The phloem
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what does the phloem transport around plants?
sap
sap is made up of sucrose and amino acids - together these are known as organic solutes
what is the function of the phloem?
Movement of these organic solutes is from a 'source' to a 'sink'.
The source is anywhere in the plant that produces and loads it into the phloem.
A sink is anywhere in the plant that unloads sucrose from the phloem(and converts it into sucrose) and then uses it (e.g. respiration) or stores it (e.g. as starch).
The location of sources and sinks can change throughout the year.
Movement can therefore be up or down in the phloem.
^although not up and down at the same tube at the same time.
what is a source?
anywhere in the plant that produces and loads it into the phloem.
what is a sink?
anywhere in the plant that unloads sucrose from the phloem(and converts it into sucrose) and then uses it (e.g. respiration) or stores it (e.g. as starch).
can the phloem transport molecules up and down at the same time in the same tube or not?
The movement cannot be up and down at the same tube at the same time.
fill in the gaps
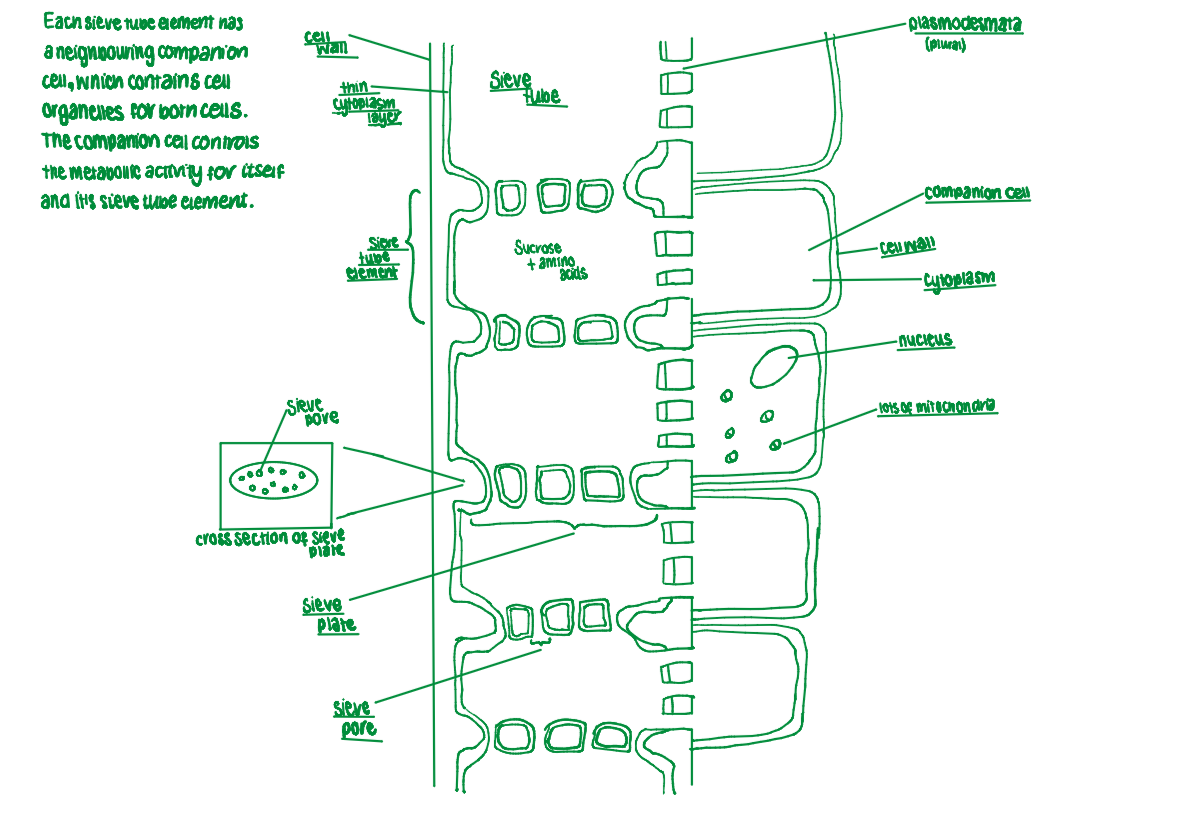
what is a companion cell?
a cell which attaches to the sieve tube element
it contains organelles for both cells
it controls the metabolic activity for itself and the sieve tube element
define sieve tube element
the main cells of the phloem that have greatly reduced living content and sieve plates between cells.