Chapter 10: Russia
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ProKnow
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What has Russian President Putin done since returning to power in 2012?
President Putin sought to reassert Russia as a great power on the global stage and to restructure an international order.
What does the Kremlin believe?
The Kremlin believes international order is tilted too heavily in favor of the United States at Russia’s expense.
How does Russia pursue foreign relations?
Russia (like the Soviet Union before it) actively pursues foreign relations on a global scale.
Who has Russia supported since 2015?
Russia has supported the al-Assad regime and military involvement in Syria since 2015
What did Russia do in 2022?
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.
Russia is one of the permanent members of what?
Russia is one of five permanent members of the U.N. Security Council.
Until 2014, Russia was a member of the ________
Group of Eight (G8)
It is also a member of ______, an alternative group of states with large economies that also includes ______, _____, ______, and _____ ______.
BRICS; Brazil, India, China, and South Africa
Russia has engaged on global issues such as ____________ (including combatting the nuclear weapons programs of Iran and North Korea), ____________, ____________, and ______ ______.
nonproliferation, counterterrorism, counterpiracy, and global health
Russia is a leading ________ exporter
oil and gas
the second largest ________ exporter in the world
major weapons
Russia has constructed nuclear power plants in ______, ______, ______, and ______ with more under construction or planned.
Europe, Iran, India and China
In addition, Russia has cultivated a variety of ________ ________ around the globe.
bilateral partnerships
In Asia, Russia’s main partner is ______, with which it has close ______, ______, and ______ relations…
China; security, economic, and political
Russia has cultivated good relations with _____
Japan
It also has developed good relations with ______, ______, ______, ______, and ______ ______ ______.
India, Pakistan (more recently), Afghanistan, Vietnam, and across Southeast Asia
Russia’s Syria intervention is exceptional in scope but reflects a long-standing policy of fruitful relations with regional governments including ______, ______, ______, ______, and _______.
Algeria, Egypt, Iraq, Libya, and Sudan
In ______ ______, Russia has sought to reengage with Soviet-era partners ______ and ______, as well as ______, ______, and others.
Latin America; Cuba, Nicaragua, Venezuela, Brazil
For more than ___ years, the U.S.-Russian relationship has gone through positive and negative periods.
25
The spirit of U.S.-Russian “______ _______” forged by Presidents ______ ______ and ______ ______ in the early 1990s was gradually overtaken by increasing tension and mutual recrimination…
strategic partnership; Bill Clinton, Boris Yeltsin
Presidents ______ ___. ______ and ______ ______ believed they could restore U.S.-Russian relations, particularly in the aftermath of the terrorist attacks of ______ ___, ______.
George W. Bush, Vladimir Putin; September 11, 2001
The two countries reshaped their relationship on the basis of cooperation against ______ and the economic integration of Russia with the West.
terrorism
However, tensions arose again around a number of issues, including the ______ ______
Iraq War
the so-called color revolutions in ______, ______, and ________ involving protests against electoral fraud that unseated corrupt regimes;
Ukraine, Georgia, and Kyrgyzstan
Cooperation continued in some areas, but the ______ ______ ______- ______ conflict caused bilateral ties to deteriorate to their lowest point since the ______ ______.
August 2008 Russian-Georgian; Cold War
Upon entering office, the ______ Administration believed it could prompt yet another “reset” of relations with Russia’s new president, ______ ________
Obama; Dmitry Medvedev
During a July 2009 meeting in Moscow, Presidents Medvedev and Obama established the ___-______ _______ ________ ________ consisting of ___ working groups to address a broad spectrum of issues.
U.S.-Russia Bilateral Presidential Commission; 21
U.S.-Russian relations worsened with Russia’s disputed ________ ____ parliamentary elections and _____ _____ ____ return to the presidency.
December 2011 parliamentary elections; Putin’s March 2012
In 2014, U.S. relations with Russia deteriorated further in reaction to Russia’s invasion and annexation of _______ ______ region and Russia’s sponsorship and support of separatist militants in the ______ and ______ regions (the Donbas).
Ukraine’s Crimea; Donetsk and Luhansk
The United States, in coordination with the EU and a number of other states, promised to impose increasing costs on Russia until it “abides by its _________ ________ and returns its military forces to their original bases and respects _______ _________ ___ ________ ______.”
international obligations; Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity
Russia also was removed from the ___, and the United States, EU, and other allies introduced _______ on Russia for its actions.
G8; sanctions
Since 2014, the United States has imposed sanctions on more than ___ individuals and entities in response to Russia’s aggressive actions in and toward ______.
520; Ukraine
…declared Russia’s activities in Ukraine as threatening the ______, _______, _______, ________, and __________ _______ of Russia’s neighbor…
peace, security, stability, sovereignty, and territorial integrity
On January 6, 2017, the _____ ____ ________ ________ __________ ( ___ )released a declassified report on Russian activities and intentions related to the ____ ___ _________ ______.
Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI); 2016 U.S. presidential election
Russia invaded Ukraine in _______ ____ to commence the deadliest conflict in Europe in decades.
February 2022
Many analysts assessed that “during this first stage of the war the Russian military performed ______ overall and was hindered by specific tactical choices, poor logistics, ineffective communications, and command-and-control issues.
poorly
Of particular note, the United States and other U.S. aligned world powers have imposed ______ on Russia and supported Ukraine with large amounts of _______ ___ and ______ ______ _______ (including drones, missiles, anti-armor systems, counter-artillery radars, armored vehicles, transport helicopters, guns, ammunition, and heavy artillery).
sanctions; monetary aid and modern military equipment
The United States alone has committed over ___ ______ in aid as of ___ ____.
$75 billion; May 2023
______ and _______ responded to the invasion of Ukraine by applying to join the ____ alliance…
Sweden and Finland; NATO
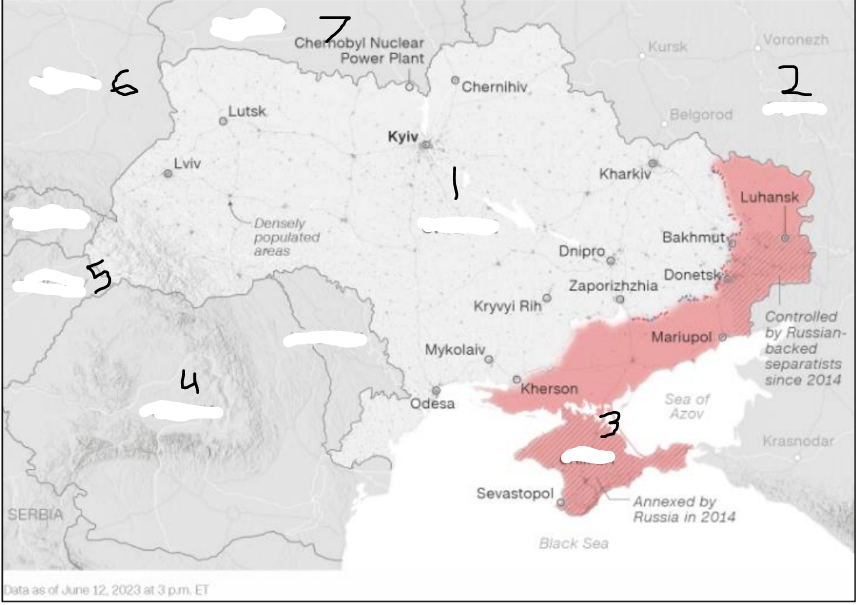
Where is Russia?
2
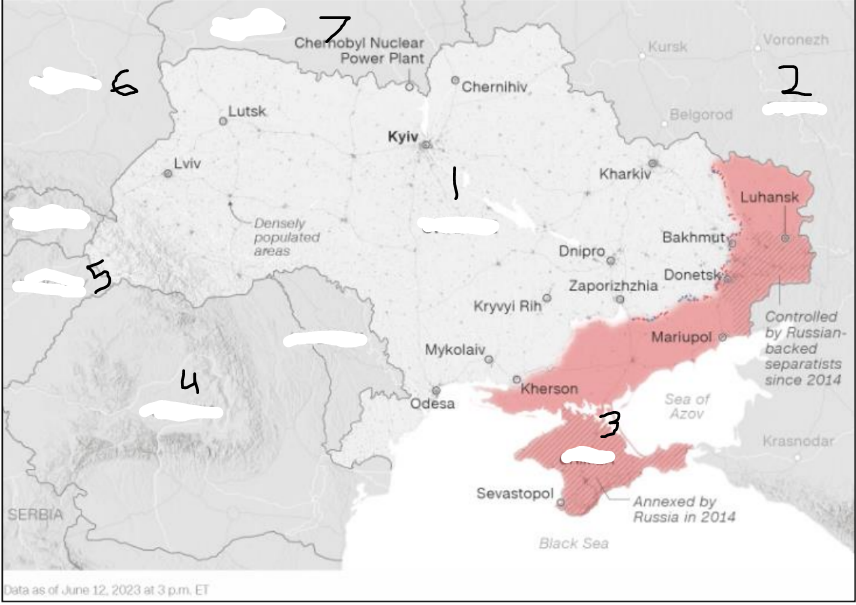
Where is the Crimea region?
3
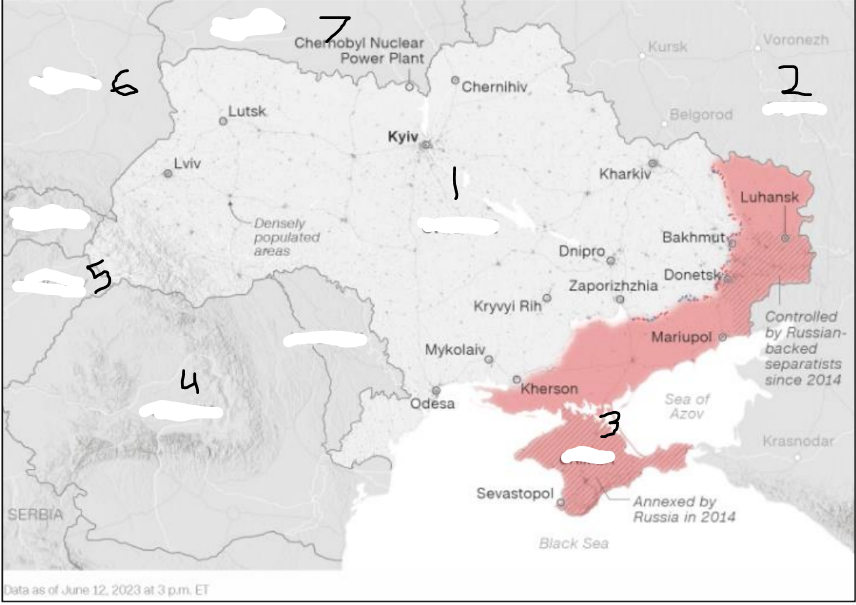
Where is Ukraine?
1
Russia’s armed forces surprised most U.S. and European observers with their actions in Ukraine (starting in ______ ____ and then the _____ invasion) and in Syria starting in September _____.
March 2014; 2022; 2015
The report states that the ______ _________ ______, the ______ ______ ________ ( ___ ), and the ______ ______ ______ have “high confidence” that President Putin “ordered an influence campaign in 2016 aimed at the US presidential election” in order to “______ ______ ______ _____ ______ ______.”
Central Intelligence Agency, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), and the National Security Agency; undermine public faith in the US democratic process
Analysts noted that the shortcomings of Russia’s military appeared to be confirmed by its relatively ________ performance in the ____ conflict with ______.
lackluster; 2008; Georgia
Russian special forces, ______ ______ _____, and ______ _______ effected a swift and bloodless seizure of ______ in ______ _____.
elite airborne troops, and naval infantry; Crimea, March 2014
The subsequent Russian involvement in the conflict in eastern Ukraine highlighted the practice of “______ ______”, centered on the use of irregular “_______” forces covertly backed by the regular military…
hybrid warfare; separatist
The Syria operation has demonstrated noteworthy capabilities, such as the launch of _____-______ ______ missiles from naval vessels in the _______ ____ and the deployment of Russia’s most modern combat aircraft.
long-range cruise; Caspian Sea
It also has highlighted the Russian military’s ability to effect “____ _______” with an air defense “______” of overlapping advanced missile systems.
area denial; bubble
In ________ _____, Russia launched a new ______ ______ ________ _______. In addition, Russia has been forming two new brigades specializing in ______ warfare.
December 2014; Arctic Joint Strategic Command; Arctic
In 2010, Russia announced a new ___-_____ ______ __________ _______ ( ____ ) for ____-____…
10-year State Armaments Program (SAP) for 2011-2020
…calling for approximately __ ______ rubles in new weapons procurement over that period (approximately $___ ______ as of ________ ____).
20 trillion; $328 billion; December 2016
The procurement goals of the SAP include:
• In the coming decade, Russian armed forces will be provided with over _#_ modern land and sea-based ____-________ ______ ______;
• _#_ _______ ________ _______ __________ and about _#_ ____-______ ________;
• Over _#_ ______ _______;
• Around _#_ ______ ________;
• Over _#_ ______ ______ including fifth generation fighter jets, as well as more than __#__ _________; 28 regimental kits of S-400 air defense systems, 38 battalion kits of Vityaz missile systems, and 10 brigade kits of Iskander-M missile systems;
• Over ___#___ _______ ______, about 2,000 self-propelled artillery systems and vehicles, and more than 17,000 military vehicles.
400, inter-continental ballistic missiles;
8 strategic ballistic missile submarines, 20 multi-purpose submarines;
50 surface warships;
100 military spacecraft;
600 modern aircraft, 1,000 helicopters;
2,300 modern tanks
Accompanying an overall decline in defense spending from 2016, the approval of a new __-______ ruble (approximately $492 billion) SAP for the period _____-_____ was postponed until 2018 due to the instability of economic conditions.
30-trillion; 2016-2025
The Russian Navy is composed of what fleets?
Northern Fleet
Pacific Fleet
Baltic Fleet
Black Sea Fleet
Caspian Flotilla
Northern Fleet Joint Strategic Command (OSK)
Northern Fleet
Eastern Military District/(OSK)
Pacific Fleet
Western Military District/(OSK)
Baltic Fleet
Southern Military District/(OSK)
Black Sea Fleet
Eastern Military District/(OSK)
Caspian Flotilla

Admiral Kuznetsov Class Aircraft Carrier
Admiral Kuznetsov Class Aircraft Carrier
the ski-jump catapult
sits at 1,001 ft in length.
intended to support and defend strategic missile-carrying submarines, surface ships, and naval missile-carrying aircraft of the Russian Navy.
18x SU-33 fighters, 6x MIG-29K fighters, 4x KA-31 helicopters, 2x KA-27 helicopters
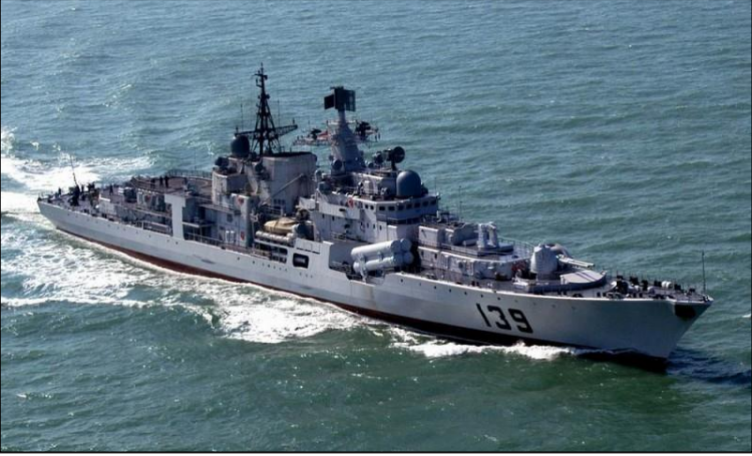

Sovremenny Class Destroyer
Sovremenny Class Destroyer
two four-cell anti-ship missile launchers installed port and starboard of the forward island and set at an angle about 15°
tasked with anti-ship warfare, while
also providing sea and air defense for warships and transports under escort.
1x Ka-27 series helicopter
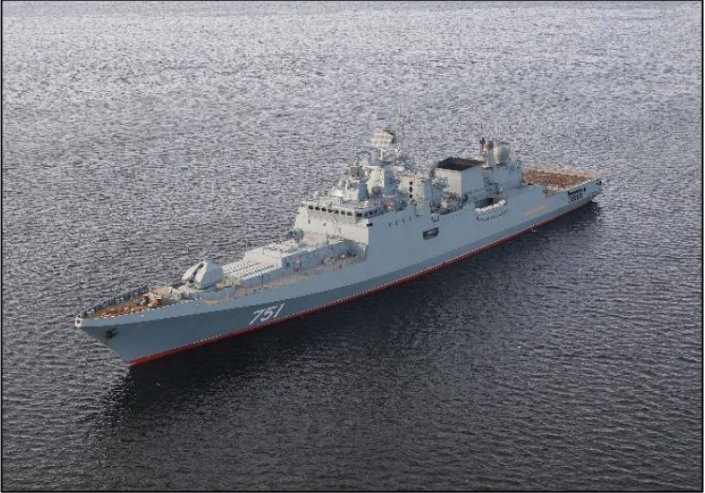

Admiral Grigorovich Class Frigate
Admiral Grigorovich Class Frigate
black search radar located behind the main super structure
sits at 409 ft in length.
air defense, escorting of other
warships and anti-submarine warfare.
1x Ka-27 anti-submarine warfare helicopter, or 1x Ka-31 airborne early warning helicopter
Russia currently has __ submarines.
65
Historically the backbone of the Russian Navy, ___ of the ___ operational submarines are over 20 years old and are slowly being replaced
75%; 65
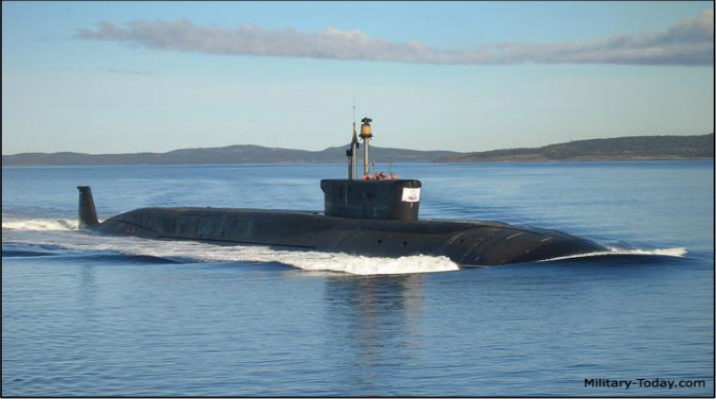

Borei Class Strategic Missile Submarine
Borei Class Strategic Missile Submarine
also referred to by the Russian designation Project 955 Borei, is a class of nuclear-powered
intended to replace the Soviet-era Delta III, Delta IV and Typhoon classes
Crew: 107 total
Propulsion: Nuclear

Yasen Class Attack Submarine
Yasen Class Attack Submarine
also referred to by the Russian designation Project 885
series of newest and most advanced Russian nuclear-powered cruise missile submarines
replace Russia's Soviet-era nuclear attack submarines.
Crew: 64 total
Propulsion: Nuclear

Akula Class Attack Submarine
Akula Class Attack Submarine
Project 971 are series of nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs).
incorporates a double hull system composed of an
distinctive "bulb" or "can" seen on top of the
Crew: 73 total
Propulsion: Nuclear

Varshavyanka Class Patrol Submarine
Varshavyanka Class Patrol Submarine
Project 636
anti-shipping and anti-submarine operations in relatively shallow waters.
Crew: 52 total
Propulsion: Diesel-electric

Su-35 Flanker-E
Su-35 Flanker-E
They are single-seat, twin-engine, and supermaneuverable aircraft.
electronics and weapons capabilities have caught up with those of Western equivalents, like the F-15 Eagle.
SS-N-26 Strobile
a Soviet / Russian supersonic anti-ship cruise missile.
Advantages:
- Over-the-horizon (OTH) firing range
- Full autonomy of combat use ("fire and forget")
SS-N-27 Sizzler
surface ship, submarine-launched and airborne anti-ship and coastal anti-ship (AShM), land attack cruise missiles (LACM) and anti-submarine missiles.
can be launched from a surface ship using a Vertical Launch System (VLS).
These talks eventually led to a formal agreement signed by both sides in Moscow on ____ ___, ____ (“______________________________________ ”).
May 25, 1972; Agreement on the Prevention of Incidents on and Over the High Seas
Russian military intervention in the ______ Civil War began in _______ ____…
Syrian; September 2015
At the end of _______ ____, the Russian government said its troops would be based in ______ permanently.
December 2017; Syria
April 2016 (Incident)
A pair of Russian Su-24 fighter jets performed several low-altitude passes on the USS DONALD COOK Arleigh Burke class guided missile destroyer while the ship was conducting exercises with a Polish helicopter in international waters in the Baltic Sea 70 nautical miles (130 km; 81 mi) off Kaliningrad.
February 2017 (Incident)
Multiple Russian SU-24 “Fencer” fighter jets and an Il-38 sub-hunting quad-engine aircraft buzzed the U.S. Navy destroyer USS PORTER (DDG 78) in the Black Sea.
January 2018 (Incident)
A Russian Sukhoi SU-27 “Flanker” fighter jet came within five feet of an EP-3 Aries before crossing through the U.S. aircraft’s flight path, forcing the EP-3 to fly through the SU-27’s flight wash.
November 2018 (Incident)
A Russian fighter jet flies dangerously close to a U.S. Navy reconnaissance plane on Monday over the Black Sea. A Navy EP-3E Aries II reconnaissance aircraft was flying in international airspace when it was intercepted by a Russian Su-27 fighter in an interaction that lasted about 25 minutes.
June 2019 (Incident)
A Russian Sukhoi SU-35 fighter jet harassed a U.S. Navy P-8A Poseidon patrol plane over the Mediterranean Sea.
June 2019 (Incident)
On 7 June 2019 the USS CHANCELLORSVILLE (CG 62) came close to a collision with the Russian destroyer Admiral Vinogradov. United States Seventh Fleet stated the Russian destroyer came within 50 to 100 feet of USS CHANCELLORSVILLE and did not adhere to proper “rules of the road".