Kin 202 Test 2 JMU Sanders Study guide questions
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is a force?
Forces - pushes or pulls
What do we call the sum of all forces acting upon an object?
Net Force
When an object's motion is not changing (no change in direction or velocity), what is the size of the Net Force acting on that object?
Gravitational force, downward force of gravity. Net force = Zero
What happens when the Net Force acting on an object is not 0?
There will be a motion in the object.
Provide examples of common contact forces in sport/physical activity.
Tennis - Hitting the tennis ball with your racket, Kicking a soccer ball.
Muscle forces can be concentric/isometric/eccentric. When a muscular force results in a concentric contraction, what does this tell is about the magnitude of the muscular force (in comparison to other forces present)? […Repeat the question above for isometric/eccentric]
The magnitude of the muscular force in a concentric contraction must be greater than the opposing external forces
In an isometric contraction, the magnitude of the muscular force is matched by the opposing external forces (such as gravity or the weight being held), resulting in no net movement at the joint.
In an eccentric contraction, the magnitude of the muscular force is less than the opposing external forces (such as gravity or the weight being lowered), resulting in controlled movement in the direction of the external force.
What is the length-tension relationship - and what influence does this have on muscle force?
Less than optimal length - Fewer cross bridge interactions = reduced tension development.
Optimal Length - Maximal cross-bridge interactions = maximal tension development. Can generate the most and best amount of force.
Greater than Optimal Length - No cross-bridge interactions = no tension development. Can't generate as much force.
What is the force-velocity relationship - and what influence does this have on muscle force?
The higher velocity the lower the force, the slower the speed the more force needed.
More force development during the eccentric weight.
What causes a gravitational force? What is the force of gravity on earth?
Related to the mass of two objects and the distance between them. G
The force of gravity is 9.8m/s^2
What is inertia?
"A body will move with constant velocity unless compelled to change by a net force."
An object at rest will stay at rest, object in motion will stay in motion
What factor(s) determines how much inertia an object possesses?
the larger the mass, the greater the inertia
What is "moment of inertia"? (rotational/angular motion).
a quantity expressing a body's tendency to resist angular acceleration
What factors determine the moment of inertia an object?
Mass distribution, Distance from axis (middle)
Provide examples from sport in which moment of inertia can be modified to influence performance.
Football, being larger and being heavier it is difficult to move that player due to higher inertia
Swimming depending on how much you tuck when you dive will change the moment of inertia and how you can manipulate your speed depending on your position.
What is a ground reaction force (GRF) - and what is its' magnitude (size) and direction?
Based on the idea that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
the ground reaction force is the force exerted by the ground on a body in contact with it. Its magnitude is typically equal to the body weight of the individual, and its direction is perpendicular to the ground surface, pointing upward.
How does the magnitude and duration (time) of a GRF differ between walking and running?
Walking the size of the force is much lower than running. When running the heel of your foot causes a lot bigger of a force than walking. A shorter force but much stronger
How does running mechanics influence the placement of a GRF on the foot?
Rearfoot strikers - Runners tend to land on the heel,
Midfoot strikers - Tend to land in a more neutral position on there foot. Lands in the center of the foot and spreads through to the front of the foot. More of a neutral pattern.
When moving through air/fluid, an object will ALWAYS experience a drag force. What direction do drag forces act on objects?
Drag force - opposes forward movement - influenced by friction drag and the turbulence of the wake.
Drag force is a direction opposite force of wherever the object is moving. If moving forward the drag force is backwards
What factors influence the magnitude of the drag force?
The surface
Smooth surface - small friction, lower drag force
Rough surface - rough surface, higher drag force
What is frictional force and how does it influence drag? Provide sport-specific examples of actions that can reduce frictional forces of an object moving through air/fluid - be specific how this action influences drag and performance.
In swimming the shark suits were so good they were banned because the suit was so skin tight and so smooth that is almost created no friction whatsoever which lowered the drag force allowing the swimmers to swim faster without almost any friction. The higher the frictional force the higher the drag force.
What is turbulence?
Turbulence air flow creates a region of low pressure, in response it results in a drag force
What effect does turbulent flow have on drag?
The more turbulence the greater the drag force
What factors influence the size and turbulence of the wake behind an object moving through air/fluid? Provide sport-specific examples of actions that can reduce the size/turbulence of the wake behind an object moving through air/fluid - be specific how this action influences drag and performance.
In racing for example 3 cars lined up in a streamline will reduce the amount of turbulence behind each car compared to a car that is driving by itself and not using the streamline of air to its benefit to reduce the turbulence thus reducing the drag force.
Biking it is the same thing; they would wear certain helmets that help reduce the turbulence they also could buy a certain shaped bike that would prevent more turbulence thus preventing drag force.
Objects moving through air/fluid will also experience a lift force under certain conditions – what are these conditions. Using principles from Bernoulli and Newton, explain how these conditions result in lift forces.
Lift force - if an object is asymmetrically shaped, being in an angle position, or rotating and spinning.
Bernoulli - Air flow moving around an object having drag force, a plane since it is asymmetrically built. High velocity creates low pressure resulting in lift force, causing an upward force to try and match either side of the wing.
Newton - More to do with the asymmetrically shaped air flow is coming in and deflection of the bottom of the wing resulting in lift force.
The Magnus effect is a type of lift force that is related to the _______ of an object.
Rotation
Provide sport-specific examples of how athletes purposely create lift forces/Magnus forces to influence performance.
1. Soccer: When a soccer player takes a curved free kick or a bending shot, they impart spin to the ball to create a Magnus force. The spin causes the ball to curve in flight, making it difficult for the goalkeeper to predict its trajectory.
2. Tennis: A tennis player can apply topspin or backspin to the ball to create Magnus forces. Topspin causes the ball to dip down quickly after crossing the net, while backspin can make the ball float longer in the air, both affecting the opponent's timing and positioning.
3. Golf: In golf, players can apply spin to the ball by imparting sidespin or backspin with their club. This allows them to control the trajectory and direction of the ball, particularly when hitting shots around obstacles or onto sloped greens.
What is the center of mass of an object?
Where the middle of the weight is distributed. Does not have to be in the middle, imagine balancing a baseball bat, most of the weight is on the top of the bat so the center of the mass would not be in the middle of the bat and would be a little more towards the heavier side. Another example a pool ball is just a ball and acts almost like a particle the center of mass for a pool ball would be directly in the middle of the ball.
How does COM change during human movement (i.e. provide examples)?
Long run jumpers for example when ready to jump they move there hands up just like basketball players when they jump. This is to move more of your bod weight to a higher position so that the center of mass becomes higher in your body allowing you to jump higher.
How can we measure center of mass?
Segmentation method - Allows center of mass to be determined during activity. People wear jumpsuits with little white dots on the suit to determine where the center of the mass is Infront of a green screen. Think of the 2k green screen player animations being created.
What is torque, and what variables influence the magnitude of a torque?
Torque - A description of how effectively a force causes rotation.
Torque = Force x distance
Dependent on:
The size of the force
The moment arm length -
Using wrench - at a 1m wrench you can generate a force of 20N, at a 2m wrench you can generate a force of 10N
For example when using a longer wrench you would get a lower force.
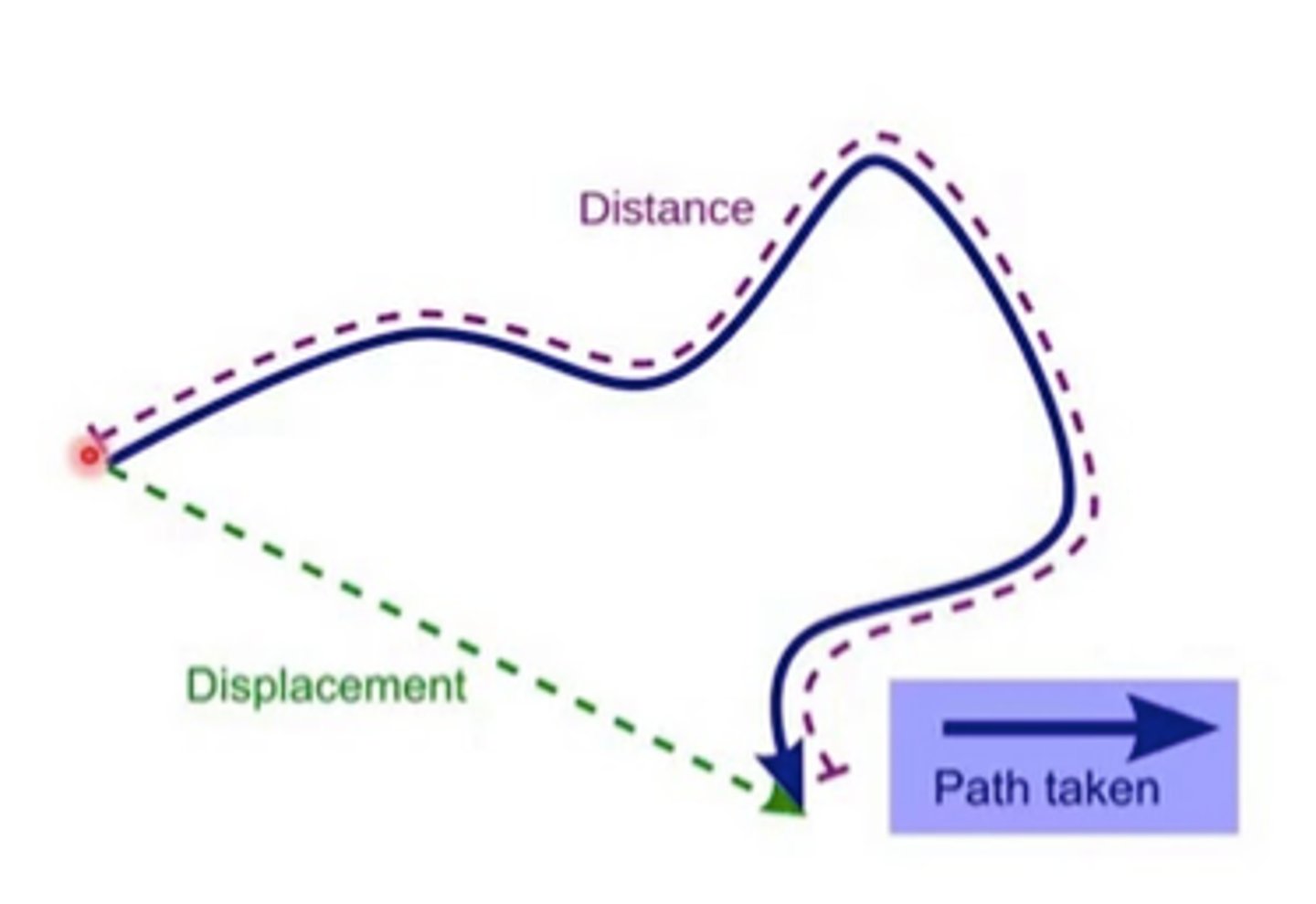
What are distance and displacement, and how are they different (hint: vector/scalar)?
Displacement - Change of object from the starting point to the ending point
Distance - the exact route the object traveled
What are speed and velocity, and how are they different (hint: vector/scalar)?
Speed - Scalar quantity - distance over time.
Velocity - Vector quantity - distance of displacement over time
Define acceleration?
Acceleration - Change in velocity or speed. Slowing down, Speeding up, or changing direction is always some form of acceleration
If an object has a negative acceleration, what does that mean?
A negative acceleration means that the object is slowing down from the acceleration that they were at.
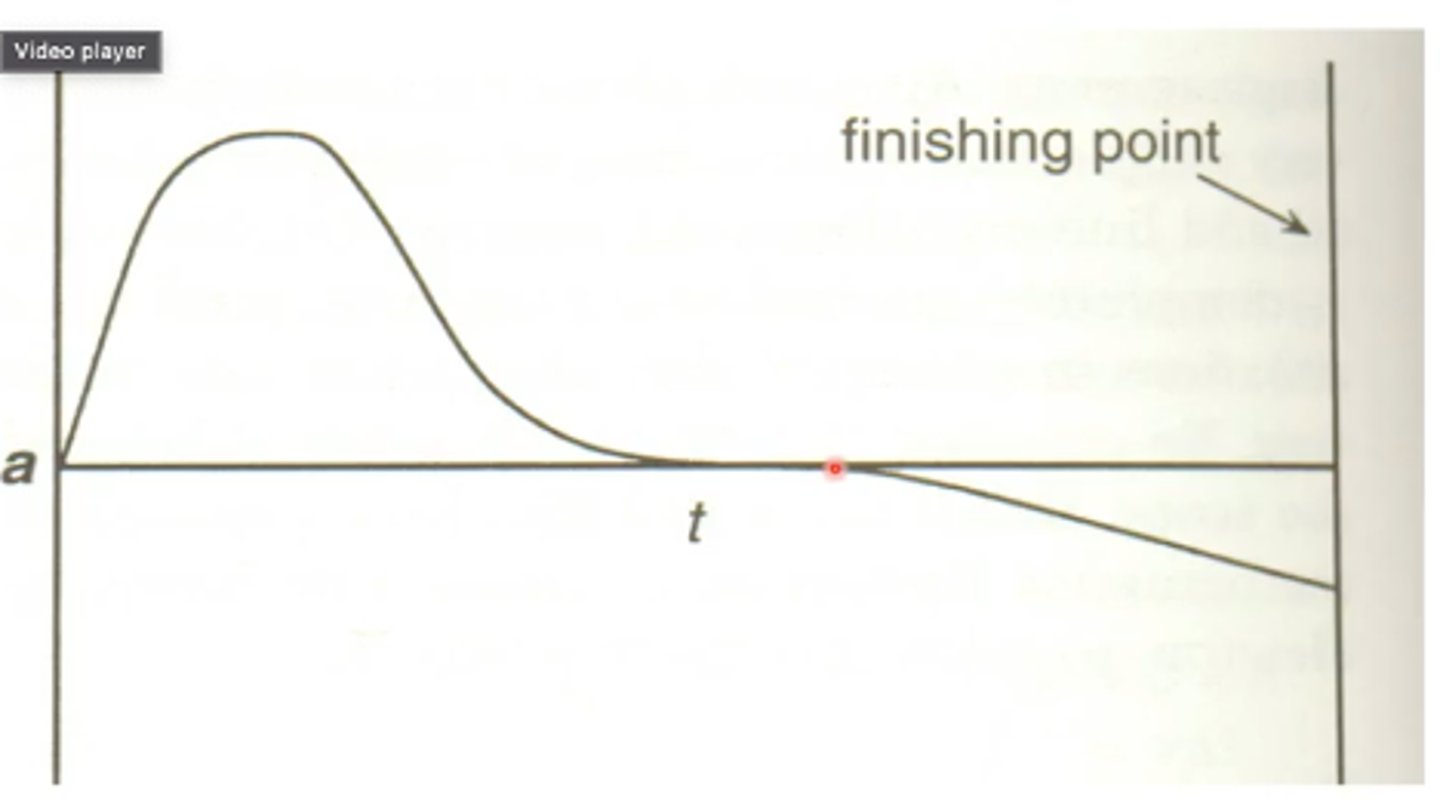
If an object has an acceleration = 0, what does that mean?
It just means that are not accelerating anymore. For example like in the picture above where the red dot is where the sprinter hit an acceleration of 0 which just means he is at his top speed and not getting any faster anymore. It does not mean that it is not moving anymore it just means that it is no longer getting faster.
What two variables influence an object's linear momentum?
More mass and more velocity will have an object to have more linear momentum. Bigger and heavier or higher velocity will have a higher linear momentum.
What is the law of conservation of momentum (LCM)? Based on the LCM, what variables can a baseball batter change if they want to hit a pitched ball farther (i.e. cause it to leave their bat with a higher velocity)?
A baseball batter can carry a heavier bat or increase the velocity of when they swing the bat which can create a greater momentum when they hit the ball to change the distance of how far the ball goes. They contradict each other because the heavier the bat the slower you will swing the bat.

What is the coefficient of restitution?
Describes what we call relative elastic of impacts (0-1) For example to explain this, when you drop a gold ball from your hand it would not bounce completely all the way back to your hand it would bounce half way up which would be its coefficient of restitution. Basketballs have a higher coefficient of restitution designed to bounce back higher. Softballs do not have a higher coefficient of restitution because if it was a high coefficient of restitution it would be too easy for the batter to hit the ball farther.
If a ball has a coefficient of restitution of 0.5, how high will it bounce if it is dropped from a height of 4 feet?
IT will bounce back up to 2 feet.
4 x .05 = 2
What three variables influence the angular momentum of an object? Provide sport-specific examples of how an athlete might alter their angular momentum to alter their performance.
1. Mass
2. Angular Velocity
3. Moment of Inertia
4. Figure Skating: Figure skaters often manipulate their body position to change their moment of inertia and angular momentum during spins and jumps. By pulling their arms closer to their body, they reduce their moment of inertia, allowing them to rotate faster and generate more angular momentum, leading to faster spins or more rotations in jumps.
5. Gymnastics: Gymnasts use their body position and momentum to execute various maneuvers on apparatus like the uneven bars and rings. By controlling their body's angular momentum, they can perform flips, twists, and other acrobatic movements with precision and control.
6. Diving: Divers adjust their body position and movements to control their angular momentum during dives. By tucking or extending their body, they can alter their moment of inertia and angular velocity, allowing them to execute complex dives with optimal rotation and entry into the water.
What two variables influence work?
Work = Force x Distance
If work is negative, what does that mean regarding the direction of movement of an object in relation to the force applied? If work = 0, what does that mean regarding the movement of an object?
Resistance force of friction,
Cyclist when going in a race going against the wind creates a higher resistance force which might be higher than the work of the cyclist
Define kinetic energy?
Kinetic Energy is the energy an object possess as a result of its motion and is a measured of its capacity to do work.
Kinetic energy is the amount of energy an object has after it becomes hit or moved.
What two variables influence the amount of (linear) kinetic energy that an object possesses?
1. Mass: The mass of the object is a crucial factor. Objects with greater mass possess more kinetic energy when they are in motion compared to objects with lesser mass, given the same velocity.
2. Velocity: The velocity, or speed, of the object is another significant factor. Kinetic energy increases with the square of the velocity. This means that doubling the velocity results in four times the kinetic energy, and tripling the velocity results in nine times the kinetic energy, and so on.
Which of the two variables has a larger influence on kinetic energy?
Velocity has a larger influence on kinetic energy compared to mass. This is because kinetic energy is directly proportional to the square of the velocity, whereas it is linearly proportional to mass. Therefore, changes in velocity have a greater impact on the amount of kinetic energy possessed by an object compared to changes in mass.
Define potential energy?
Potential energy is a form of energy that an object possesses due to its position or condition. It is energy that is stored within an object and has the potential to be converted into other forms of energy and perform work under the influence of forces or other factors.
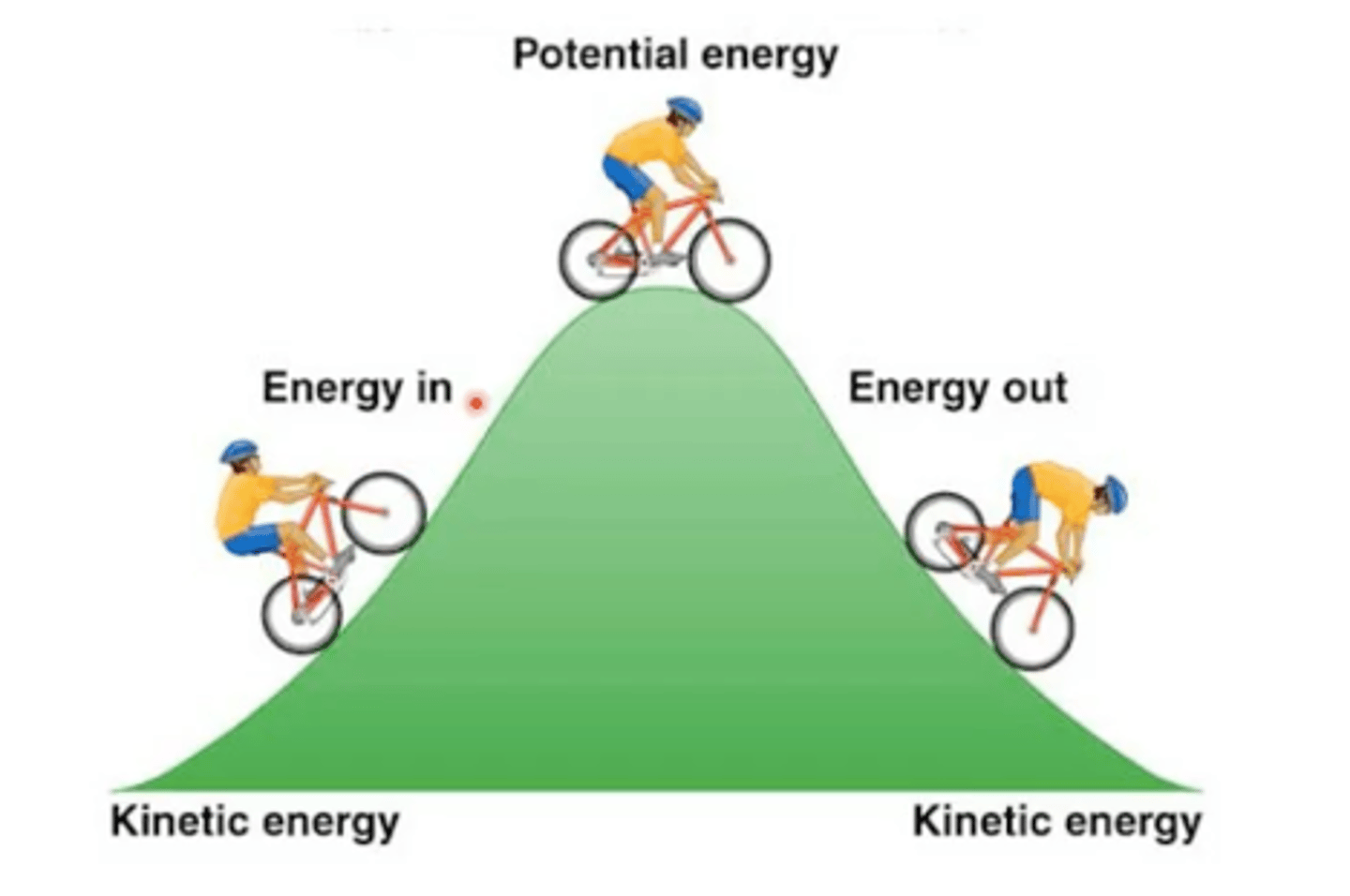
What three variables influence the amount of potential energy that an object possesses?
Mass
Gravitational Acceleration
Height
According to the law of conservation of energy, a falling object will lose potential energy at the same rate that it is gaining ______________
Kinetic Energy .
Define power – how is it related to work?
Power is the rate at which work is done, The amount of work over the amount of time to get that work done
Provide examples of sports in which producing high maximal power is critical for performance. Provide examples of sports in which producing sub-maximal power with high efficiency is critical for performance.
Power Sports which need high maximal power would be weight lifting and football.
Endurance Sports where sub maximal power is beneficial would be Long distance running, cycling, swimming.
Define mechanical efficiency. What does it mean if a person is 22% efficient? (i.e. "22% of their energy is..."). How is "movement economy" different from "efficiency", and why do we measure movement economy in running instead of efficiency?
Mechanical efficiency is a measure of how effectively a mechanical system converts input energy into useful output energy. It is typically expressed as a ratio or percentage and represents the relationship between the useful output work done by a machine and the total input energy supplied to it.
Efficiency - The percentage of energy expenditure devoted to mechanical work
Movement Economy - psychological cost of doing a fixed amount of work
How do changes in leg length/mass/inertia with age influence stride length & frequency during walking & running (i.e. from age 5 to 20 y)?
Younger limb lengths = shorter and lighter, the amount and effort for each stride is a lot less but they have smaller strides.
If adults and kids ran at the same speed, the kids would take more steps per minute as they have a lower stride and adults would have less steps per minute because there strides are longer.
How does this affect movement economy during walking/running? Provide other examples of changes in body size/shape/composition with age (or between sexes) that could influence biomechanical movements.
AS treadmill speed increases the energy cost is a direct correlation and increases
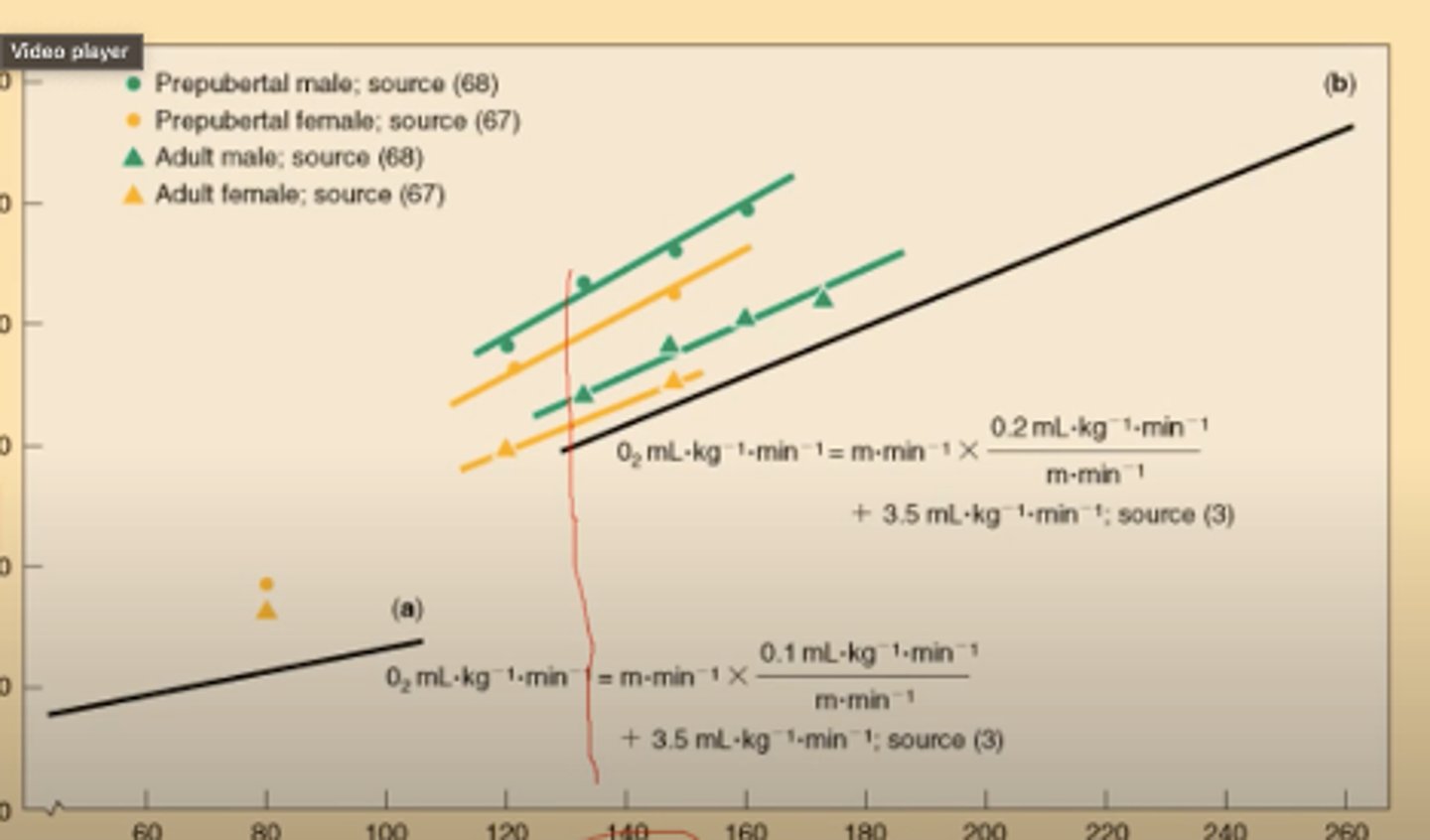
Prepubertal males at any given movement speed you can see that children have a higher energy cost at moving at the same speed as adults. Kids have poorer movement economy than adults.
Males always spend more energy per step, adult males use more than adult females, boys use more energy than girls
Many sports involve 'contacts' (or releases) in which high movement speeds are desired (i.e. striking a ball in golf/tennis/baseball/softball, shooting in hockey/lacrosse/soccer, etc.). Describe the common biomechanical pattern used to optimize movement speeds these types of activities
The common biomechanical pattern we are talking about optimization.
Optimization - practicing and training in a certain way you are perfecting that movement
Trying got optimize speed of the speed/release.
Movement patterns: Timing of segment involvement
Golfer- impact golf ball, trying to impact at the highest club volcity while maintain the direction.
Basketball - releasing the ball at the exact right angle, time and speed
Swimmers - trying to accelerate the rate of the arm and use the hand when it gets in the water to generate a lot of power.
What is a "proximal-to-distal" body segment involvement, and describe how it is used in one of these activities).
"Proximal-to-distal" body segment involvement refers to the sequential activation of body segments from the center of the body (proximal segments) outward toward the extremities (distal segments) during movement. This pattern is often observed in many athletic movements and is biomechanically advantageous for generating efficient and powerful movements.
Describe common movement patterns (techniques) that allow athletes to utilize stored elastic energy from eccentric contractions.
Acts like an elastic band, where when you let go of the band it generates more power when released
Provide examples of biomechanical alterations that elite performers utilize to achieve higher peak movement velocities than average performers (i.e. in activities such as those described in the previous question).
When batting in baseball, when bringing the bat backwards before swing it builds up energy and doesn't last long which is why timing is very important

To improve movement economy/efficiency, elite athletes generally recruit (less/more) muscle mass to complete sub-maximal activities?
Less
To optimize power, what two variables must an athlete develop? How does resistance training influence these variables?
Strength and Speed.
Resistance training influences these variables in several ways:
1. Increased Muscle Strength: Resistance training, such as weightlifting or resistance exercises, stimulates muscle hypertrophy (growth) and increases muscle strength over time. By progressively overloading the muscles with resistance, athletes can enhance their maximal strength, allowing them to generate greater force during explosive movements.
2. Improved Rate of Force Development: Resistance training can also improve the rate of force development, which is the ability to generate force rapidly. Through explosive and high-speed resistance exercises, athletes can train their muscles to contract more quickly, enabling them to generate power more rapidly during explosive movements.
In many sports, performance can be enhanced by using well-designed equipment. Provide examples of sports equipment that can improve performance, and provide a specific biomechanical rationale for this effect (i.e. HOW does it improve performance).
1. Running Shoes with Cushioning and Arch Support:
2. Tennis Rackets with Larger Sweet Spot:
3. Swimming Suits with Compression Technology:
4. Golf Clubs with Adjustable Weighting: