L12: Glucose Regulation Pt. 2
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is Tacrolimus (Prograf/Astagraf)
=> anti-rejection med, preventing the body from rejecting a transplanted organ
- T-cell suppression (immunosuppresant meds)
- narrow TI
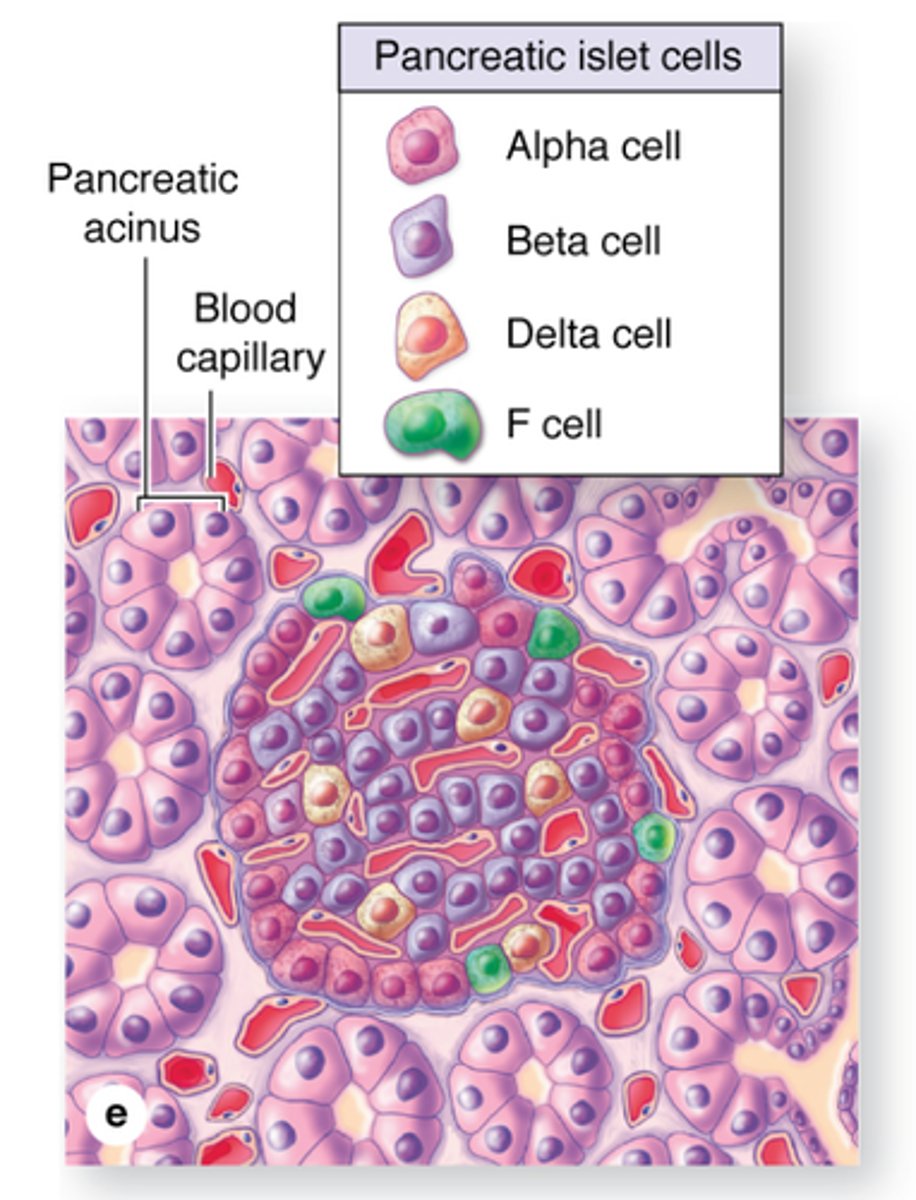
What are islet cells
Islet cells are pancreatic cells that produce hormones (eg. insulin or glucagon)
What is an alternate tx choice for DM I?
- beta cell transplant + immunosuppressant drugs (eg. Tacrolimus)
- 2-3 infusions of islet cells required (over time)
- challenges: donor numbers; chronic immunosuppression
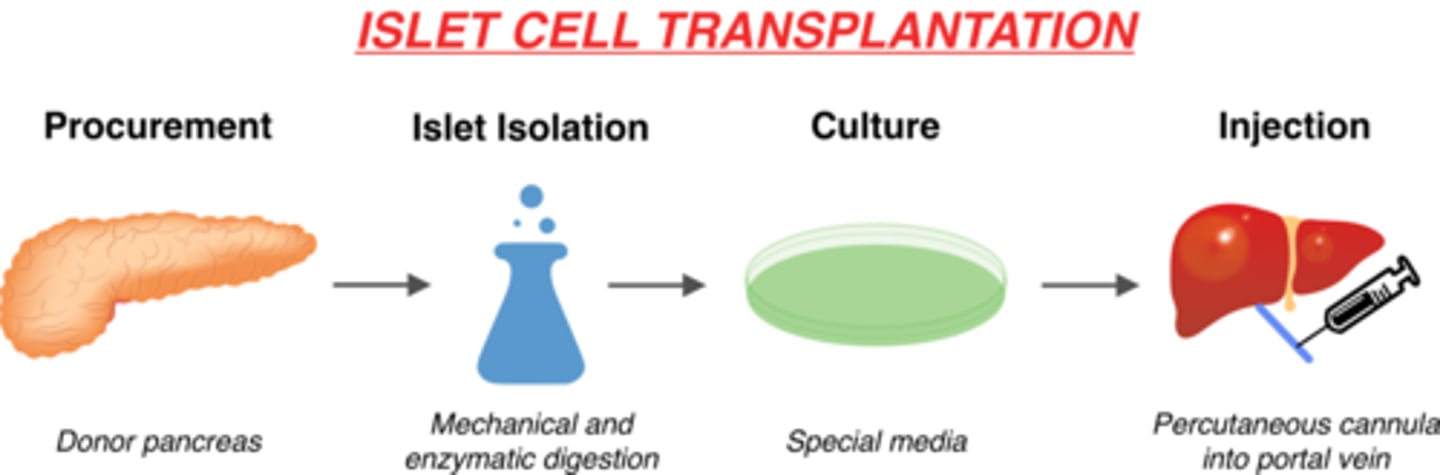
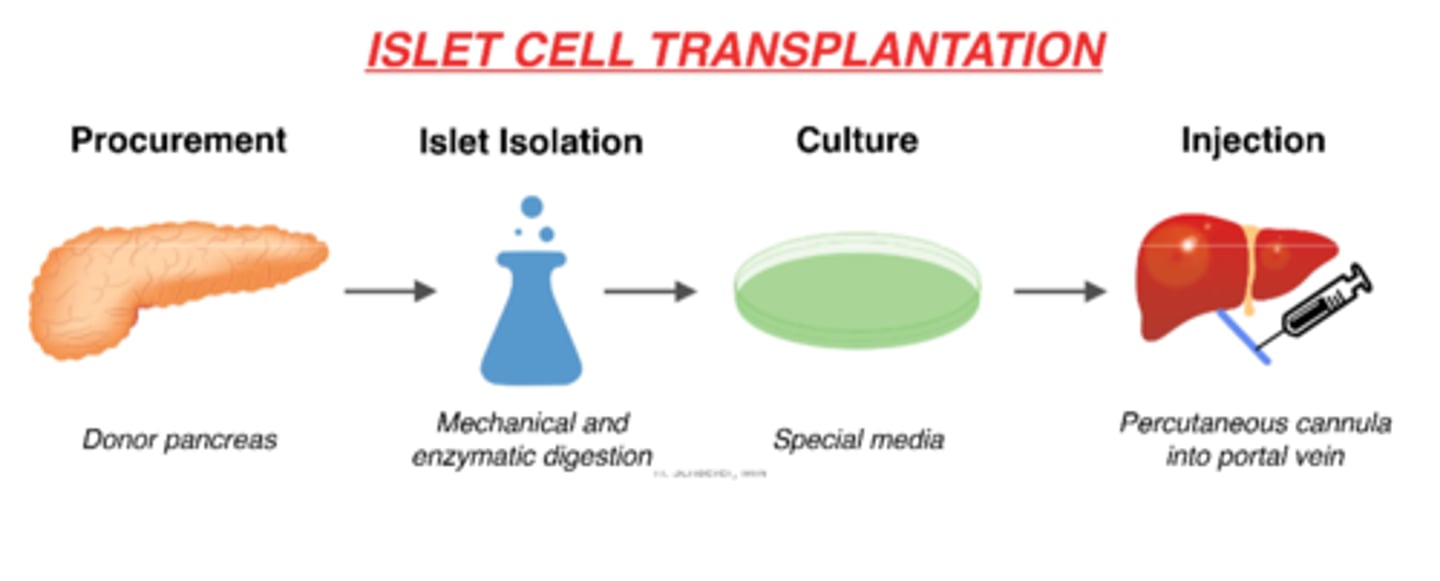
How does an islet cell transplant work?
1. procurement (removal) of donor pancreas
2. islet isolation via mechanical & enzymatic digestion in lab
3. culture on special media in lab
3. injection of islet cells via percutaneous cannula into portal vein
4. islet cells in the body!
What are the BG levels in a hypoglycemic pt?
blood glucose <4 mmol/L

What is hypoglycemia caused by? (with or without diabetes)
- with diabetes: too much insulin or diabetes meds
- without diabetes: eating less, exercising more than usual, alcohol, some meds, or underlying conditions

What are the s&s of hypoglycemia
- hunger, fatigue, shaking
- sweating, pallor, headache, dizziness
- confusion, slurred speech, blurred vision
- fainting, seizures, coma
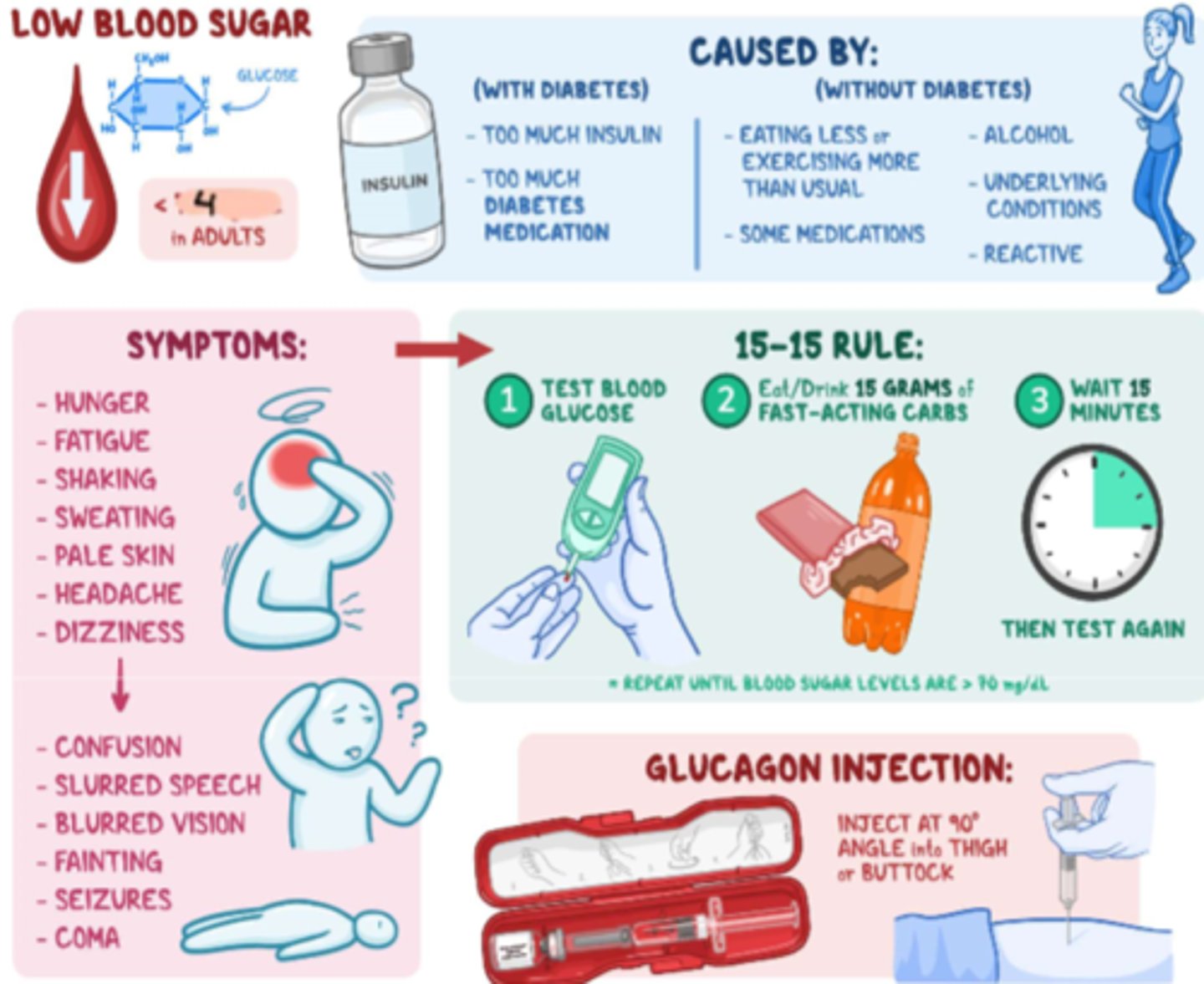
How to tx hypoglycemia
- first assess: conscious or unconscious?
- conscious tx: Glucose PO (glucose tablets, honey, apple juice; eg. 15 g of Glucose)
- unconscious tx: Glucagon IM injection (eg. 1 mg - 90 deg. angle into thigh or buttock) + D50W IV infusion
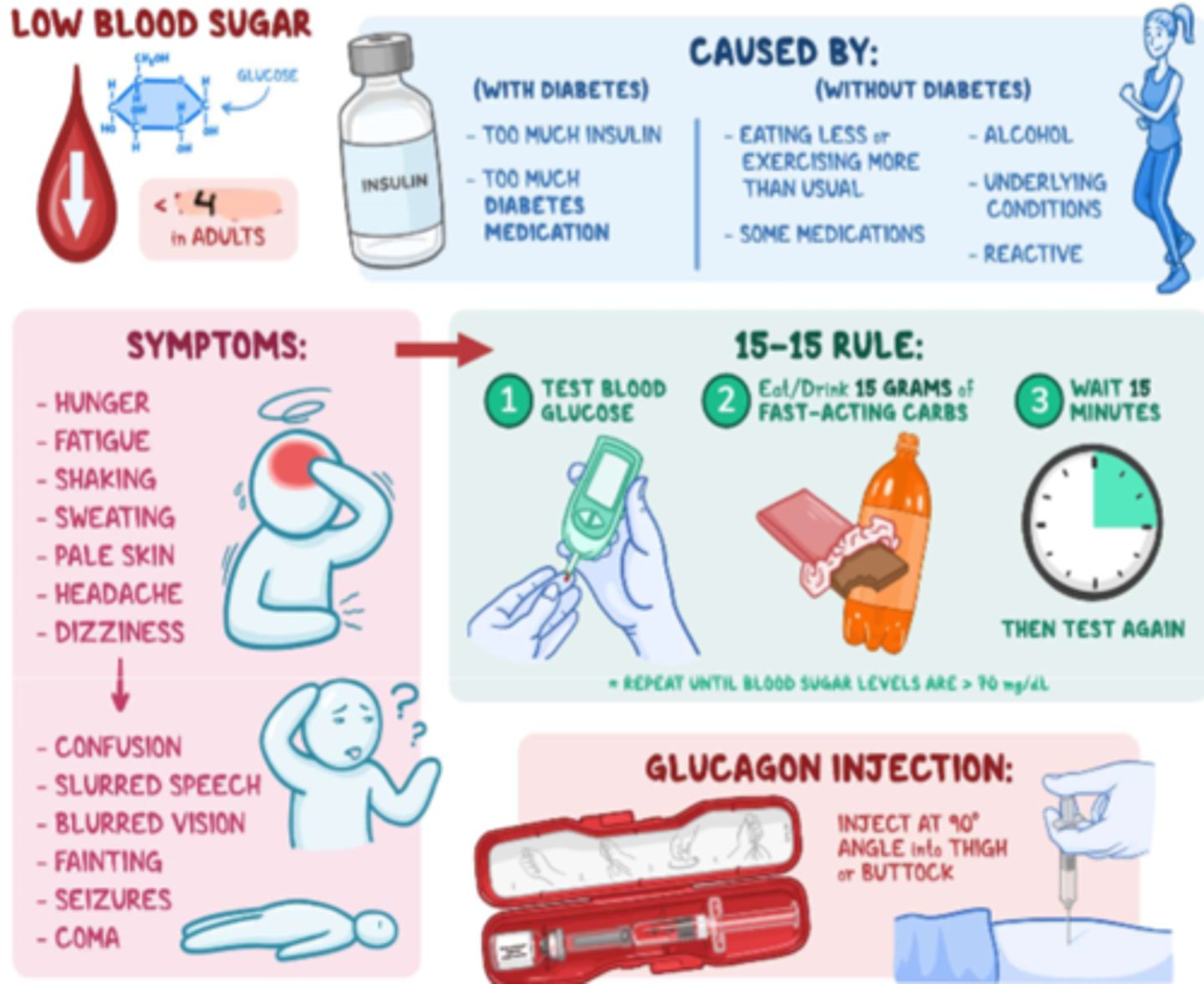
What is the protocol in a hypoglycemic pt?
- 15-15 rule
- tx as per conscious or unconscious tx, then reassess q 15 min by testing BG again and tx again PRN

What is DM III and how to tx
- aka pancreatic disease induced DM
- Tx: with Insulin (DM I protocol) until recovery (if not full recovery, maybe DM II)
What is a glucose challenge test?
- aka "one-hour" glucose tolerance test
- measures body's response to sugar
- routine test in 2nd trimester of pregnancy to test for GDM
What is DM IV
- DM during pregnancy => aka 'Gestational DM' (GDM)
- Pregnancy hormones cause Insulin resistance, including: Estrogen, Human Placental Lactogen, & Cortisol
- glucose challenge test to dx @ approx. 24 weeks (once placenta matures)
- routine screening: Glucose challenge & fasting Glucose BW
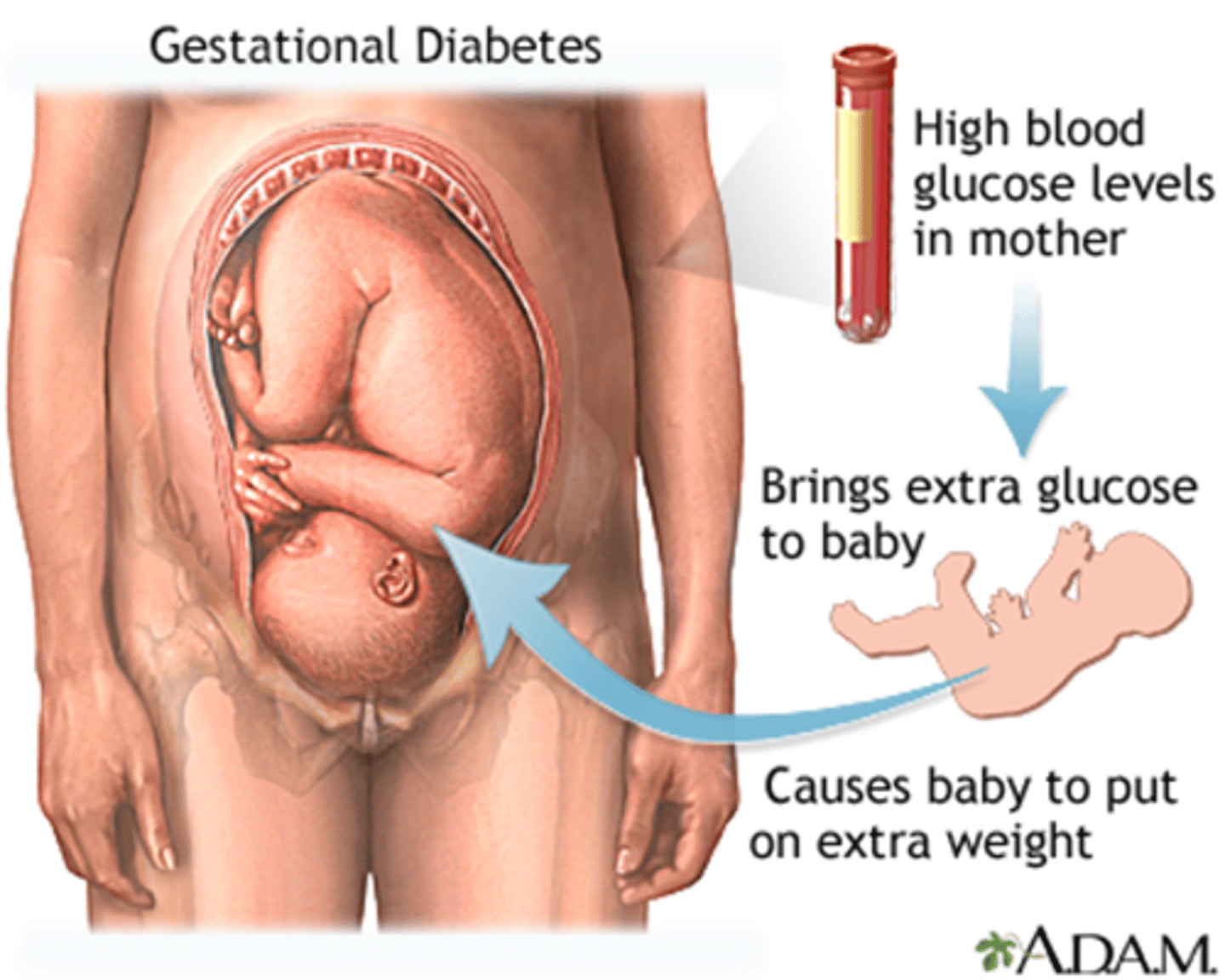
How to tx GDM/DM IV
Tx: diet &/or Insulin until delivery (L&D reversal; risk for DM II)

What risk is put on the baby in GDM
High BG levels in mother brings extra glucose to baby, causing baby to put on extra weight
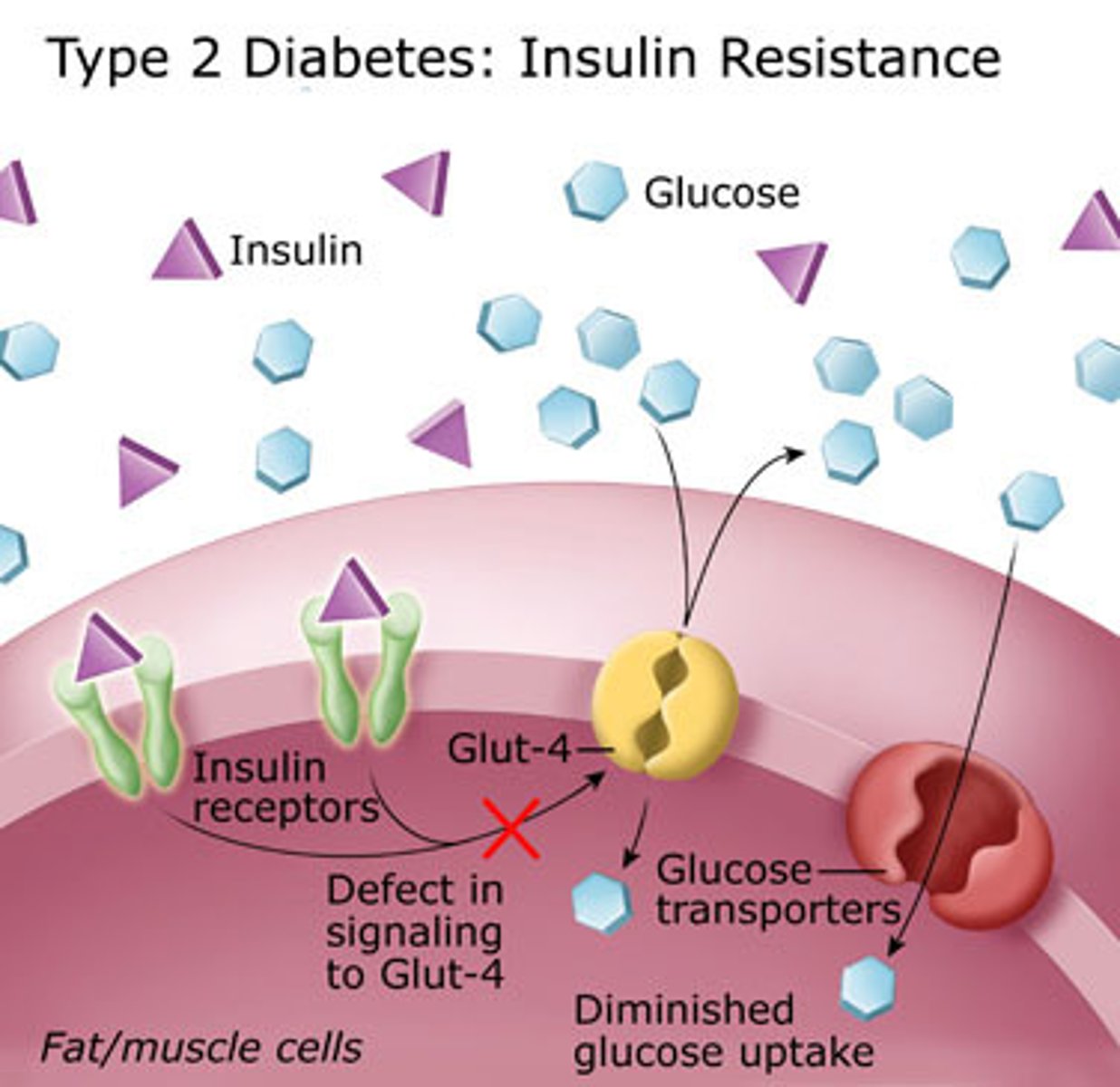
What is diabetes mellitus type II (DM II)
- relative insulin deficiency, resulting in an insufficient production of it (NOT autoimmune b-cell destruction (DM I)), muscle is now unable to use glucose due to resistance, resulting in high BG and low cellular BG
- strong lifestyle link (OBESITY is the leading cause => up to 90% of DM II pts are overweight)
- also strong genetic link
- could be caused by pancreatic disease or pregnancy
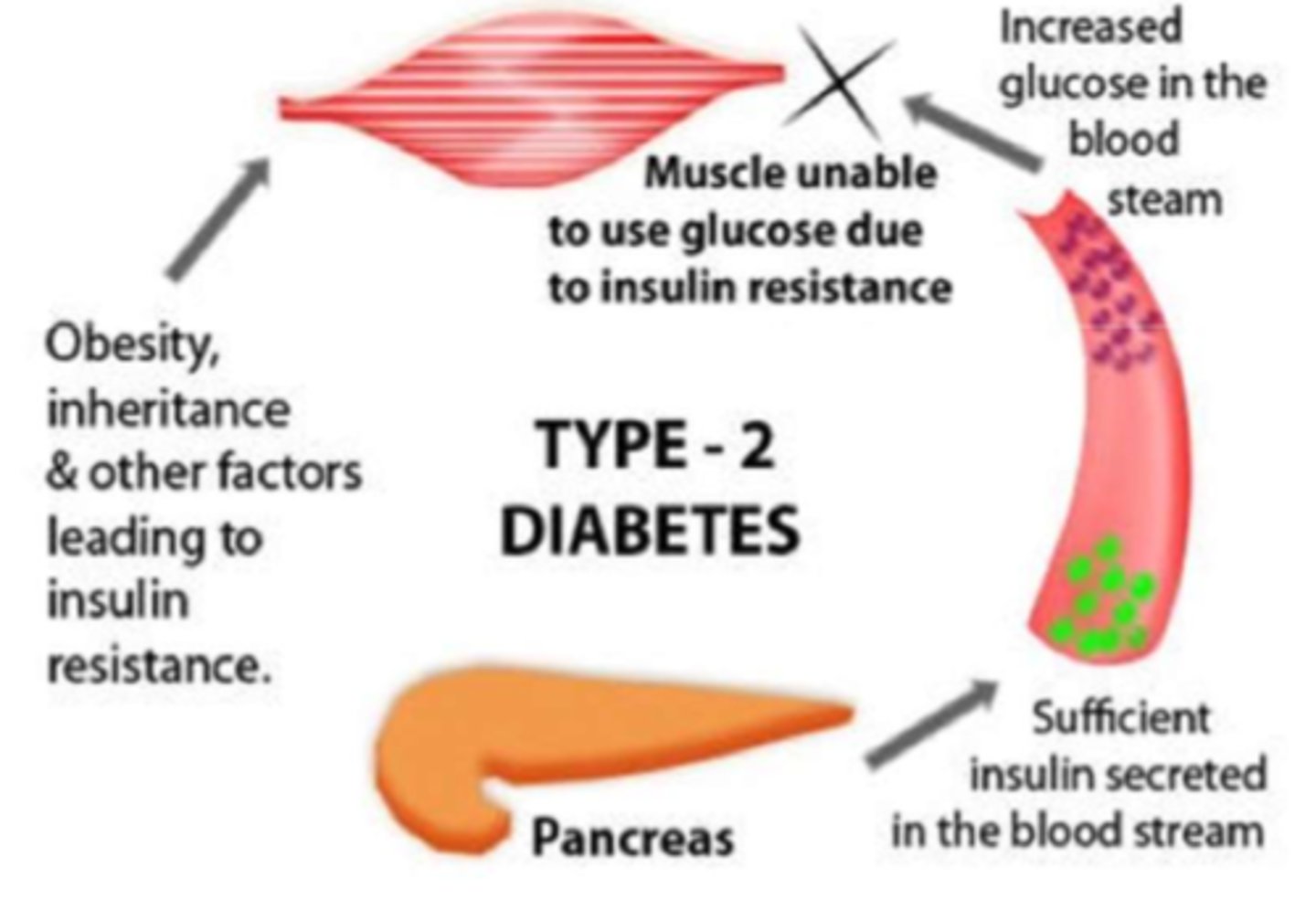
How can obesity cause insulin resistance (DM II)
- increased tissue resistance (caused by obesity), causes low adiponectin & high cytokine presence
- adiponectin is low b/c of high WAT accumulation, which also causes cytokine release and therefore a mild state of inflammation
- altogether causes insufficient production of insulin as tissues cannot produce insulin
Non-pharmacotherapeutic tx of DM II?
- weight loss
- exercise
- exceptions apply (eg. post-GDM, advanced age => 'old age diabetes')
Overall way we tx DM II
- 1st: Antidiabetic drugs
+ Insulin (if anti-diabetic drugs ineffective)
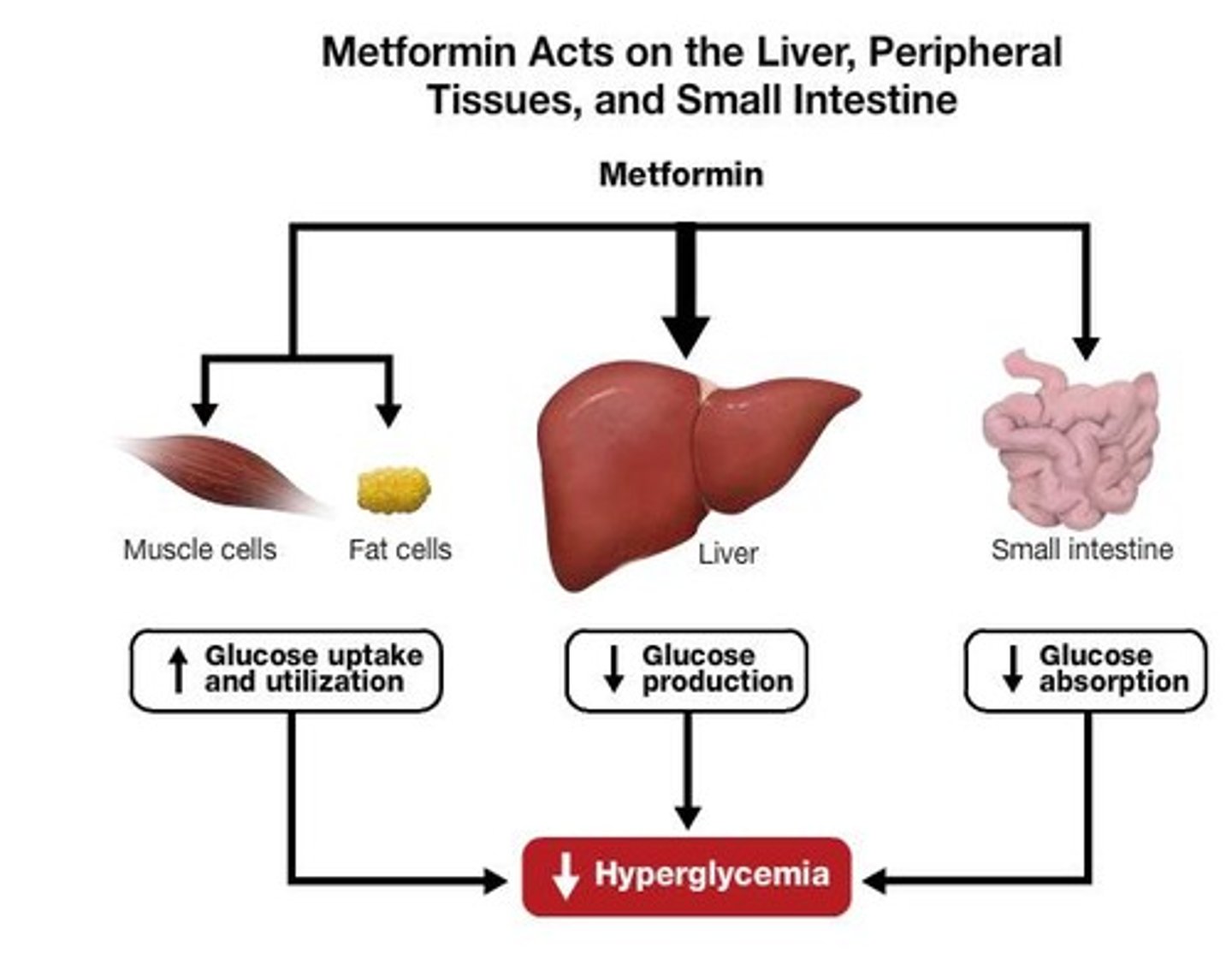
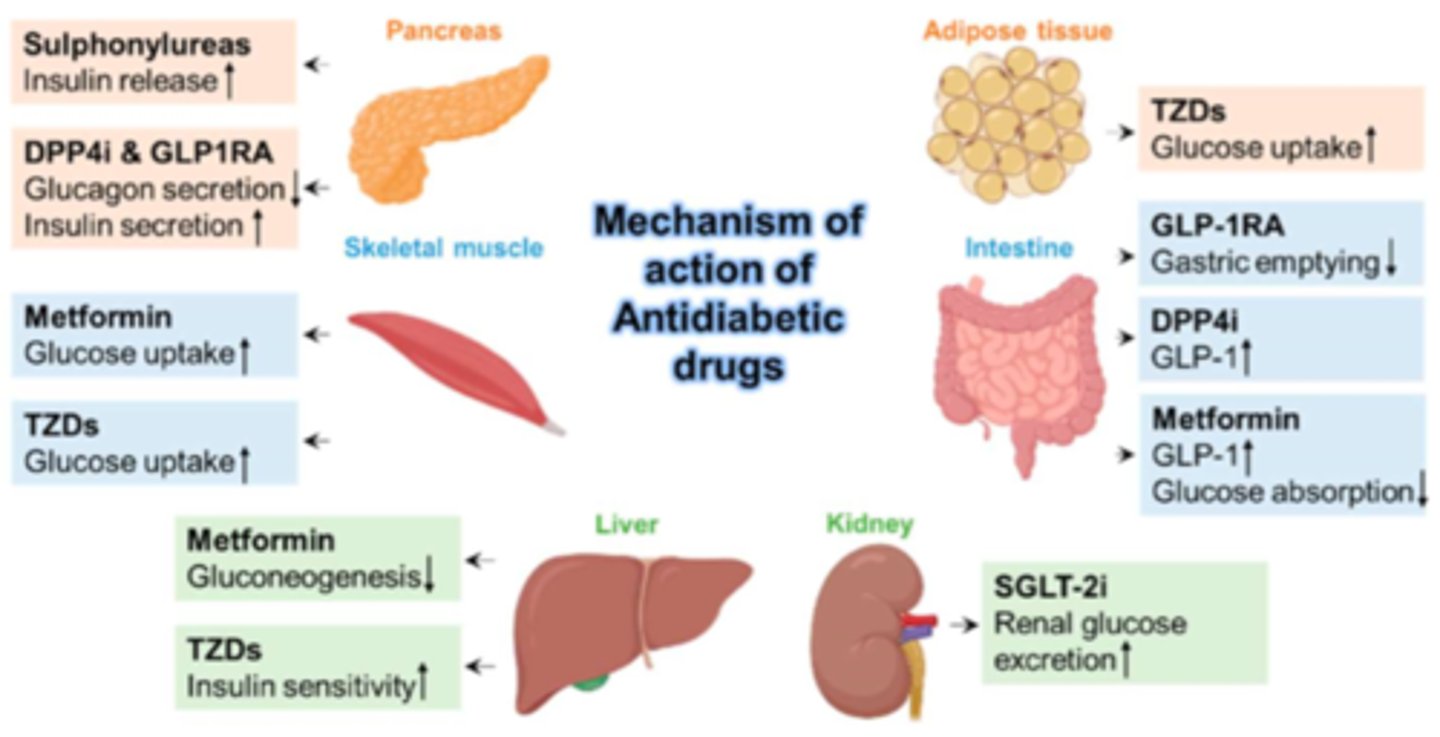
What is Metformin (Glucophage)?
- antidiabetic agent recommended by health canada for DM II
- drug class: Biguanides (decrease glucose production, lowering BG)
- always PO
- 1st line recommendation
- fx: decrease glucose absorption + increase glucose tissue uptake. decreased gluconeogenesis (liver, inhibit AMPK enzyme)
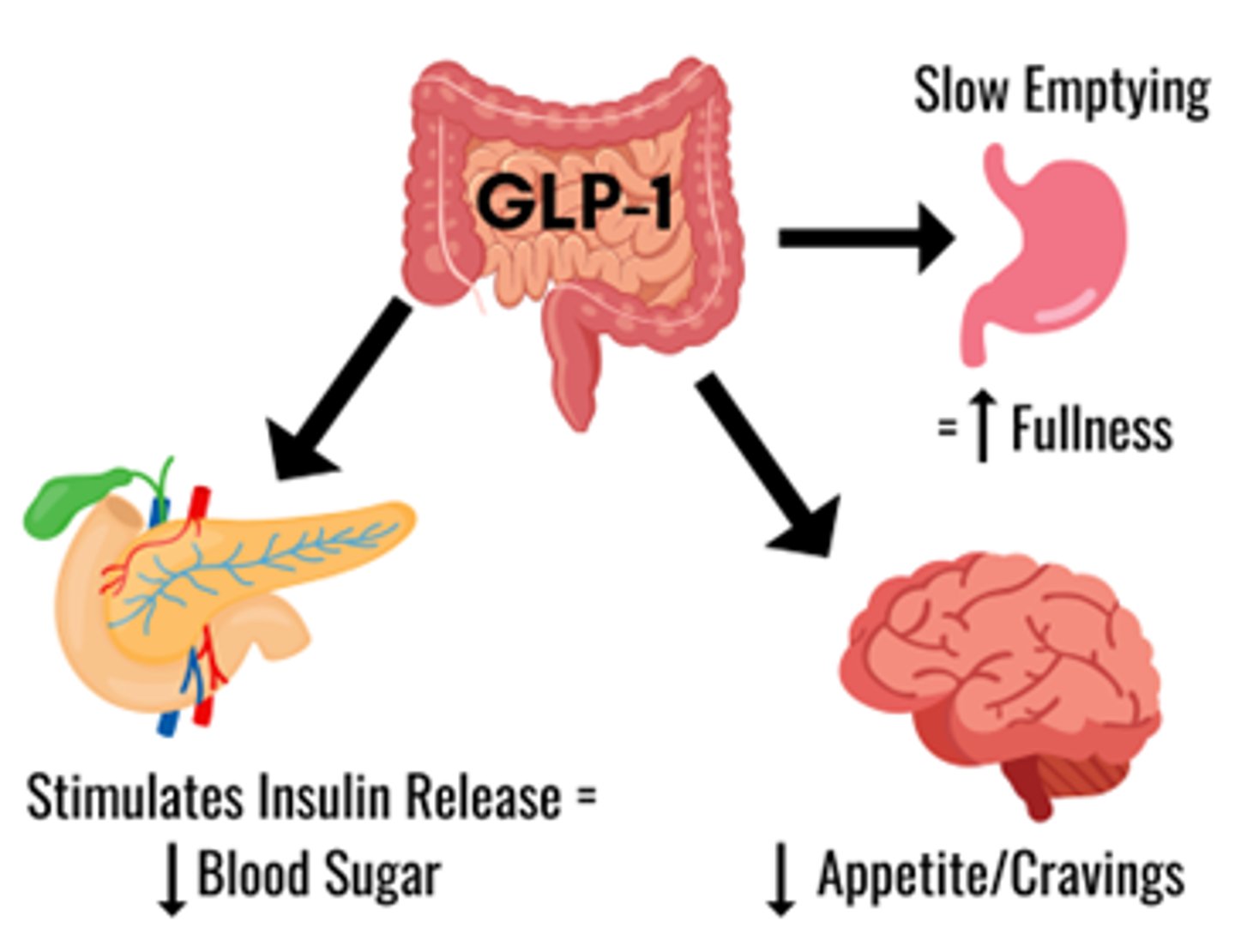
What is the drug class Incretin Enhancers (GLP-1 agonist)
- antidiabetic agents for DM II
- bind GLP-1 receptor (beta cell) & simulates satiety (fullness) causing decreased appetite & decreases GI glucose uptake
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity, SC)
- Semaglutide (Ozempic, SC; Rybelsus, PO, Wegovy, SC)
What are the GLP-1 agonists of choice for DM II? (hint: G is for glutide)
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity, SC)
- Semaglutide (Ozempic, SC; Rybelsus, PO, Wegovy, SC)
s/e of semaglutide (ozempic)
(most relate to metabolic changes)
- appetite loss, followed usually by a lack of taste
- N&V, constipation
- pancreatitis, cholecystitis (inflamed gallbladder), renal failure, thyroid tumors
- appearance "ozempic face" (lose all cushion, look hollowed out)

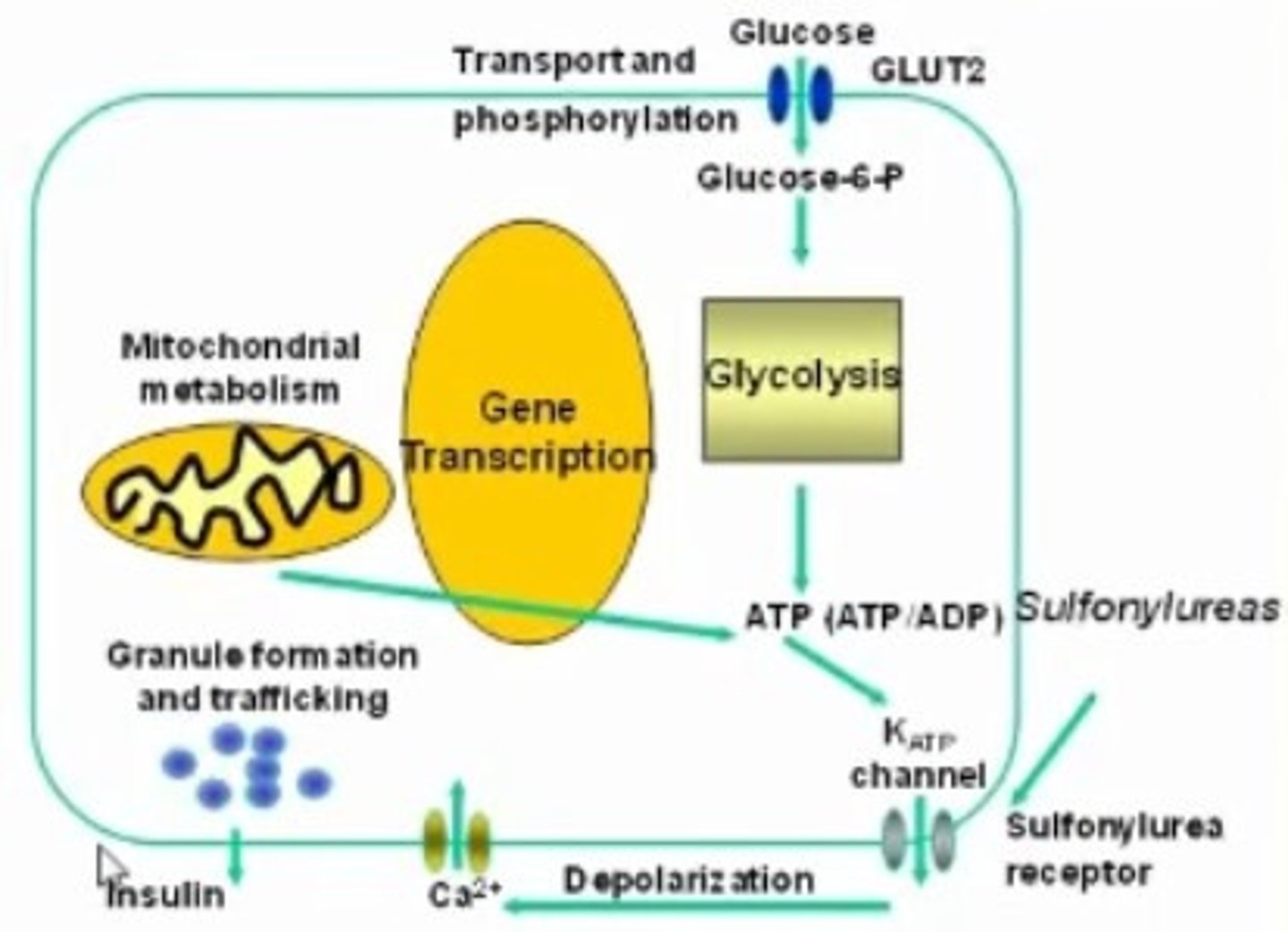
What is Glyburide (DiaBeta)? (hint: Dia = DM II, Beta = beta cell synthesis)
- antidiabetic agent for DM II
- drug class: Sulphonylureas
- fx: Increase beta cell synthesis to increase insulin
- risk of hypoglycemia! (fatigue big s/e)
What is Sanagliflozin (Invokana)? (hint: S = SGLT2 inhibitor)
- antidiabetic agent for DM II
- drug class: SGLT2 inhibitors
- fx: increase renal glucose excretion
What is HHS
- hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state
- DM II hyperglycaemic consequence (similar to DKA in DM I => overlapping S&S with DKA can exist)
- risk factor: infection (UTI most common) or poor BG control
- note: won't see high ketones b/c body still has some insulin
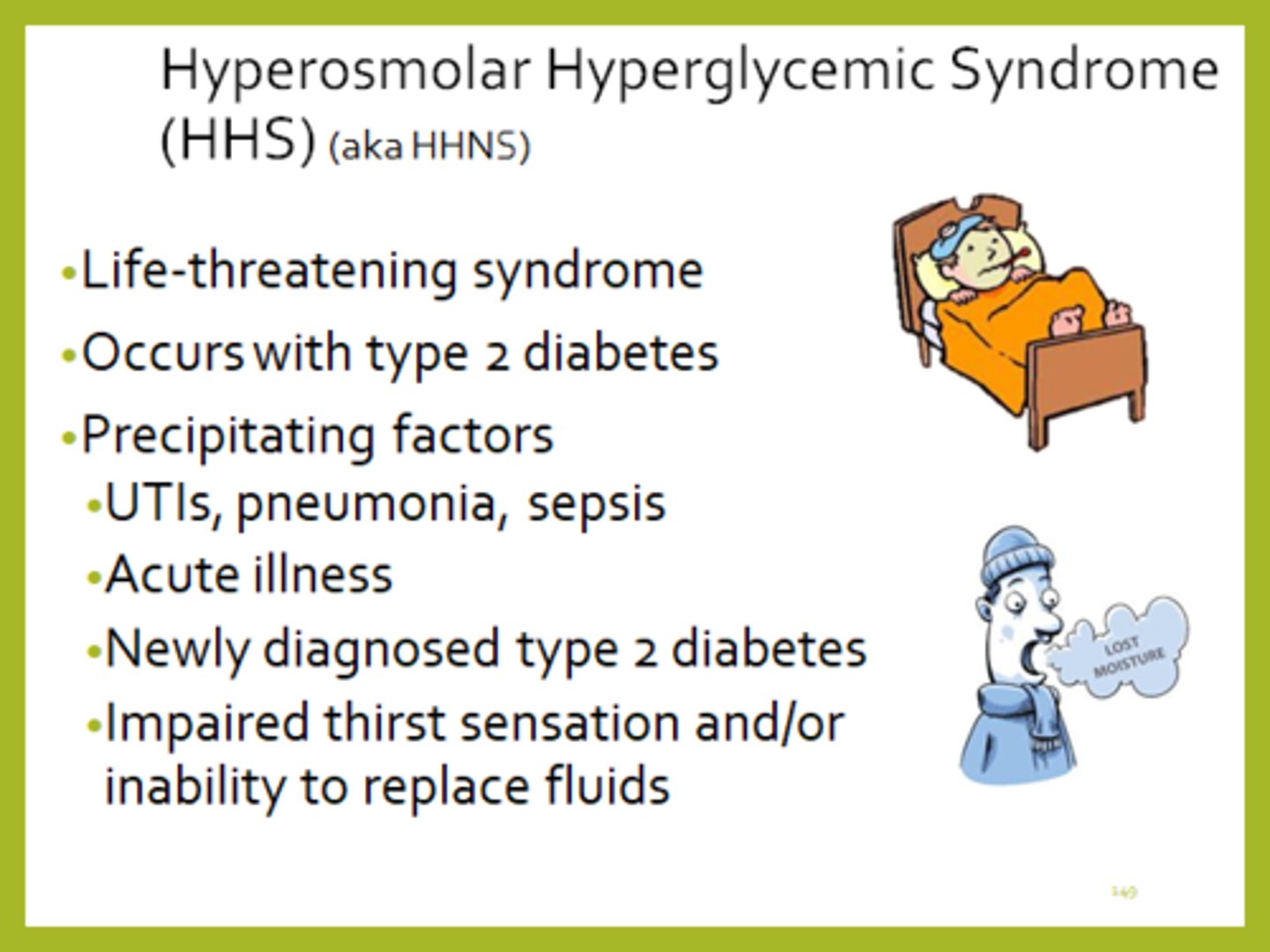
Hallmark s&s of HHS
- hallmark s&s: dehydration! affects LOC
- due to hyperosmolarity (eg. 320 mmol/L) & hyperglycaemia (eg. 32 mmol/L)
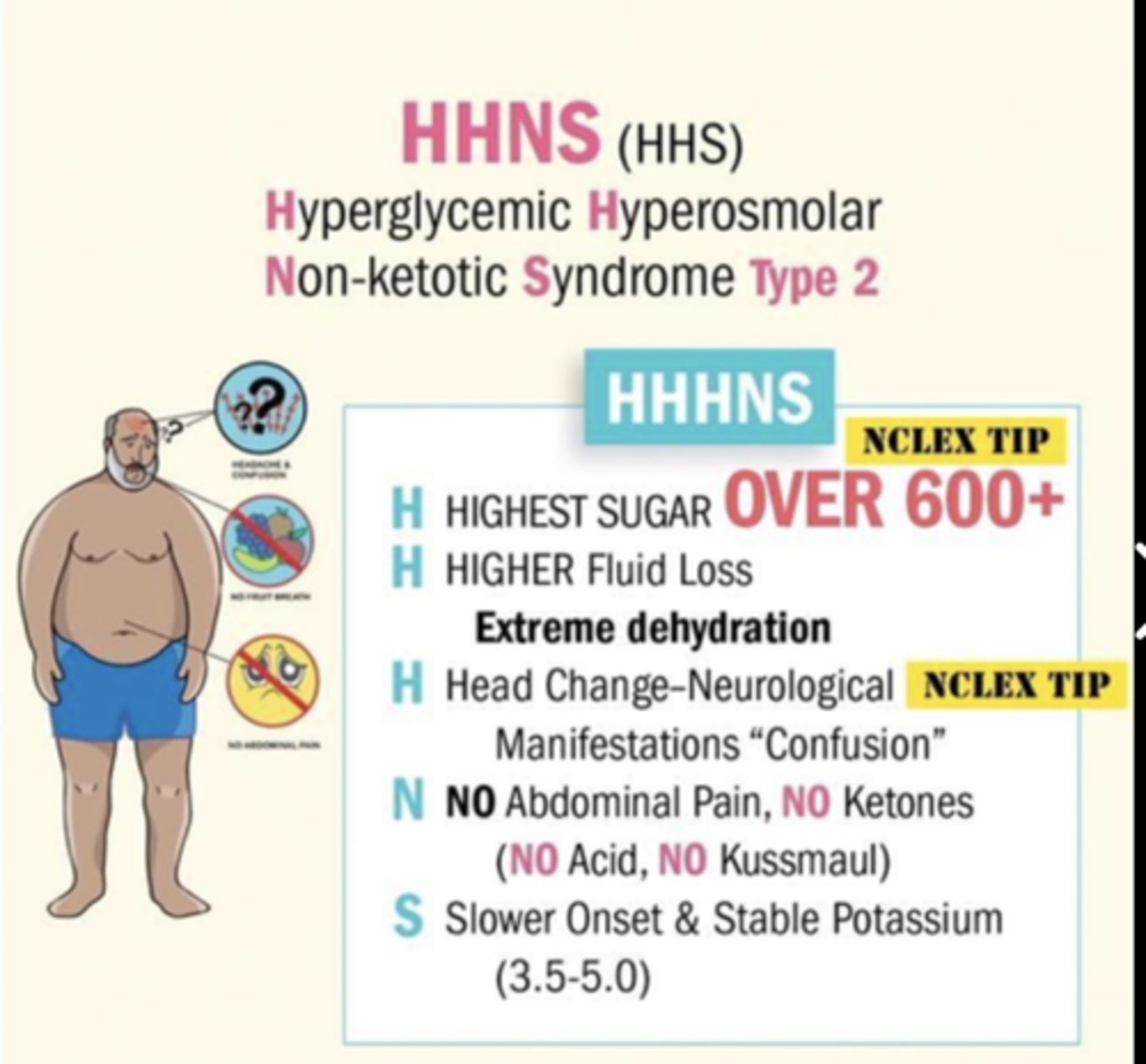
How to tx HHS
- rehydrate, recover K+, Insulin (same sequence as DKA)
- tx of underlying cause (eg. abx)
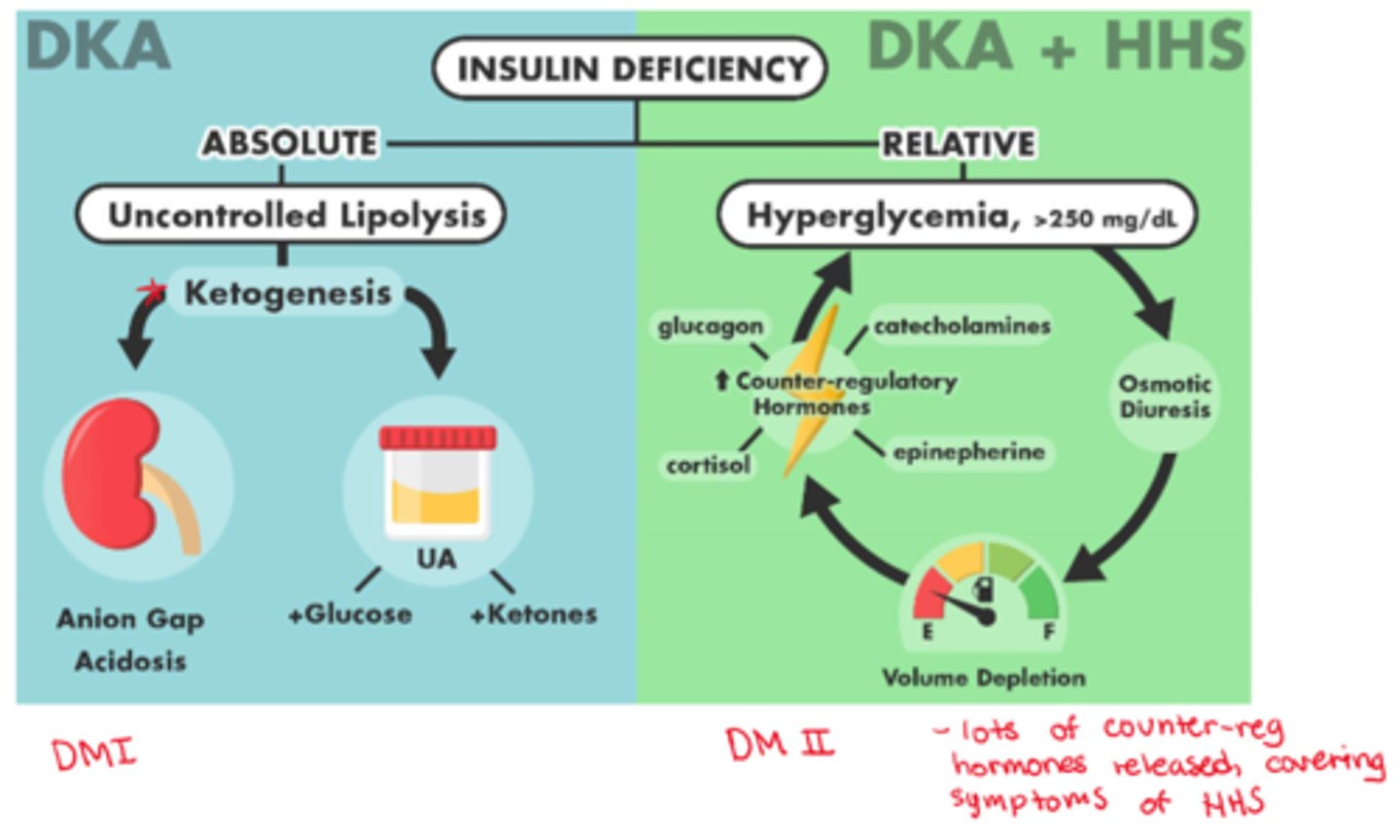
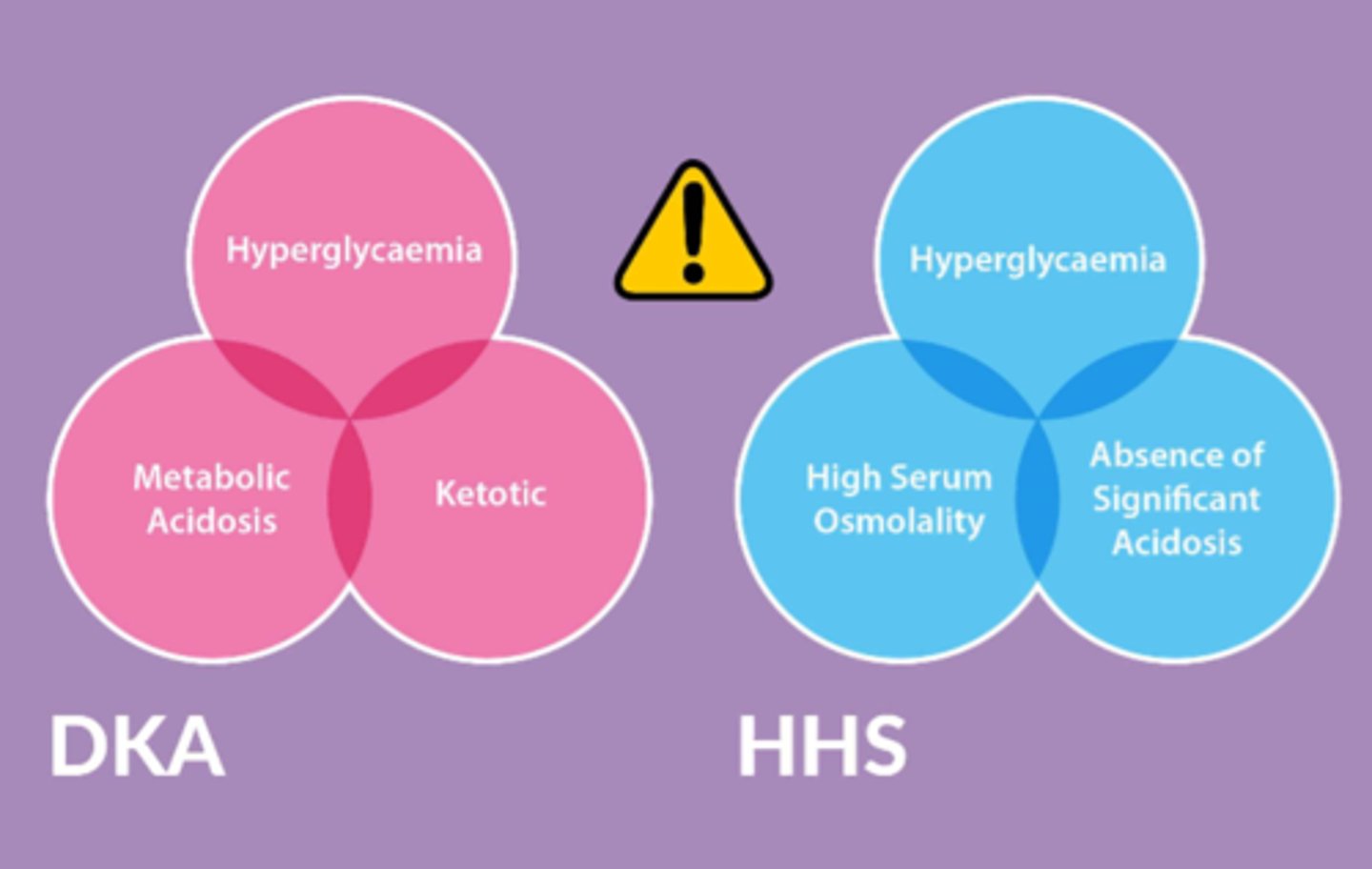
Major differences between DKA & HHS
- DKA: hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, ketotic
- HHS: hyperglycemia, high serum osmolality, absence of significant acidosis
What is a keto (ketogenic) diet
- weight-loss diet, low-carbohydrate (eg <40 g; 1 banana = 27 g)
- keto diet centers on fat for 90% of total daily calories
- deprivation of carbohydrates
- supervision by a physician

What happens at cellular level in a keto diet (no carb only fat)
- quick satiety (due to high fat intake), b/c body switches to lipolysis = fatty acids as a source of
energy => metabolism yields ketones = 'ketosis state'
- if unchecked, leads to ketoacidosis

What do we need to test in pts on a keto diet?
cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL, HDL, liver enzymes, GFR, CBC, BG, lactate

What are the risks of a keto diet?
- high lipid intake => CAD risk
- Liver stress - high demand
- Kidney stress - high byproduct excretion
- GI stress - low fibre; nutrient deficiency
- Low Glucose to CNS - headaches, mood swings, low energy, etc
