❤️🔥 1.5 - Growth and Evolution
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Acquisition
Method of external growth that involves one company buying a controlling interest (majority stake) in another company, with the agreement and approval of the target company's Board of Directors.
Average costs
Refers to the cost per unit of output.
Backward vertical integration
Occurs when a business amalgamates with a firm operating in an earlier stage of production, such as a car manufacturer taking over a supplier of tyres or other components.
Conglomerates
Businesses that provide a diversified range of products and operate in a range of different industries.
Demerger
Occurs when a company sells off a part of its business, thereby separating into two or more businesses. It usually happens due to conflicts, inefficiencies and incompatibilities following an earlier merger of two or more companies.
Diseconomies of scale
Cost disadvantages of growth. Average costs are likely to eventually rise as a firm grows due to a lack of control, coordination and communication.
Economies of scale
Lower average costs of production as a firm operates on a larger scale due to gains in productive efficiency, such as easier and cheaper access to source of finance.
External diseconomies of scale
Occur due to factors beyond its control which cause average costs of production to increase as an industry grows.
External economies of scale
Occur when an organization's average cost falls as the industry grows. Hence, all firms in the industry benefit.
External growth (inorganic growth)
Occurs when a business grows and evolves by collaborating with, buying up or merging with other organizations.
Financial economies of scale
Cost savings made by large firms as banks and other lenders charge lower interest (for overdrafts, loans and mortgages) because larger businesses represent lower risk.
Forward vertical integration
Growth strategy that occurs with the amalgamation of a firm operating at a later stage in the production process, such as a book publisher acquiring book retailers.
Franchising
Refers to an agreement between a franchisor selling its rights to other businesses (franchisees) to allow them to sell products under its corporate name in return for a fee and regular royalty payments.
Horizontal integration
External growth strategy that occurs when a business amalgamates with a firm operating in the same stage of production.
Internal diseconomies of scale
Occur due to internal problems of mismanagement, causing average costs of production to increase as a firm grows.
Internal economies of scale
Occur within a particular organization (rather than the industry as a whole) as it grows in size.
Internal growth (organic growth)
Occurs when a business grows using its own capabilities and resources to increase the scale of its operations and sales revenue.
Joint venture
Growth strategy that combines the contributions and responsibilities of two or more different organizations in a shared project by creating a separate legal enterprise.
Lateral integration
Refers to external growth of firms that have similar operations but do not directly compete with each other, such as PepsiCo acquiring Quakers Oats Company.
Marketing economies of scale
Occur when larger businesses can afford to hire specialist managers, thereby improving the organization's overall efficiency and productivity.
Merger
Form of external growth whereby two (or more) firms agree to form a new organization, thereby losing their original identities.
Optimal level of output
Most efficient scale of operation for a business. This occurs at the level of output where the average cost of production is minimized.
Purchaser
Refers to the acquiring company in an acquisition or the buyer of another company in a takeover.
Purchasing economies of scale
Occur when larger organizations can gain huge cost savings per unit by purchasing vast quantities of stocks (raw materials, components, semi-finished goods and/ or finished goods).
Risk bearing economies of scale
Occur when large firms can bear greater risks than smaller ones due to having a greater product portfolio.
Specialization economies of scale
Occur when larger firms can afford to hire and train specialist workers, thus helping to boost their level of output, productivity and efficiency.
Strategic alliances
Formed when two or more organizations join together to benefit from external growth, without having to set up a new separate legal entity.
Synergy
Benefit of growth, which occurs when the whole is greater than the sum of the individual parts when two or more business operations are combined. Synergy creates greater output and improved efficiency.
Takeover (hostile takeover)
Occurs when a company buys a controlling interest in another firm without the prior agreement or approval of the target company's Board of Directors.
Target company
Refers to the organization that is purchased by another in an acquisition or takeover deal.
Technical economies of scale
Cost savings by greater use of large-scale mechanical processes and specialist machinery, such as mass production techniques which help to cut average costs of production.
Vertical integration
Takes place between businesses that are at different stages of production.
How might the notion of economies and diseconomies of scale be shown on a diagram?
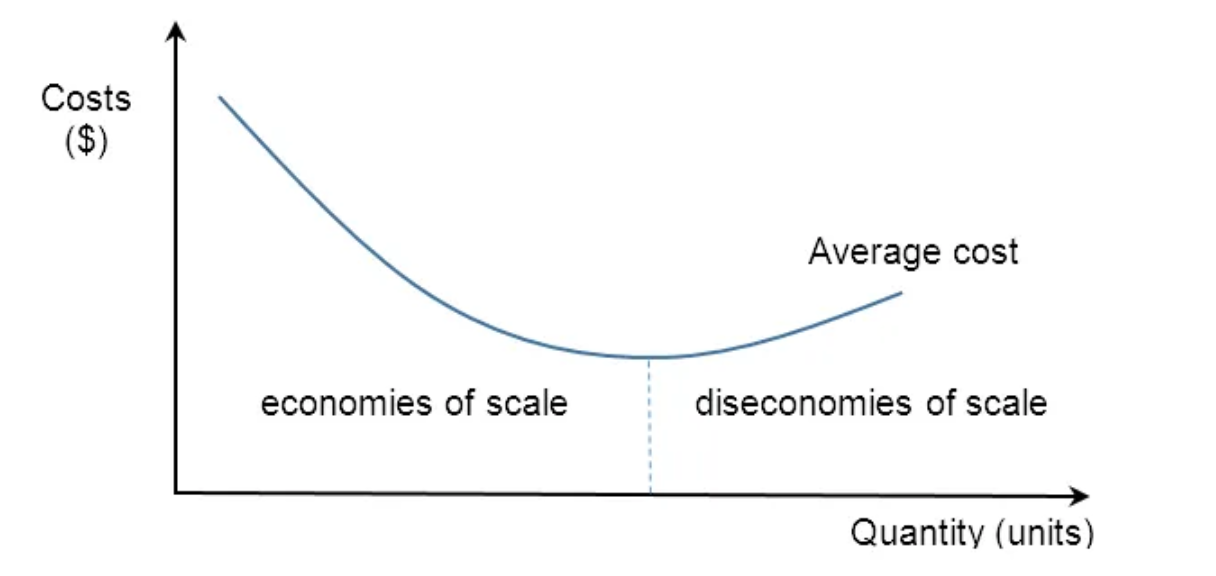
Optimal size of a business
Appropriate size of a business to operate efficiently and maximize profit, whilst keeping average costs low.
Main types of external economies of scale
Technological progress
Improved transportation networks
Skilled labor
Regional specialization
Main reasons why businesses seek to grow?
Market share
Total sales revenue
Size of workforce
Profit
Capital employed
Main reasons why some businesses stay small?
Cost control
Loss of control
Financial risks
Government aid
Local monopoly power
Personalized services
Flexibility
Small market size
‘Mergers and acquisitions (M&As)’
Integration of two or more businesses to form a single company. New and larger business entity will benefit from improved synergies.
Merger vs aquisition
Merger: integration of businesses of similar sizes
Acquisition: occurs between two companies that are not of equal stature.
Reasons why businesses become takeover targets:
Growth potential but lack sufficient funds for internal growth
Seen as a small rival that has growth potential
Widely recognized corporate name or brand but face a liquidity or financial crisis.
Vulnerable due to drop in profits or share price
Evaluation of joint ventures
Advantages:
Competitive advantage
Entry to foreign markets
Relatively cheap
Synergy
Disadvantages:
Rely heavily on the resources and goodwill of their counterparts
Dilution of the brands
Possibility of organizational cultural clashes
Benefits and drawbacks of franchising for the franchisee.
B:
lower start-up costs as the idea has been developed
low risks
lower costs due to ‘free’ advertising and promotion
larger degree of autonomy
D:
hinder entrepreneurial talents of the franchisee
expensive to buy the franchise
have to pay a significant percentage of sales revenues to the franchisor.
Benefits and drawbacks of franchising for the franchisor.
B:
rapid growth and cheaper as the franchisee pays for the rights
lack of running costs
receive royalty payments and membership/registration free
D:
high risk as reputation may be damaged
difficult to control daily operations
not as quick as external methods such as M&As