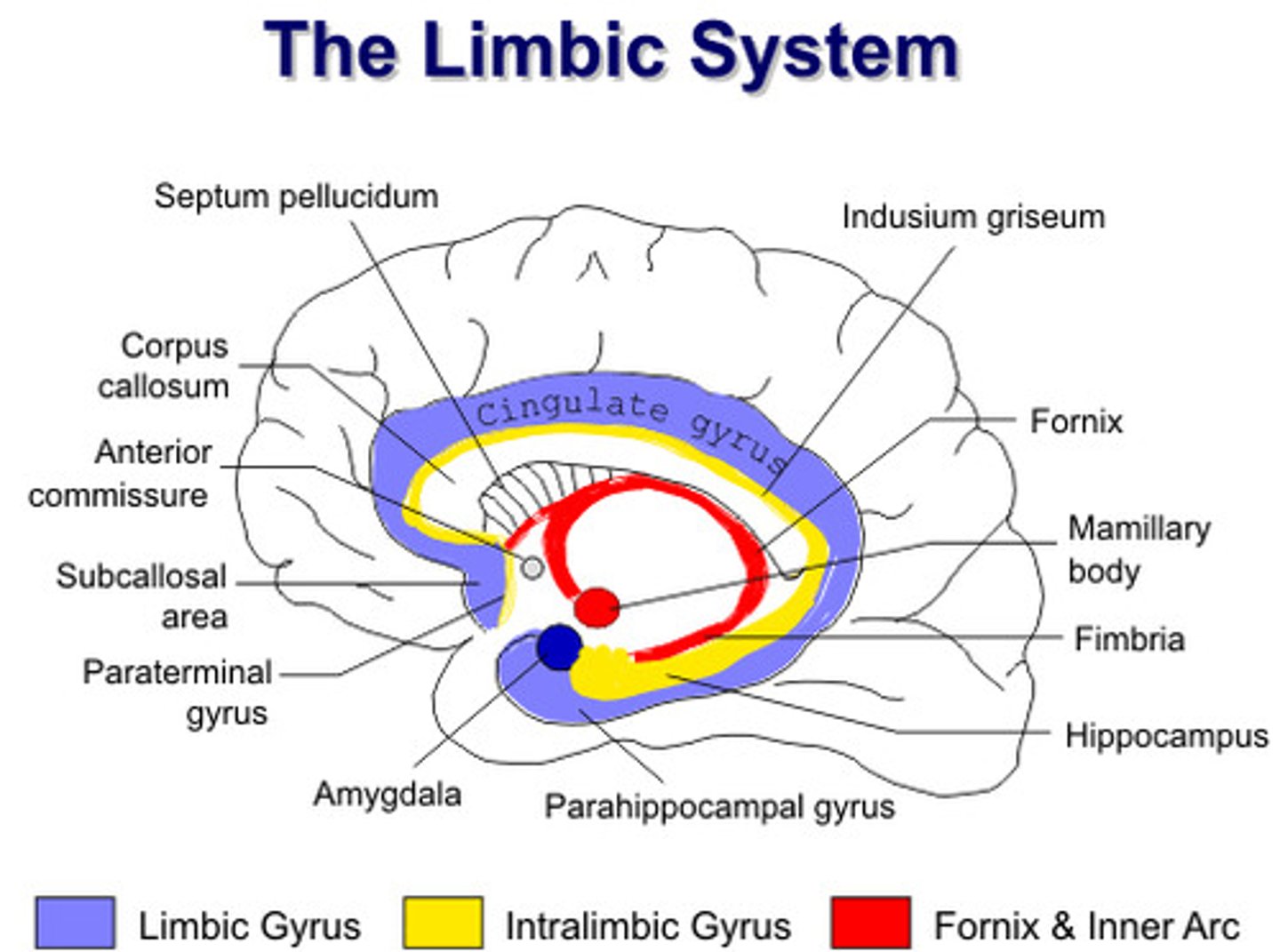
what are the subcortical components?
- amygdala
- olfactory bulb
- hypothalamus
- anterior and dorsomedial nuclei of thalamus
- mamillary bodies
- septal nuclei
- fornix
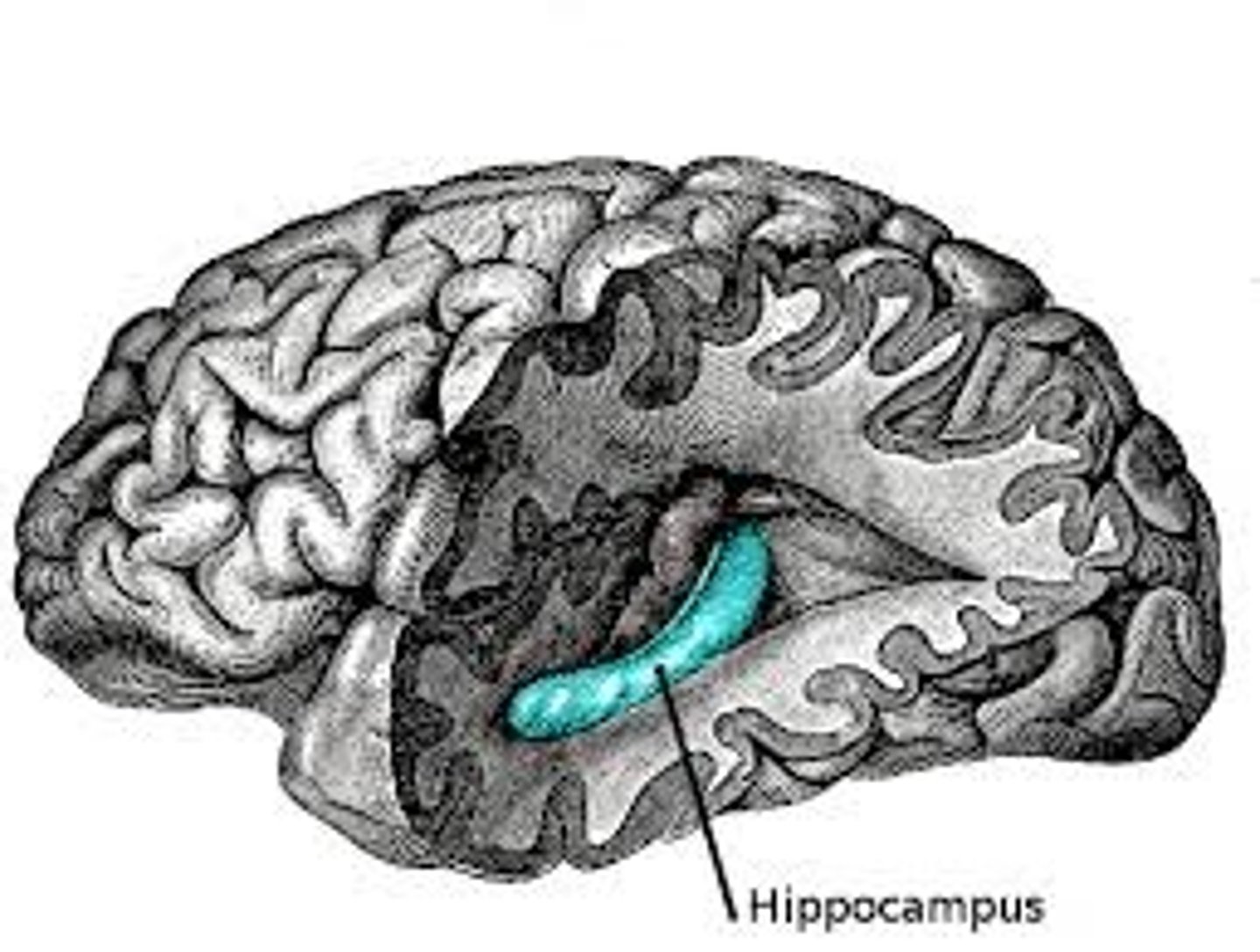
what is the hippocampus involved in?
- conversion of short term to long term memory
- learning
- spatial navigation
what is the insular cortex involved in?
desires, cravings and addictions
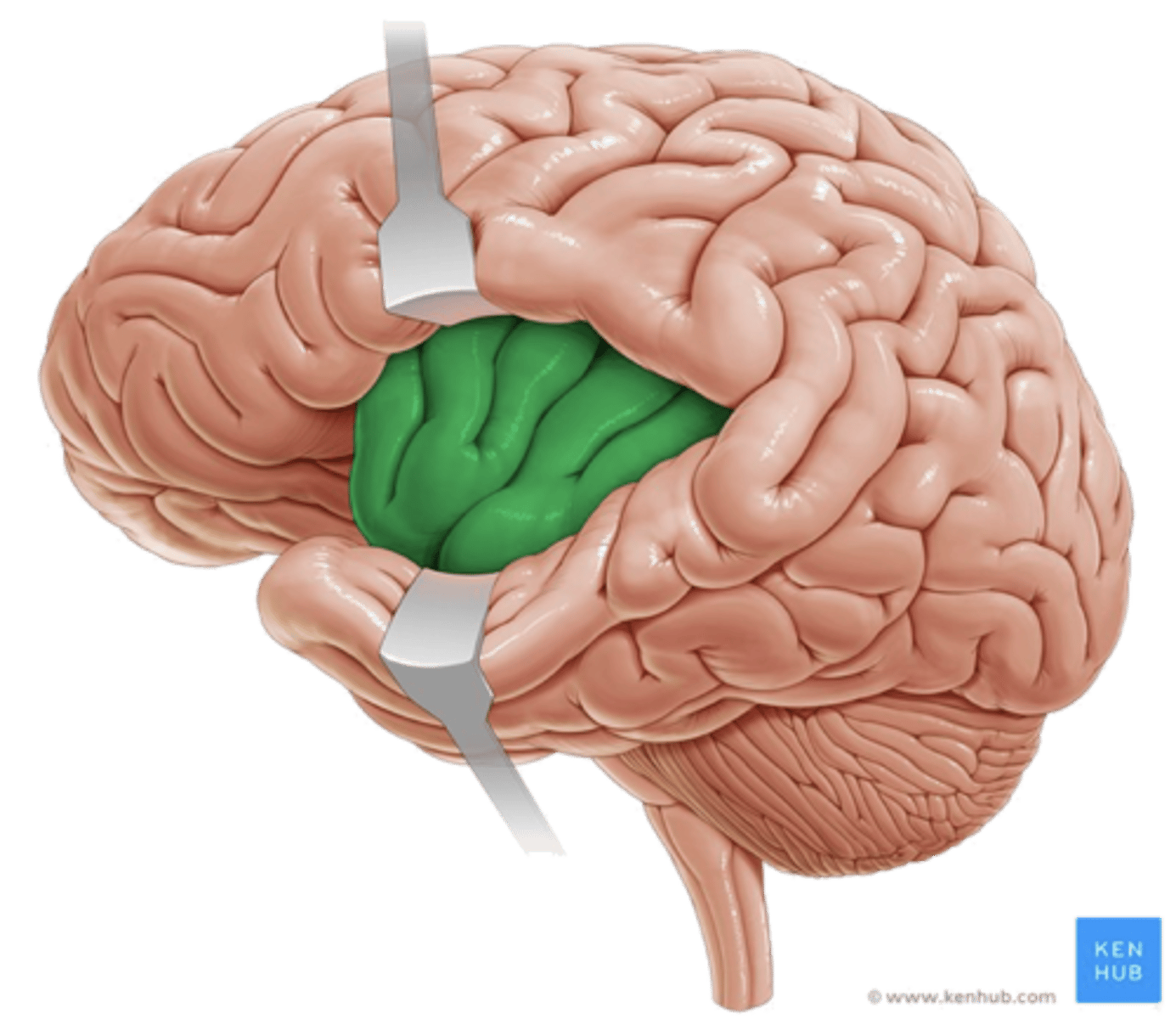
what is the (anterior) cingulate gyrus involved in?
- perception of neuropathic pain and nociception
- error recognition
- connects sensory input to emotions
- emotional bonding
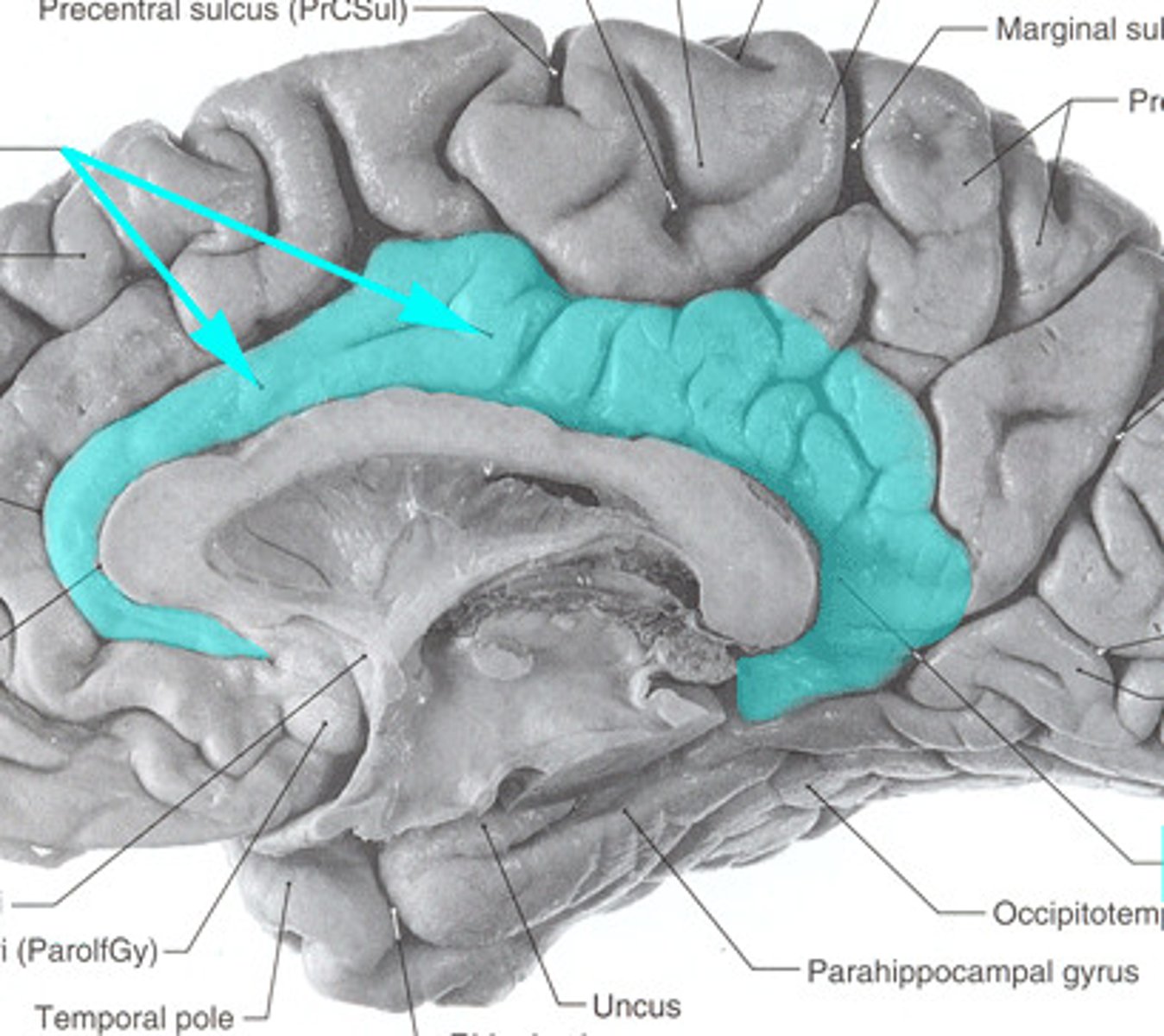
what psychiatric condition does the cingulate gyrus link to and why?
- OCD
due to the error recognition role
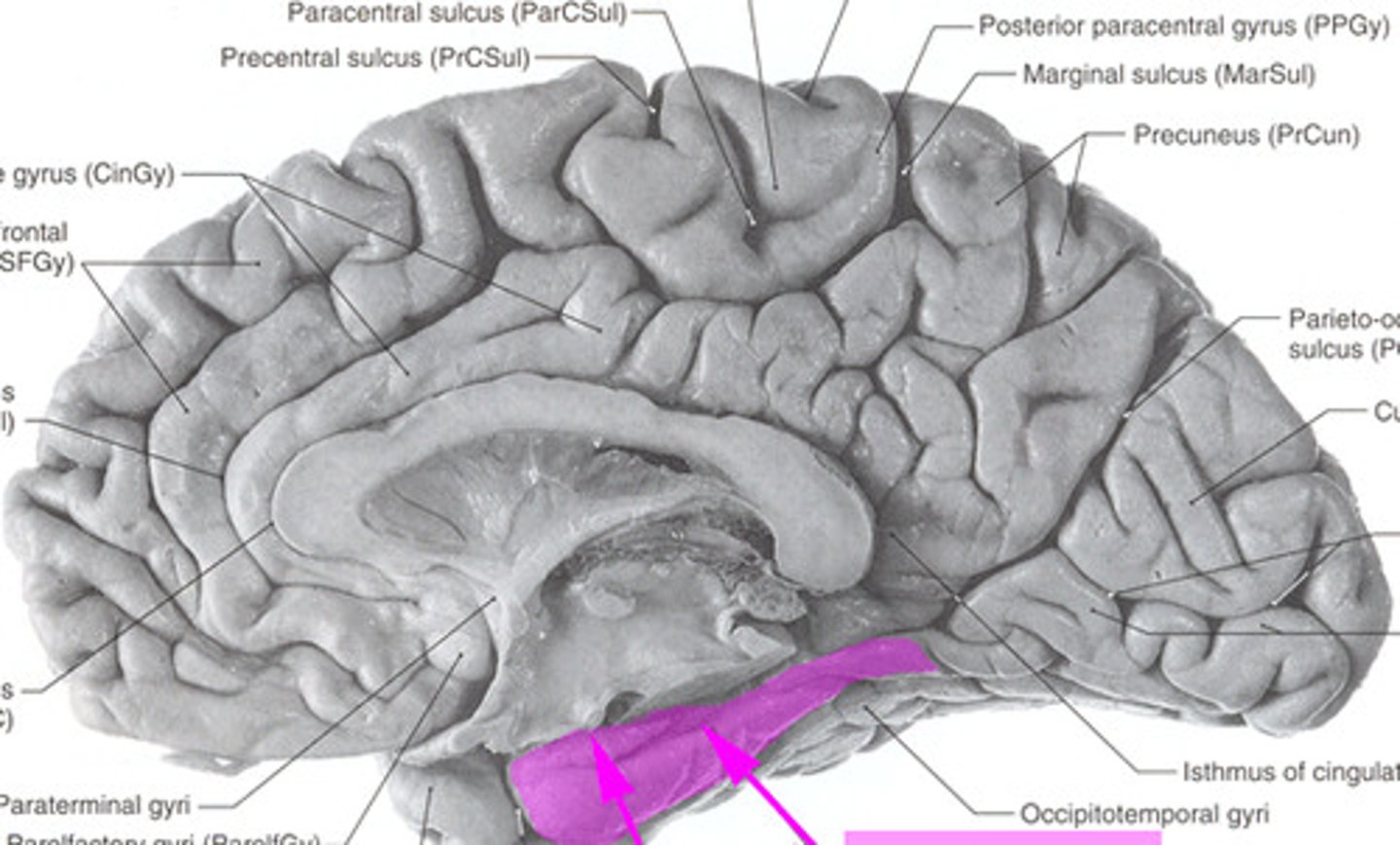
what is the parahippocampal gyrus involved in?
provides a path for communication between the cortical association areas and the hippocampus
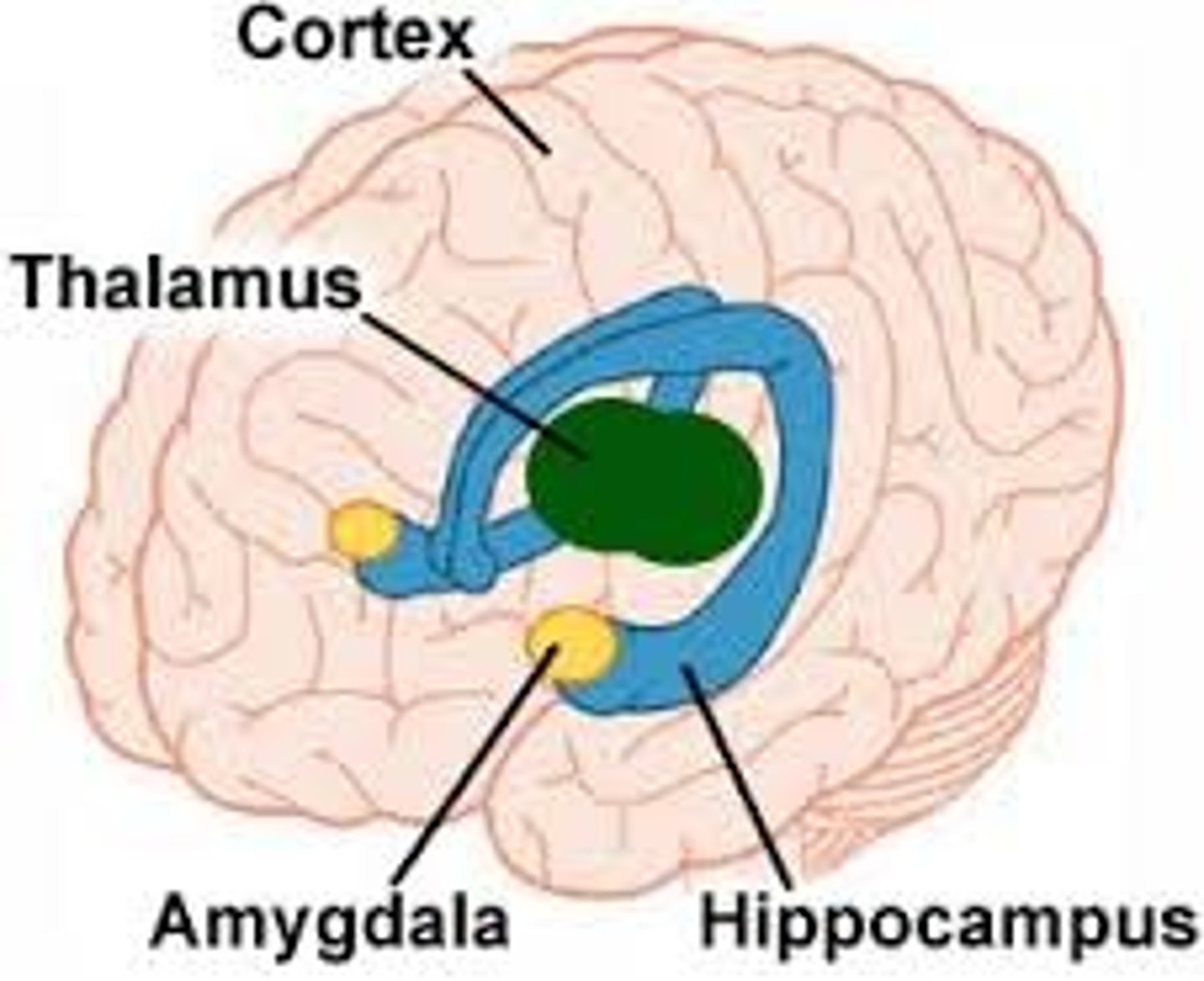
what is the amygdala involved in?
- emotion - particularly fear and anxiety
- formation of new memories
- fight or flight response
- involved in sexual drive
- involved in hunger + satiety
what is the olfactory bulb involved in?
receiving olfactory input to process smells
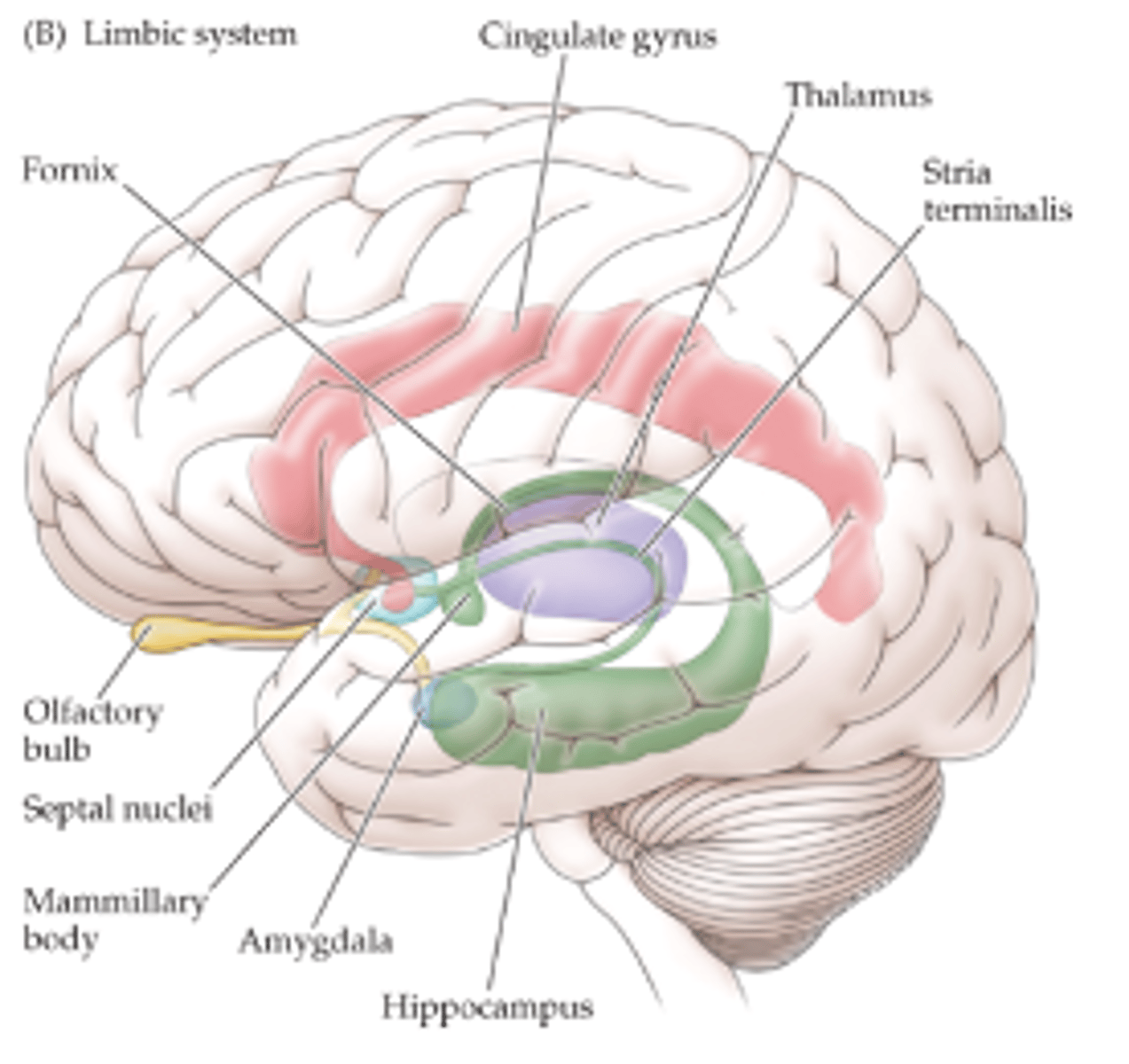
what is the fornix?
a paired, arch-shaped white matter structure that connects the hippocampus to the hypothalamus
what is the hypothalamus involved in?
group of nuclei that link the nervous and endocrine systems:
- homeostasis
- hunger and thirst
- satiety
- mood
- sex drive
- sleep
what is the anterior nuclei of the thalamus involved in?
memory + learning
what are the mammillary bodies involved in?
episodic memory - everyday events i.e. location, time, date, associated emotions
what is the role of the pre-frontal cortex?
- bit that makes you YOU!
- higher order cerebral functions
- understanding social norms
what pathology are the mammillary bodies involved in?
wernicke-korsakoff syndrome
what is wernicke-korsakoff's syndrome
- anterograde amnesia
- retrograde amnesia
- related to chronic alcohol consumption
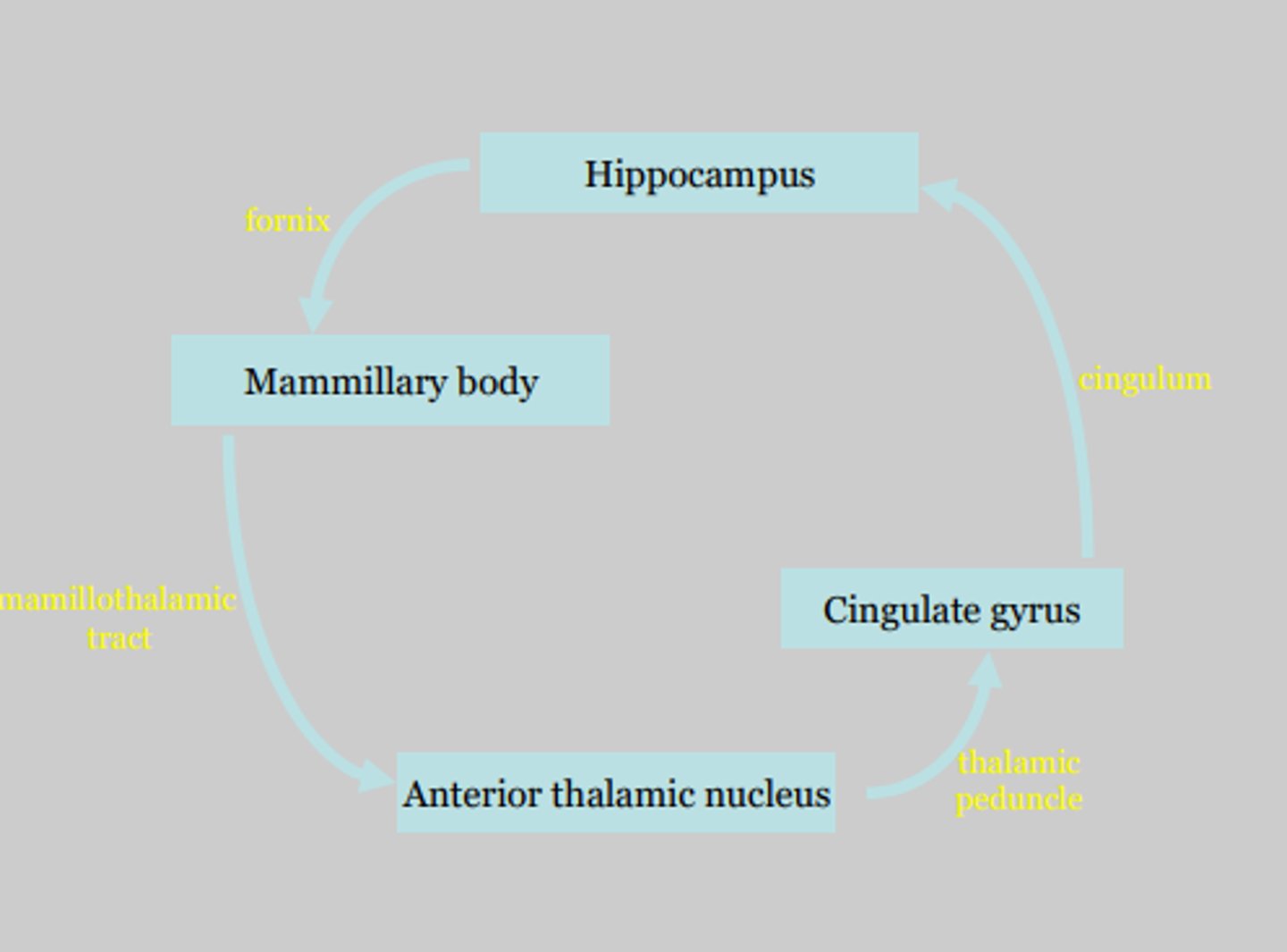
what is the papez circuit?
looped circuit of the limbic system involved in establishing emotional significances of memory and learning
what is damage to the papez circuit associated with?
- alziehmer's
- parkinson's
- wernicke-korsakoffs
what is the pathway of the papez circuit?
Hustlers Find Money At Car Parks Delightfully:
hippocampus
fornix
mammillary bodies
anterior nuclei of thalamus
cingulate gyrus
parahippocampus
dentate of hippocampus
what are the two pathways of fear?
short - thalamo-amygdala pathway
long - thalamocortico-amygdala pathway
what is the route of the short pathway?
emotional stimulus activates sensory thalamus
↓
the thalamus sends characteristic info of the stimulus to the amygdala
↓
the hippocampus sends the context of the stimulus to the amygdala
↓
the central nuclei of amygdala forms the emotional response
what is the route of the long pathway?
emotional stimulus activates sensory thalamus
↓
thalamus sends signals to primary sensory cortex (then to unimodal and polymodal association cortex)
↓
the cerebral cortex sends info about the object and conceptualisation of the stimulus to the amygdala
↓
the hippocampus again sends info about the context of the stimulus to the amygdala
↓
the central nuclei of amygdala forms the emotional response
what does the amygdala do once stimulated?
stimulates hypothalamus
what does the hypothalamus do? (2)
- release CRH
and
- posterior hypothalamic nuclei stimulate sympathetic NS
what is the major difference between the short and long pathways of fear?
short pathway is subcortical (no cognition is involved) so has a fast response for fight or flight reactions
what is the motivation pathway?
amygdala
↓
ventral tegmental area of midbrain - DOPAMINE RELEASED
↓
nucleus accumbens of basal ganglia - mesolimbic pathway
OR
pre-frontal cortex - mesocortical pathway
↓
REWARD
what is the feeding pathway?
amygdala
↓
hypothalamus
↓
ventromedial nucleus - satiety
or
lateral hypothalamic nucleus - hunger
what is the olfaction pathway?
olfactory bulb
↓
amygdala - emotion to smell
AND
parahippocampal gyrus - memory of smells
what is the sexual pathway?
amygdala
↓
hypothalamus
↓
paraventricular nucleus - oxytocin release
AND
medial pre-optic nucleus - GnRH release
↓
increased sex drive