The Humanistic approach
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is the humanistic approach?
the belief that humans have free will and so progress along their path to fulfil their deficit needs and achieve congruence and self actualisation
what are the basic assumptions of this approach?
Optimistic!
Person-centred
Acknowledges people have ‘Free Will’
Holistic (not reductionist)
how is the HA optimistic?
focus on growth and potential, not pathology/failure (which are emphasised in other approaches)
how is the HA person centred?
Looks at behaviour through the person’s OWN eyes, focuses on human experiences, uniqueness, meaning, freedom to change, personal growth and ability to choose
how to the HA consider free will?
Acknowledges people have ‘Free Will’ and seek personal growth and self-direction - behaviour is NOT simply determined/forced by our environment or subconscious influences
how is the humanistic approach holistic?
Views people as whole, complete beings who are active agents in their experience- rejects the scientific method as an invalid way of understanding human behaviour – we are too unique
what did Abraham Maslow believe?
humans are motivated by needs beyond those of basic biological survival.
All 4 lower levels of the hierarchy must be met before an individual can work towards self- actualisation
he was not interested in what went wrong with people but rather What went right with them?
what did Maslows hierarchy of needs emphasise?
the importance of personal growth and fulfilment
what did M’s hierarchy of needs lead to?
opened the door for later movements in psychology such as positive psychology and happiness.
define self actualisation
a form of peak experiences, moment of extreme inspiration during which individuals are able to leave behind doubts and fears and inhibitions
how did rogers describe self actualisation?
its the drive to realise ones true potential
how did maslow define self actualisation
its the final stage of his hierarchy of needs
what are the characteristics of someone who has achieved self actualisation?
creative
accepting of other people
have an accurate perception of the world around them
what does Maslow’s theory emphasise?
uniquely human motivational factors - higher level needs are a later evolutionary development of the human species
what is Hierarchy of needs?
the motivational theory proposed by Maslow often displayed as a pyramid, the most basic needs are at the bottom and the higher needs are at the top, Each level has to be completed and fulfilled before an individual can progress to the next one
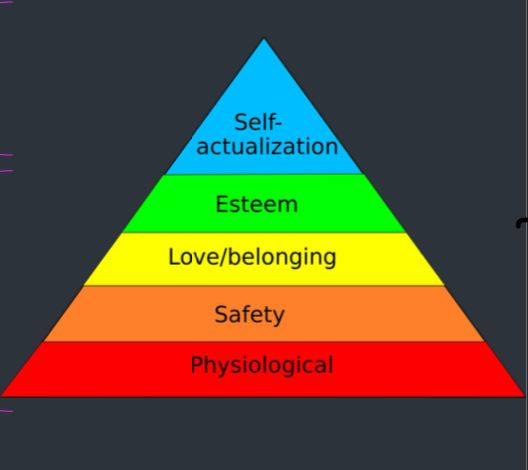
what do physiological needs consist of?
breathing
food
water
sex
sleep
excretion
what do safety needs consist of?
security and safety
health
income
property
control
what do love/belonging needs consist of?
friendship
family
community
social inclusion
what do esteem needs consist of?
self-esteem
confidence
respect (for and by others)
what do self actualisation needs consist of?
moments of extreme inspiration and fufilment
morality
appreciation of beauty
creativity
problem-solving
acceptance
lack of prejudice
define perceived self
how we see ourselves
define ideal self
how we really want to see ourselves
what is congruence?
if there is similarity between a persons ideal self and self image, a state of congruence exists
what is incongruence?
when there is a big difference between self-concept and ideal self- leads to low self-esteem
what is self esteem?
the degree to which we value ourselves
define unconditional positive regard
being valued by others regardless of what we do
define conditions of worth
being valued by others only when we have met their conditions
what is client-centred therapy?
if therapist gives client unconditional positive regard , genuineness and empathy, the client can reduce the level of incongruence and build self-esteem – helps them function better and achieve self-actualisation
what are the strengths of this approach?
Holistic, not reductionist (in contrast to other approaches, more than the sum of their parts loss of humanity lose the richness)
emphasis on free will (behaviourist approach says our behaviour is conditioned, biological genetic make up, emphasis optimistic active agents able to make choices)
practical application (counselling therapy, present problems self discovery growth)
how is the HA being useful for therapies a strength?
it’s particularly beneficial due to acknowledging the individuals do have free will and do have the ability to improve themselves through folksinging or developing solutions to the patients current problems
what are the limitations to this approach?
is not scientific (can be subjective not based on lab experiements with highly controlled conditions, use quality i’ve research methods case studied self reports, emphasise on individual experiences how’re gives us more depth)
some people / (cultures, needs may appear in a different order – or may even be absent altogether! self actualisation applied to western societies not collectivist cultures, achievement of group may be valid more highly, ethnocentric)
why isn’t the HA scientific?
most of the evidence used to support this approach fails to establish a casual relationship between variables
how is the HA subjective?
Rogers’ approach focuses solely on the patient's internal self-evaluation, ignoring situational factors
how to humanist therapists regard themselves?
as guides or facilitators to help people understand themselves and to find ways to enable their potential
why might people with low congruence use defence mechanisms?
most people prefer to see themselves in ways that are consistent with their self image. They may use defence mechanisms in order to feel less threatened by inconsistencies between how they would like to be and how they really are.