Chapter 11: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (4%)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
oxidation
(OIL RIG → OIL = “oxidation is loss” of electrons)
Oxidation vs. Reduction
A loss of electrons
Increase in oxidation state
reduction
(OIL RIG → RIG = “reduction is gain” of electrons)
Oxidation vs. Reduction
A gain of electrons
Decrease in oxidation state
oxidation, reduced
An oxidizing agent facilitates the ___________ of another compound & is itself ___________ in the process (i.e. it gains electrons)
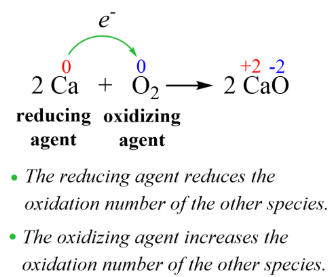
reduction, oxidized
A reducing agent facilitates the ___________ of another compound & is itself ___________ in the process (i.e. it loses electrons)
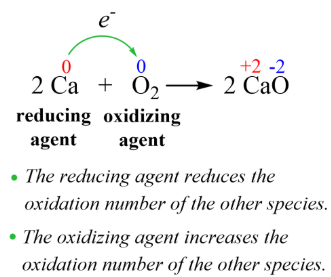
OIL RIG
(Oxidation Is Loss of electrons, Reduction Is Gain of electrons)
mnemonic for remembering how redox reactions work
oxygen (or a similarly electronegative element)
the element that almost all common oxidizing agents contain
metal ions, hydrides (H-)
the 2 elements that almost all reducing elements contain (one or the other)
oxidation number
Represents the # of electrons an atom has gained or lost when forming a chemical bond
Positive integers = the atom has lost electrons compared to its neutral state
Negative integers = the atom has gained electrons compared to its neutral state
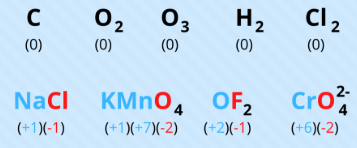
0
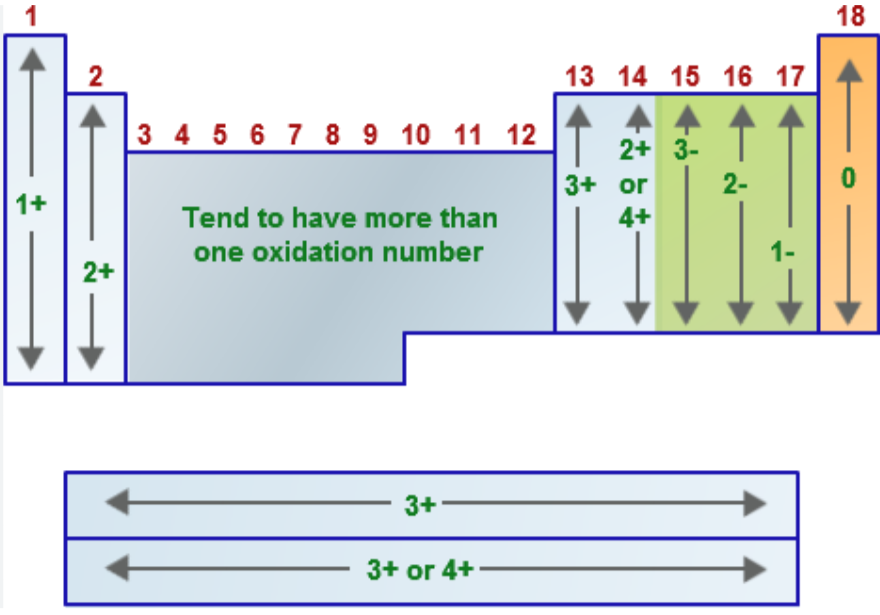
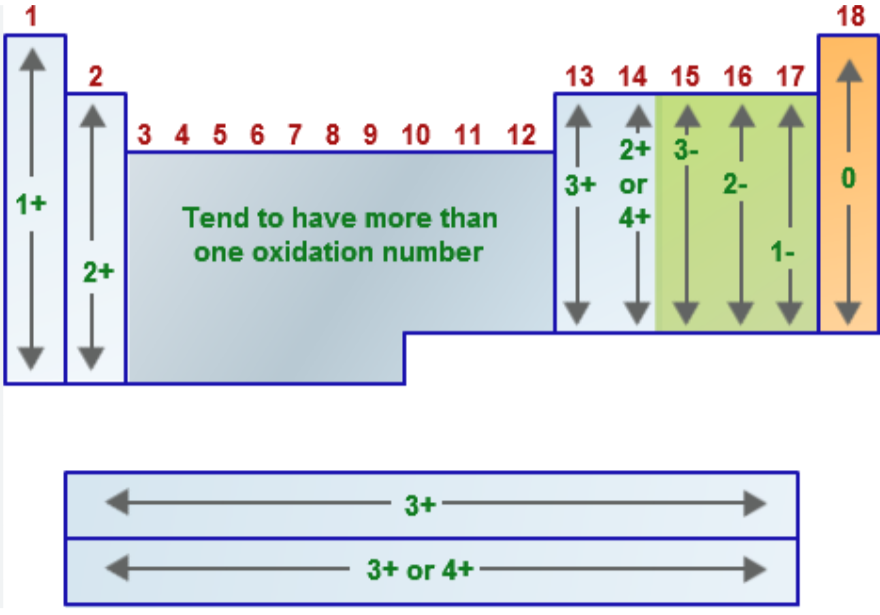
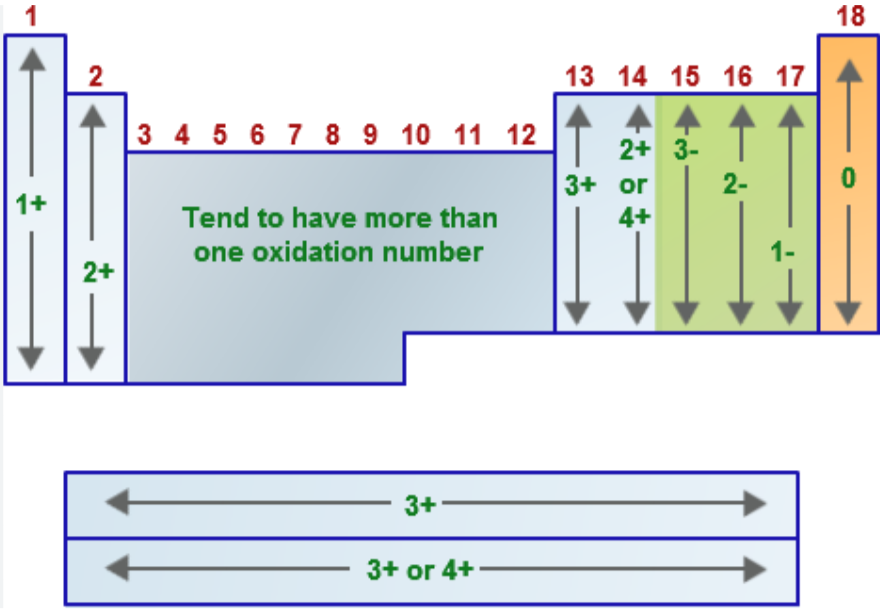
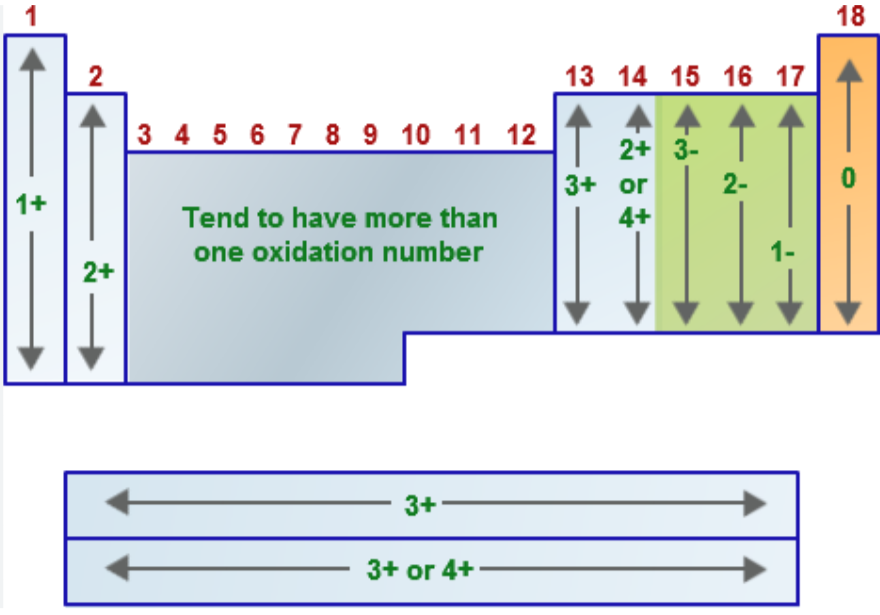
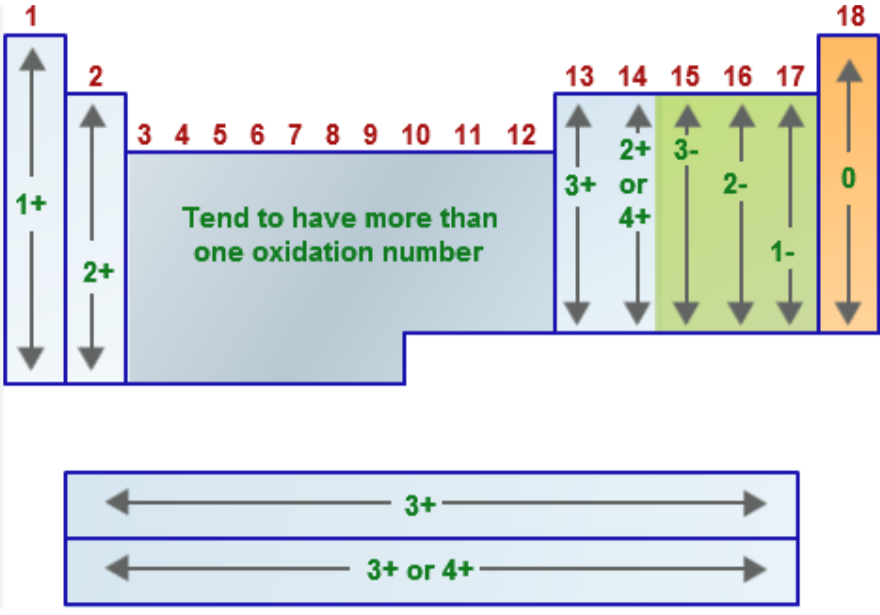
Name the oxidation number for the following:
any free element or diatomic species
EX: Fe, Li, Ar, N2, P4)
(***a free element is considered to be any element in an uncombined state, whether monatomic or polyatomic)
equal to the charge of the ion
Name the oxidation number for the following:
monatomic ion (composed of one atom)
EX: Na+, Cu2+, Se2-
+1
Name the oxidation number for the following:
Group 1A metals (alkali metals = Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr) when in a compound
EX: LiH, NaCl, K2SO4
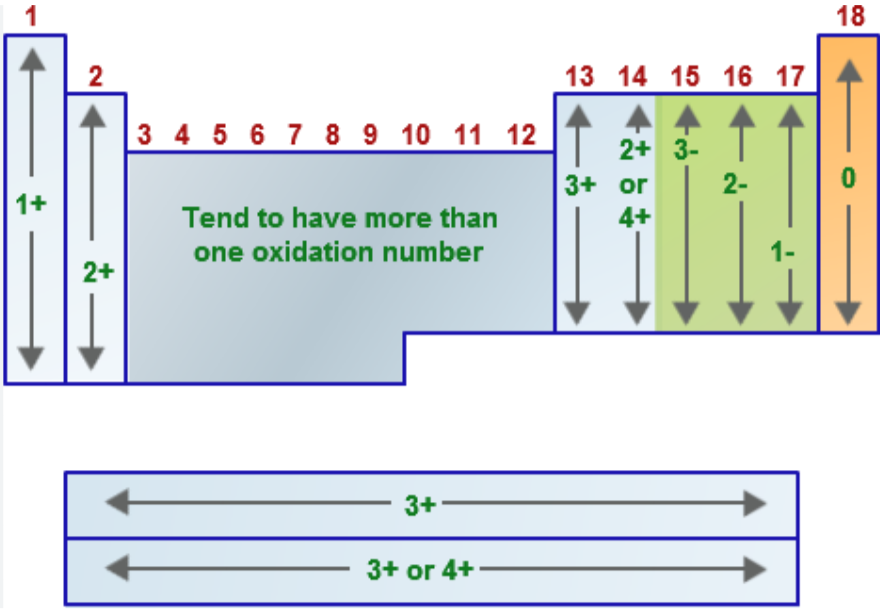
+2
Name the oxidation number for the following:
Group 2A metals (alkaline earth metals = Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra) when in a compound
EX: CaO, MgCl2, CaCO3
-1 (unless combined with an element with higher electronegativity)
Name the oxidation number for the following:
Group 7A/17 elements (halogens = F, Cl, Br, I, At) when in a compound
EX: NaCl, HBr
+1
(because hydrogen is less electronegative than most nonmetals)
Name the oxidation number for the following:
hydrogen (usually → when bonded to nonmetals)
-1
(because hydrogen is more electronegative than metals, forming metal hydrides)
Name the oxidation number for the following:
hydrogen when paired with metals (such as elements in Groups 1A and 2A)
-2
(oxides (O2-) & water (H2O))
Name the oxidation number for the following:
oxygen (usually → in oxides & water)
-1
Name the oxidation number for the following:
Oxygen when in peroxides
EX: O2-2, H2O2, Na2O2
+2
(however, in O2F2, it has an oxidation # of +1)
Name the oxidation number for the following:
Oxygen when paired with more electronegative elements
EX: OF2
charge
the sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms present in a compound is = to the overall _______ of that compound
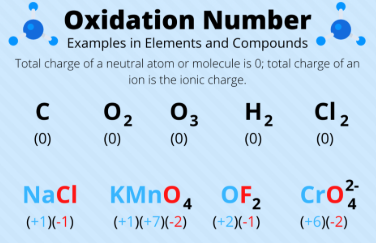
oxidation number
Oxidation Number vs. Formal Charge
assumes UNEQUAL division of electrons in bonds

formal charge
Oxidation Number vs. Formal Charge
assumes EQUAL division of electrons in bonds

complete ionic equation
Complete vs. Net Ionic Equation
Accounts for all the ions present in a reaction
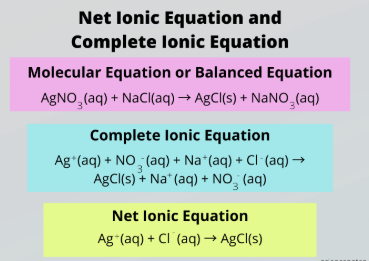
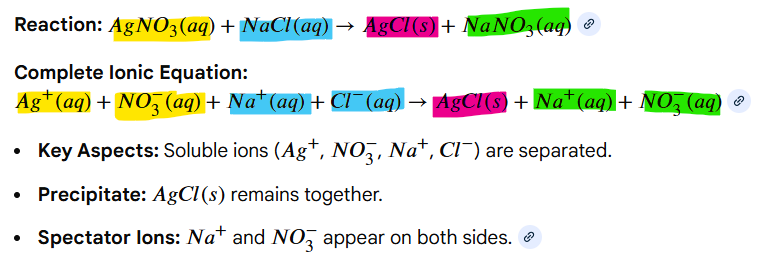
aqueous, solid salts
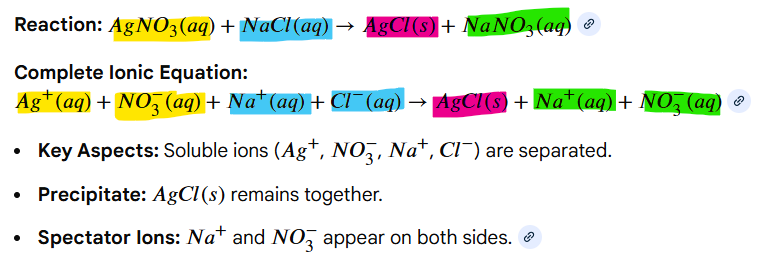
To write a Complete Ionic Reaction, split all __________ compounds into their relevant ions and keep _______ ______ intact
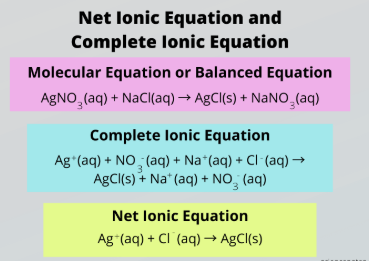
net ionic equation
Complete vs. Net Ionic Equation
Ignore spectator ions to focus only on the species that actually participate in the reaction
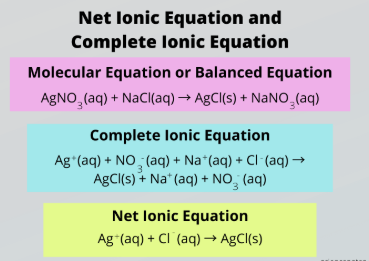
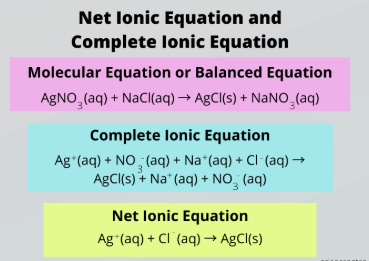
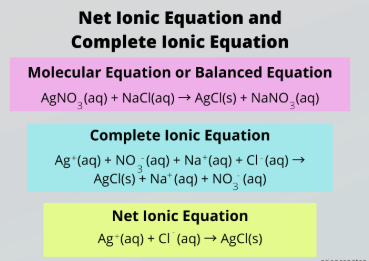
subtract, spectator ions, aqueous, solid salts

To obtain a Net Ionic Reaction, _________ the ions appearing on both sides of the reaction, which are called __________ _____.
Then split all __________ compounds into their relevant ions and keep _______ ______ intact
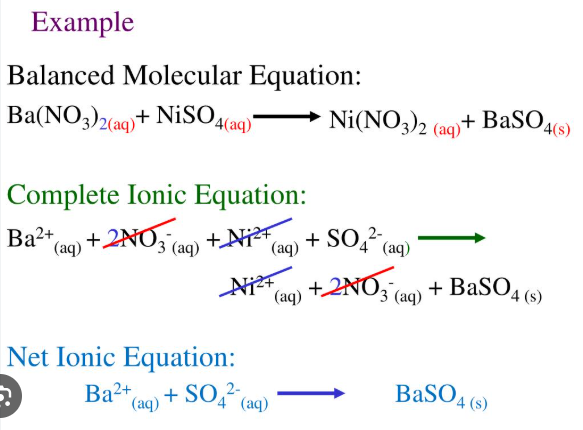
aqueous salts
For reactions that contain no _________ _____, the net ionic equation is generally the same as the overall balanced reaction
solid salt, remain, oxidation number
For double displacement reactions that do not form a _____ ____, there is no net ionic reaction because all ions ________ in solution and do not change __________ _______
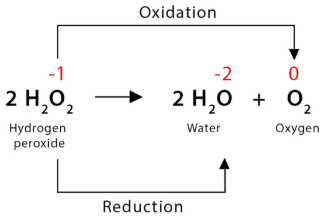
dismutation (disproportionation)
A type of redox reaction in which one element is both oxidized and reduced, producing two different products with higher and lower oxidation states, respectively
These are usually accomplished by enzymes
charge, electrons
Titrations
Whereas acid-base titrations follow the movement of protons, redox titrations follow the transfer of _______ (as __________) to reach the equivalence point
voltages
Titrations
Indicators used in redox titrations change color when certain __________ of solutions are achieved
potentiometric titration
Titrations
A form of redox titration in which a voltmeter or external cell measures the electromotive force (emf) of a solution
Uses an indicator electrode and a reference electrode, instead of a visual indicator
Equivalence point is determined by a sharp change in voltage