3.1.4 colour vision
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
what photopigments are responsible for mediating colour vision
short, medium, long wavelength sensitive pigments. S,M, L
what categories of congenital colour vision deficiency are there
how many photopigments are present, or if the photopigment is abnormal
what names are given to those who have 2 photopigments
dichromat
what is an anomalous trichromat
have all 3 pigment but one has abnormal sensitivity
what is L missing called
protanope
what is M missing calling
deuteranope
what is S missing called
tritanope
what is a monochrome
they lack cones or have one cone, very rare
why are men more likely to get colour vision defect
X linked
what wavelength are deuteranopes not seeing
530nm and after, detected by L cones
how can a deutranope tell differences in colour past 530nm
by their relative brightness
what environment should colour vision test be done at
illuminated 350-400 lux lamp of colour 6500k
what distance is ishihara done at
75cm
describe D15 test
caps placed in random orders one lamp
viewing distance 50cm
px ordrrs caps in box so colour appearance changes progressively
practitioner turns caps over and plots them in the numerical order
describe the city test
does at 35cm
3rd edition
First part- 3 dogs say which one is different for screening
Second part-each page has central dot and 4 dots around, report which dot looks most similar to middle. Detection
test sheet shows normal proton, deutan and triton repsonses
how do you interpret ishihara results
fail more than 3 plates
describe the plates of ishihara
2-9 are transformation plates, different number seen by proton/deutan
10-17 are vanishing plates, number not see by protan/deutan
does not detect tritanope
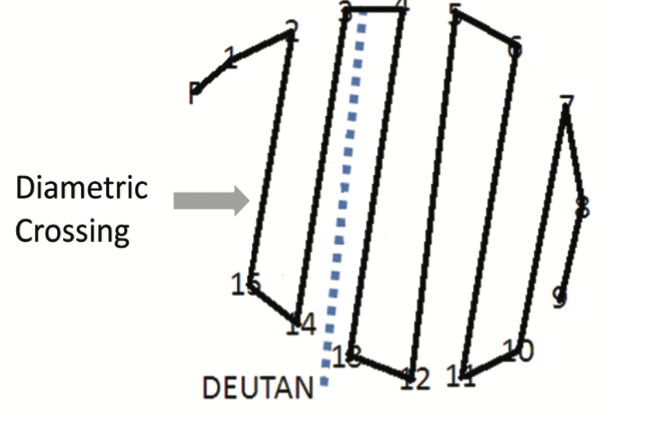
describe D15 results
if one or more diametric crossing are made it indicates mod/severe prtoan/deutan CCVD
up to 2 adjacent crossing allowed
can detect tritan
describe city results
one or more error made on any 10 plates indicated mod/severe proton/deutan CCVD
how do colour vision test work
make use of confusion zones to grade severity of CCVD
plotted on CIE 1931 Chromaticity diagram
what effects of CCVD are there
comparative tasks matching colours
connotative tasks, like red matched with stop
where colour used to organise display and catch attention
colour used to make a mood
what test is done if Ishihara is failed
lantern test, name coloured lights. any error is failure
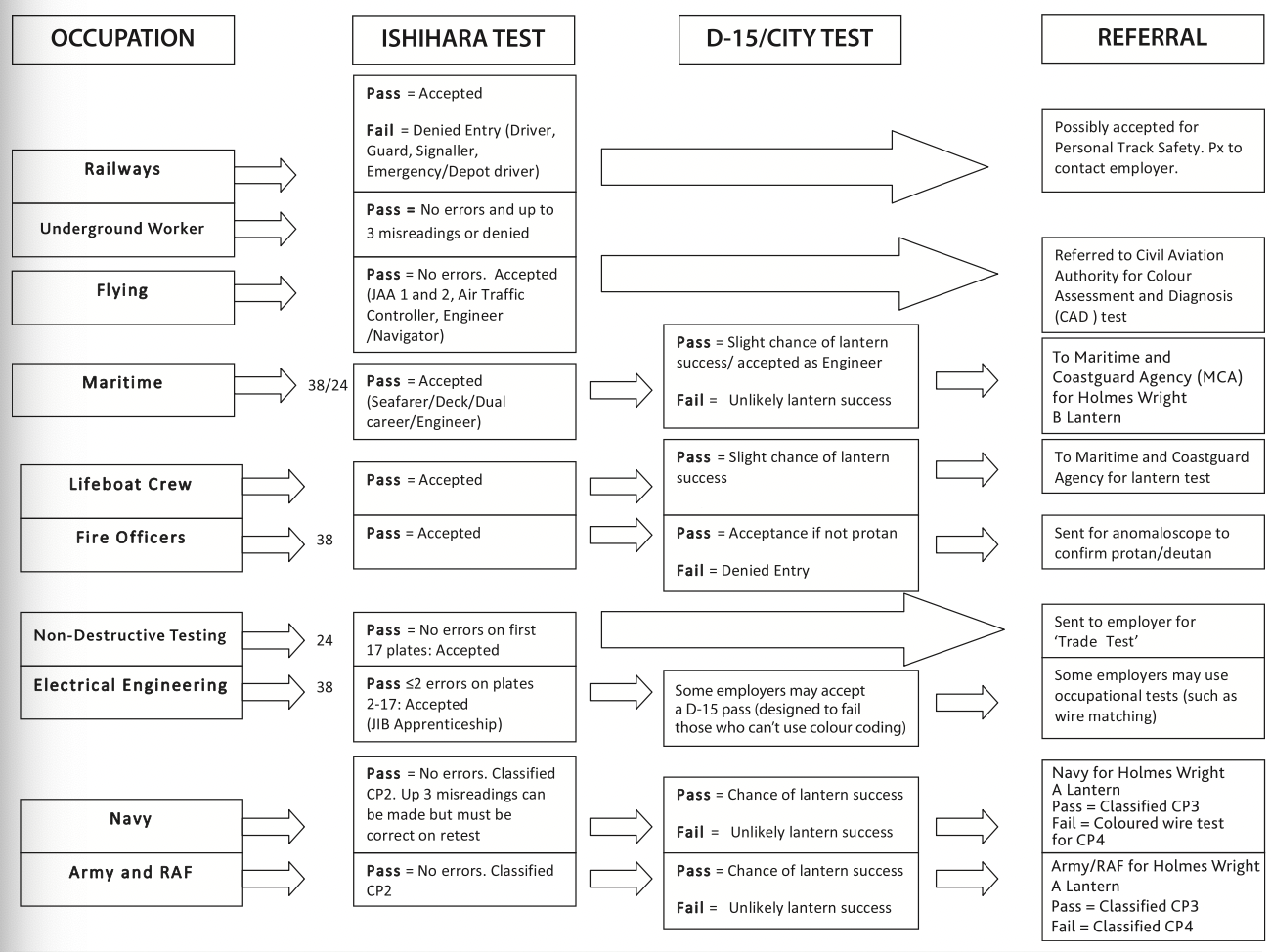
what occupations can be affected
which Ishihara test is preferred and why
38 plate test, contains most efficient plates for detection
what symptoms of a rod monochromatic are there
no functioning cones
VA reduced 6/60-6/36
photophobic
nystagmus
what symptoms of cone monochromats are there
single cone response
VA reduced 6/24-6/9
photophobic
nystagmus if VA below 6/18
what X linked defects are there
protanopes/protanomalous trichromats
deuteranopes/deuteranomolous trichromats
what colours do protanopes confuse
black with dark shades of red
dark brown with dark green, dark orange and dark red
some blues with some reds, purples and dark pinks
mid greens, some oranges
what colours do deuteranopes confuse
confuse mid reds with mid greens
blue greens with grey and mid pinks
bright greens with yellows
pale pinks with light grey
mid reds with mid brown
light blues with lilac
what colours do tritanopes confuse
light blues with greys
dark purples with black
mid greens with blue
oranges with reds
how are
what are acquired defect characteristics
symptomatic
type and severity of defect can fluctuate-Kollner’s rule
unstable
monocular differences
VA reduced, VF defects, contrast sensitivity issues
equal among sexes
reversible
what is Kollners rule
disease of outer retina and media changes result in blue-yellow colour defects
diseases of inner retina, optic nerve, visual pathway and visual cortex result in red green defects
what can causes acquired colour vision defects
ocular pathology
intracranial injury
drug/toxin induced
psychological eg hysteria rare and transient defects
cataract alters colour pereception
AMD can cause triton deficiency
what is type 1 acquired defects
similar to protan
progressive cone dystrophies
macular dystrophies
loss of va
what is type 2 acquired
similar to deutan defect
optic neuritis
optic atrophies, (Leber’s)
optic nerve intoxication
what is type 3 acquired defect
blue yellow defect
cataract
CSR/AMD
rod and Cone dystrophies retinitis pigmentosa
retinal vascular disorders CRVO/CRAO/Diabetes
peripheral retinal lesion (chorioretinitis, retinal detachment)
glaucoma
vitamin A deficiency ( alcoholism, chronic liver disease).
what effects of ethyl alcohol are there
optic neuritis
optic atophy
what effects of methyl alcohol are there
red/green defect
progresses to blue/yellow defect
what effects does tobacco have
papillomacula bundle
central scotoma
red/green defect
what effect does digoxin have
type 2 defect, red/green
scintilling scotomas
episodic coloured vision
transient visual field defects
colour vision recovers after cessation of drug
what effects of ethambutol are there
type 2 defect red/green sudden onset
colour vision records after cessation
what effect does hydroxycloroquine have
type 3
type 1 at advanced stages
what other defects for examination are there
changes in VA, pupil responses changed, VF defect, amsler chart
what is an anomaloscope
colour matching technique not used
distinguished between dichromate vs anomalous trichormats
what test should be done for acquired defects
the city test done monocularly