ch. 12 - solids and modern materials
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
four predominant classifications for solids
1. metallic solids
2. ionic solids
3. covalent-network solids
4. molecular solids
2
New cards
metallic solids
* metal atoms held together by a “sea” of collectively shared valence electrons
* allows metals to conduct electricity
* makes metals strong w/o being brittle
* allows metals to conduct electricity
* makes metals strong w/o being brittle
3
New cards
ionic solids
* anions and cations held together by mutual electrostatic attraction
* do not conduct electricity well; are very brittle
* do not conduct electricity well; are very brittle
4
New cards
covalent-network solids
* atoms are held together by an extended network of covalent bonds (shared e⁻)
* results in extremely hard materials (diamond)
* responsible for semiconductor properties
* results in extremely hard materials (diamond)
* responsible for semiconductor properties
5
New cards
molecular solid
* discrete molecules held together by IMFs
* soft solids w/ low melting points (ice)
* soft solids w/ low melting points (ice)
6
New cards
polymers
* long chains of (usually carbon) atoms connected by covalent bonds w/ chains held together by IMFs
* stronger w/ higher melting points than molecular solids
* more flexible than metallic, ionic, or covalent solids
* stronger w/ higher melting points than molecular solids
* more flexible than metallic, ionic, or covalent solids
7
New cards
nanomaterials
* solids in which the dimensions of individual crystals are 1-100nm
8
New cards
crystalline solids
* solids in which atoms are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern
* usually have flat surface/face that leads to a highly regular shape
* ex. NaCl, quartz, diamond, pyrite
* usually have flat surface/face that leads to a highly regular shape
* ex. NaCl, quartz, diamond, pyrite
9
New cards
amorphous solids
* solids that lack order, are structurally similar to liquids but lack freedom of movement
* ex. rubber, glass, obsidian
* ex. rubber, glass, obsidian
10
New cards
unit cell
* the smallest group of atoms in a unique arrangement that can be repeated to embody the whole structure of a solid
11
New cards
crystal lattice
* unit cells stacked over and over to create the structure of the solid
12
New cards
crystalline solids structure are defined by
1. size and shape of unit cell
2. location of atoms within the unit cell
13
New cards
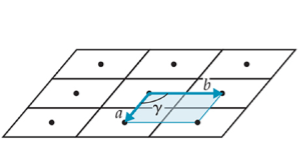
2-D
oblique
14
New cards
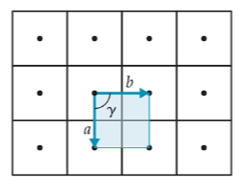
2-D
square
15
New cards
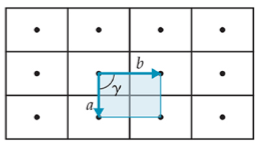
2-D
rectangle
16
New cards
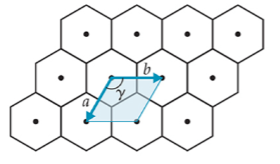
2-D
hexagonal
17
New cards
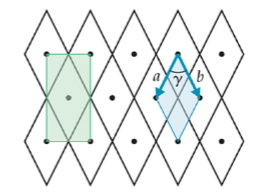
2-D
rhombic
18
New cards
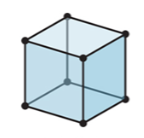
3-D
cubic
19
New cards
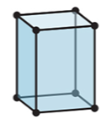
3-D
tetragonal
20
New cards
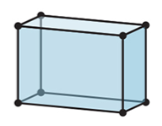
3-D
orthorhombic
21
New cards
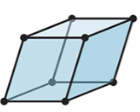
3-D
rhombohedral
22
New cards
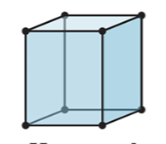
3-D
hexegonal
23
New cards
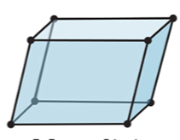
3-D
monoclinic
24
New cards
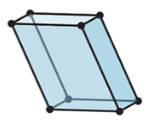
3-D
triclinic
25
New cards
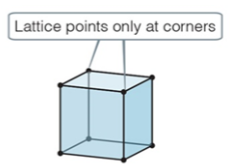
primitive/simple
26
New cards
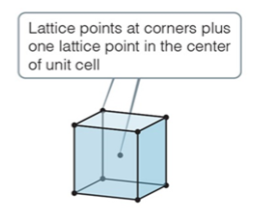
body-centered
27
New cards
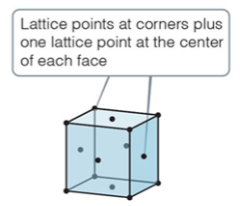
face-centered
28
New cards
primitive/simple cubic
* have atoms only in the lattice points
29
New cards
centered lattices
* have atoms at lattice points at the corners
30
New cards
body center cubic
* have one lattice point in the center of the cell
31
New cards
face center cubic
* have one lattice point at the center of each face
32
New cards
simple case
* identical atoms
* atoms are at lattice points
* only possible for elements
* atoms are at lattice points
* only possible for elements
33
New cards
motif
* a group of atoms
34
New cards
corners contain
* 1/8 of an atom
35
New cards
face contains
* 1/2 of an atom
36
New cards
center contains
* 1 whole atom
37
New cards
alloys
* contain more than one element and have properties of a metal
* allow us to modify properties of pure metallic elements
* ex. pure gold is too soft to be used in jewelry
* allow us to modify properties of pure metallic elements
* ex. pure gold is too soft to be used in jewelry
38
New cards
substitutional alloy
* atoms of a solute occupy positions normally occupied by a solvent atom
* similar atomic radii
* similar atomic radii
39
New cards
interstitial alloy
* solute atoms occupy “holes” between solvent atoms
* often a nonmetal, much smaller atomic radius
* often a nonmetal, much smaller atomic radius