Hearing Science: Outer Ear
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What are the major divisions of the outer ear?
pinna and external (outer) ear canal
How is the pinna (auricle) attached to the skull?
skin, cartilage, ligaments and muscles
What are the ten key features of the pinna?
Helix
Anti-helix
Triangular fossa
Tragus
Intertragal notch
Anti-tragus
External auditory meatus
Concha
Darwin's tubercle
Earlobe
Helix
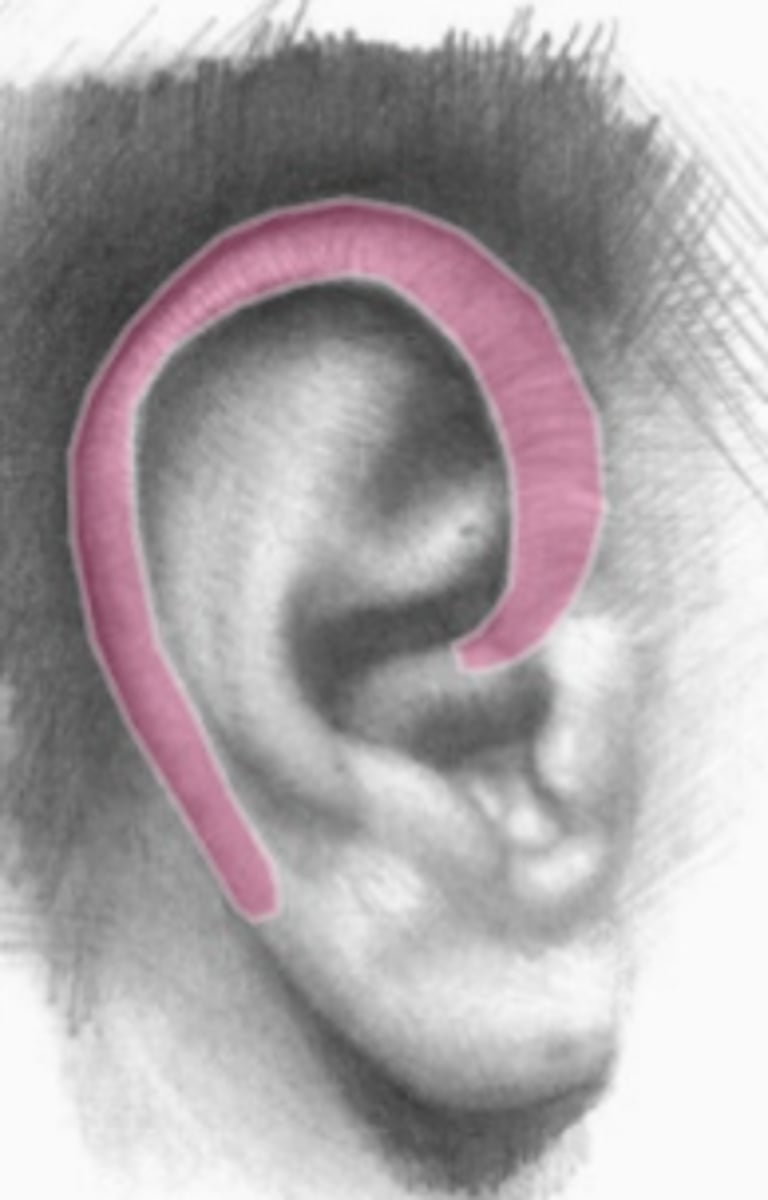
Anti-helix
anterior or forward of the helix

Tragus
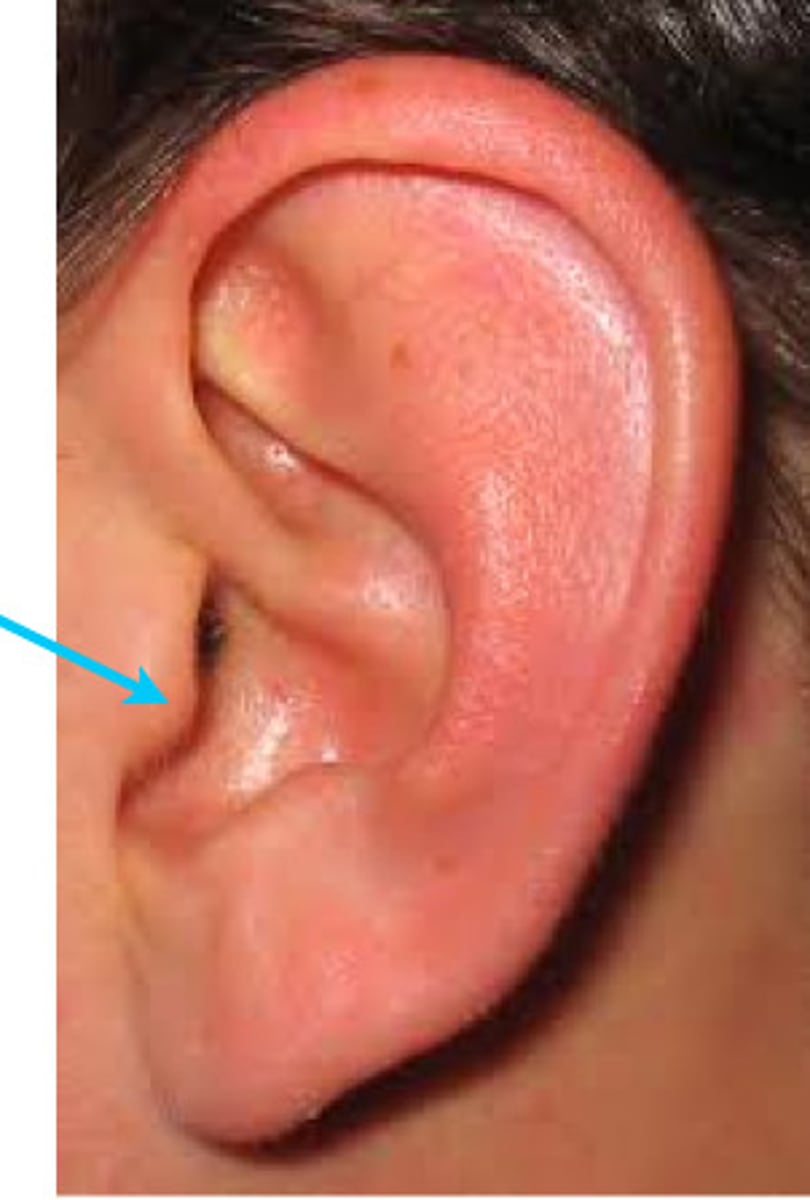
Anti-tragus
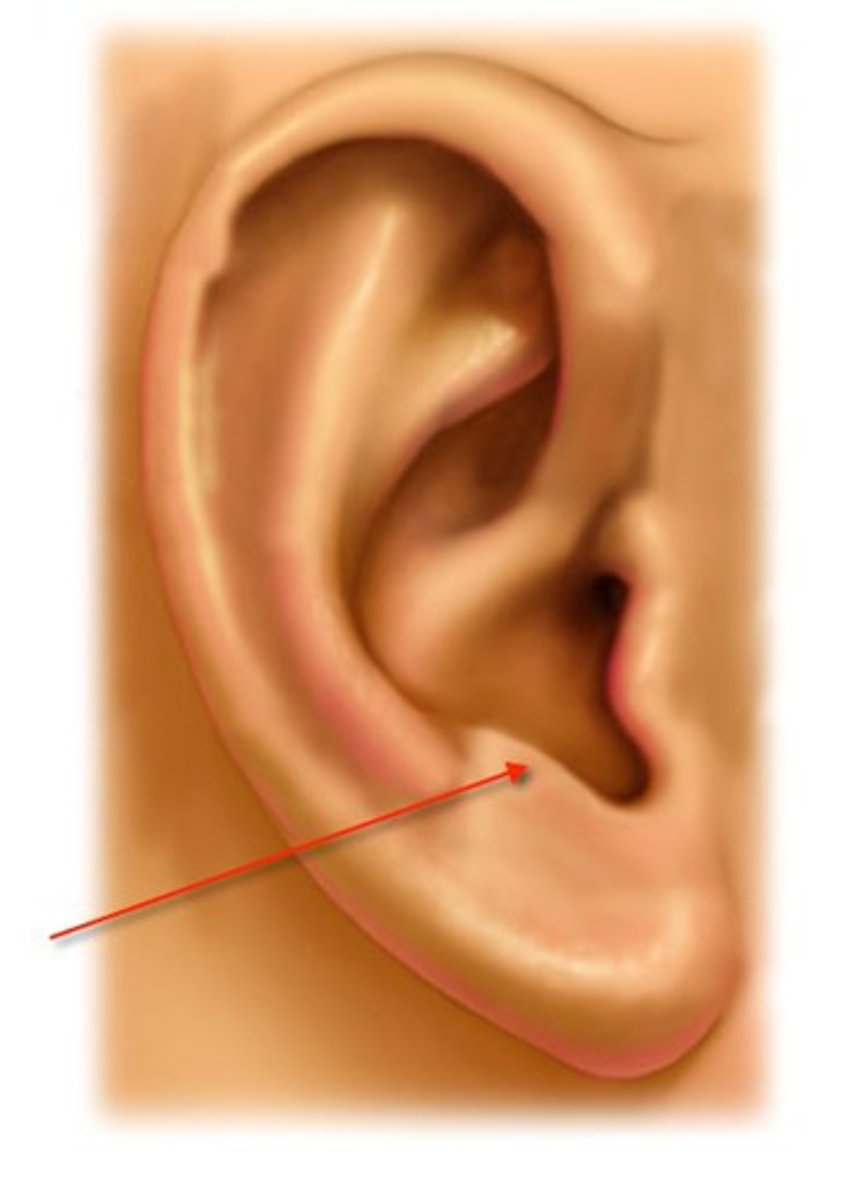
Intertragal Notch

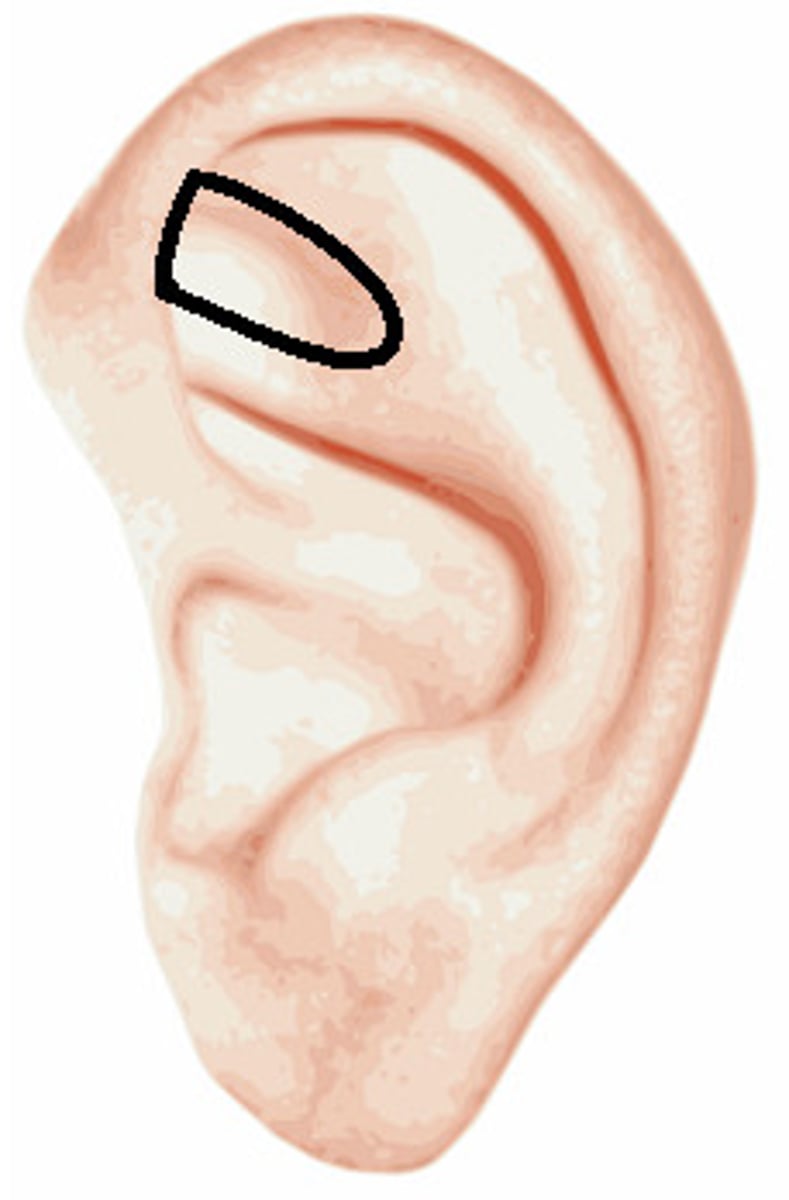
Triangular Fossa
a depression of the antihelix
How is the concha divided?
into two parts, separated by the limb of the helix
What are the two parts of the concha?
concha cymba and concha cavum
External Auditory Meatus
the opening of the ear
-meatus: opening or passage
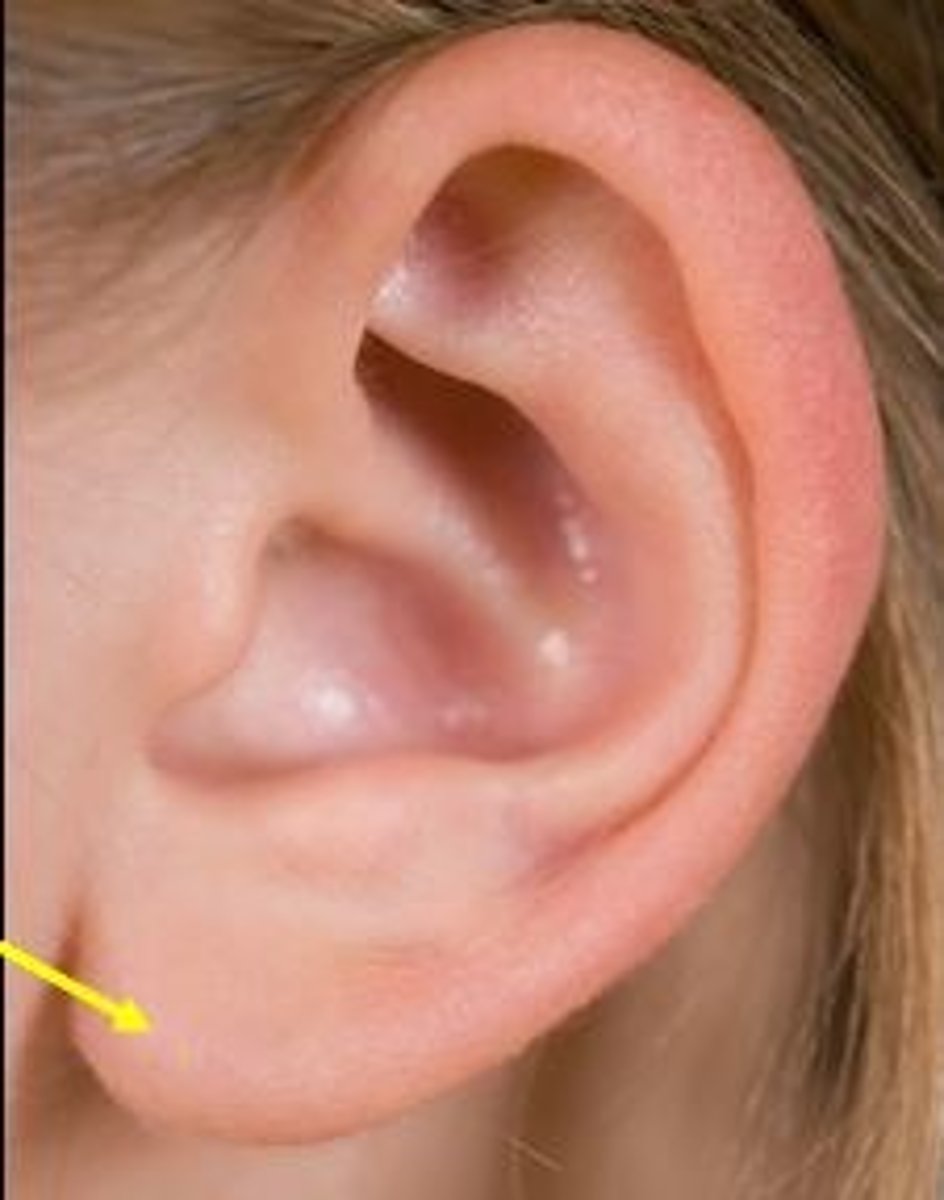
Earlobe
consists mostly of fat cells
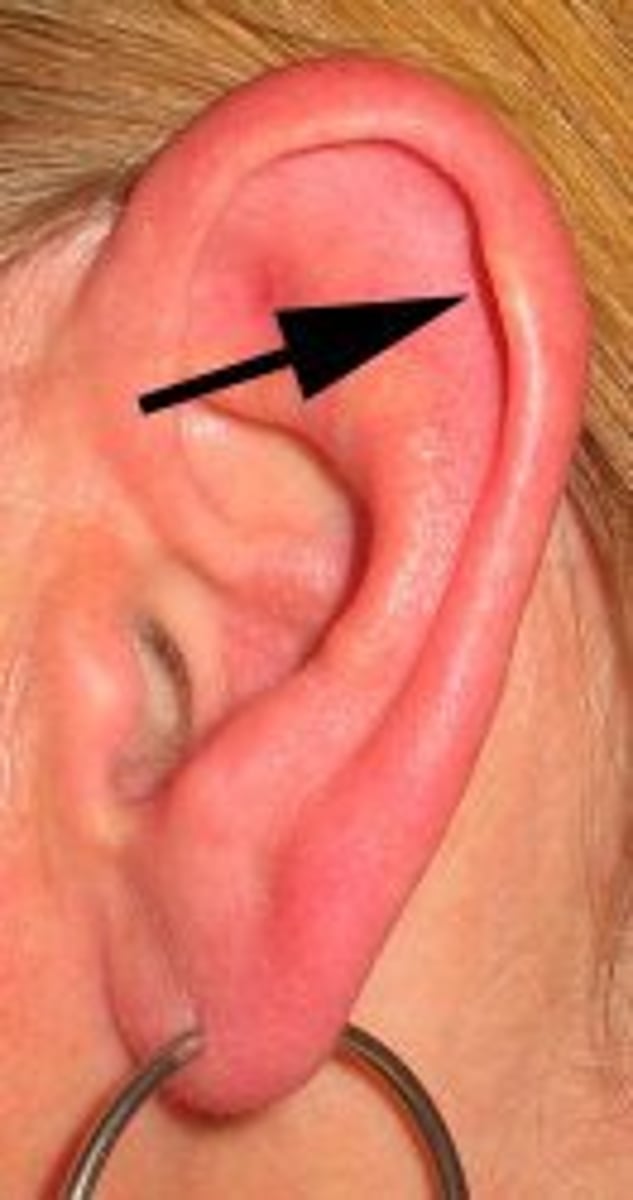
Darwin's Tubercle
only about 10% of the population have a visible one
What is a vestigial structure?
a very small remnant of something that was once much larger or more noticeable
What are the two sections of the ear canal?
Outer section: cartilaginous
Inner Section: osseous (bone)
What is the outer section of the ear canal made up of?
-relatively thick layer of skin
-cerumen glands (ear wax)
-hair follicles
What is the inner section of the ear canal made up of?
-relatively thin
-no hair follicles
-no cerumen glands
The anatomy of the external ear canal is...
-irregular in shape and course
-oval shaped
What is the average length of the external ear canal?
2.5 cm (1 inch)
What is the average volume of the external ear canal?
approximately 1.0-1.4 cc
cc = cubic centimeters
What course does the ear canal take?
"lazy s" with two shallow bends
What do ear impressions reveal?
the shape of the pinna and ear canal
What are ear impressions used for?
fabricate hearing aids, custom earplugs, in-the-ear monitors
What are the three physiological contributions of the outer ear to hearing?
-protection of middle ear and eardrum and provides for a hygienic condition
-resonance
-localization
What does hygienic mean?
tends to promote or preserve health
How does the outer layer of the skin lining the ear canal and tympanic membrane migrate?
laterally
What does the lateral migration of the outer layer of skin allow?
this allows for self-cleaning of the tympanic membrane and the removal of the wax and trapped debris from the inside of the ear canal
What is the rate of skin cell migration?
approximately 100 microns per day
Cone of Light
reflection of light from otoscope
-reflects off the tempanic membrane
What is visible on the other side of the tympanic membrane?
the manubrium of the malleus
When cerumen (ear wax) obscures the view of the tympanic membrane, does this cause hearing loss?
No, because there is still room for the sound waves to pass through
What are the negative results of using a Q-tip?
-may result in damage to the canal walls
-may plunge the ear wax deep into the ear canal and create a wax earplug that may be difficult to remove
Why can some types of earplugs be dangerous to a damaged ear canal?
could result in further damage, discomfort and/or bleeding
What quality does ear wax (cerumen) have?
protective
If someone has excessive earwax, how can they get it removed?
by a physician
Ear Canal Resonance Graph
x-axis = frequency (Hz)
y-axis = gain (dB)
measuring the amplification of sound provided by the ear canal resonance
Ear Canal Resonance Testing answers the question:
How does the level of sound change from just outside the ear (pinna) to inside the ear canal?
Sound Level Meter
a sound level meter is used to measure the level of sound
What units does a sound level meter measure in?
dB SPL or dBA
What are the steps for ear canal resonance?
1. Speaker delivers sound (frequency) to the ear
2. The sound level is measured just outside the ear
3. The sound level is measured in the ear canal
200 Hz of sound is produced, with 60 dB SPL recorded outside of the ear and 63 dB SPL inside the ear. How did the sound change?
by 3 dB SPL (or 3 dB of Gain at 200 Hz)
What does the x-axis of an ear canal resonance graph represent?
frequency (Hz)
What does the y-axis of an ear canal resonance graph represent?
gain (dB)
How was the value of the x-axis contained?
the frequency (Hz) is determined by the technician
How was the value of the y-axis determined?
the level inside the ear - the level outside the ear = gain
What are the steps to obtain the value for the y-axis?
1.Pick frequency and present it
2.Measure the level outside the ear
3.Measure the level outside the ear
4.Calculate inside-outside = gain
On a table related to the ear canal resonance graph, what is the input?
the sound level measured outside of the ear canal
On a table related to the ear canal resonance graph, what is the output?
the sound level measured inside of the ear canal
Why should humans have the capacity in their canals to amplify sound? Is their any use?
Yes, because it allows us to hear higher pitches (children's voices)
-also to help hear low level high frequency sounds
When is ear canal resonance a good thing?
amplifies low level and high frequency sounds (voiceless fricatives)
-tone and speech
When is ear canal resonance a dangerous thing?
if listening to a high level sound the ear canal resonance amplifies it even more
Sound Localization
the ability to determine the source location of a sound
When is the sound level the same on both the left and right ear?
for low frequency sounds
When is the sound level different on both sides?
for high frequency sounds
When the sound source is on the left side, what happens to the amplitude of high-frequency sounds?
amplitude of high- frequency sound is greater in the left ear than in the right ear
The Head-Shadow Effect
the blockage of high frequencies waves by the head, causing the difference in high frequencies reaching the ears
If a child is deaf on the left side, but in the classroom on the right side, will the child have difficulty hearing?
yes because of the head-shadow effect (which effects high frequency sounds
Will a sound with a frequency wavelength that is less than the size of the head be affected as it moves past the head?
yes because high frequencies produce shorter wavelengths
Will a sound with a frequency wavelength that is greater than size of the head be affected as it moves past the head?
no because low frequencies have shorter wavelengths
Since sound waves and beams of light both travel in straight lines they both...
cast shadows
Unilateral Hearing Loss
single-sided deafness (SSD)
-head shadow reduces high frequency speech sounds as they reach the hearing ear