pacing, capture, thresholds
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
polarization
layers of negative and positive ions that surround the electrode during the pulse stimulus
it can slow the movement of charge
capture
successful depolarization of cardiac tissue from a pacing stimulus
stimulation threshold
minimum amount of energy required to cause depolarization
conduction
movement of a charge under the influence of an electrical field
voltage
force/push that drives a current
amplitude
variable
pulse width
duration of time in a pacing impulse (ms)
ex. 2.0V @ 0.4ms
current
flow of electrons measure in mAs
not programmable
calculated
constant
output capacitor
stores and delivers pacing impulses
impedance
resistance to the flow of current within an electrical circuit (ohms, Ω)
true
T/F: thresholds can change
true
T/F: auto capture algorithms can be tricked
true
T/F: a threshold can be checked on a pacemaker dependent patient
false, don’t want to pace faster than A-fib rhythm
T/F: A-fib always needs a threshold check
beginning of life
BOL
elective replacement interval
ERI
end of life
EOL
phase 0
rapid depolarization, Na+ rushes in
phase 1
initial repolarization
phase 2
plateau phase
phase 3
final repolarization
phase 4
alert period/resting phase
amplitude
how many volts are delivered per pacing impulse
safety margin
2:1
rheobase
smallest amplitude that stimulates the myocardium at an infinitely long pulse duration
used to calculate chronaxie
chronaxie
threshold pulse duration at 2x the rheobase voltage
approximates the point of minimum threshold energy
battery longevity
energy consumption determines what?
strength-duration curve
defines lowest amount of energy to reliably capture the heart
Ohm’s law
V = I x R
I = V/R
R = V/I
V → voltage
I → impedance
R → resistance
energy equation
E = (V2/R) x t
E → energy
V → voltage
R → impedance
t → pulse width
lead integrity
lead location
medications
electrolyte imbalance
arrhythmias → A-fib, A-flutter, sinus tach, slow VT
factors affecting threshold
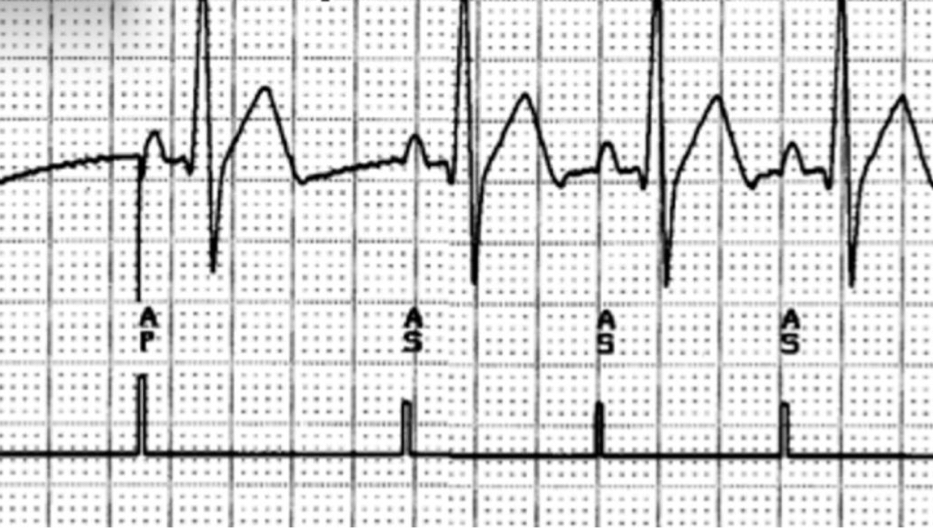
appropriate atrial capture
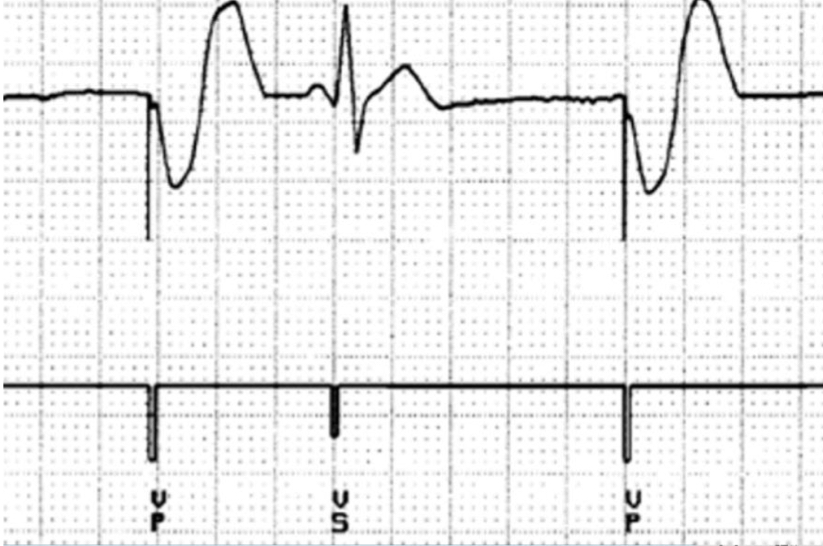
appropriate ventricular capture
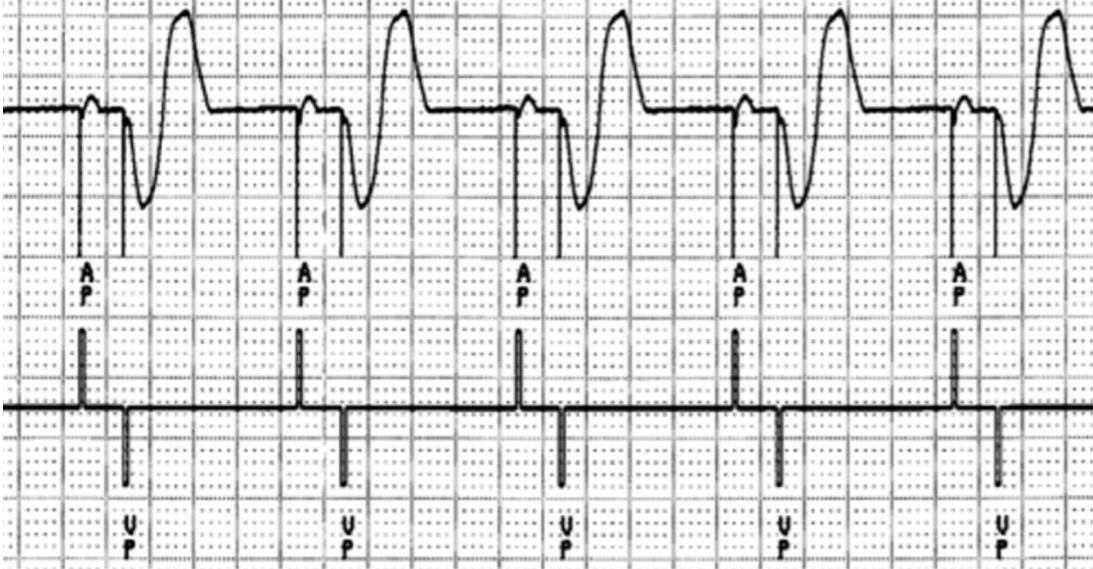
appropriate dual chamber capture
atrial failure to capture
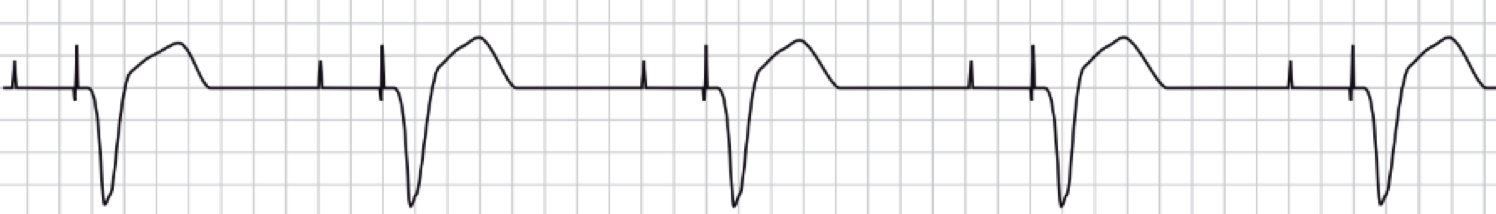
ventricular failure to capture
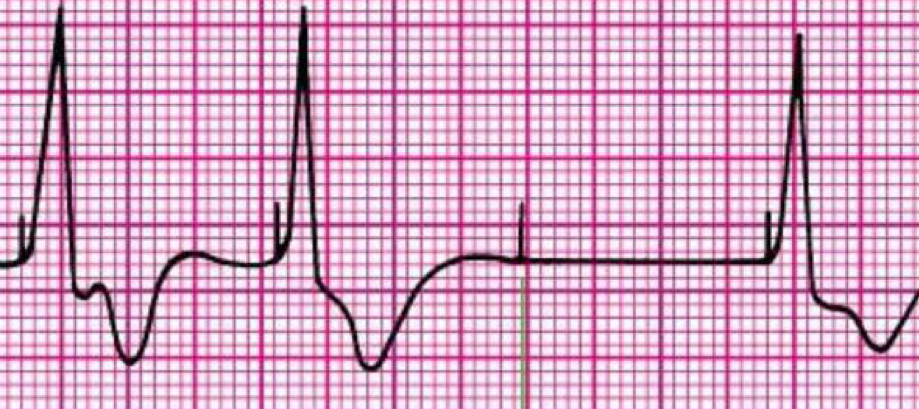
lead dislodgment
poor connection at connector block
lead maturation (exit block)
lead failure
low output (inappropriate programming)
failure to capture causes