B5
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
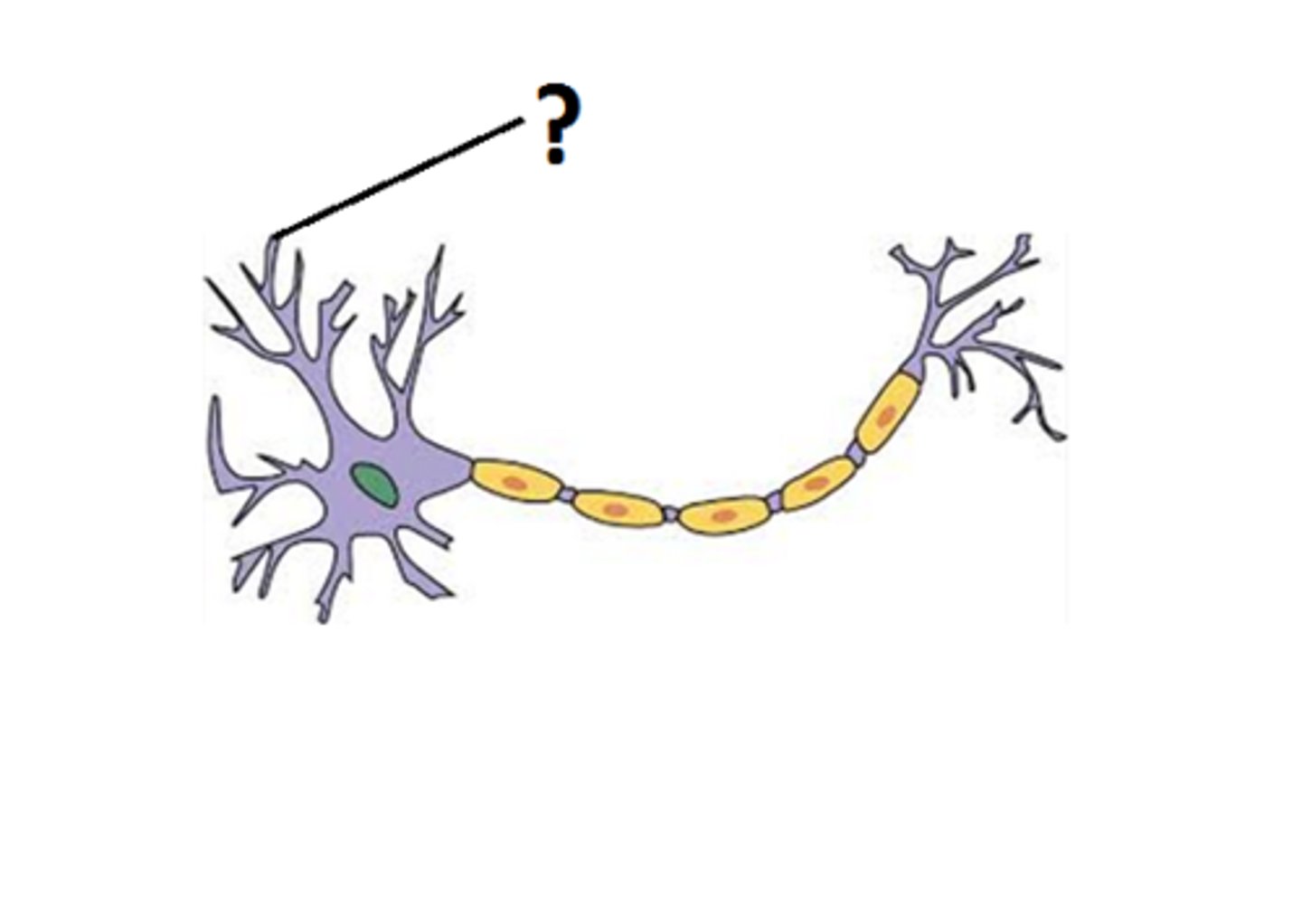
what part of the nerve cell is this ?
dendrites
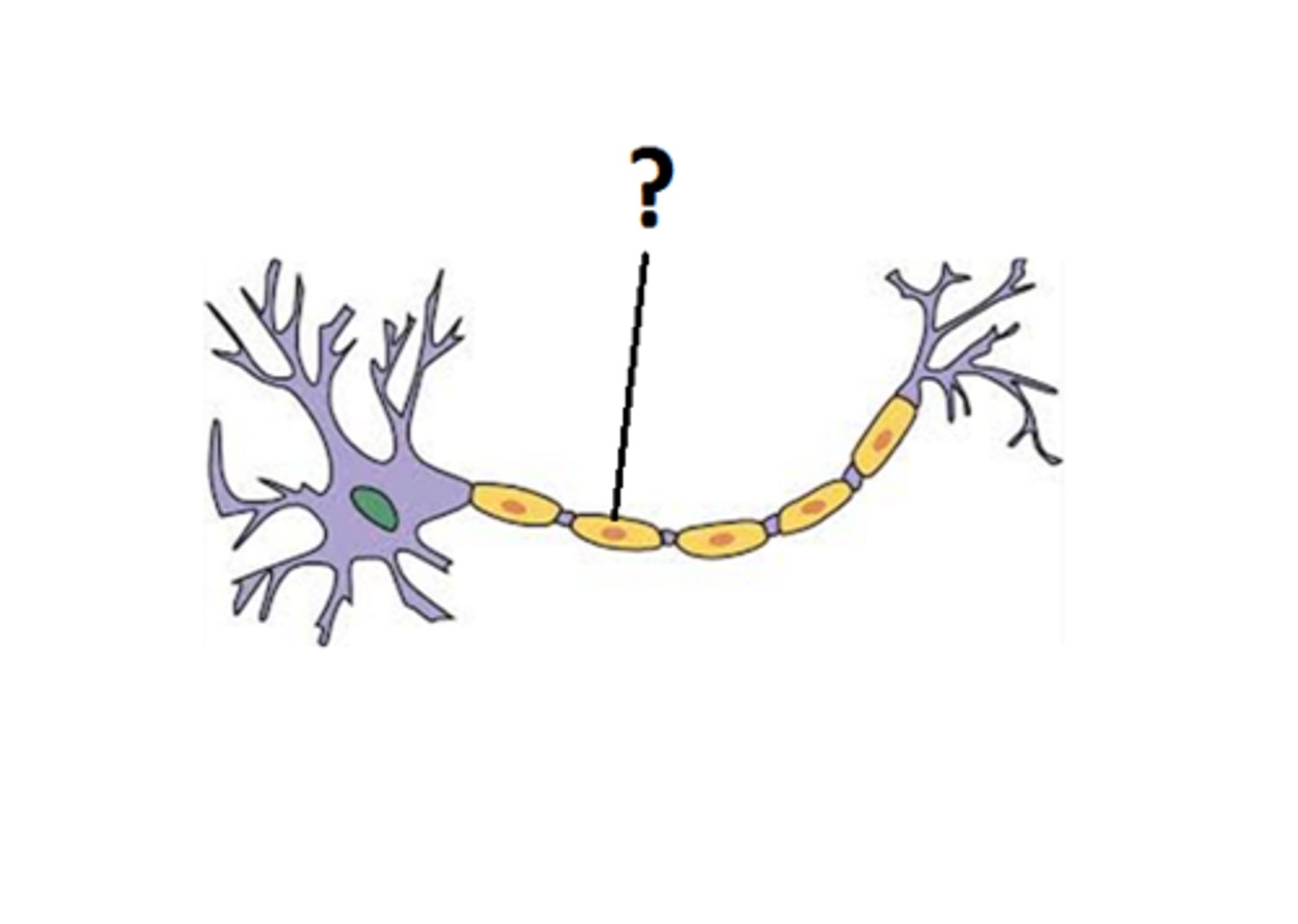
what part of the nerve cell is this ?
Axon
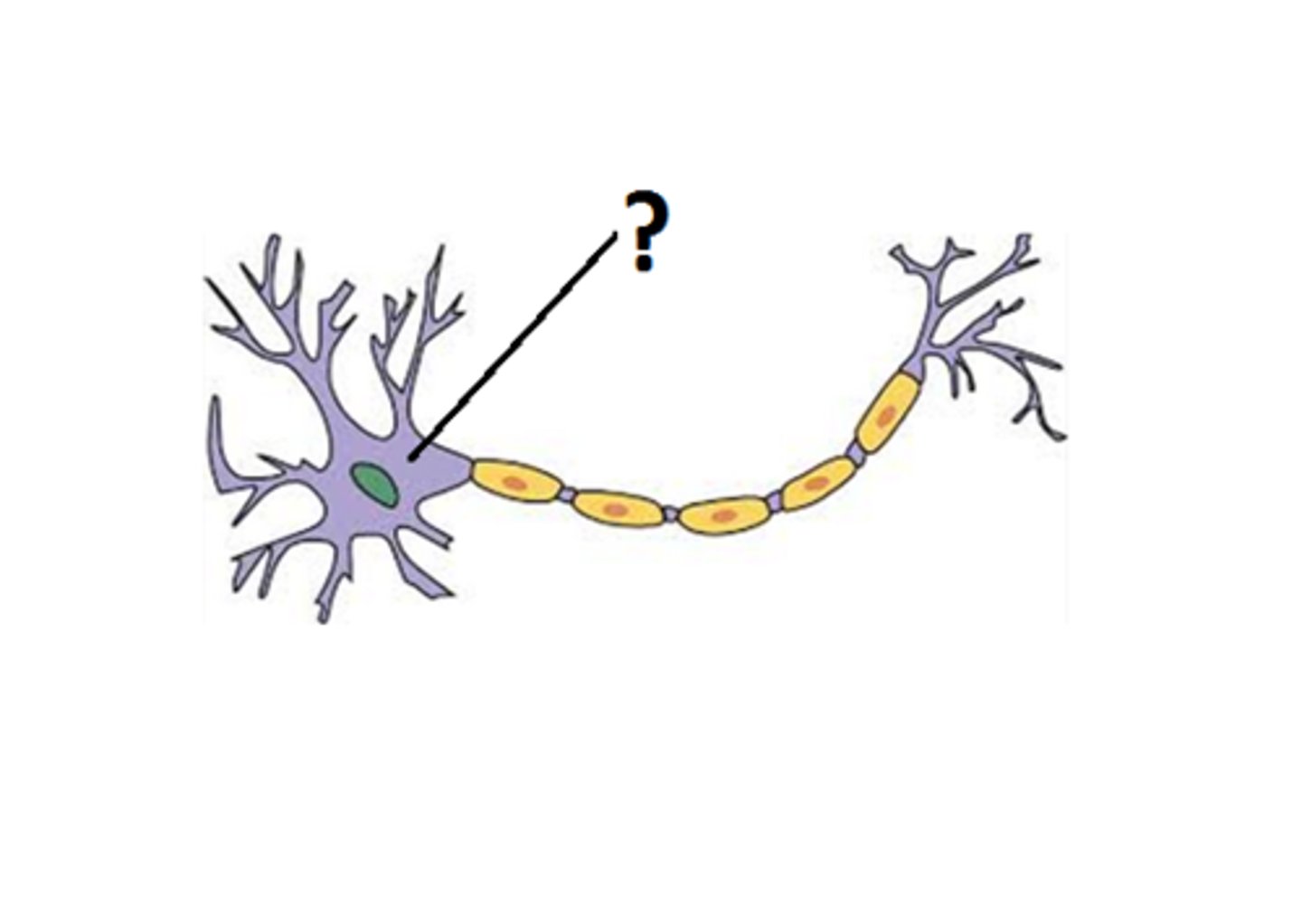
what part of the nerve cell is this ? (green part )
nucleus
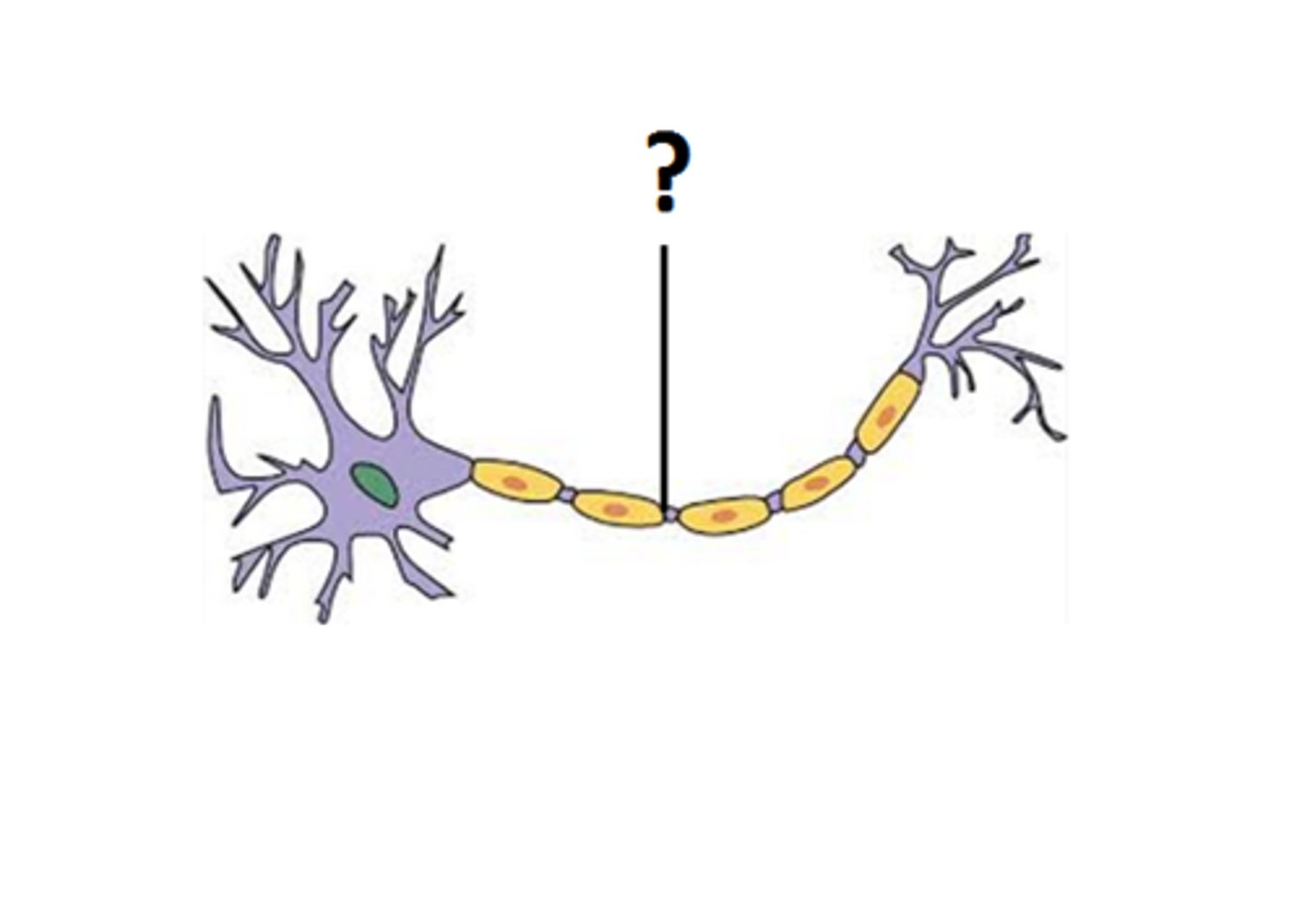
what part of the nerve cell is this ?
myelin sheat
what does the myelin sheath do ?
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
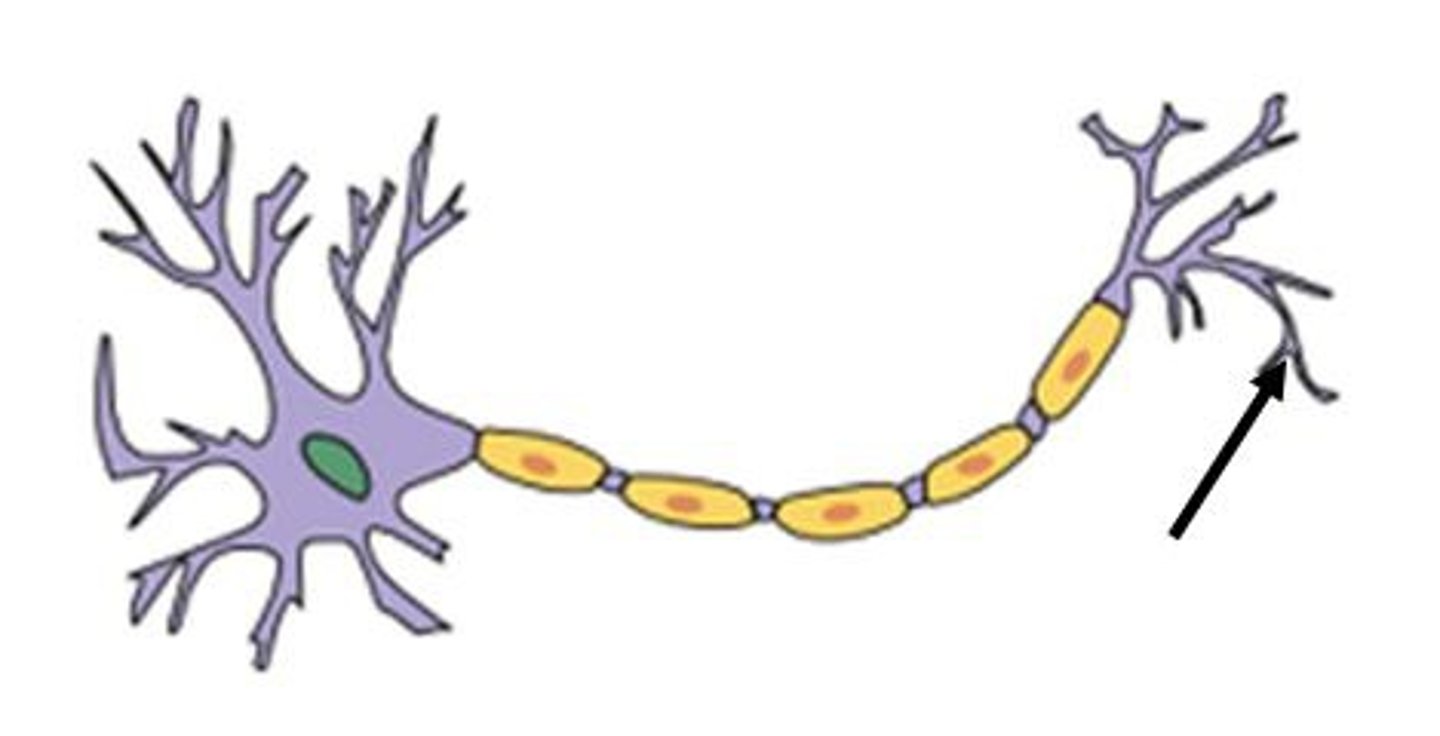
what part of the nerve cell is this ?
axon terminal
What is thermoregulation?
regulation of body temperature
What is homeostasis?
the regulation of internal conditions in the body
what organ controls homeostasis
the brain and the spinal cord
Why does homeostasis occur?
happens bc of he coordination of your nervous system , your endocrine system and your body organs all working together
________ contols homeostasis
hypothalamus
What does the pituitary gland do?
Secretes hormones to regulate other glands.
what is a gland
a group of cells which release smth e.g. tears , saliva , hormones
what is the nervous system made up of
lots of interconnected neurones
whats a hormone
a chemical messenger
the endocrine system consits of g________ which release __________ that are carried in the b__________
glands , hormones , blood
what should your core body temp be
37
the h_____________ detects if your core body temp is too high/low
hypothalamus
the hypothalamus contains ___________ receptors to detect the temp of the blood
temperature
what are the two parts of the nervous system
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
What does the nervous system do?
controls our muscles and glands by sending electrical impulses
stimuli
Changes in the environment
receptors
found on sensory organs they detect the stimuli
order of a voluntary pathway
1- stimulus
2- receptors detect stimulus
3-electrical impulse goes along sensory neurone
4-it reaches CNS decides on action
5-electrical impulse goes along motor neurone to effector (muscles/glands)
6-response happens
what is a reflex
a fast , involuntary response that protects from harm which doesn't involve the conscious parts of the brain .
reflex arc pathway
1-stimulus
2-receptors detect stimuli
3-electrical impulse travels up sensory neurones
4-relay neurone ->spinal chord which decides on action
5-new electrical impulse down motor neurone
6-to effector
Note - between neurones info passes between a synapse as a chemical
cerebral cortex
highly folded outer layer connected with consciousness ,intelligence ,memory ,language
Cerebellum
coordination of muscle activity
medulla
controls unconscious activities like breathing and your heartbeat
why is treating brain disorders so difficult
the brain is so complex and different regions cant be studied in isolation
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
A technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain
-cancer cells , clots +abnormal blood flow
MRI advantages
non invisible
-no ionising radiation
-safer than CT scans
-vv safe detailed images
- non invasive
MRI disadvantages
- expensive
- not portable
- not suitable for everyone
EEG scans
Measures electrical activity within the brain via electrodes can detect epilepsy fits +memory problems
EEG scans advantages
no electricity
-vv safe
- can show abnormal brain changes
-maps brain activity
EEG scans disadvantages
cant detect cancer
CT scans
Multiple X-Rays of successive slices of the brain. Looks at brain structure.
CT scans advantages
- detailed x rays
- diagnoses conditions
- monitors conditions
- guides further tests or treatment
-non invasive
-quick
CT scans disadvantages
-not portable
-risk of ionising radiation
brain surgery benifits
maybe needed in case of a tumor in brain to save / prolong life
risks Brain surgery
may cause brain damage and infection -possible stroke
brain implants benefits
can help the brain function
brain implants risks
may cause brain damage
radiotherapy chemo therapy benefits
destruction of tumours (can save lives )
radio/chemotherapy risks
can damage normal cells
monoclonal antibodies benefits
offer hope in treatment of cancer /tumor
monoclonal antibodies risks
skin changes e.g. red and sore skin or itchy rash
stem cell therapies benefits
offer help in repairing damages to nervous system tissue
stem cell therapies risks
stem cells may be rejected . ethical / moral issues
factors which increase reaction time
distractions , alcohol , fatigue
factors which decrease reaction time
practice , caffeine , no distractions
ways ruler practical could be improved
could use a computer to calculate reaction times
- perform investigation on several other people
- use more different time intervals
how do we see ?
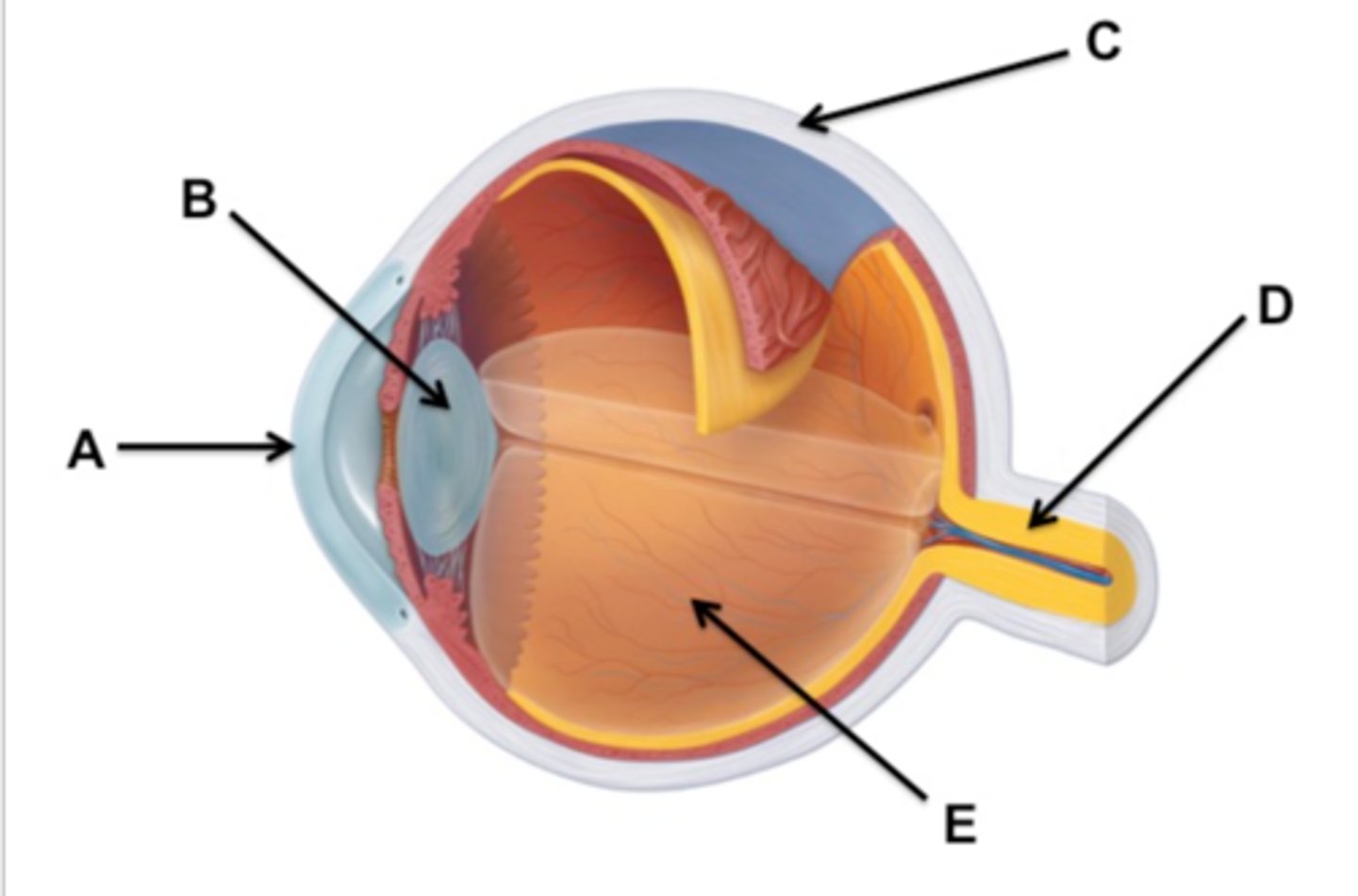
light enters cornea which reflects light inwards . light goes through the pupil (controlled by the iris ) . light is refracted more by the lens which is a convex shape onto the retina . the receptors on the retina convert light into electrical impulses , which are sent to the brain via the optic nerve .
in a dark room what happens to your pupils ?
they get bigger
- radial muscles contract
-circular muscles relax
- pupil dilates
- more light enters
in a bright room what happens to your pupils
- get smaller
- radial muscles relax
-circular muscles contract
- pupil constricts
-less light enters
the light that reaches your eyes from distant objects is travelling in ________ rays
parallel
the light that reaches your eyes from a nearer object is d_______ strongly
diverging
what is accommodation
the process of changing the shape of the lens with the help of the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments
soft lense (contact lenses )
-made from silicone gel
-permeable to allow oxygen to enter the cornea
-more comfortable
hard lenses (contact lenses )
-rigid
-durable
-less comfortable
-longer lasting
what does laser eye surgery do
changes the shape of the cornea
side effects of laser eye surgery
blurred vision -infection
What does negative feedback do?
maintains homeostasis and counteracts change to keep your internal environment stable
What is the CNS composed of?
brain and spinal cord
What is the CNS connected to the body by in mammals ?
Sensory and motor neurones
What are sensory neurons?
The neurons that carry information as electrical impulses from the receptors to the CNS
What are motor neurons?
The neurons that carry electrical impulses from the CNS to effectors
What are effectors?
All your muscles and glands, which respond to nervous impulses
What is a synapse?
Gap between two neurons
Two examples of receptors
Taste receptors on the tongue and sound receptors in the ears
What do effectors do?
muscles contract and glands secrete hormones
What happens at a synapse?
When a nerve impulse reaches the synapse at the end of a neuron, it cannot pass directly to the next one. Instead, it triggers the neuron to release a chemical neurotransmitter. The neurotransmitter drifts across the gap between the two neurons and then sets off a new electrical signal in the next neurone
what different methods do scientists use to study the brain ?
studying patients with brain damage , electrically stimulating the brain , MRI scans
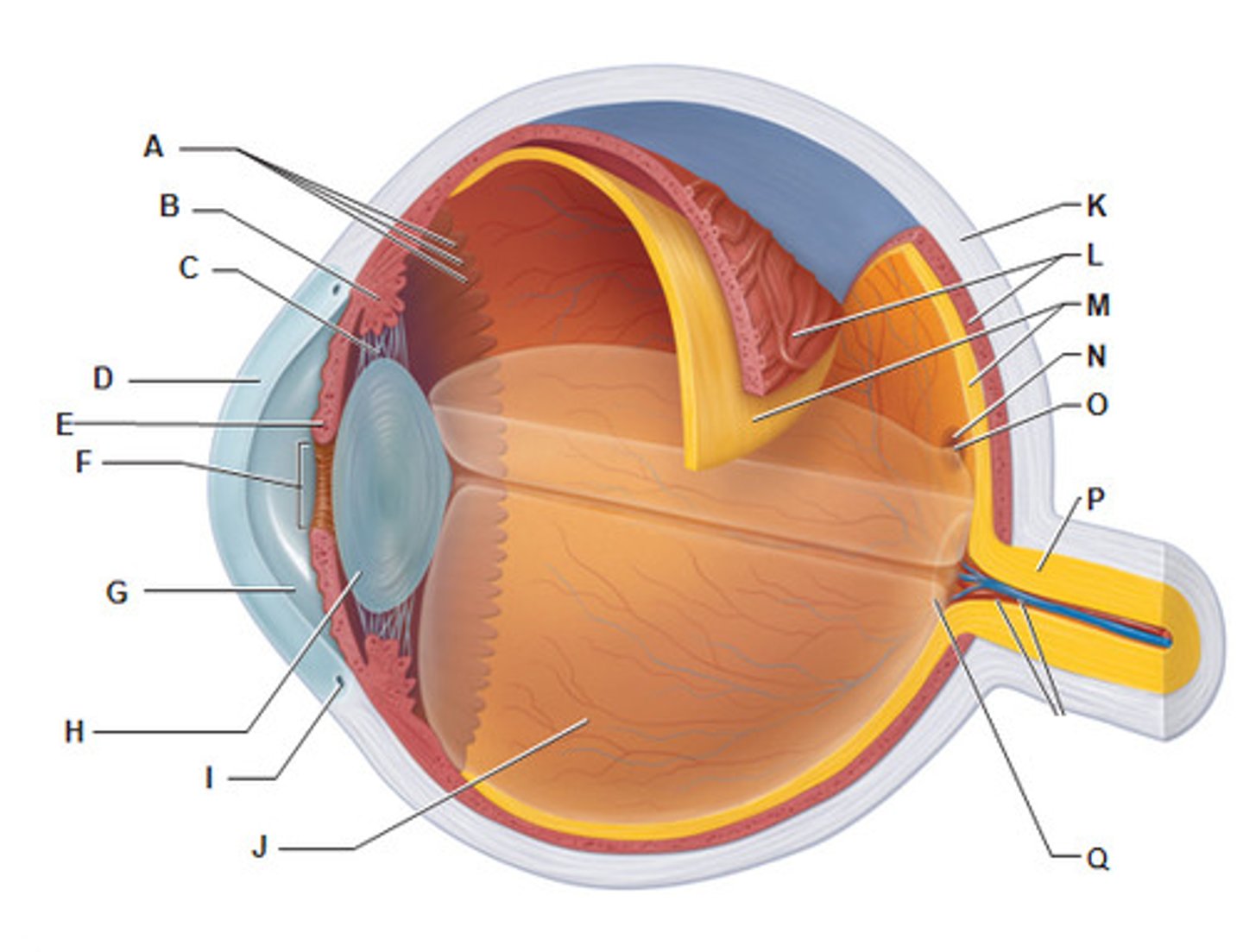
the tough, supporting wall of the eye
the sclera (K)
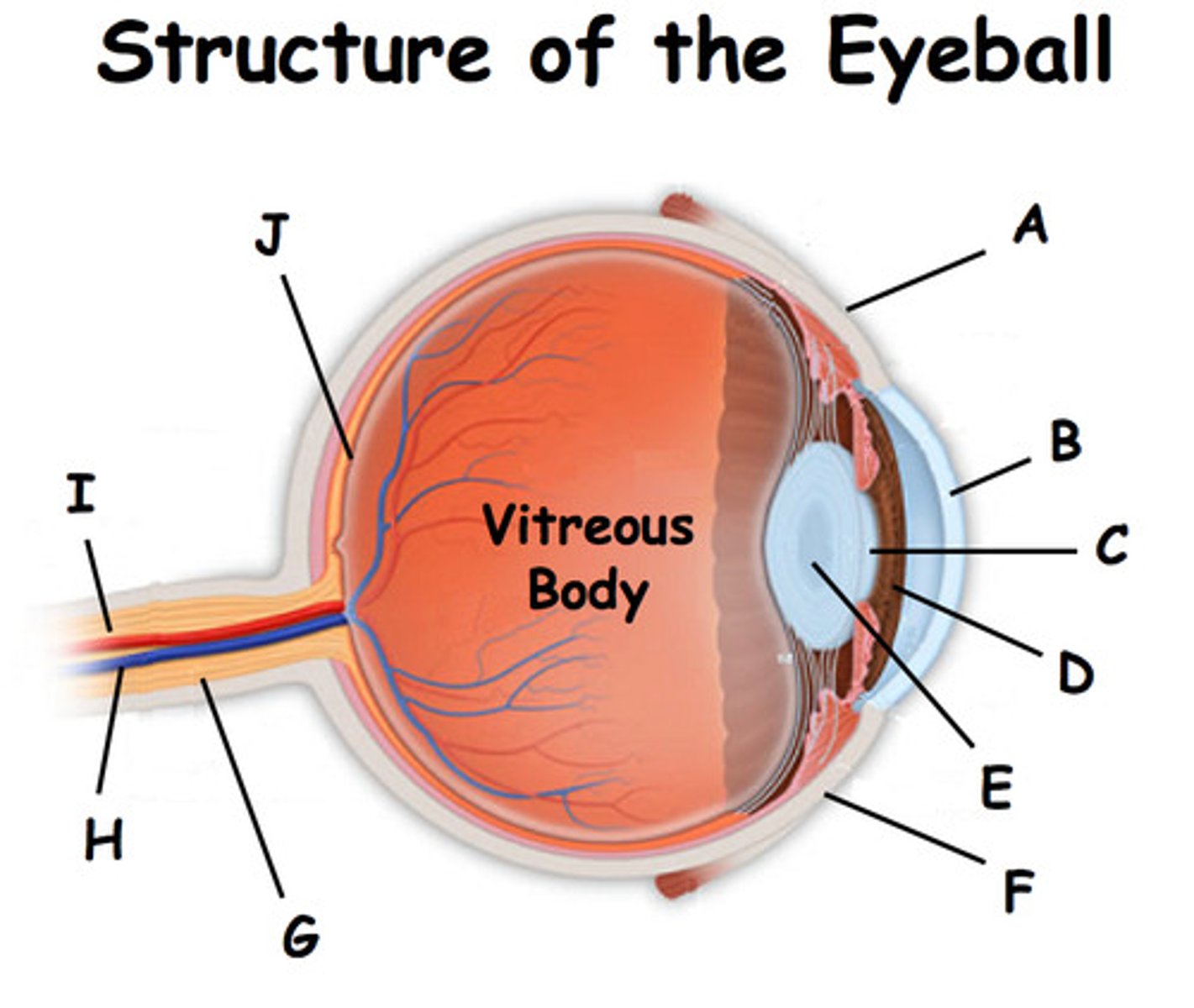
what is The cornea (B)
Transparent outer layer of the eye
what does the cornea do ?
Refracts light into the eye
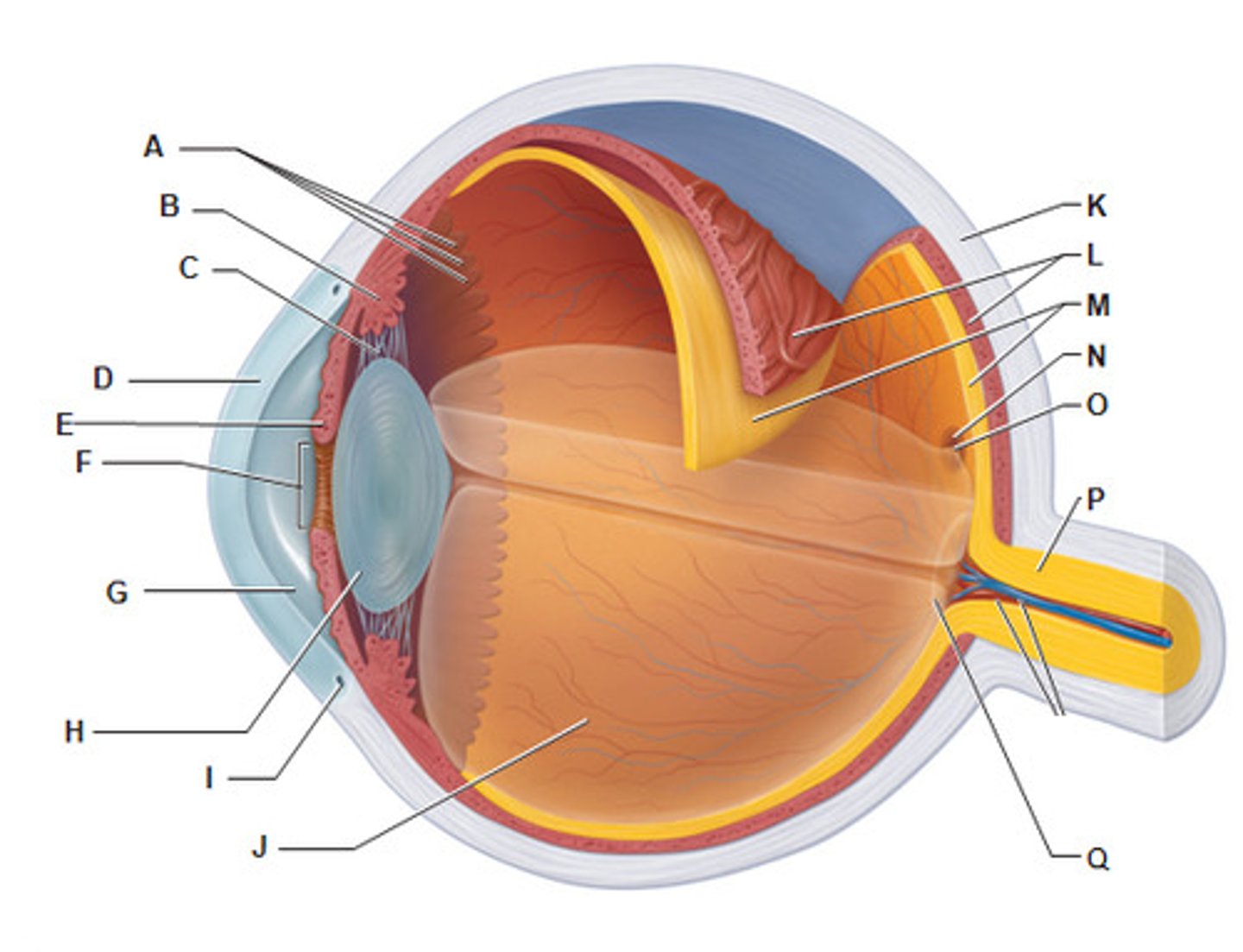
what is the iris (E)
a ring of muscle tissue that forms the coloured portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening
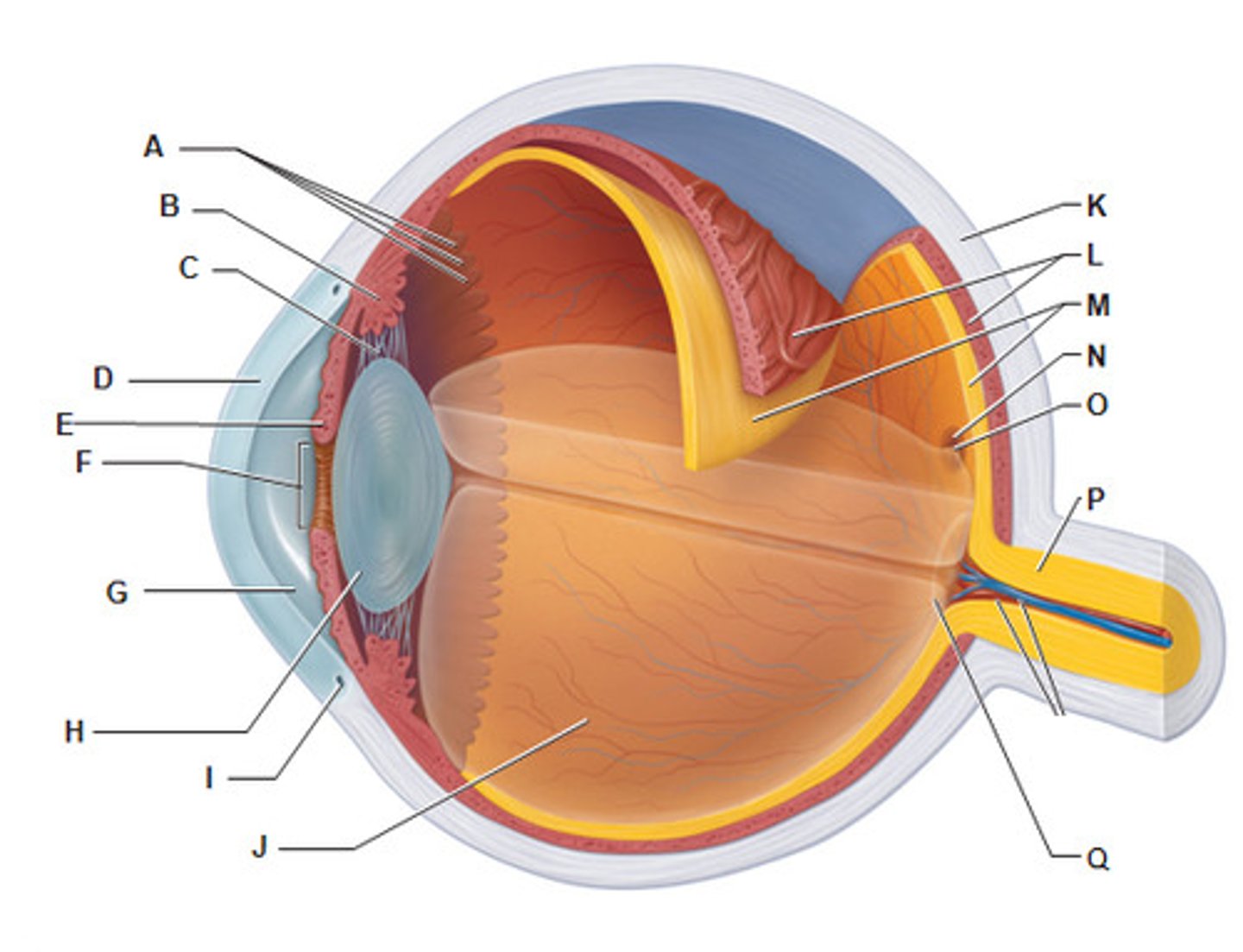
what is the lens (H)
the transparent structure behind the pupil that focuses light onto the retin
the shape of the lens is controlled by __________
ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments
the optic nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the receptors on the retina to the brain
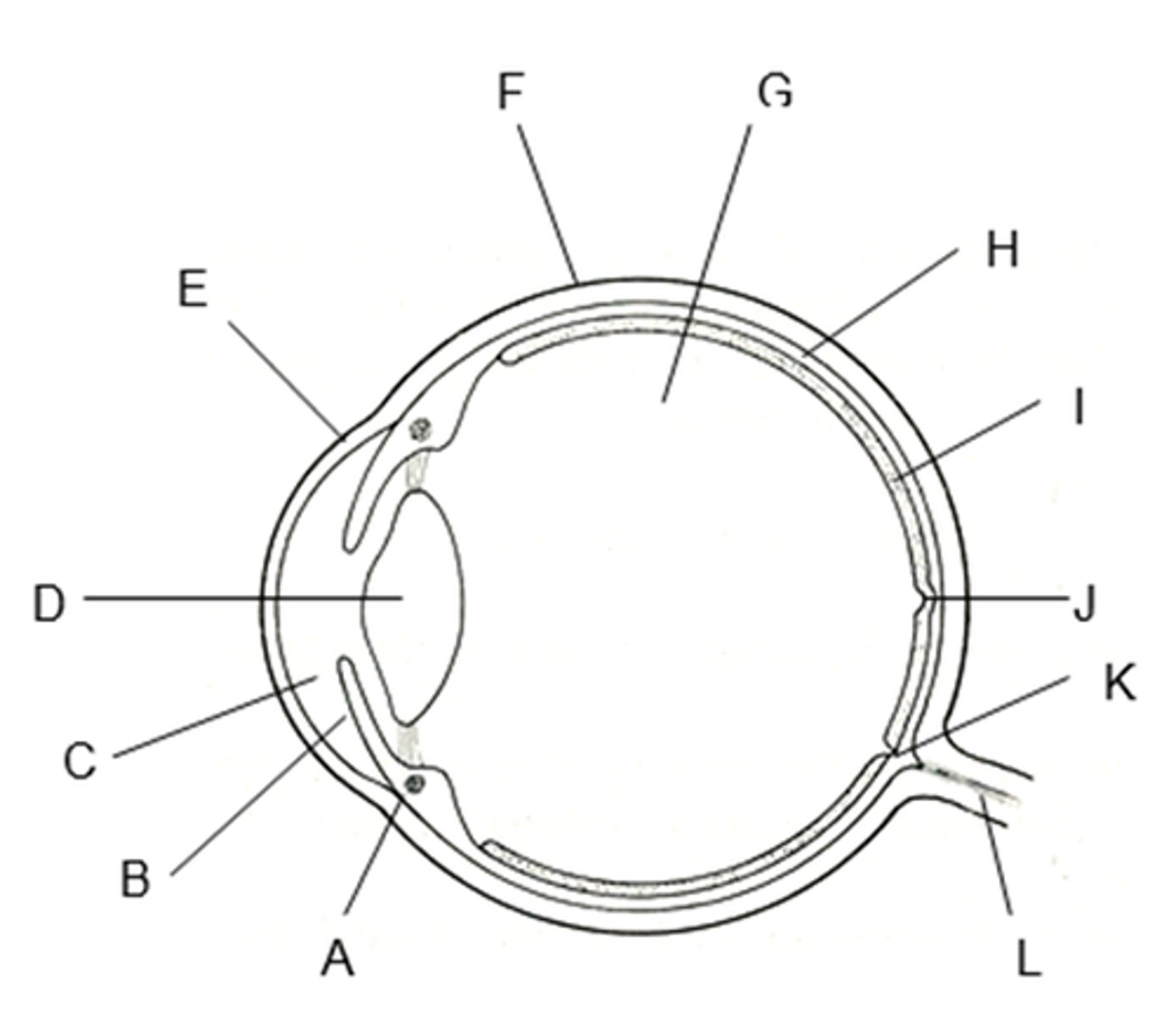
which letter is the sclera
F
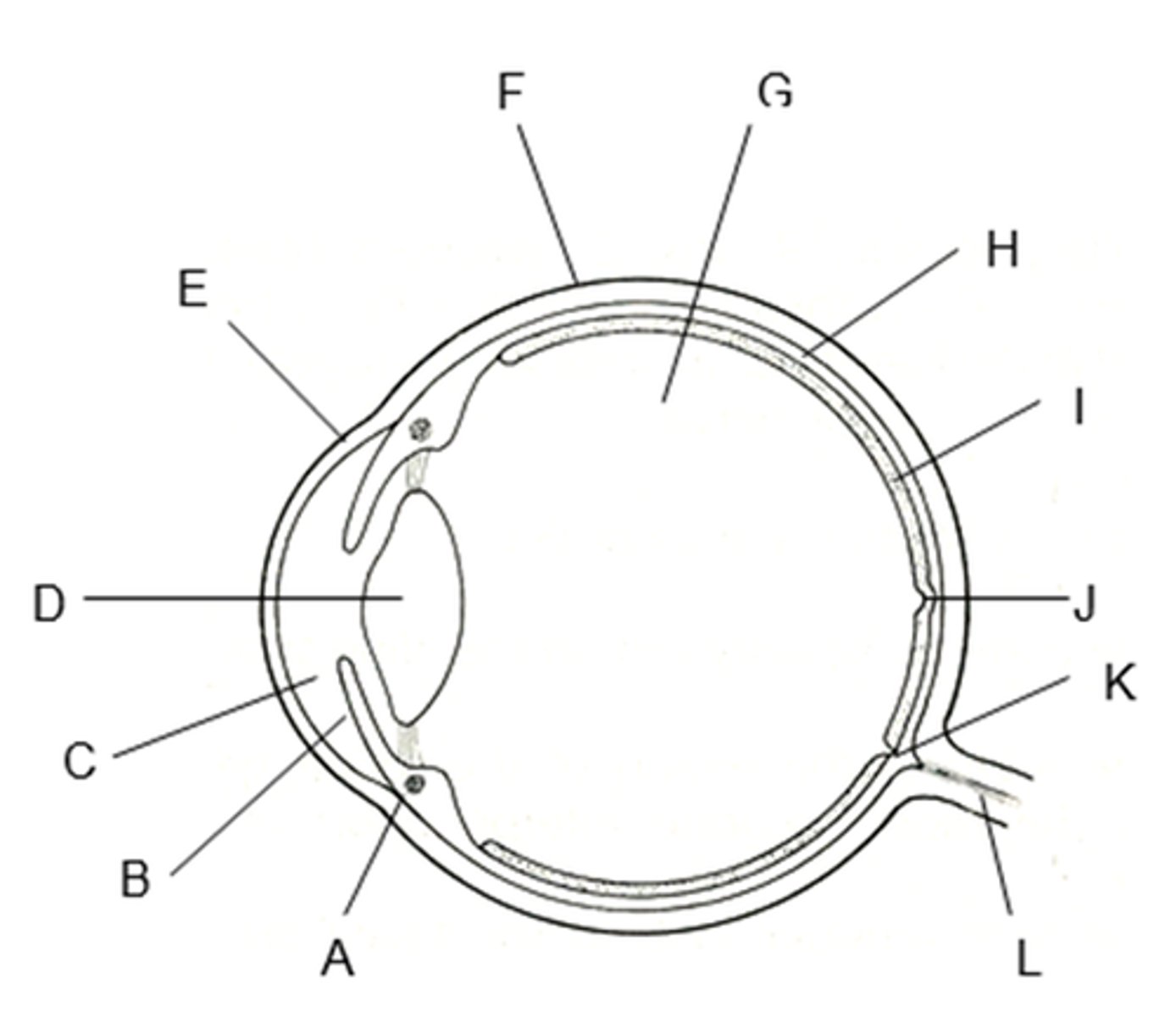
which letter is the cornea ?
E
which letter is the lens ?
B
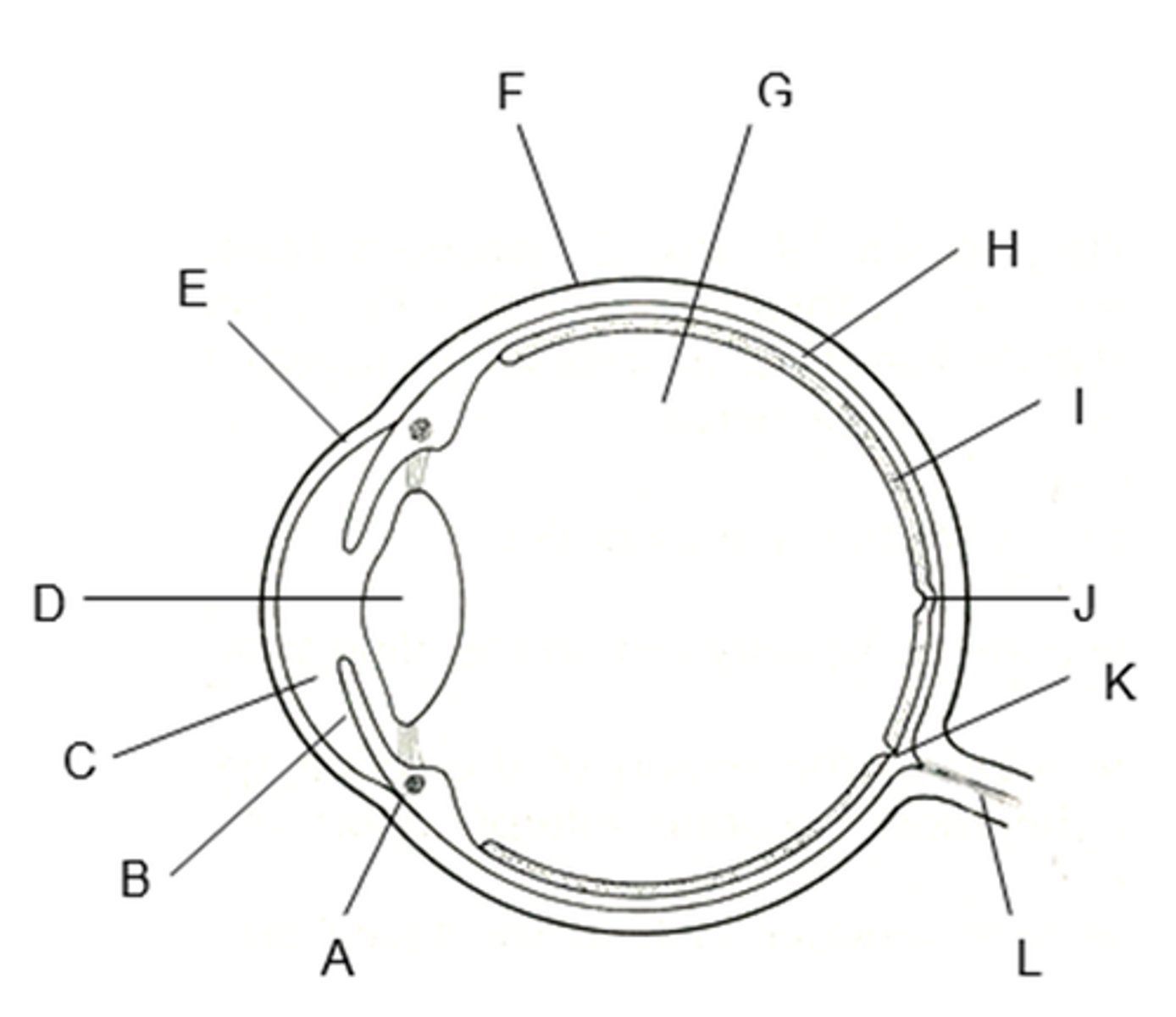
what letter is the iris ?
A
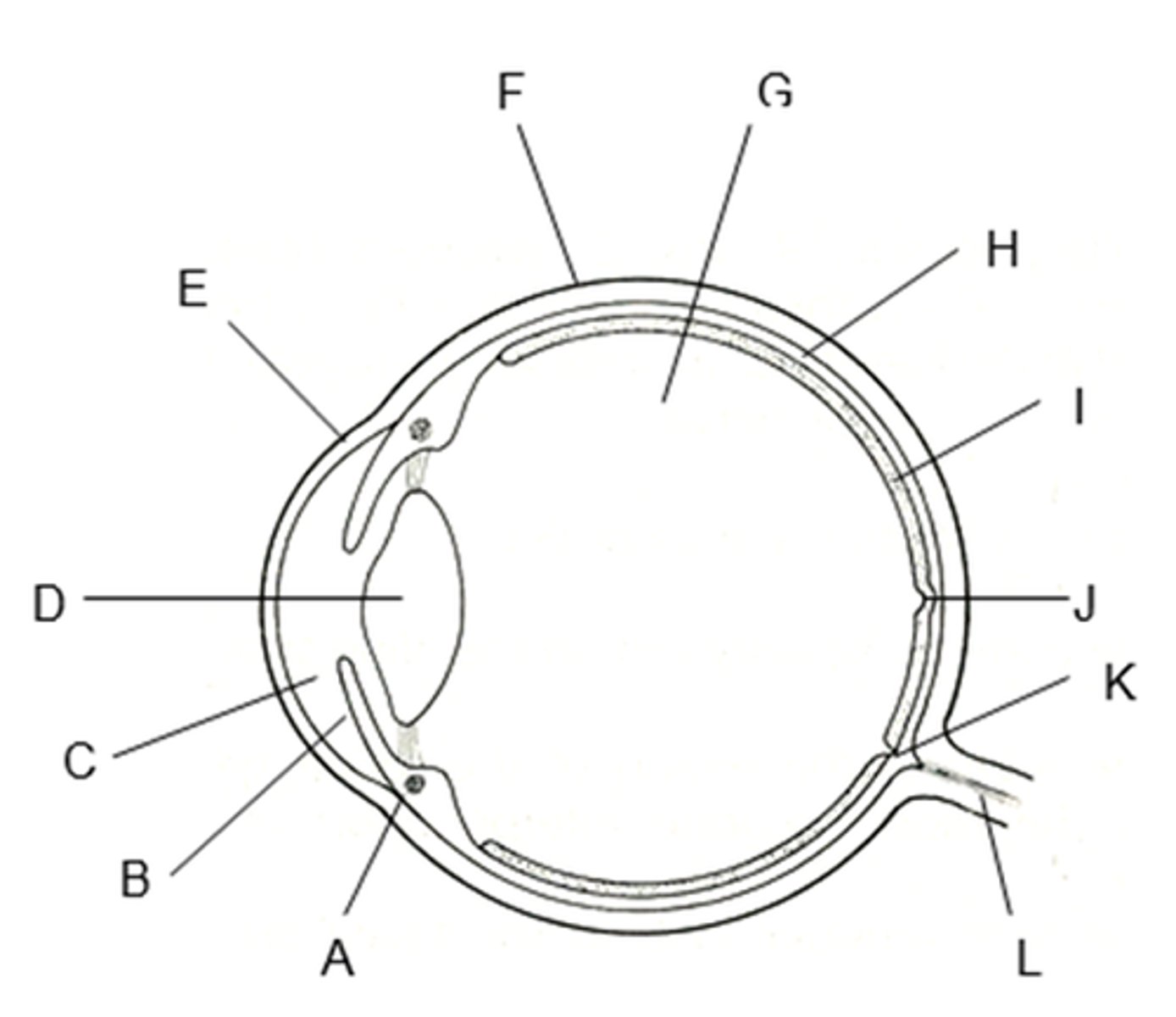
which letter is the optic nerve ?
L
To look at near objects _____
The ciliary muscles contract, which slackens the suspensory ligament.
The lens becomes fat (more curved)
This increases the amount by which it refracts light
To look at distant objects _____
The ciliary muscles relax, which allows the suspensory ligaments to pull tight
This makes the lens go thin (less curved)
So it refracts light by a smaller amount
Why are long sighted people unable to focus on near objects?
their lens is the wrong shape and doesn't refract the light enough or their eyeball is too short and so the images of near objects are brought into focus behind the retina .
what can help longsightedness
glasses with a convex lens to refract the light rays so they focus on the retina
what is the medical term for longsightedness
hyperopia
Why are short sighted people unable to focus on distant objects?
their lens is the wrong shape and refracts light too much or their eyeball is too long and so the images o distant objects are brought into focus in front of the retina
What can correct myopia?
glasses with a concave lens so the light rays focus on the retina
Alternatives to wearing glasses
Contact lenses, laser eye surgery and replacement lens surgery.
When you're too hot
hairs lie flat
sweat is produced by sweat glands and evaporates from the skin which transfers energy to the environment .
the blood vessels supplying the skin dilate so more blood flows close to the surface of the skin . this called vasodilation which helps to transfer energy from the skin to the environment .
What is vasodilation?
the dilatation or widening of blood vessels, which decreases blood pressure.
when you're too cold
Hairs stand up to trap an insulating layer of air
No sweat is produced
Bloody vessels supplying the skin capillaries constrict to close off the skins bloody supply. This is called vasoconstriction
When you're too cold you shiver too (your muscles contact automatically). This needs respiration, which transfers some energy to warm the body
Thyroid gland
produces thyroxine which helps to regulate things like the rate of metabolism , heart rate , and temperature
what is metabolism ?
sum of all chemical reactions in the body
Adrenal gland
A pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones that produce adrenaline for a 'fight or flight ' response
Nerves vs Hormones
Nerves - very fast, act for a short time, act on a very precise area.
Hormones - slower, act for a long time, act in a more general way.