Personality and Individual Differences
1/33
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
How many different definitions of personality did Allport (1937) identify before creating his own?
49
Most common definition of personality in most textbooks
The set of psychological traits and mechanisms within the individual that are organised and relatively enduring and that influence his or her interactions with, and adaptions to, the intrapsychic, physical and social environments
5 different domains of study of personality
Psychodynamic/intra-psychic
Cognitive-social learning
Humanistic-existential
Biological and evolutionary
Dispositional trait
Psychodynamic or intra-psychic domain
Argues for internal mental processes that influence how we interact with our environment
Cognitive-social learning domain
How our cognitive and social processes influence and reinforce who we are
Humanistic-existential domain
How people aspire to be the best version of themselves
Dispositional trait domain
Narrowing focus to core traits that define personality which are fundamental to the human condition
3 levels of personality analysis (Kluckhohn and Murray, 1948)
Human nature
Individual and group differences
Individual uniqueness
Intrapsychic
A focus on fundamental internal human instincts or needs that shape individuals’ thoughts, emotions and behaviours, sometimes outside of conscious awareness
What was Sigmund Freud heavily influenced by in his creation of the psychoanalytic approach?
His reading of natural selection
What does the psychoanalytic approach argue the development of personality is based on?
How a person resolves the conflicts between their innate instincts and living in a regulated civilised society
How can personality be viewed from a lens of studying motives?
Differences between people in the strength and intensity of fundamental human needs
What did Murray (1938) argue about human needs?
Each person has a unique hierarchy of needs and this influences their perception of situations and behaviours
What are the human needs that have received the most attention from researchers?
Achievement, power, affiliation and autonomy
What is human personality due to, according to the cognitive approach?
Differences between personal histories of reinforcement and we all interact with the world differently
What did Bandura (2001) argue that individuals’ behaviour is determined by?
Self-efficacy
Self-efficacy
The extent to which people believe they can exercise control over events in their lives
How is self efficacy enhanced?
Mastery experiences, vicarious experiences, social persuasion
Mastery experiences
Successful past experiences
Hierarchy of needs (in order)
Physiological needs, safety needs, love and belongingness needs, esteem needs, self-actualisation needs
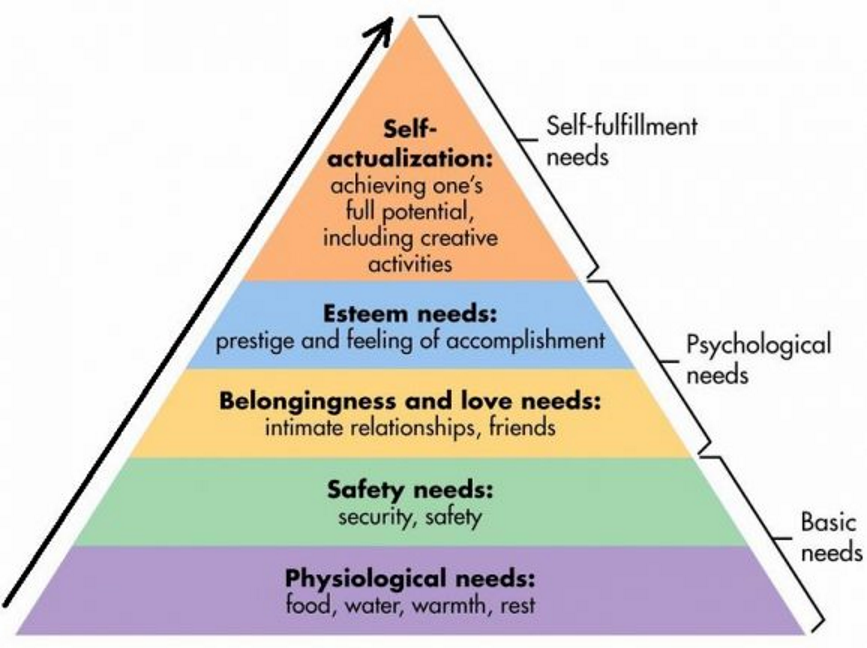
What shapes human behaviour according to Maslow (1971)?
Deprivation of needs - when self-actualisation needs are met, all humans will express the same characteristics
What did Buss (1991) suggest that personality is?
An adaptive mechanism to promote survival and reproduction (deterministic view)
Buss (1991) core adaptive personality dimensions (5)
Surgency/extraversion
Agreeableness
Emotional stability
Conscientiousness
Openness to experience
Personality trait definition (Larsen et al, 2017)
The set of psychological traits and mechanisms within the individual that are organised, relatively enduring and influence their interactions with, and adaptions to, the intrapsychic, physical and social environment
Properties of a personality trait (6)
Temporal stability
Cross-situational consistency
Internal (biological) basis attributed to within the person
Predictive validity
Minimal overlap of characteristics within traits
Inter-individual differences
5 ways to evaluate the biological underpinning of traits
Physiological substrate - personality related to different brain regions
Hereditary or genetic contribution - should see similarities within families
Similar traits in non-humans (especially primates)
Cross-cultural evidence
Temporal stability
Descriptive summaries view of causality of personality traits
The trait describes an expressed behaviour, but no attributions of the cause are made
Structure of personality traits (in order)
Domains → facets → behaviours
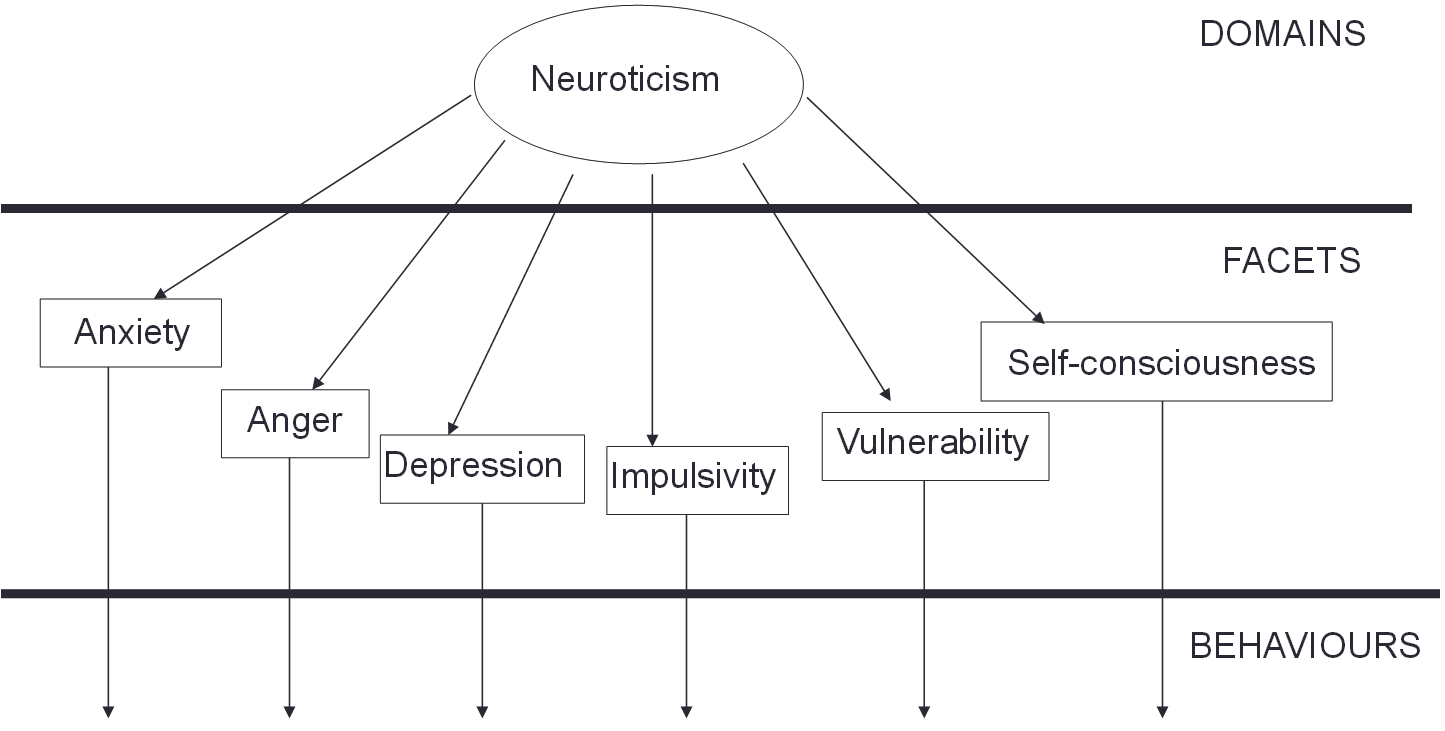
4 key questions in trait approach to personality
How many personality traits are there?
How are personality traits structured and organised?
What are the origins of personality traits?
What are the correlations and consequences of personality traits on human behaviour?
What did Mischel (1968) conclude about behavioural consistencies within personality traits?
They were not robustly observed e.g. for trait of honesty, correlation was very low - cheating on an exam did not correlate to cheating in basketball, for example
What did Mischel (1968) claim personality psychologists should focus on?
Situationism - explaining behaviour in terms of situational differences
How can interactionism be expressed? (Shoda et al, 1994)
In terms of ‘if, then’ statements - B = f(P x S) - considers interaction of personality and situation
Three methods of self-report questionnaire development
Lexical - traits expressed in natural language
Statistical - factor analysis to identify clusters
Theoretical - a priori theory on most important traits
Issues with self-report questionnaires (3)
Carelesness when answering questions
Faking or concerns of desirability
Barnum statements that apply to everyone