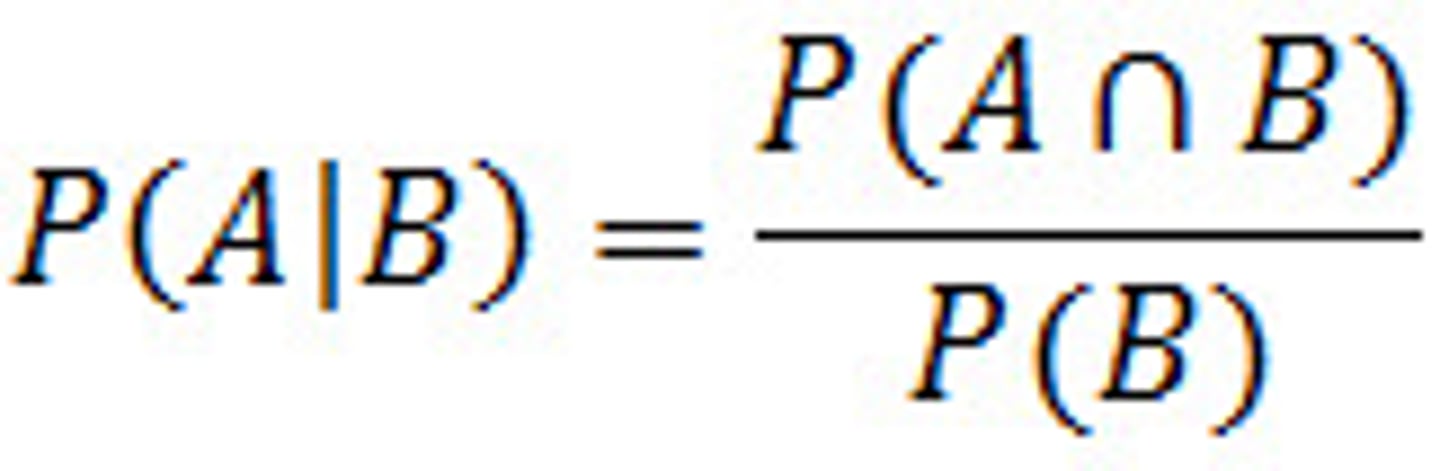Thẻ ghi nhớ: Probability rules | Quizlet
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is the term for the likelihood of an event occurring?
Probability of an Event (P(E))
What is the range of values a probability can take?
0 to 1 (0 = impossible, 1 = certain)
What are specific sets of outcomes within the sample space called?
Events
What rule applies when calculating the probability of either of two mutually exclusive events (A or B)?
Addition Rule: P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
What rule applies when calculating the probability of both independent events (A and B) occurring?
Multiplication Rule: P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B)
What rule relates the probability of an event (A) to its complement (not A)?
Complement Rule: P(not A) = 1 - P(A)
What is the probability of event A happening given that event B has already occurred called?
Conditional Probability: P(A|B) = P(A and B) / P(B)
What is the collection of all possible outcomes in a scenario called?
Sample Space
Probability of an Event (P(E))
This represents the likelihood of an event E occurring. It's expressed as a number between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates the event is impossible and 1 indicates it's certain.
Sample Space
This refers to the collection of all possible outcomes in a given experiment or scenario.

Events
These are specific outcomes or sets of outcomes within the sample space.
Addition Rule (for Mutually Exclusive Events)
This rule applies when two events (A and B) cannot happen together (they are mutually exclusive). The probability of either A or B occurring is the sum of their individual probabilities. P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)

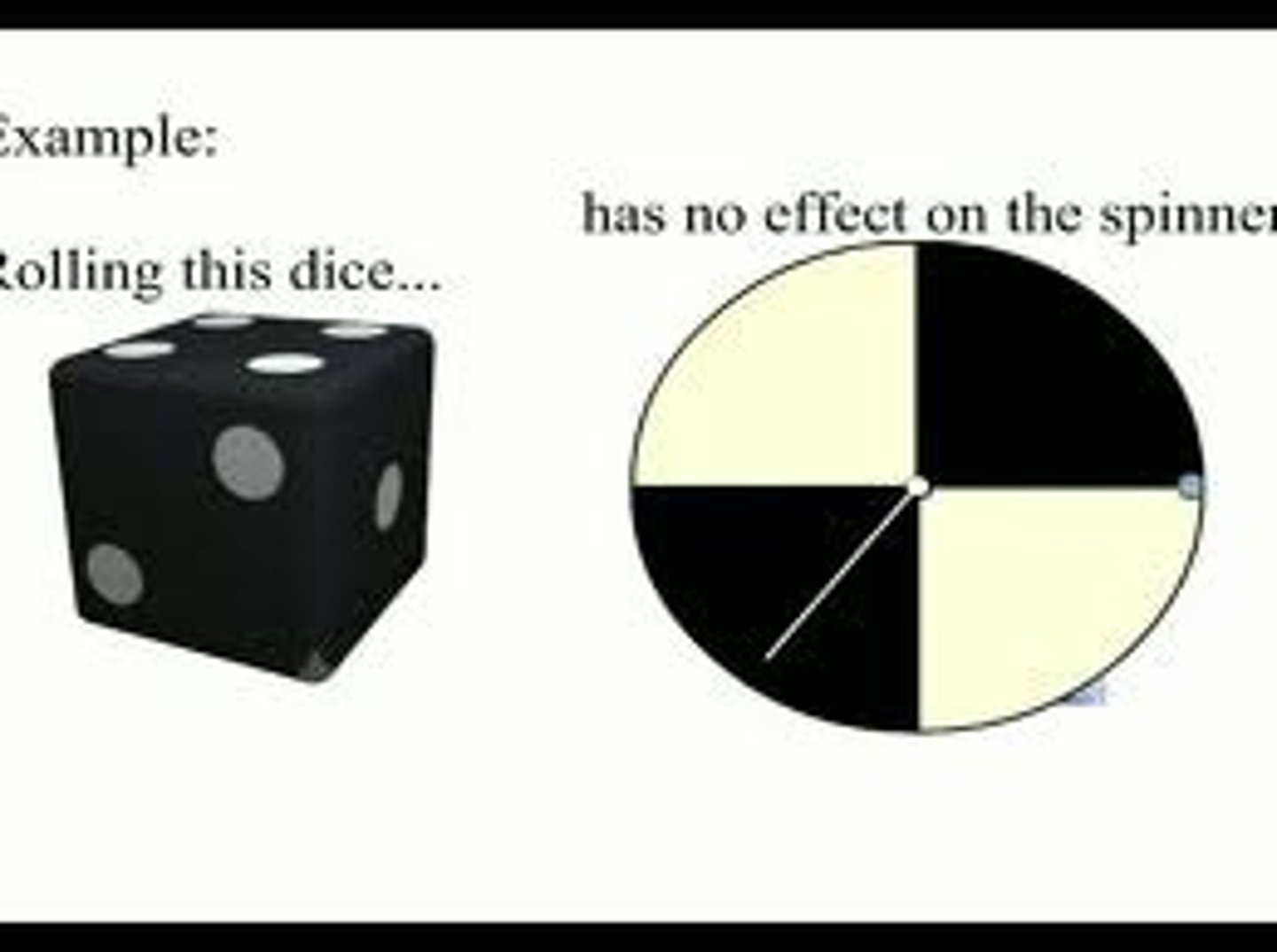
Multiplication Rule (for Independent Events)
This rule applies when two events (A and B) are independent (the outcome of one doesn't affect the other). The probability of both A and B occurring is the product of their individual probabilities. P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B)
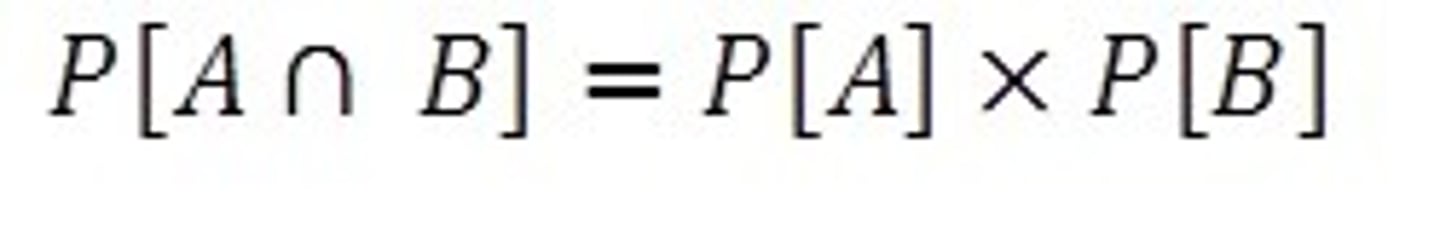
Complement Rule
The probability of the event A NOT happening (complement of A) is 1 minus the probability of A happening.P(not A) = 1 - P(A)
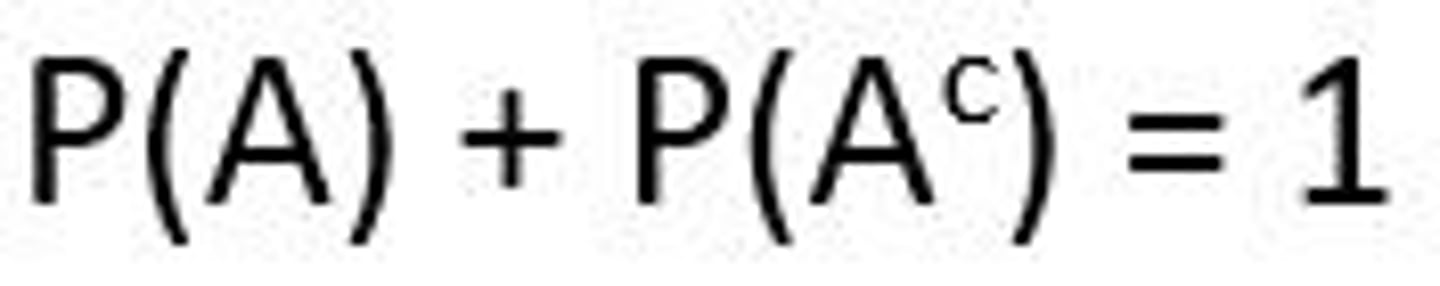
Conditional Probability
This is the probability of event A happening given that event B has already occurred. It considers the influence of B on the likelihood of A. P(A|B) = P(A and B) / P(B)