Anatomy of The Respiratory System
1/121
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
How many pairs of ribs
12
What are costal cartilages?
‘bars’ of hyaline cartilage - lengthen ribs at anterior ends, medial extension to articulate with sternum
Ribs 1-7 are known as…
True ribs
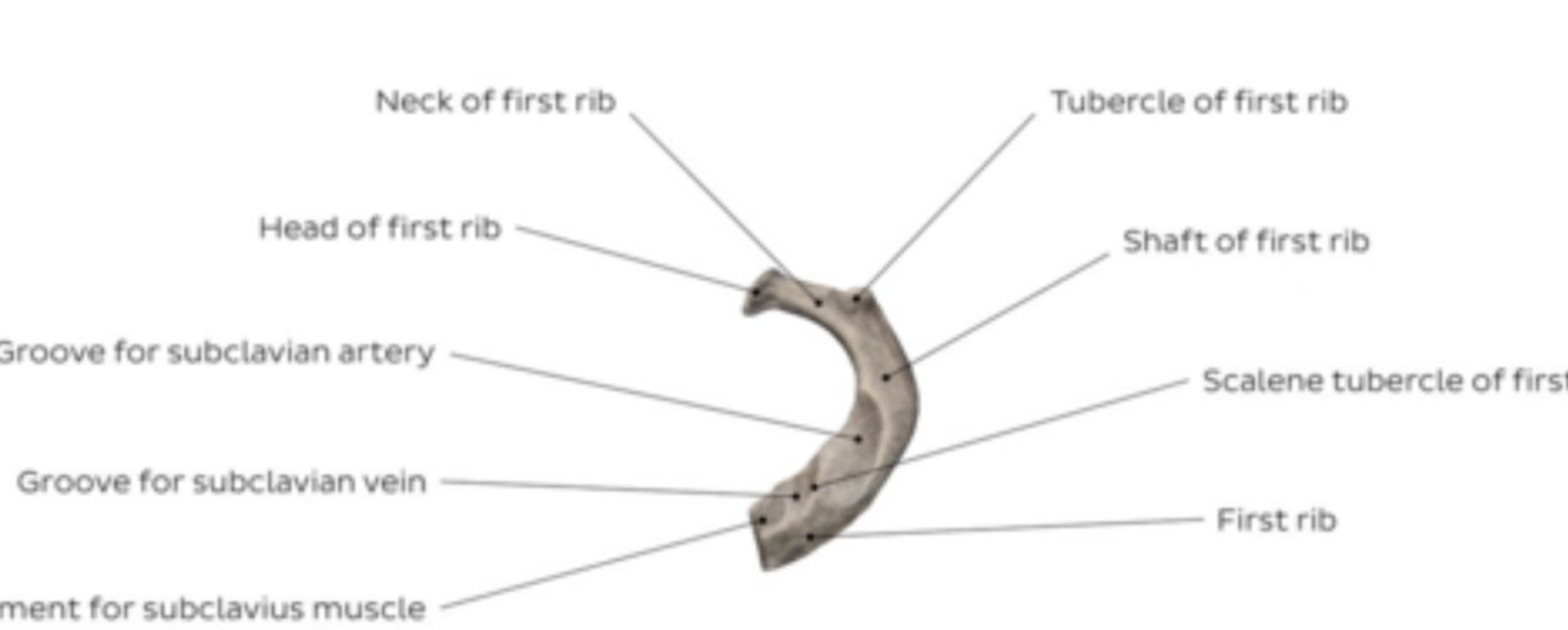
Rib 1 features
short
curved
flat
no costal groove
tubercule
Which ribs are false ribes? what defines them?
ribs 8-10
articulate posteriorly with vertebral column
attach to rib 7 costal cartilage to form costal margin (don’t directly articulate with sternum)
Ribs 11-12 are… describe their features
Floating ribs
articulate posteriorly with vertebral column
no costal cartilage
no anterior articulation with costal cartilage or sternum
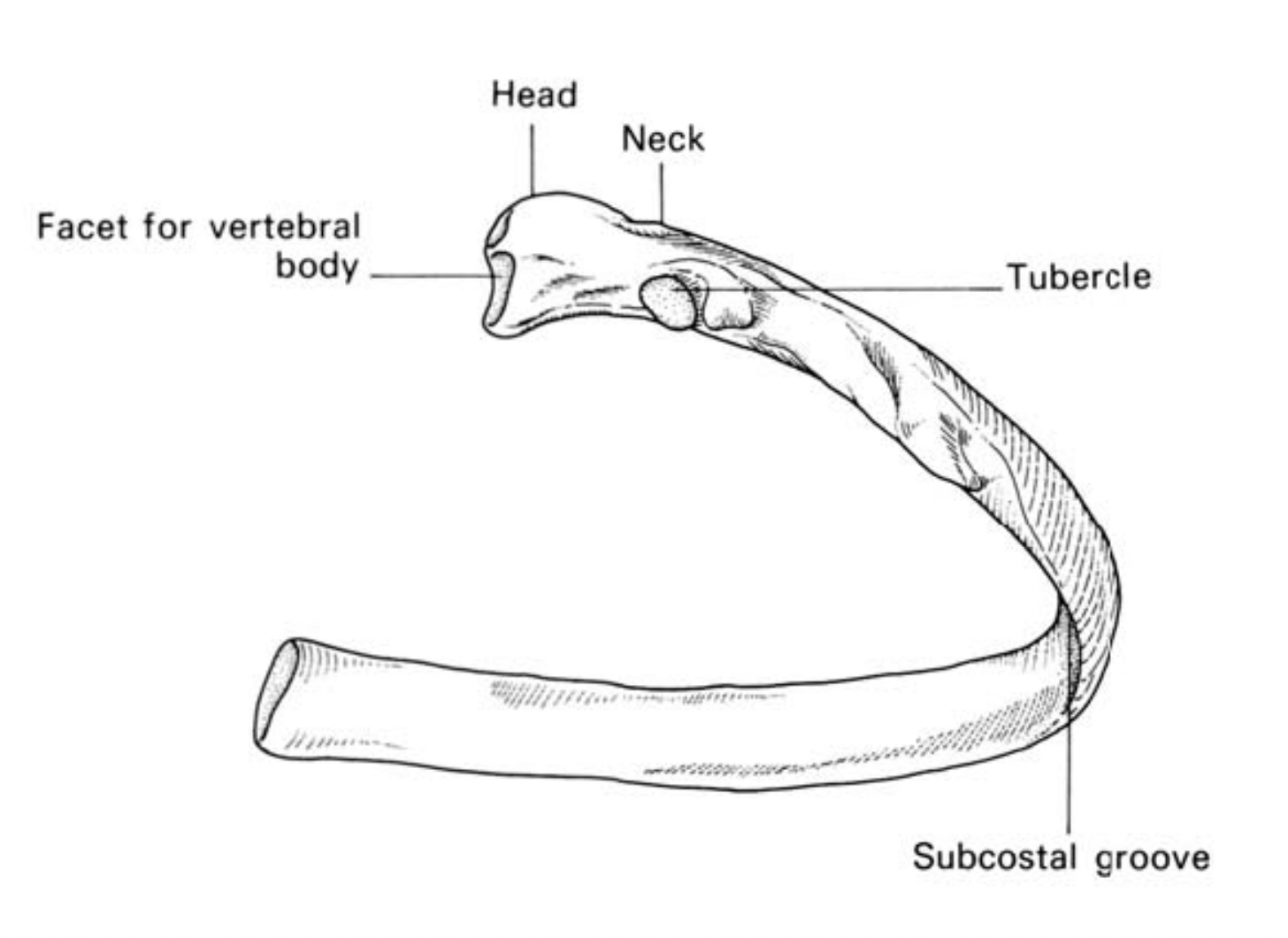
Features of typical ribs
head
neck
tubercule
curved
body
costal groove
Which ribs are typical ribs?
2-10
Which ribs are atypical?
1, 11, 12
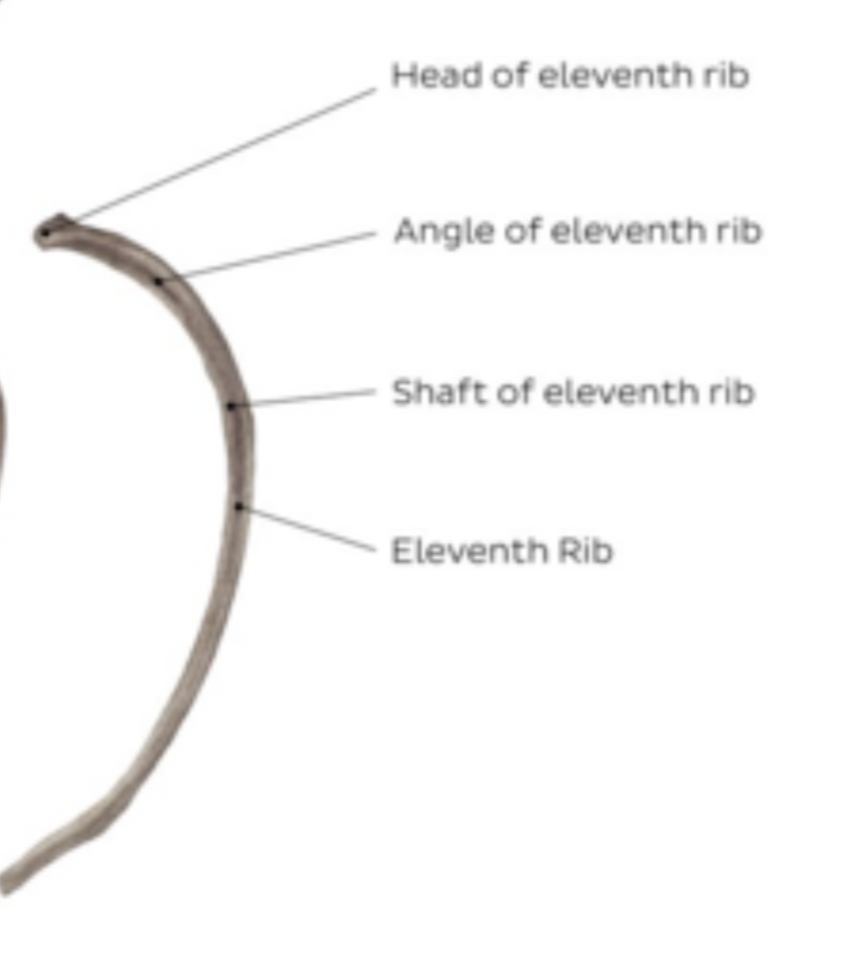
Rib 11 features
no neck
no tubercule
less curved then typical ribs
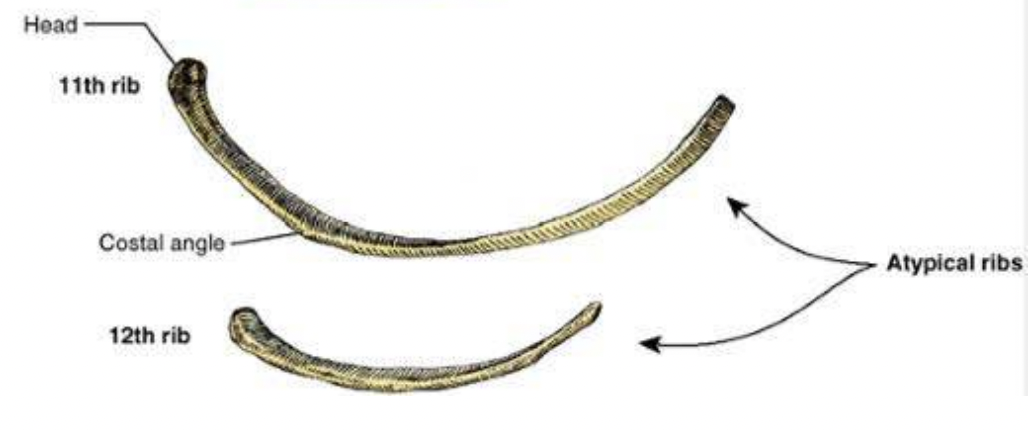
Rib 12 features
no neck
no tubercule
less curved then typical ribs
no costal groove
Function of costal groove
Intercostal veins and blood vessels run through
What is a supernumeracy rib? Risk associated?
extra rib
most likely to occur at cervical level (C7 at vertebra)
Can cause compression of neurovascular structures
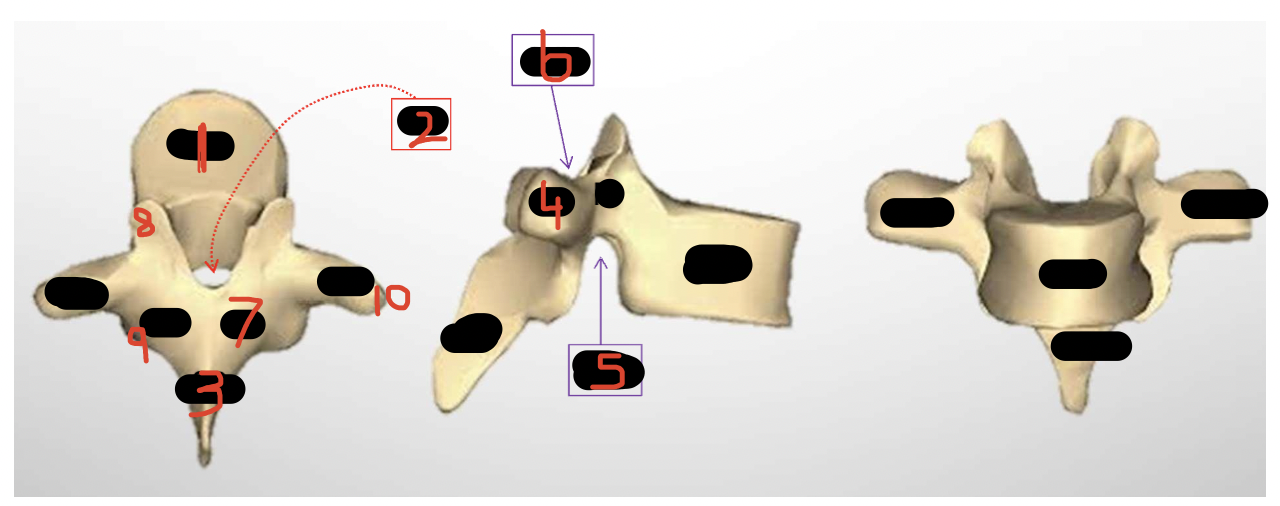
Label the thoracic vertebra
Vertebral body
Vertebral foramen
Spinous process
Transverse process
Inferior vertebral notch
Superior vertebral notch
Lamine
Superior articulator notch (articulation with other vertebrae)
Inferior articulator notch (articulation with other vertebrae)
Articulate facet (articulates with rib)
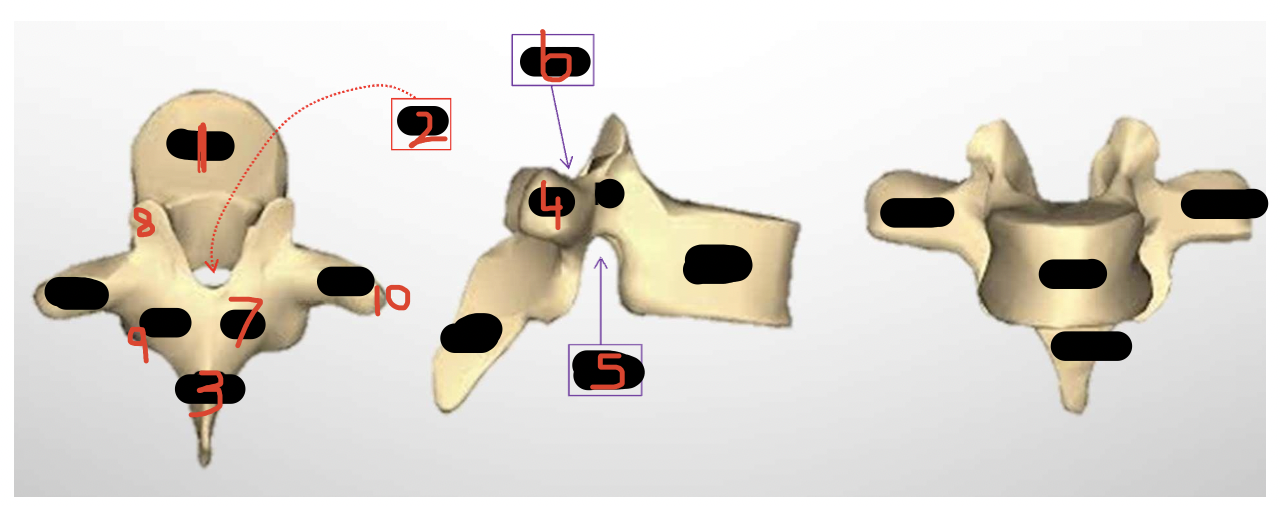
3 parts of the sternum
Manubrium
Body
Xiphoid process
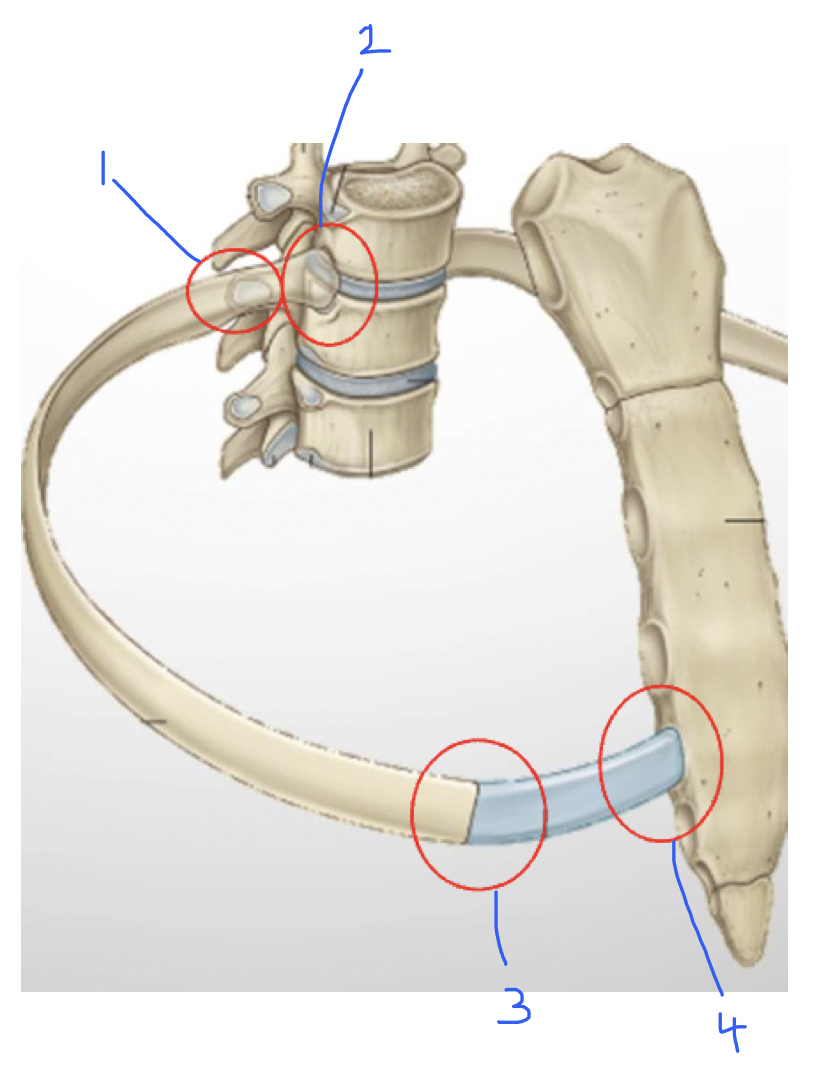
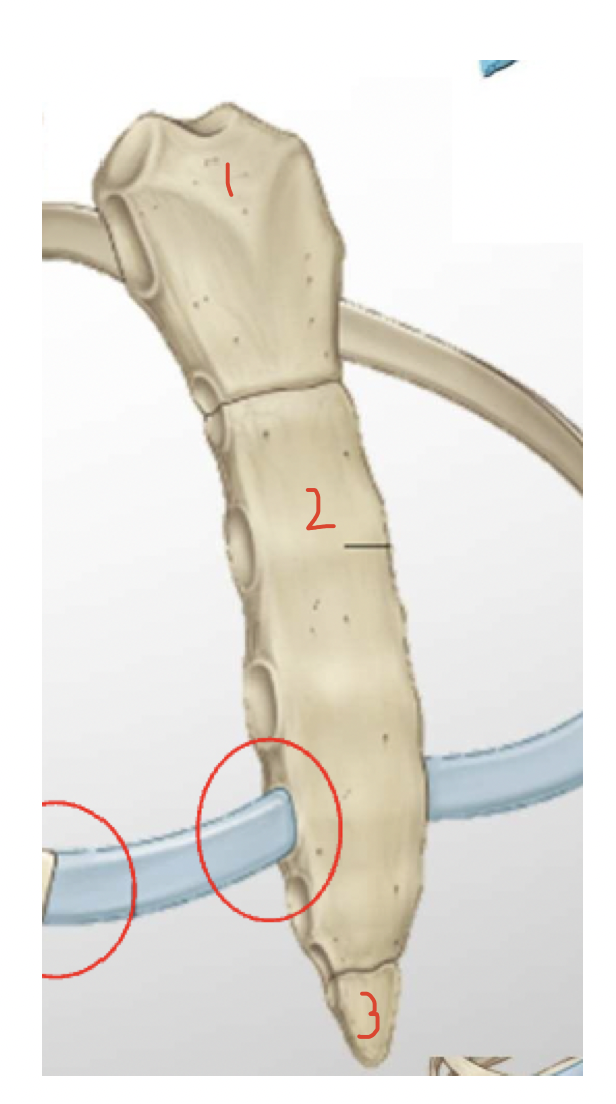
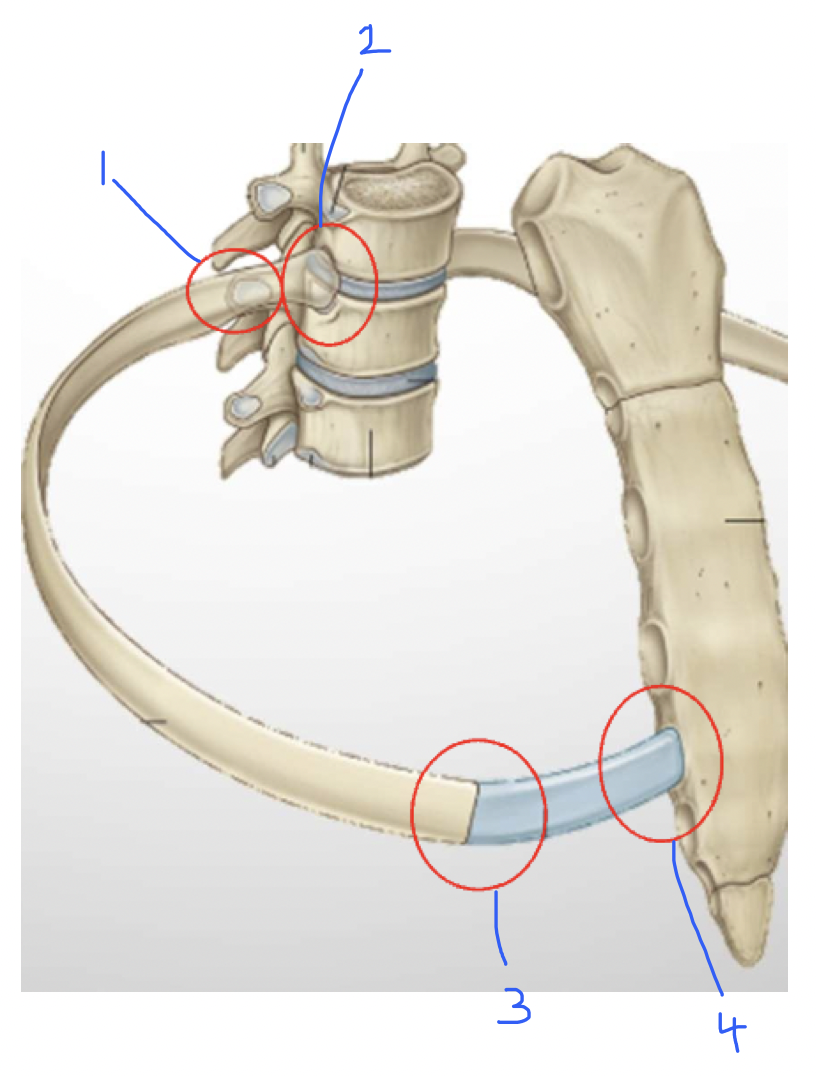
Costovertebral joint - rib articulates with superior and inferior articulator facets
costo transverse joint - articulation of rib’s tubercule with articulator facet of the transverse process of the vertebra
costochondral - primary cartilagenous joint (costal cartilage-rib)
sternocostal joint - costal cartilage - sternum
Features of ribs from infants - 2
almost horizontal (as in full inspiration position in adults)
Ribs from 2 years up & benefit?
Oblique - increases thoracic breathing
Ribs in old age
lose elasticity (cartilage ossifies)
thorax less involved in respiration (more work for diaphragm)
“Pump handle” breathing /A-P expansion
sternum raises
ribs elevate (oblique - horizontal)
expansion (anterior - posterior diameter of thorax)
“Bucket handle” breathing/Lateral expansion
movement of sternocostal joints & vertebral column
rivs raise (oblique-horizontal)
expansion (lateral diameter thorax)
Diaphragm at rest
Domed
Diaphragm on inhale/during inspiration
Flattens
Pulls down central tendon
Increases vertical diameter of thoracic cavity
Where is diaphragm located?
Attached to costal margin, xiphoid process, vertebral column (at level T12 + L2)
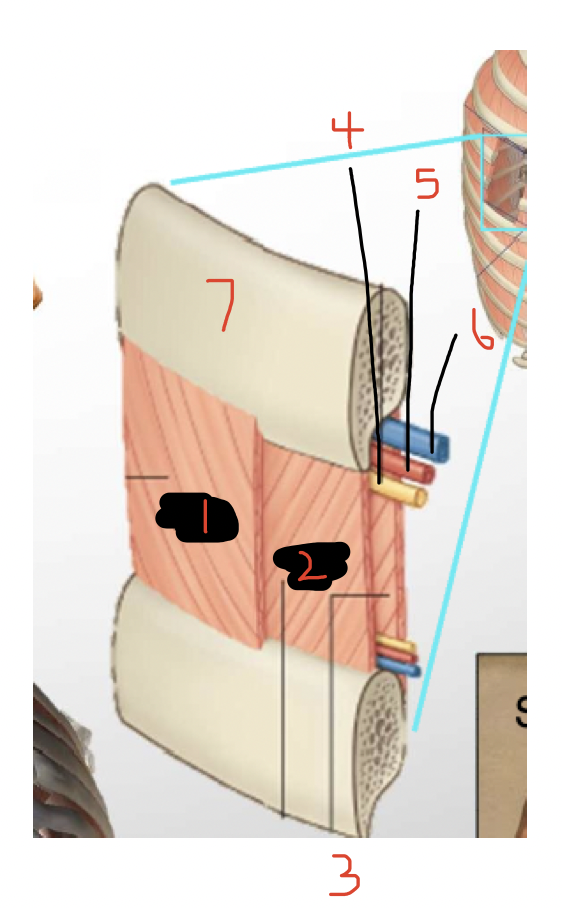
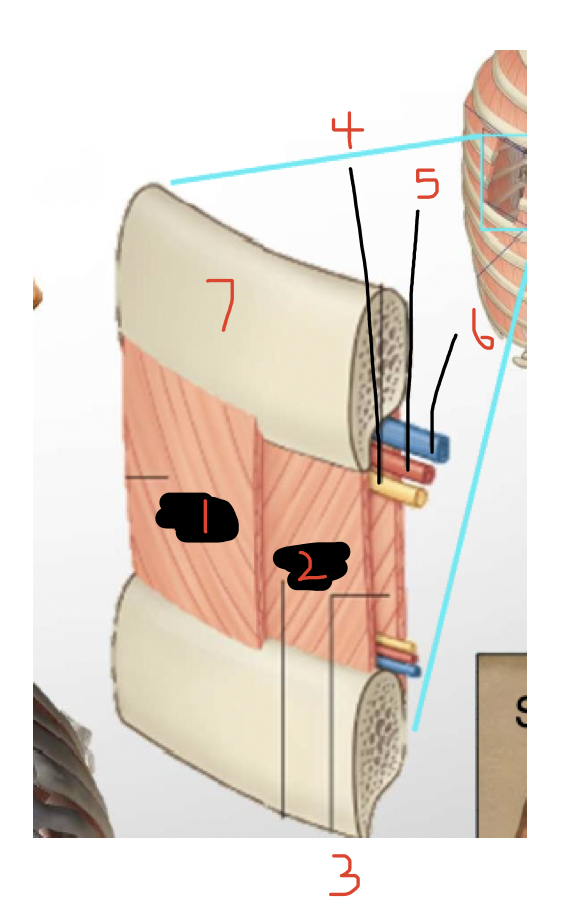
Label
External intercostal muscle
Internal intercostal muscle
Innermost intercostal muscle
Nerve
Artery
Vein
Rib
(4,5,6 - neurovascular bundle - run in costal groove)
Primary muscle of inspiration?
Diaphragm
Right dome of diaphragm higher than left, why?
Liver
Other functions of diaphragm
septum between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity
aids in increasing intra-abdominal pressure (facilitates defecation, micturition, parturition)
Thoraco-abdominal pump - forcing blood to heart (vena cava)
Nerves supplying diaphragm?
C3, 4, 5 keeps the diaphragm alive - Phrenic nerve
Openings in diaphragm
Caval opening (vena cava and branches of phrenic nerve)
Oesophageal opening (Oesophagus and vagus nerve)
Aortic opening -behind diaphragm (aorta and thoracic duct)
Role of external intercostal muscles?
Muscles of inspiration
Role of internal intercostal muscles?
Muscles of expiration
Role of innermost intercostal muscles
Stabilise chest wall
Accessory muscles - role in breathing?
Assist in deep inspiration or in respiratory distress

Name accessory muscles
Pectoralis major/minor
Serratus anterior
Sternocleidomastoid
Pectoralis minor
Latissimus dorsi

Muscles engaged in forced expiration?
Intercostals
Abdominal muscles
At vertebral level of T3…
Jugular notch
At vertebral level of T4/5…
Manubrial sternal joint/Sternal angle
At vertebral level of T9…
Xiphoid process
Vessels that supply the thorax?
Subclavian artery
Thoracic aorta
Axiliary artery
Posterior intercostals 1 & 2 are supplied by…
Subclavian artery
Posterior intercostals 3 - 11 are supplied by…
Thoracic aorta
Anterior intercostals are supplied by…
Subclavian artery (branch called: Internal thoracic artery)
Each intercostal never is a branch of …
a spinal nerve (ventral raumus)
Pathway of the phrenic nerve?
Runs alongside the anterior scalene muscle
Mediastinum is
Large compartment of thoracic cavity, contains vital organs
Organs found in mediastinum:
Heart
Great vessels
Pericardium
Trachea
Oesophagus
Thymus
Lymph nodes
What are the pleura?
2 double lined sacs, contain the lungs, located in thoracic cavity
Purpose of serous fluid
prevents friction during breathing
Where is serous fluid produced?
mesothelial cells in pleural cavity
What is the hilum of the lung?
entrance of the lung - for blood, oxygen
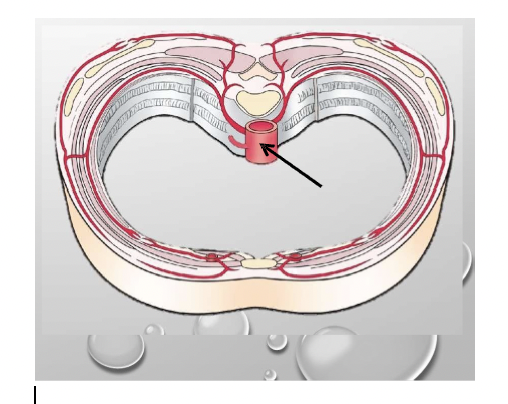
Label
Thoracic aorta
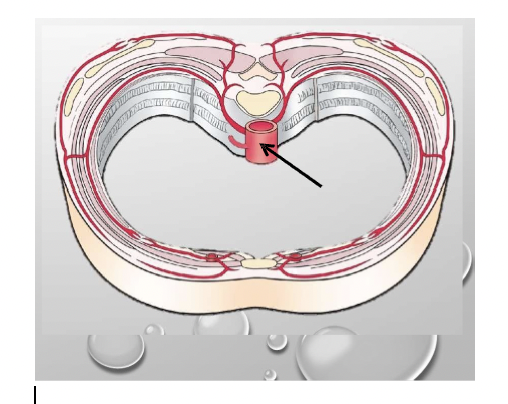
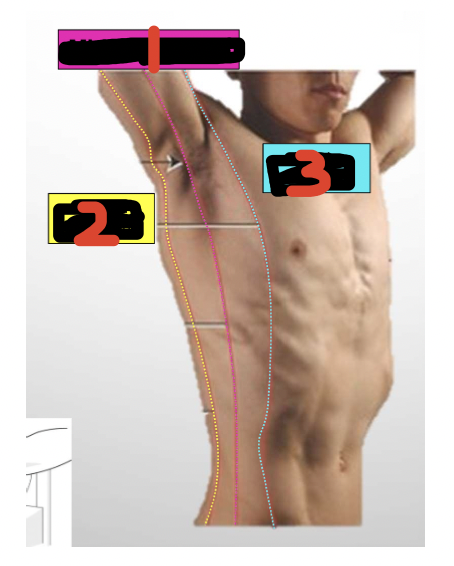
Label
Midaxillary line
Posterior axillary line
Anterior axillary line
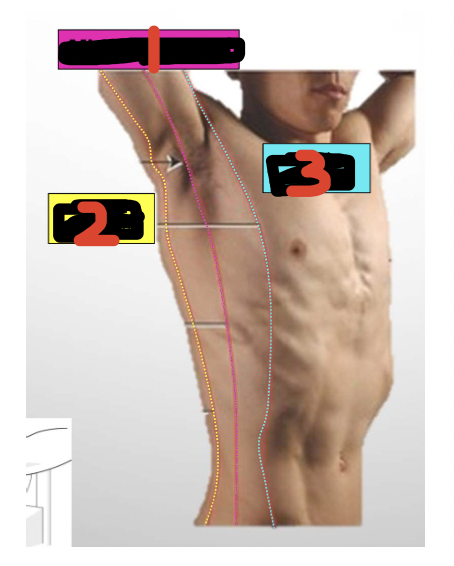
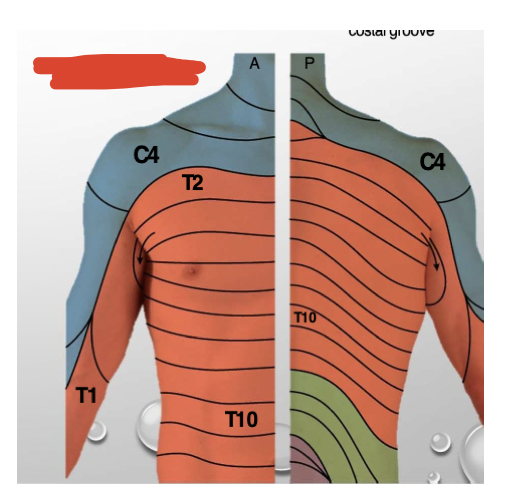
Name and explain
Dermatomes
Areas of skin that connect to a specific nerve root from the spine. Info travels through nerve to and from brain
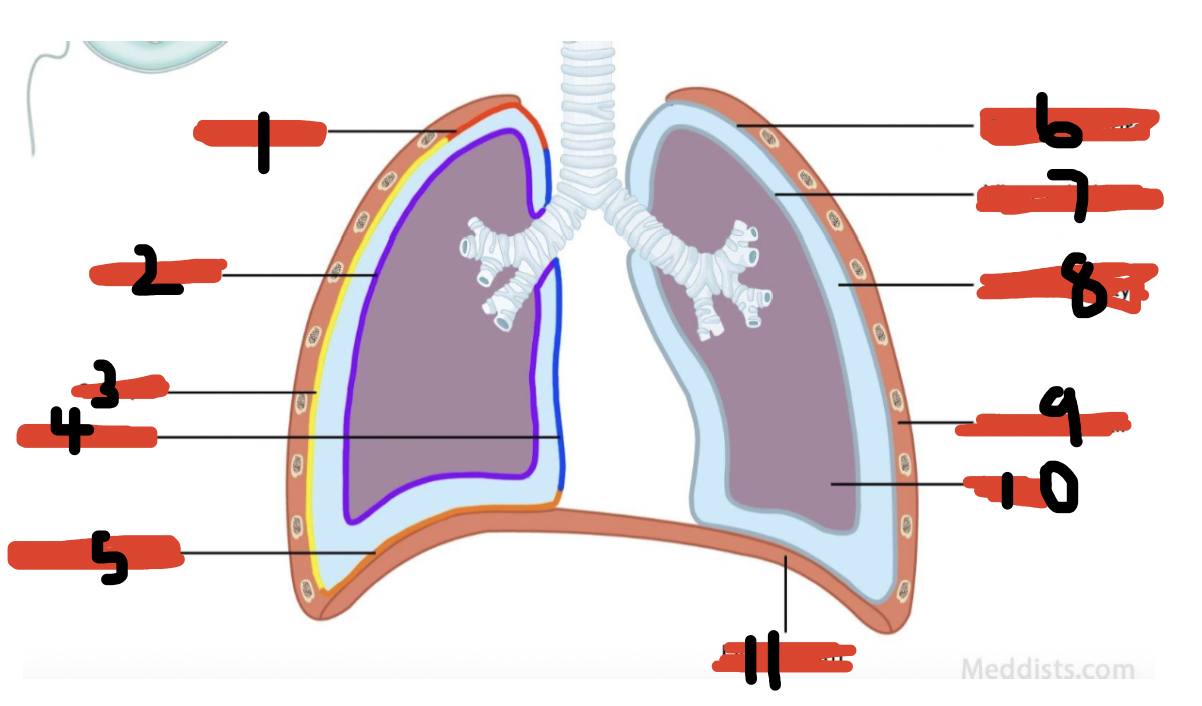
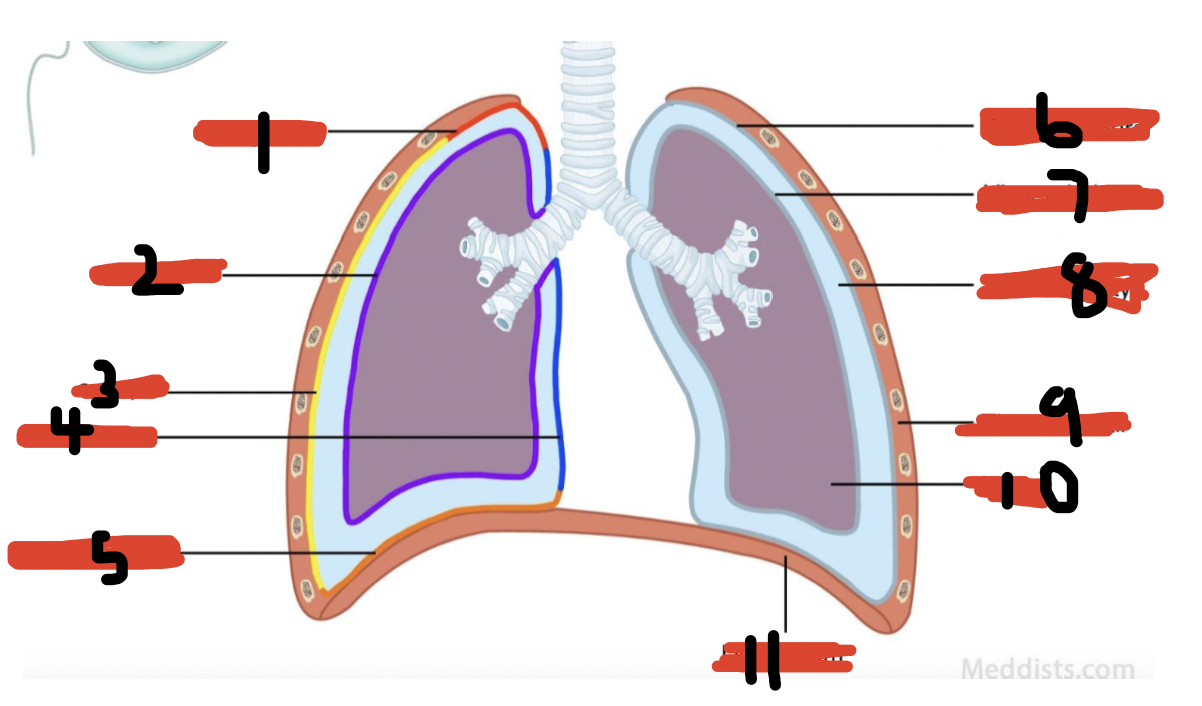
Label thoracic cavity
cervical pleura
visceral pleura
costal part
mediastinal part
diaphragmatic part
parietal pleura
visceral pleura
pleural cavity
thoracic wall
lung
diaphragm
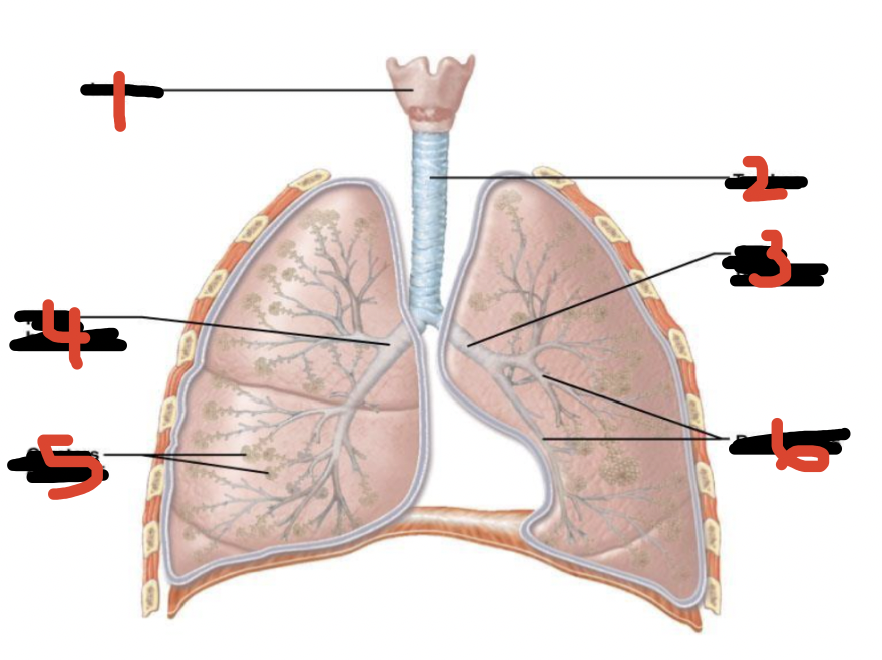
Label lungs
Larynx
Trachea
Left bronchus
Right bronchus
Alveoli (clusters)
Bronchioles
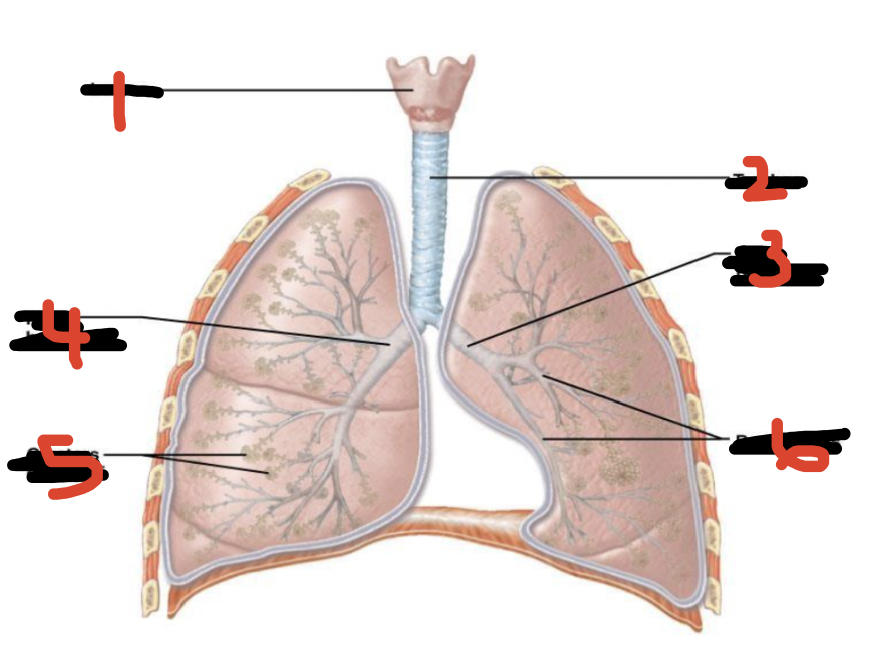
Function of trachea
Transports air to lungs
Structure of bronchi…
Trachea bifurcates into 2 branches (R&L) to enter into lungs
Main bronchus splits into lobar bronchi:
Right bronchus (3) - supply 3 lobes of lung
Left bronchus (2) - supply 2 lobes of lung
Lobar bronchi splits into segmental bronchi
What happens in the lungs?
Air transported to alveoli for gaseous exchange
In the alveoli…
Gaseous exchange occurs
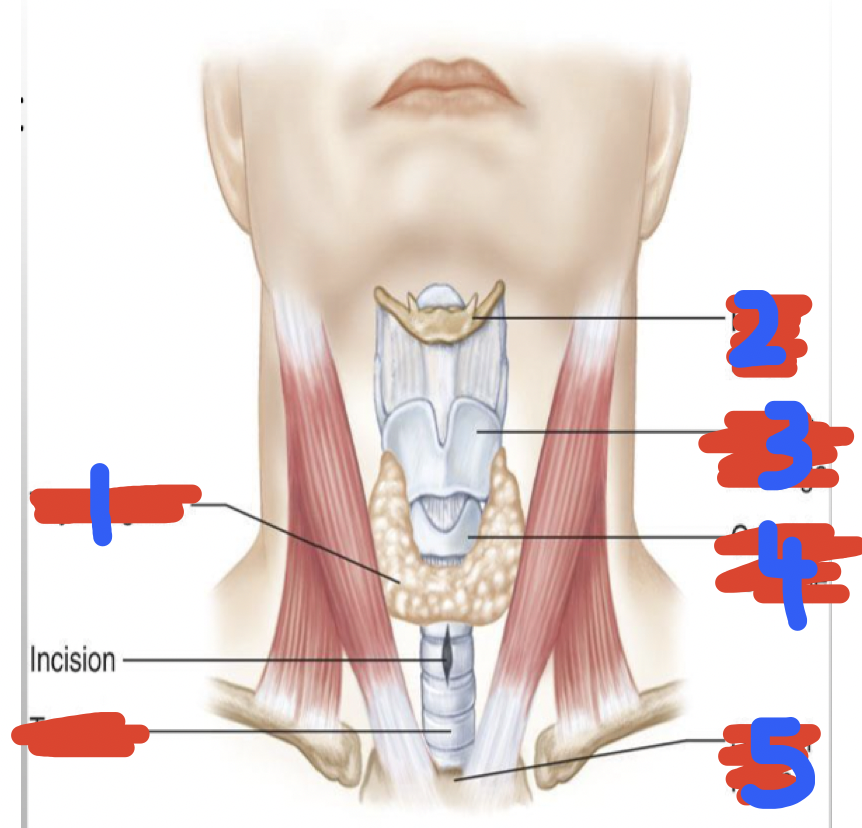
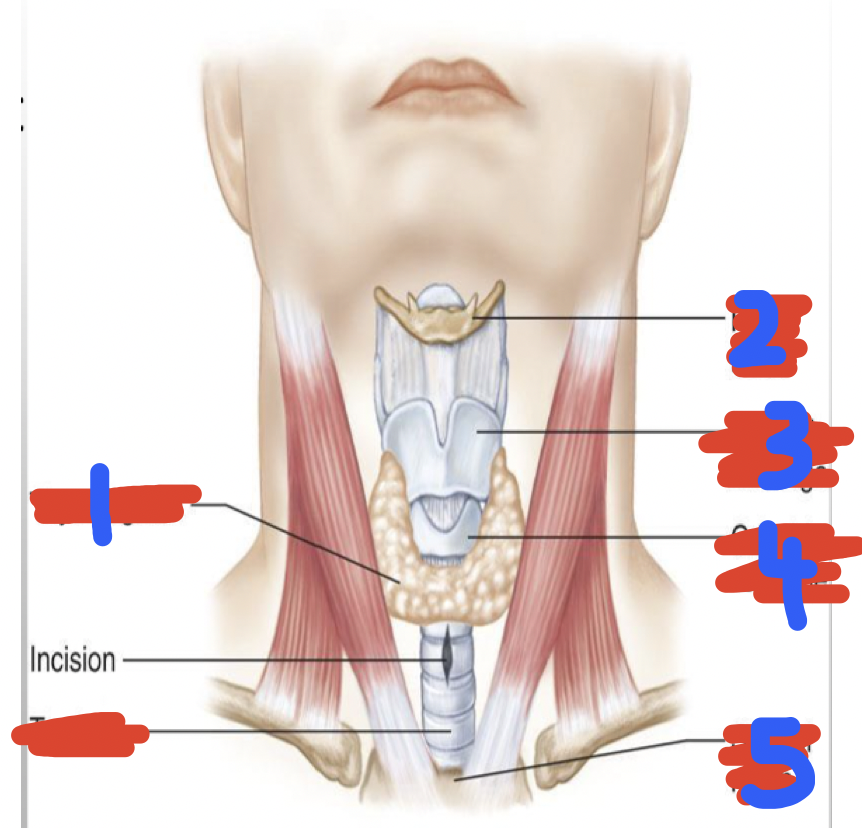
Label lower respiratory tract
Thyroid gland
Hyoid bone
Thyroid cartilage
Cricoid cartilage
Sternal notch
Trachea
Alveoli terminate into…
Alveolar sacs
Function of surfactant
Prevents alveolar walls from collapsing and sticking together
3 major types of cell in alveolar wall
Phagocyte
Type II cells
Alveolar macrophages
Pulmonary surfactant is produced by
epithelial type II cells
Functions of pulmonary surfactant:
Lowers surface tension at the air/liquid interface within the alveoli
Stabilises alveoli - prevents them from collapsing during inhalation
Increases lung compliance (easier to expand)
Alveoli are covered by…
Pulmonary capillaries
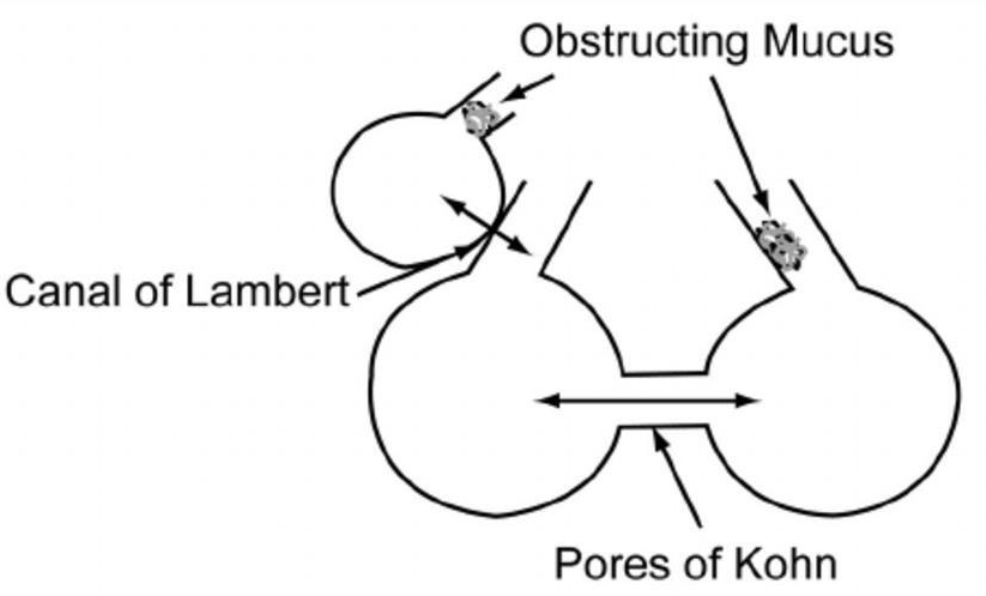
Pores of Kohn are…
Small holes in the walls of adjoining alveoli (alveolar septa) for movement of alveolar liquid, surfactant, macrophages
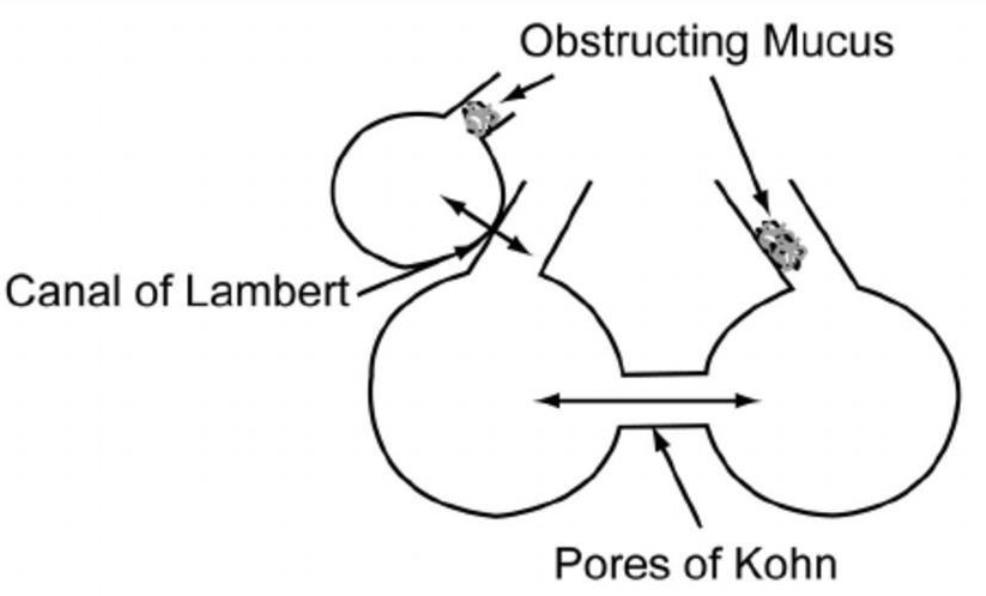
Canals of Lambert
connections in the lungs between some bronchioles and their adjacent alveoli - facilitate collateral movement of gases
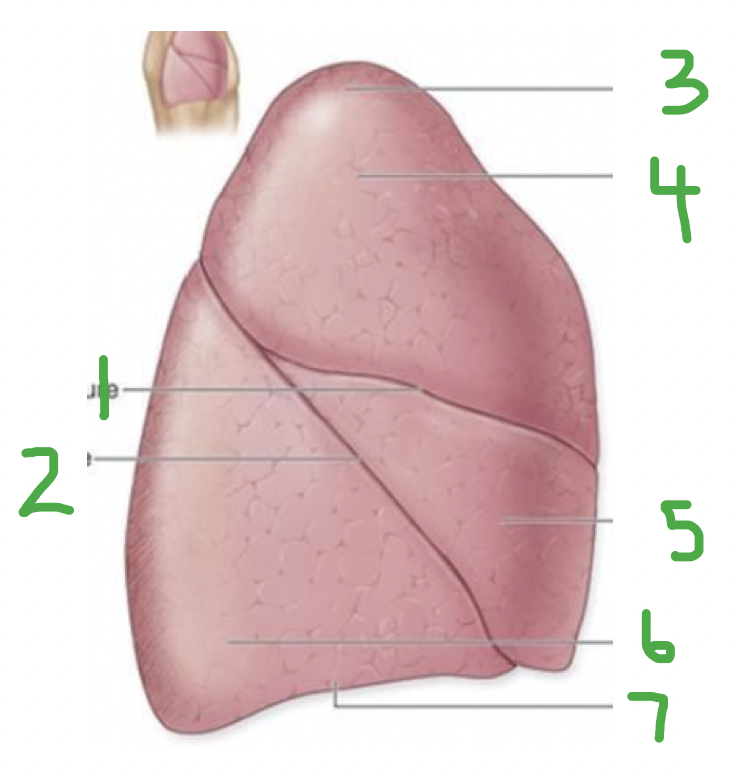
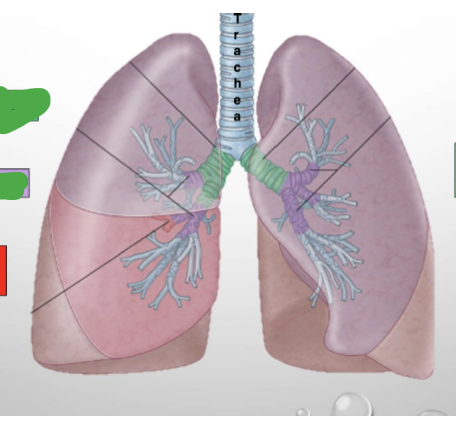
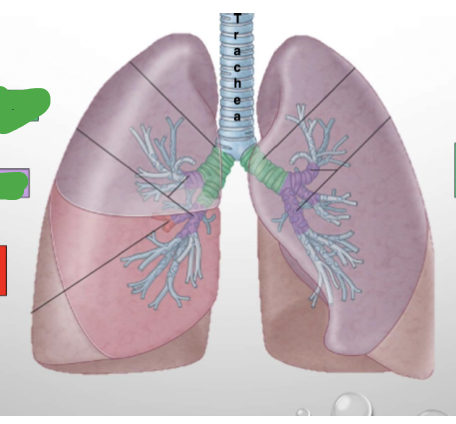
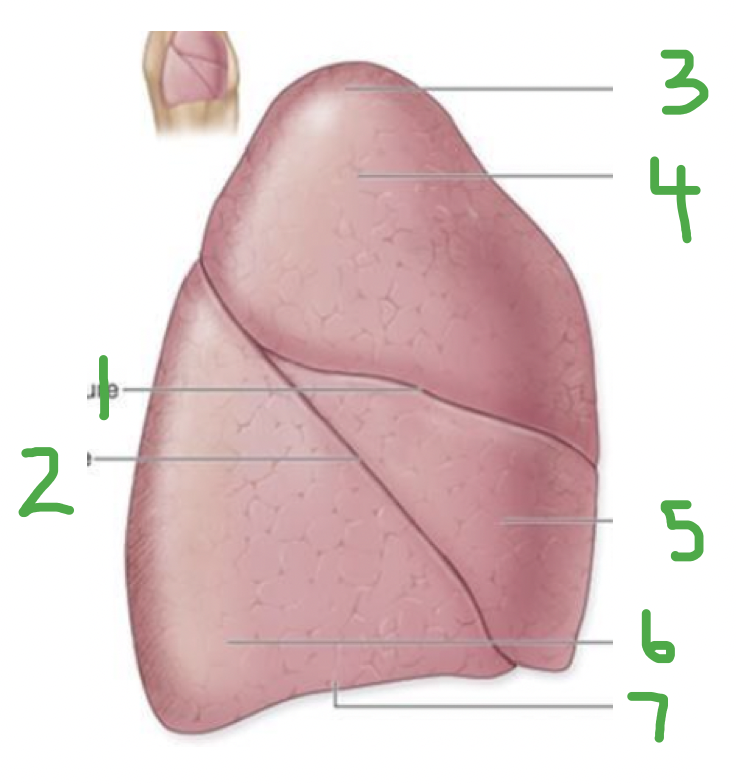
Which lung? Label.
Right lung
Horizontal fissure
Oblique fissure
Apex
Superior lobe
Middle lobe
Inferior lobe
Base
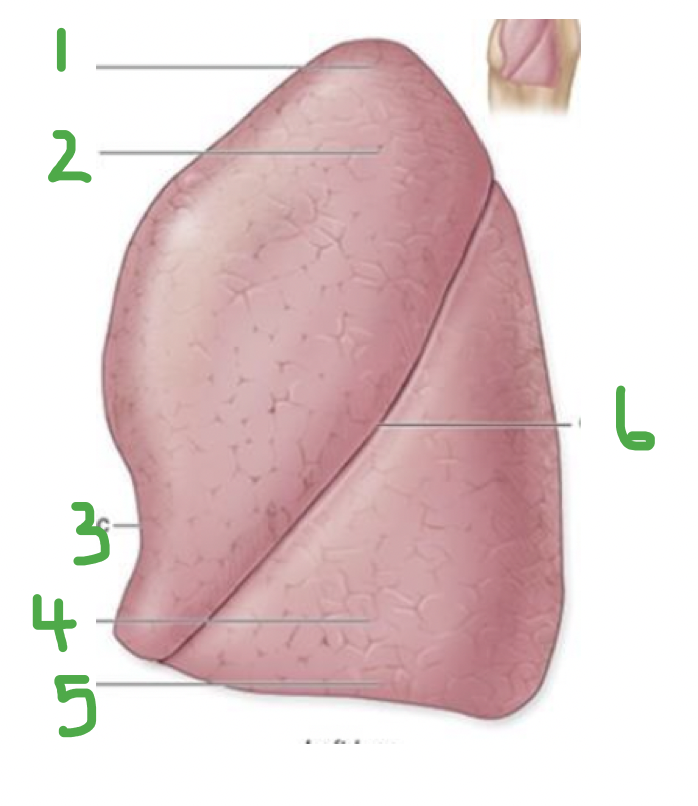
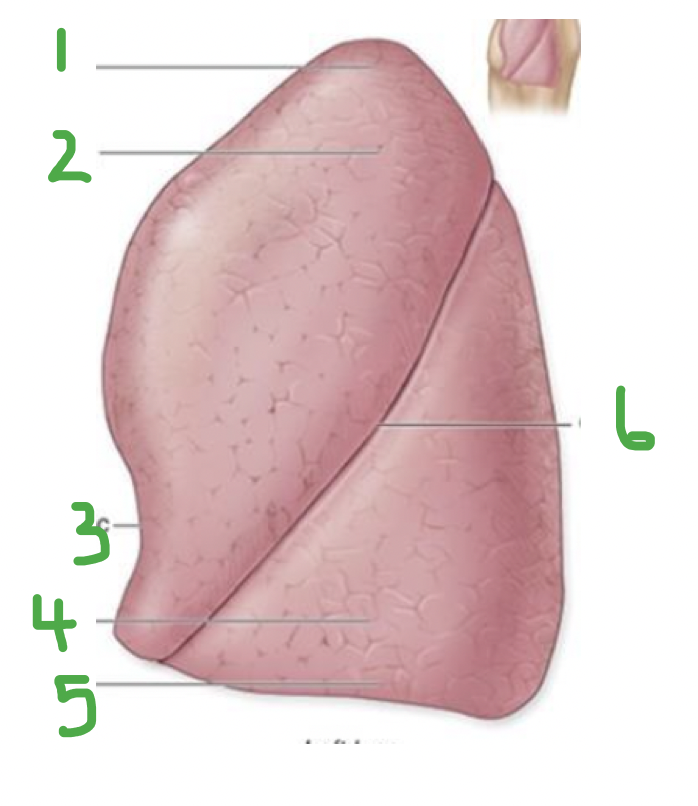
Which lung? Label.
Left lung
Apex
Superior lobe
Cardiac notch
Inferior lobe
Base
Oblique fissure
& Lingula describes projection in upper lobe - homologue of middle lobe (right lung)
Lungs are covered by a double layered sac called…
the pleural membrane
Layers of the pleural membrane:
Outer layer: Parietal layer
Inner layer: Visceral layer
Space between: Pleural cavity - pleural fluid/lubricant
Respiration involves…
The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between organism and external environment (involves respiratory and circulatory systems)
Conducting zone involves:
Larynx - terminal bronchioles
Air: larynx to lungs (no gas exchange)
air is filtered, warmed, moistened
involved in phonation
Respiratory zone involves:
respiratory bronchioles - alveolar sacs
contains sites of gaseous exchange
Alveolar pores are…
means of collateral ventilation - in the case of partial deflation, some ventilation
Type I alveolar cells
cover 95% of alveolus surface
physical support for alveoli
fast gaseous exchange
Type II alveolar cells are…
5% of alveolar wall surface area
Produce pulmonary surfactant
repair alveolar wall - replace damaged type I/II
Components of thoracic wall
spinal column
ribs
sternum
intercostal muscles
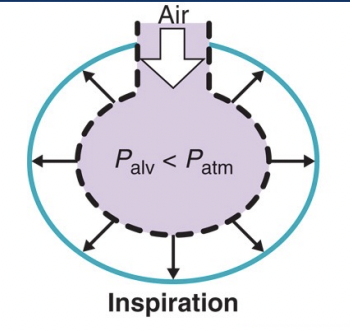
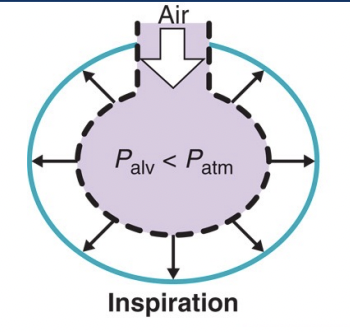
During inspiration…
Alveolar pressure < atmospheric pressure
air from external environment flows into lungs to balance pressure
movement stops when pressure stabilises
At rest alveolar pressure = atmospheric pressure
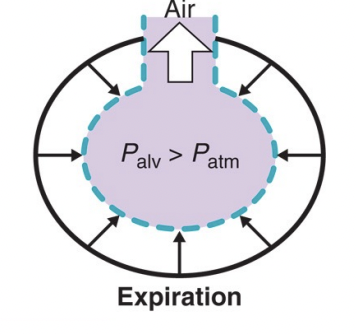
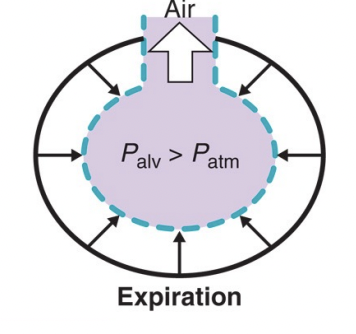
During expiration…
alveolar pressure > atmospheric pressure
air flows out of lungs to balance pressure
when pressure stabilises, air stops flowing out
At rest alveolar pressure = atmospheric pressure
Alveolar pressure =
760mmHg
Atmospheric pressure =
760mmHg
True or false: Lungs are active
False. Movement of air is regulated by volume/pressure
Lung volume depends on:
Transpulmonary pressure - between the inside and outside of the lungs
‘Stretchability’ of the lungs
What is transpulmonary pressure?
pressure difference between the inside and the outside of the lung
Transpulmonary pressure =
alveoli pressure - intrapleural pressure
At rest, alveoli pressure is…
0mmHg
At rest, intrapleural pressure =
-4mmHg
At rest, transpulmonary pressure =
4mmHg
Chest wall pressure =
intrapleural pressure - atmospheric pressure
At rest, chest wall pressure =
-4mmHg
What causes negative value for resting chest wall pressure?
Natural tendency for chest wall to spring forward (musculoskeletal anatomy); neg. pressure required to reduce chest cavity volume
What causes changes to transpulmonary pressure?
Contractions of respiratory muscles (change in volume) - changes in chest wall pressure = changes to transpulmonary pressure
Residual volume (RV) describes:
Amount of air remaining in lungs after maximum exhalation
Functional residual capacity (FRC) describes
Amount of air remaining in lungs after normal exhalation
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Amount of air in excess of tidal expiration that can be exhaled with maximum effort
Tidal Volume (TV)
Amount of air that can be inhaled/exhaled in one breath