Biology CLEP
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CLEP Website: https://clep.collegeboard.org/clep-exams/biology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
What type of bond joins oxygen to hydrogen within a single water molecule?
polar covalent bond
Why is the bond between oxygen and hydrogen within a single water molecule a polar covalent bond?
The oxygen atom has a higher electronegativity than the hydrogen atoms, causing the shared electrons to be pulled closer to the oxygen, resulting in a partial negative charge on the oxygen and a partial positive charge on each hydrogen. This is an unequal sharing of electrons.
Polar Covalent Bond
A type of chemical bond where electrons are shared unequally between two atoms due to a difference in their electronegativity, resulting in one atom having a slightly positive charge and the other having a slightly negative charge. One atom pulls the shared electrons closer to itself more strongly than the other atom does
Nonpolar covalent bond
A type of chemical bond where two atoms share electrons equally, meaning there is no uneven distribution of electrical charge between the atoms involved, typically occurring when the atoms have similar electronegativity values; essentially, both atoms “pull” on the shared electrons with the same force. Key points: EQUAL ELECTRON SHARING and SIMILAR ELECTRONEGATIVITY
Peptide bond
A covalent bond that links amino acids together to form a protein
Ionic Bond
Results from the attraction between oppositely charged ions
Hydrogen Bond
A dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. Results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as N, O, or F and another electronegative atom.
Dipole-Dipole
Polar molecules align so that the positive end of one molecule interacts with the negative end of another molecule. Weaker than ionic or covalent but stronger than London and ion-ion. Not very effective in the gaseous state because molecules are far apart.
The smallest unit of matter that has the properties of a particular element is a/n
atom
A carbohydrate monomer is called a/n
monosaccharide
Carbosaccharide
Organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Main source of energy for the body (controls blood glucose and insulin metabolism) and structural components in plants (glucose chains in amylose and amylopectin)
Monosaccharide
The simplest form of carbohydrates, which are simple sugars. Examples include glucose and fructose.
What are glucose and fructose?
Monosaccharides
Monohydrate
A chemical term for a substance that contains one molecule of water for each molecule of combining compound.
What substances are monohydrates found in?
creatine and dextrose (sweetener, energy source and bulking agent)
What are monohydrates used for?
To improve muscular endurance, recovery and energy levels
How are monohydrates made?
They are made outside the body from sarcosine and cyanamide. Then these compounds are heated and pressurized in a reactor to form creatine crystals.
Amino Acide
molecules that combine to form proteins. The result of proteins being digested or broken down
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids that are linked together by peptide bonds. Essential for the structure and function of cells and tissues.
Which of the following RNA sequences would bond to this DNA strand?: AATAG
UUAUC
DNA and RNA base pairing
Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) in DNA and uracil in DNA
Guanine (G) always pairs with cytosine (C) in both DNA and RNA
The key difference is that DNA uses thymine while RNA uses uracil as its complementary base to adenine
DNA base pairs
Adenine (A) with Thymine (T), Guanine (G) with Cytosine (C)
RNA base pairs
Adenine (A) with Uracil (U), Guanine (G) with Cytosine
Importance of DNA and RNA base pairs
This complimentary base pairing is crucial for maintaining the structure of DNA and RNA molecules, as well as for processes like transcription (copying DNA into RNA) and translation (converting RNA into proteins)
Transcription
The process of creating an RNA molecule from a DNA template
AAUAG
TTATC
UUAUC
AATAG
TTATG
AAUAC
AATAG
UUAUC
A covalent bond occurs when
two atoms share electrons between them, effectively filling their outer electron shells and achieving stability by forming electron pairs
Two atoms are attracted to each other
chemical bond
One atom donates an electron to another
Ionic bond
Two atoms share an electron
Covalent bond
One atom steals an electron from another
Ionic bond
What property of water allows life to exist in a lake when temperature is below freezing?
Solid ice has a lower density compared to its liquid state. The ice floats on water, creating an insulating layer on the surface and allowing aquatic life to survive in the liquid water below the ice.
The nearly universal nature of the genetic code supports the view that
all living organisms on Earth share a common ancestor
Structure and Function of Cell Organelles
cell basics
Cytoplasm and cell membrane
Nucleus
Ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondria and chloroplasts
Cytoskeleton Cell Wall
Properties of cell membranes
membrane basics
selective permeability
transport basics
passive transport
active transport
Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
cell basics
prokaryotic cell characteristics
eukaryotic cell characteristics
Castes
specialized groups within a social insect colony, each with a distinct function and morphology like the queen, workers and soldiers in an ant colony
Arthropod
A phylum. Possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, differentiated segments and paired jointed appendages
Thermal stratification
The formation of distinct, stable layers in a body of water (like a lake or ocean) due to temperature differences, with warmer, less dense water at the surface and colder, denser water at the bottom
Batesian mimicry
A harmless species mimicking a dangerous one for predator avoidance
Mullerian mimicry
Multiple harmful species sharing similar warning signals, both benefiting from reduced predator learning costs
The aerobic cellular respiration of glucose is different from the simple burning of glucose in that the aerobic respiration of glucose does which of the following?
occurs at a lower temperature
releases no heat
releases more energy
requires no oxygen
releases hydrocarbons
occurs at a lower temperature
Aposematic coloration
An adaptation where animals signal their unpalatability or danger to predators through conspicuous colors or patterns
Agonistic behavior includes these behaviors
aggression, threat, appeasement, avoidance
Agonistic Behavior
The complex of behaviors, including aggression, threat, appeasement and avoidance that occur during conflicts or contests between members of the same species
Appeasement
Behaviors that signal submission or a lack of aggressive intent, such as rolling on the back, lowering the head, or presenting the neck
Cryptic coloration
A defense strategy where organisms use color patterns and textures to blend in with their surroundings, making themselves harder to spot by predators or prey
The path of urine out of the kidney
ureter → bladder → urethra → out
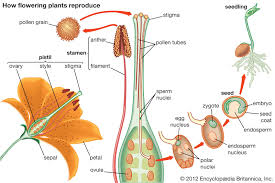
Stamen
Male reproductive organ in plants

Pistil
The female reproductive organ in plants
PMAT (C)
Prophase, metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase (Cytokinesis)
King Philip Can Order Fried Goat Sometimes
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
What makes up the four biomolecules
CHO-CHO-CHON-CHONP
mEiosis
E for egg, sex cells
mItosis
I for identical ccells
Analogous
structures or traits in different species that have similar functions but evolved independently, not from a common ancestor, due to convergent evolution
Homologous
similar structures in different species that share a common evolutionary origin
Convergent
Organisms that aren’t closely related evolve similar features or behaviors, often as solutions to the same problems. The process can result in matching body shapes, color patterns or abilities
Divergent
When individuals in one species, or closely related species, acquire enough variations in their traits that it leads to two distinct new species
Enzyme
A protein produced by cells of living organisms. It functions as a catalyst, accelerating or instigating specific biochemical reactions within an organism
What protein produced by the cells of living organisms functions as a catalyst, accelerating or instigating specific biochemical reactions within an organism?
Enzyme
Eukaryote
Cells that contain membrane-bound organelles, including a true nucleus enclosed by a nuclear envelope and a mitochondrion that acts as an energy-producing powerhouse of the cell
Pinocytosis
A form of endocytosis in which cells engulf extracellular fluid that is not permeable through the cell membrane
Cytokinesis
A division of a parent cell’s cytoplasm that occurs after mitosis is complete
Daughter cell
During mitosis, a parent cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells, which contain the same type and number of chromosomes as the parent
Histones
Proteins that are found in chromatin and function as spools around which DNA strands can wrap themselves. They organize DNA strands into structures known as nucleosomes
Germline mutation
An inherited mutation that arises from alterations made to the sperm and egg cells; it is transmitted to offspring
Lysosome
A membrane-bound organelle created by the Golgi apparatus and used to break down food material found in animal cells that contain enzymes
Lagging strand
The strand of DNA that undergoes replication discontinuously in fragments during the elongation process
Pluripotency
The ability of a stem cell to give rise to multiple specialized cell types
Allele
One version of a pair of genes that is found on the same spot on a chromosome and controls the same trait in an organism. Individual inherit one of these from each parent.
Allosome
Refers to the X and Y chromosomes, which determine the sex of an offspring. All other nonsex chromosomes are called autosomes
Plasmid
DNA-containing molecules that are separate from chromosomal DNA and replicate independently. They are typically small, circular, form in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes, and commonly used in genetic engineering techniques
Adaptive radiation
A major mechanism of evolution in which a gene pool rapidly diversifies when a species is introduced to a new environment and must fill multiple new ecological niches
Background extinction rate
Teh background extinction rate is a measurement of how often species become extinct during a period of time
Incomplete dominance
A form of inheritance that occurs when one allele is not completely dominant over another allele, which results in a phenotype that expresses elements of both alleles
Epistasis
This occurs when a modifier gene expresses an expressed phenotype of another gene
Lysosome
A membrane bound organelle created by the Golgi apparatus and used to break down food material found in animal cells that contain enzymes