Bio 006 - 13A: Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Sex
Biological classification based on anatomical traits.
Gonads
Organs producing gametes; testes or ovaries.
Secondary Characteristics
Physical traits developed during puberty, like breasts.
Chromosomes
Structures carrying genetic information; XX or XY.
Bimodal
Classification allowing for more than two categories.
Sex Chromosomes
Chromosomes determining biological sex; X and Y for humans.
Y Chromosome
Small chromosome with ~25 proteins in humans.
Homologous Regions
Similar regions on X and Y chromosomes.
X-Linked Genes
Genes on the X chromosome, can be dominant or recessive.
Recessive Trait
Trait requiring two copies for expression in females.
Dominant Trait
Trait expressed with only one copy in males.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene, e.g., XN and Xn.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a trait.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait.
Hemizygous
Having only one allele for a gene, as in males.
Law of Segregation
Mendel's principle that alleles separate during meiosis.
Gregor Mendel
Scientist who studied inheritance using pea plants in the 1860s
Walter S.
Scientist building on Mendel's work in 1902
Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
Genes are located on specific chromosomes.
Drosophila melanogaster
Fruit fly studied by Thomas Morgan
Easy to breed → new generation every 2 weeks
Only have 4 sets of chromosomes → can see all of them under a microscope
Wild type
Most common phenotype in natural populations.
Thomas Morgan
Geneticist who studied inheritance in fruit flies in 1908 and found solid evidence for specific gene
Mutant phenotype
Variation from the wild type in traits.
X-linked traits
Traits associated with genes on the X chromosome.
P generation
Parental generation in genetic crosses.
F1 generation
First filial generation from parental mating.
F2 generation
Second filial generation from F1 mating.
3:1 ratio
Observed ratio of traits in F2 generation.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene.
Loci
Specific positions of genes on chromosomes.
Meiosis
Cell division producing gametes with half chromosomes.
Crossing-over
Exchange of genetic material during Prophase I.
Independent Assortment
Genes segregate independently during gamete formation.
Sex-linked inheritance
Traits linked to sex chromosomes.
Linked Genes
Genes inherited together due to proximity on chromosome.
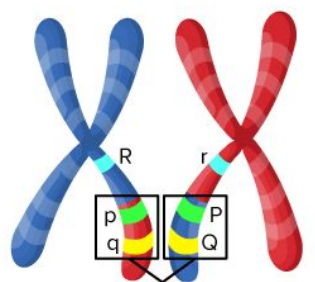
Recombination
Separation of genes during crossing over in meiosis.
Chromosomal Abnormalities
Changes affecting entire chromosomes, impacting organism.
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate during this meiosis stage.
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate during this meiosis stage.
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis.
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes in an organism.
Monosomic
Condition of having one less chromosome than normal.
Trisomic
Condition of having one extra chromosome than normal.
Trisomy 21
Aneuploidy condition with three copies of chromosome 21.
Klinefelter Syndrome
XXY males with underdeveloped testes and breast tissue.
XYY Males
Generally normal males, might be taller than average.
Trisomy X
XXX females, usually normal but may have disabilities.
Turner's Syndrome
Monosomy X condition in females, sexually underdeveloped.
Swyer Syndrome
XY individuals with female phenotype, normal chromosomes.
Deletion
Removal of a segment from a chromosome.
Duplication
Repeating a segment within a chromosome.
Inversion
Reversing a segment within a chromosome.
Translocation
Moving a chromosome segment to a non-homolog.
Cri du Chat Syndrome
Deletion on chromosome 5 causing severe disabilities.
Fused Gene
Gene created by translocation, leading to uncontrolled growth.