Coelom, Cardiovascular, and Lymphatic Systems Lecture
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering major anatomical and physiological terms from the lecture on body cavities, serous membranes, blood, cardiovascular, and lymphatic systems.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
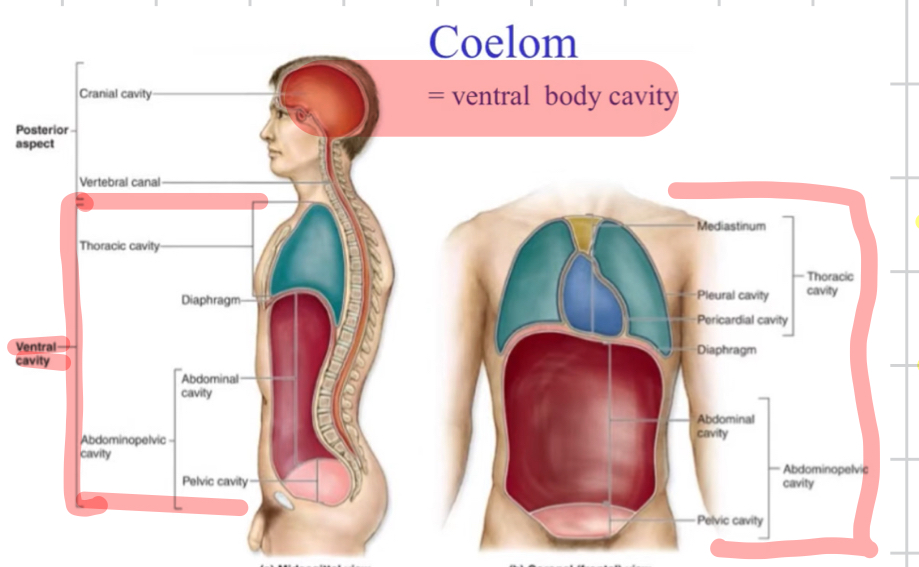
Coelom
A fluid-filled body cavity completely lined by mesoderm, housing internal organs.
another name for ventral cavity
the ventral body cavity( thoracic & abdominalpelvic)
Viscera
The internal organs located within the body cavities, especially those of the thorax and abdomen.
Peritoneum
Serous membrane lining the abdominopelvic cavity and covering its organ
mbn lining
Membrane (anatomical)
Thin, flexible sheet of tissue, composed of Epithelial layer& underlying CT (includes mucous mbn, serous mbn, cutaneous mbn, synovial mbn) that serves various functions such as protection, lubrication, and supporting organs.
Embryonic germ layers
The three primary cell layers—ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm—formed during gastrulation that give rise to all body tissues.
Pleura
Serous membrane surrounding the lungs and lining the thoracic cavity.
Pericardium
Double-walled serous sac enclosing the heart and defining the pericardial cavity.
Ventral body cavity
Large anterior cavity subdivided into thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Thoracic cavity
Superior subdivision of the ventral cavity containing pleural cavities and the pericardial cavity.
Abdominopelvic cavity
Inferior subdivision of the ventral cavity containing abdominal and pelvic organs.
Peritoneal cavity
Potential space between parietal and visceral peritoneum filled with serous fluid.
Parietal peritoneum
Layer of peritoneum lining the internal surface of the abdominopelvic wall.
Visceral peritoneum
Layer of peritoneum directly covering abdominal organs.
Omentum
A double layer of peritoneum extending from stomach to other organs; includes greater and lesser omenta.
Mesentery proper
Peritoneal fold attaching the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall.
Mesocolon
Peritoneal fold anchoring parts of the colon to the posterior abdominal wall.
(Peritoneal) Ligament
Double layer of peritoneum connecting one organ to another or to the abdominal wall without a conduit for vessels.
Serous membrane
Moist, friction-reducing membrane composed of simple squamous epithelium and areolar connective tissue; lines closed cavities.
Mucous membrane
Epithelial membrane lining cavities that open to the exterior and secreting mucus.
Retroperitoneal
Describes organs located posterior to the parietal peritoneum and only partly covered by it.
Diaphragm ( openings)
Dome-shaped skeletal muscle with three parts (sternal, costal, lumbar) separating thoracic and abdominal cavities.
Caval opening
Central tendon aperture in the diaphragm for the inferior vena cava.
Esophageal hiatus
Diaphragmatic opening for the esophagus and vagal trunks.
Aortic hiatus
Posterior diaphragmatic passageway for the aorta, thoracic duct, and azygos vein.
Femoral canal
Medial compartment of the femoral sheath conveying lymphatics; potential site of femoral hernia.
Inguinal canal
Oblique passage in the anterior abdominal wall transmitting the spermatic cord in males and round ligament in females.
Zygote
Single-cell stage formed by fertilization, beginning human development.
Organogenesis
Embryonic period during which the germ layers differentiate into organs and organ systems.
Circulatory system
The transport network comprising cardiovascular and lymphatic systems.
Cardiovascular system
Heart and blood vessels circulating blood
fxn: Transport O2, deliver nutrients, and waste removal, hormones to/from organs, protecting (blood clots)
Lymphatic system
Network of lymphatic vessels, lymph organs, lymph nodes, lymph and tissues that return interstitial fluid to blood and mediate immunity.
Blood
Fluid connective tissue consisting of plasma and formed elements transporting substances throughout the body.
Plasma
Liquid extracellular matrix of blood containing water, proteins, and solutes.
Formed elements
Cellular components of blood—erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets.
Red blood cell (RBC)
Anucleate cell specialized for oxygen transport via hemoglobin; also called erythrocyte.
White blood cell (WBC)
Immune cell defending the body against pathogens; also called leukocyte.
Granulocyte
Leukocyte with cytoplasmic granules (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils).
Agranulocyte
Leukocyte lacking visible granules (lymphocytes, monocytes).
Pericardial sac
Fibro-serous enclosure of the heart composed of fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium (parietal & visceral).
Epicardium
Visceral layer of serous pericardium forming the outer surface of the heart wall( mesothelium & loose CT)
Myocardium
Middle, muscular layer of the heart wall responsible for contraction
striated and involuntary
Joint by intercalated dics w/gap jxns &desmosomes
Endocardium
Inner endothelial lining of the heart chambers and valves.
Loose CT & endothelium
Heart chambers
Two atria and two ventricles that receive and pump blood.
Great vessels
Large arteries and veins entering or leaving the heart: aorta, pulmonary trunk, SVC, IVC, pulmonary veins.
Cardiac valves
Atrioventricular and semilunar valves ensuring unidirectional blood flow through the heart.
Coronary circulation
Network of vessels supplying blood to the myocardium.
Pulmonary circulation
Route carrying deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs and back with oxygenated blood.
Systemic circulation
Route delivering oxygenated blood from heart to body tissues and returning deoxygenated blood.
Hepatic portal circulation
Venous system directing nutrient-rich blood from digestive organs to the liver before entering systemic circulation.
Artery
Blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart; thick muscular walls.
Elastic artery
Large artery with abundant elastin (e.g., aorta) that dampens pressure fluctuations.
Arteriole
Small artery regulating blood flow into capillary beds by vasoconstriction or dilation.
Capillary
Microscopic vessel where exchange between blood and tissues occurs.
Venule
Small vessel receiving blood from capillaries and beginning the return to the heart.
Vein
Vessel returning blood to the heart; contains valves and thin walls.
Venous return mechanisms
Muscle pump, respiratory pump, and venous valves assisting blood return to the heart.
Continuous capillary
Capillary with uninterrupted endothelium; most common type, found in muscle and skin.
Fenestrated capillary
Capillary with pores allowing increased filtration; found in kidneys and endocrine glands.
Sinusoidal capillary
Leaky capillary with large gaps; found in liver, spleen, and bone marrow.
Lymphatic vessels
Thin-walled channels that collect and transport lymph toward the venous system.
Lymphatic organ
Encapsulated structure (e.g., thymus, spleen, lymph node) involved in immunity and lymph filtration.
Lymphatic nodule
Unencapsulated cluster of lymphoid tissue such as tonsils or Peyer’s patches.
Primary lymphatic organs
Sites of lymphocyte production and maturation—bone marrow and thymus.
Secondary lymphatic organs
Sites where immune responses are initiated—lymph nodes, spleen, MALT.
Thymus
Primary lymphatic organ in the mediastinum where T cells mature.
Lymph node
Bean-shaped secondary organ filtering lymph and housing lymphocytes & macrophages.
Spleen
Largest lymphatic organ filtering blood, recycling erythrocytes, and mounting immune responses.
Lymphocyte
Agranular leukocyte (B, T, NK cells) central to adaptive immunity.
Macrophage
Phagocytic cell derived from monocytes that engulfs pathogens and debris.
Development sequence:
Zygote(2 gamets)→ morula→ blastocyst→ gastrulation → embryonic disc→ neurulation→ coelom formation
Where is the heart located?
in pericardial cavity, in mediastinum, in thoracic cavity, directly behind sternum
2/3 of mass lies to the left of midline