PEM Board Studying
1/474
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
475 Terms
Hypopigmented lesions associated with seiures
Tuberous sclerosis; associated with shagreen patches, ashleaf spots (hypopigmented lesions) and angiofibromas
Complication of over drainage of VP shunt
subdural hematoma
Goal of lowering BP in hypertensive emergency
Lower 25% in the first 8 hrs of the difference from current systolic BP - goal systolic BP (also get head imaging prior to lower BP).
Patient with programmable VP shunt presenting with vomiting after head imaging a few weeks ago
If not reprogrammed after imaging —> can increase risk of suboptimal drainage and increased ICP
Normal VP shunt pressure and if elevated
12 cm H20; if elevated then suspect distal shunt failure, if low then suspect proximal shunt failure
Hemiparesis, ataxia, dysarthria, oculomotor deficits after CHI
Suspect posterior circulation stroke (most common cause is vertebral artery dissection)
Age of Infantile spasms
90% < 12 months of age
Immune-mediated paraneoplastic presentation associated with neuroblastoma, sometimes others such as ganglioneuroblastoma
Opsoclonus Myclonus
Imaging to get in patients with suspected opsoclonus myoclonus
CT or MRI of chest, abdomen and pelvis
Medication of choice for neonate that prevents in severe hypoxemia with palpable liver edge
Prostaglandin gtt at 0.05 mcg/kg/min to maintain ductus arteriosus patency. Keeping of duct open allows mixing of pulmonary and arterial blood to the systemic circulation
First line therapy for patient (2 mo with sweating with feeds, liver edge palpated and delayed cap refill)
CHF —> Diuretics (Furosemide)
Older adolescent who presents with heart failure symptoms while completing drills at practice (associated JVD, CXR with cardiomegaly, murmur harsh systolic ejection murmur along the L sternal border.)
heart failure associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Treatment of heart failure associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Betabloockers (metoprolol 0.1 mg/kg) used for obstruction, diuretics contraindicated as they will worsen the LVOT obstruction)
EKG changes with pericarditis
widespread ST elevation*, PR segment depression
Elements of Pericarditis diagnosis
Pleuritic chest pain, pericardial friction rub, EKG changes, new or worsened effusion (need 2 of these)
Approach to drain pericardial effusion if able to visualize with US
L parasternal approach (5th or 6th rib space)
Diagnostic marker for Myocarditis
Troponin; EKG is low sensitivity (can show non specific ST segment or T wave changes and sinus tachycardia)
Sharp chest pain at rest or during mild exercise, localized with the finger tip at the L sternal border
Precordial catch aka Texidor’s twinge (*don’t order EKG; provide reassurance)
15 yo with acute onset neck and chest pain after inhaling helium and with exam noting neck tenderness/swelling along the SCM bilateral, fair aeration but decreased breath sounds
Spontaneous pneumomediastinum
Chest XR findings associated with spontaneous pneumomediastinum
shows air tracking around and outlining mediastinal structures
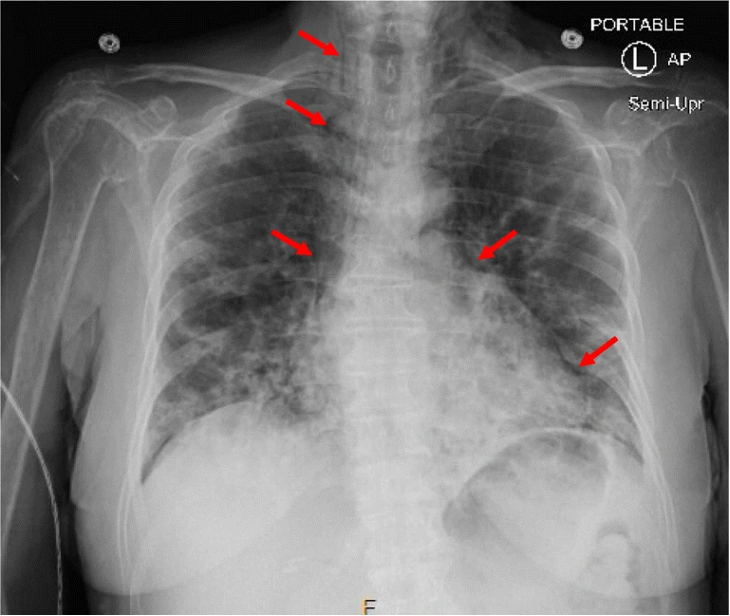
Treatment of spontaneous pneumomediastinum
self resolves and can provide oral analgesics
16 yo with flu-like symptoms, eyes “blood shot”, urine with pink twinge, febrile, has a heart murmur. What test is needed?
Concern for infective endocarditis —> blood culture
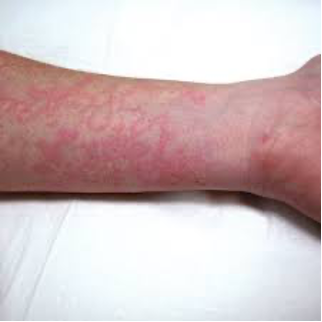
Rash in patient with heart murmur and arthritis
Concern for rheumatic fever, rash is erythema marginatum. Need 2 major criteria or 1 major and 2 minor criteria.
o Major: carditis* (pansystolic cardiac murmur at apex indicating mitral valvulitis), arthritis, chorea, erythema marginata, subcutaneous nodules
o Minor: arthralgia, fever, elevated inflammatory markers, elevated PR interval)
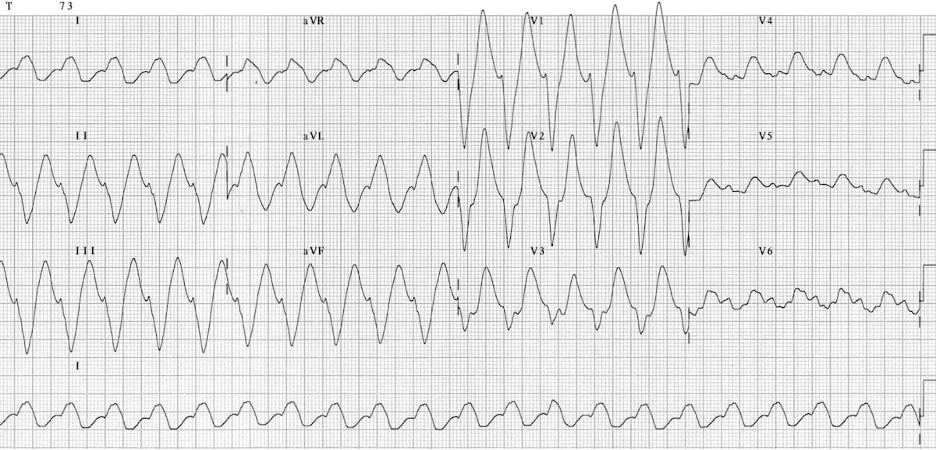
Patient overdosed on medications; what drug to give her?
Sodium bicarbonate due to concern for TCA ingestion; see prolonged PR and widened QRS
Massive hemoptysis definition
> 240 ml within 24 hrs or recurrent bleeding > 100 ml daily for several days
Vent goals in COVID PNA
Lower TV 4-6 ml/kg and optimize peep; keep O2 88-95%
Pulmonary hemorrhage vent strategy
low TV and high PEEP
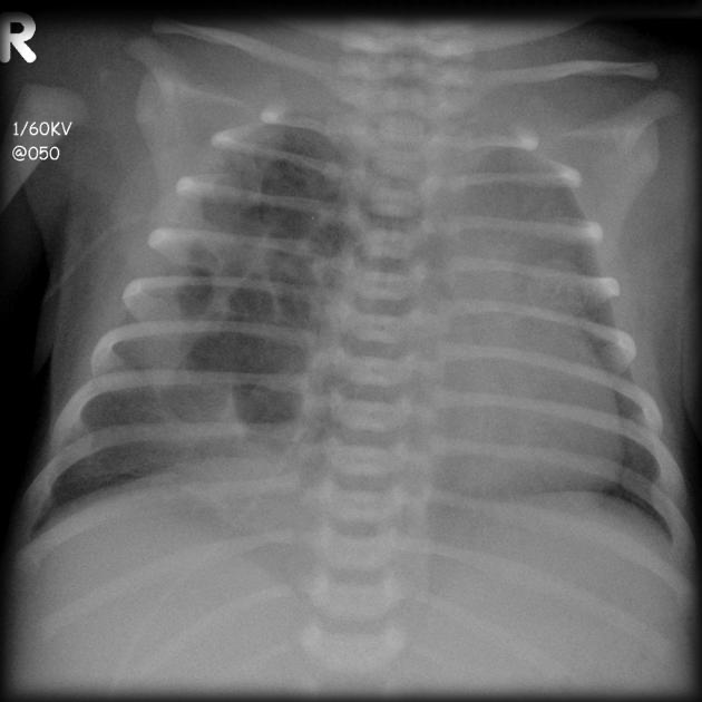
Imaging of ? and Management?
CPAM; congenital pulmonary airway malformation with cystic and adenomatous elements. Tx with surgical lobectomy in large CPAMs; consult surgery*
Chylothorax findings
triglycerides greater than 110, cholesterol lower than 200 along with lymphocyte predominance
“Kyle got 100% on his Test”
14 yo with URI symptoms with L sternal chest pain and localized area of tenderness and nonsuppurative edema over the costochondral junction
Tietz’s syndrome; -Benign, painful, nonsuppurative localized swelling of the costochondral joints, most often involving the 2nd and third ribs; tx with NSAIDs
How is diagnosis of sarcoidosis made?
lymph node biopsy (noncaseating granulomas)
Earlier complication of lung transplant
Anastosis ( Donor lungs are attached at the level of the main bronchus which is a frequent site of complications)
Later complication of lung transplant
Bronchial stenosis (in Q stem surgery was 9 mo ago); dyspnea, stridor, wheezing, post obstructive PNA and require scope for stenosis dilation
Factor for Hemophila A and B
A; factor 8, B: Factor 9
PT/PTT and plts in Hemophilia A and B
normal plts, normal PT, abnormal PTT (intrinsic pathway including VIII and IX)
PT/PTT in Factor VII deficiency
abnormal PT, normal PTT
How much correction to give in patient with Hemophilia A and head trauma
100% correction in cases of severe bleeding or high risk of bleeding
Patient with Hemphilia and presents as abdominal pain, flexure contraction at the hip, with lower extremity paresthesia
Think Psoas abscess; compression of femoral nerve from abscess causes the paresthesia - diagnose with CT of abdomen/pelvis
PT/PTT in vWD
normal; note abnormal in hemphilias and factor VII deficiency
Plt level in ITP that increases risk of ICH
< 10,000
Treatment vs. supportive care for ITP
Mucosal bleeding or significant bleeding
First line therapy for autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Steriods for first line; note labs show: anemia, high retic, +coombs, elevated LDH/bili (all signs of hemolyic anemia)
Difference between FFP and Cryoprecipitate
FFP is more broad and has all components to help with bleeding; Cryoprecipitate is made from FFP and includes vWF, fibrinogen and coagulation factors
Electrolyte abnormalities when providing significant blood transfusions
Hypocalcemia from citrate, hypomagnesemia, hypo/hyperkalemia
Lab abnormalities associated with tumor lysis syndrome
Hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, HYPOcalcemia and hyperurecemia
A neutropenic patient with RLQ pain
Consider typhlitis on differential (can influence the cecum and large intestine)
Imaging for Typhlitis
XR shows paucity of air in the RLQ and can get serial Xrs to look for development of free air (although technically US and CT can be more definitive for the diagnosis itself)
< 6 yr old with anemia, hypertension, hematuria and painless abdominal mass
Nephroblastoma/Wilms tumor (most common pediatric malignancy)
Location for most neuroblastomas
Can be 60% adrenals and 20% anterior mediastinum
Test to detect neuroblastoma
Urine catecholamines elevated in 95% of patients with this disease
Most common primary malignant bone tumor in pediatric patients and disposition if identified
osteosarcoma; need to be admitted as they are highly malignant
Age for Dtap vs. Tdap
< 6 should get Dtap
When to give Tetanus immunoglobulin
If unvaccinated with dirty wound; (if given > 3 doses of vaccine in general don’t need to give immunoglobulin)
When to give tetanus vaccine
If unvaccinated with clean or dirty wound, for dirty wound if > 5 years since last vaccine
Size of abscess for I&D of RPA
> 2.5 cm in diameter
At what age is the Monospot less sensitive and EBV titers more necessary
< 5
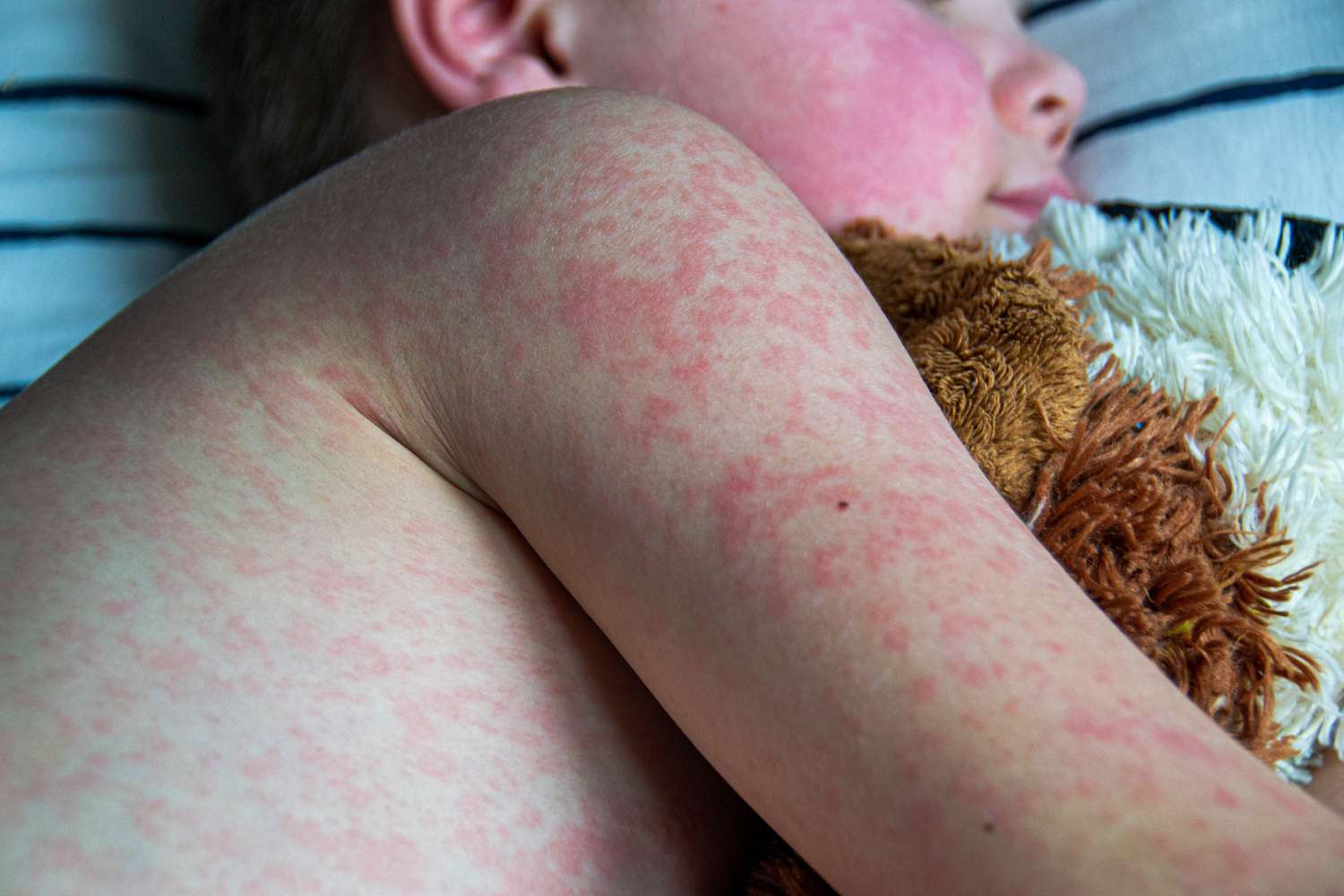
Rash spread in Measles
Head down toward the rest of the body
Most specific test of disseminated HSV
HSV PCR of blood, but in question stem it was LFTs (as the HSV PCR was not a possible response)
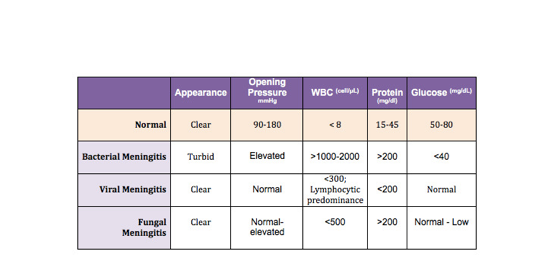
Difference between viral, bacterial and fungal meningitis labs
In fungal and viral ; you have > WBC, but not > 1000, in fungal you have elevated protein > 200 like bacterial (viral has < 200 protein), in fungal you have low glucose like bacterial, viral has normal protein
Age it is safe to give Doxy for Lyme disease
If > 8 yrs of age; less than 8 give amoxicillin
Labs in RMSF
Hyponatremia and thrombocytopenia
Rash spread in RMSF
starts on palms and soles and spreads centrally
How to test for malaria
Rapid antigen test has 85-95% sensitivity and specificity; thin and thick smear are confirmatory testing
Child with vomiting and elevated LFTs in daycare
Most likely Hepatitis A; need health department clearance prior to return to daycare (disease is self limited)
Post exposure ppx recommendations in immunocompromised patients exposed to flu?
Vaccine + osteltamivir daily x 7 days
Varecella zoster ppx in immunocompromised patients?
Should get varicella zoster immunoglobulin; NOT vaccine given that is a live vaccine
Electrolyte side effects of immunosuppressive meds (tacrolimus or mycophenolate)
hypomagnesemia; can present as spasm, tremor, EKG changes (pACs, QRS widening)
What medication can interact with tacrolimus and cause toxicity? symptoms of tacro toxicity?
azthromycin; if concerned get a tacolimus level (headache, hypertension, seizures, *hand tremors)
Presents with improved shortness of breath and oxygen saturation when lying flat (platypnea and orthodeoxia)
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (in Liver transplant patients); cause increased pulmonary capillary dilation and occasionally direct AV connections. To test get a contrast ECHO (aka bubble study)
What virus is typically positive in PTLD patients?
EBV+; labs also show elevated LDH and uric acid”
splenomegaly, thrombocytopenia and abdominal pain in patient with liver transplant
Portal vein thrombosis; need abdominal US with doppler to evaluate
Most frequent clinical manifestation of graft vs. host disease
Rash; especially seen on. palms and soles. Need skin biopsy to diagnose.
Test of Toxoplasmosis
PCR of Blood; Crypto is DFA
Test for Cryptosporidium
Stool direct immunofluorescent antibody (DFA); Toxo is blood PCR
Metabolic acidosis, hypoglycemia and NO ketones
Fatty acid disorders (MCADD); have abnormal urine organic acids and acyl carnitine profile
Metabolic acidosis, elevated lactate, + ketones
Organic aciduria; have abnormal urine organic acids
Test for PKU
abnormal serum amino acids
Labs for galactosemia
+ urine reducing substances
Neonate with lethargy, poor feeding, hypoglycemia, prolonged jaundice, cloudy corneas
Galactosemia (+ urine reducing substances)
2 yo with who presents after extended periods of fasting and present with ketonemia (high ketones) and symptoms of lethargy
Ketotic hypoglycemia (common form of childhood hypoglycemia);
different than organic acidemia who also present with hypoglycemia and ketones in that patients with ketotic hypoglycemia present between 18 mo - 5 yrs of age where as organic acidemia present in neonates
2 yo with more protein who presents with AMS and lethargy
Urea cycle disorder; high ammonia, diagnosis with: abnormal plasma amino acids, enzyme assay
Treatment of Urea cycle defect with elevated ammonia
IV fluids, sodium benzoate and arginine (scavengers); if ammonia > 200 likely need dialysis
Infant with regression of developmental milestones, difficulty feeding and failure to thrive, significant hepatosplenomegaly and cherry red spot on the macule
Lysosomal storage disorder; Gaucher is one of the most common; tested with lysosomal enzyme assay
neonate presents with lethargy, malodorous smell, hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis
Organic acidemia;’ tested with urine organic acids
Neonate with seizures in the setting of microcephaly, eczema, unusual odor
PKU; test with serum amino acids; elevated phenylalanine
lethargy, hypoglycemia most often brought on by periods of fasting or vomiting without ketones, also have metabolic acidosis
Fatty acid oxidation disorders (MCADD); metabolic acidosis, hypoglycemia and NO ketones; as opposed to organic acidemias which have similar presentation but have ketones. Diagnosed with acylcarnitine profile and urine organic acids.
Patients present with increased thrombosis risk in the setting of learning disabilities, dislocated lens, poor growth and skeletal abnormalities
Homocysteinuria; have elevated stoke risk and thrombosis; test with homocysteine level
Adolescent presents with psychiatric and behavioral issues alone with movement abnormalities and elevated LFts
Wilsons disease; elevated ceruloplasmin level
Adolescent with depression and psychosis as well as abdominal pain, blistering with sun exposure, red or brown urine
Porphyria; test with protoporphyrin level
Lab findings in DiGeorge syndrome
normal neutrophils, platelets and immunoglobulins, + lymphopenia (are at high risk of SCID with T cell deficiency) and hypoplastic thymus
Child presenting with recurrent pneumonia, abscesses, adenitis, osteomyelitis, sepsis; lab to test?
Chronic granulomatous disease; increase risk of catalase produce organisms; test with neutrophil oxidative burst index
Patient with immunodeficiency, thrombocytopenia and eczema
Wiskott Aldridge syndrome
Patient with severe immunodeficiency and eczema but NO thrombocytopenia
Job syndrome (hyper IgE); they als have facial bossing, coarse facies and retained primary teeth
Patient without tonsil adenoids or palpable lymphoid tissue
X-linked agammaglobulinemia; have severe hypogammaglobuliinemia and antibdody deficiency
What to give for patients with refractory anaphylaxis 2/2 to betablockers
Glucagon; of note; glucagon is also what you give when there is beta blocker overdose
Abnormal labs in DRESS syndrome
eosinophilia, leukocytosis, neutrophilia, liver dysfunction
How to test for adrenal insufficiency?
AM cortisol level or ACTH stim test
Neonate with bradycardia and periorbital rash
neonatal lupus
Labs in lupus
hypocomplementemia (low C3, C4 or CH50), + ANA, dddDNA, antiSm antibodies
Patient with heliotrope rash, Gotton sign, difficulty stading up and lower body weakness requiring upper body to help
Dermatomyositis