Earth's Structure, Plate Tectonics, and Climate Patterns
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What are the three main layers of Earth's interior?
Core, Mantle, and Crust
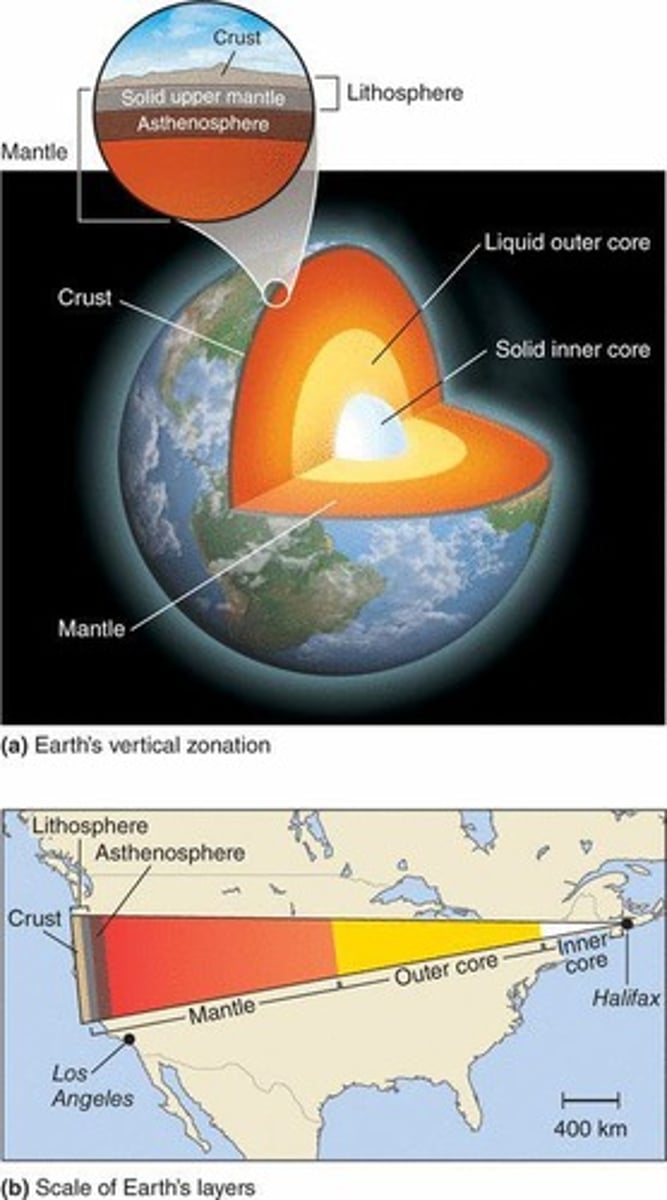
What is the composition of the Earth's core?
A dense mass of nickel, iron, and radioactive elements
What is the lithosphere?
The thin, brittle layer of rock floating on top of the mantle, broken into tectonic plates
What is the asthenosphere?
The semi-molten, flexible outer layer of the mantle beneath the lithosphere
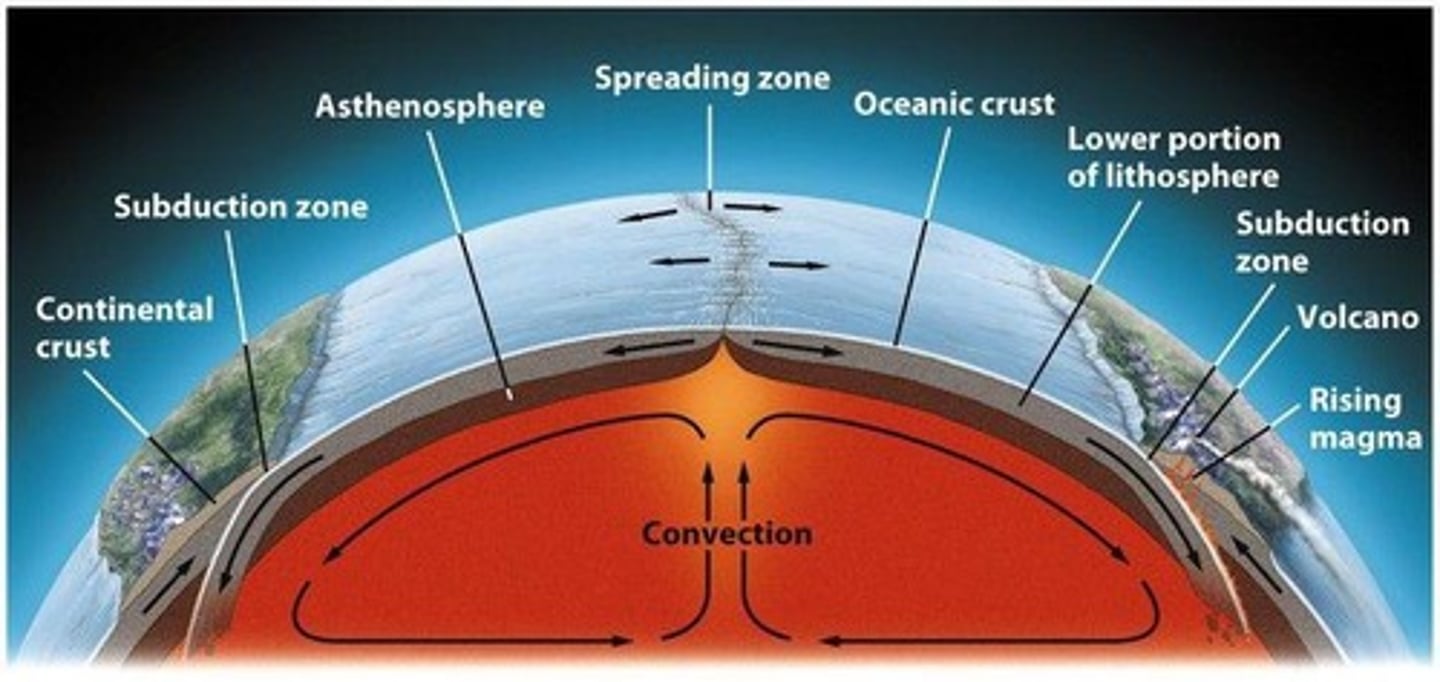
What occurs at a convergent plate boundary?
Plates move towards each other, leading to subduction
What is formed at divergent plate boundaries?
Mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and rift valleys
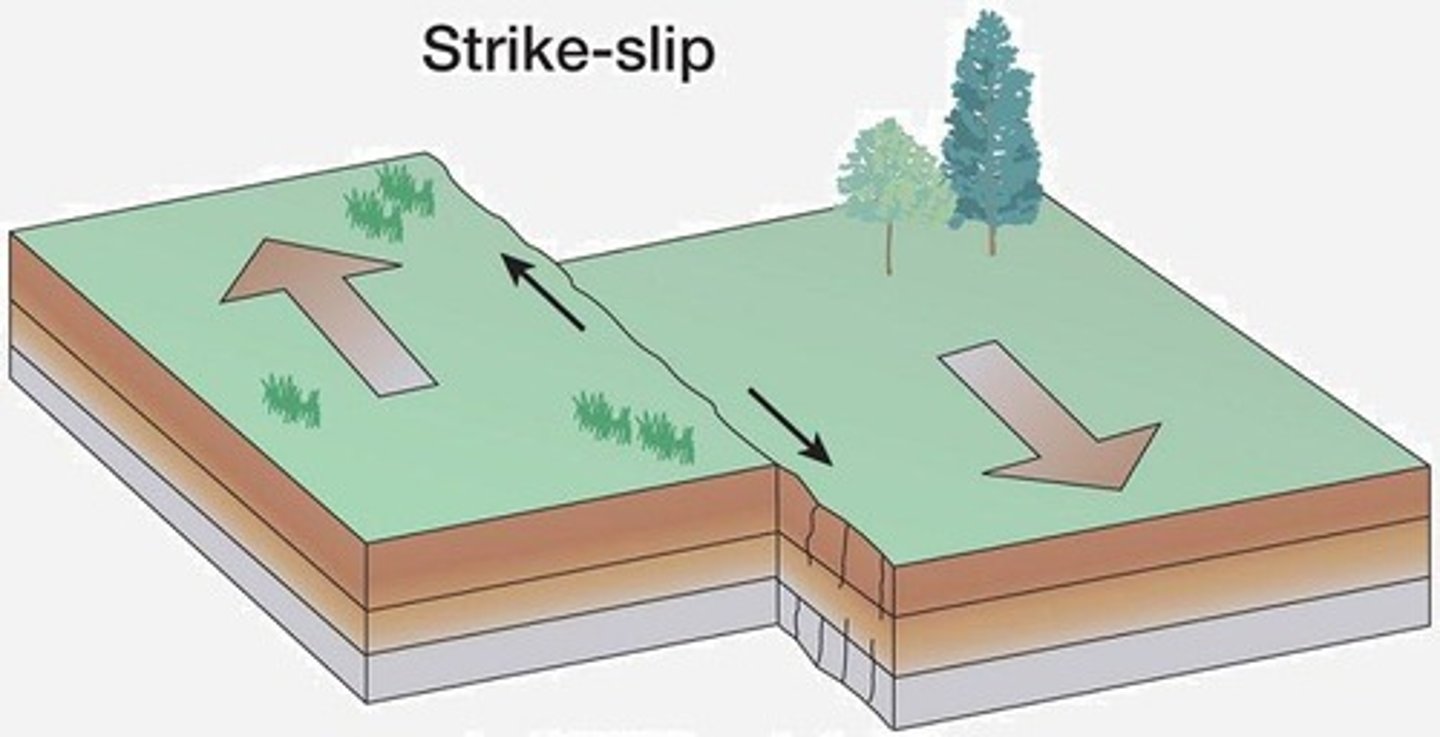
What is a transform fault boundary?
Where plates slide sideways past each other, often causing earthquakes
What drives mantle convection currents?
Heat from the Earth's core heating magma, causing it to rise and circulate
What is subduction?
When one tectonic plate is forced beneath another
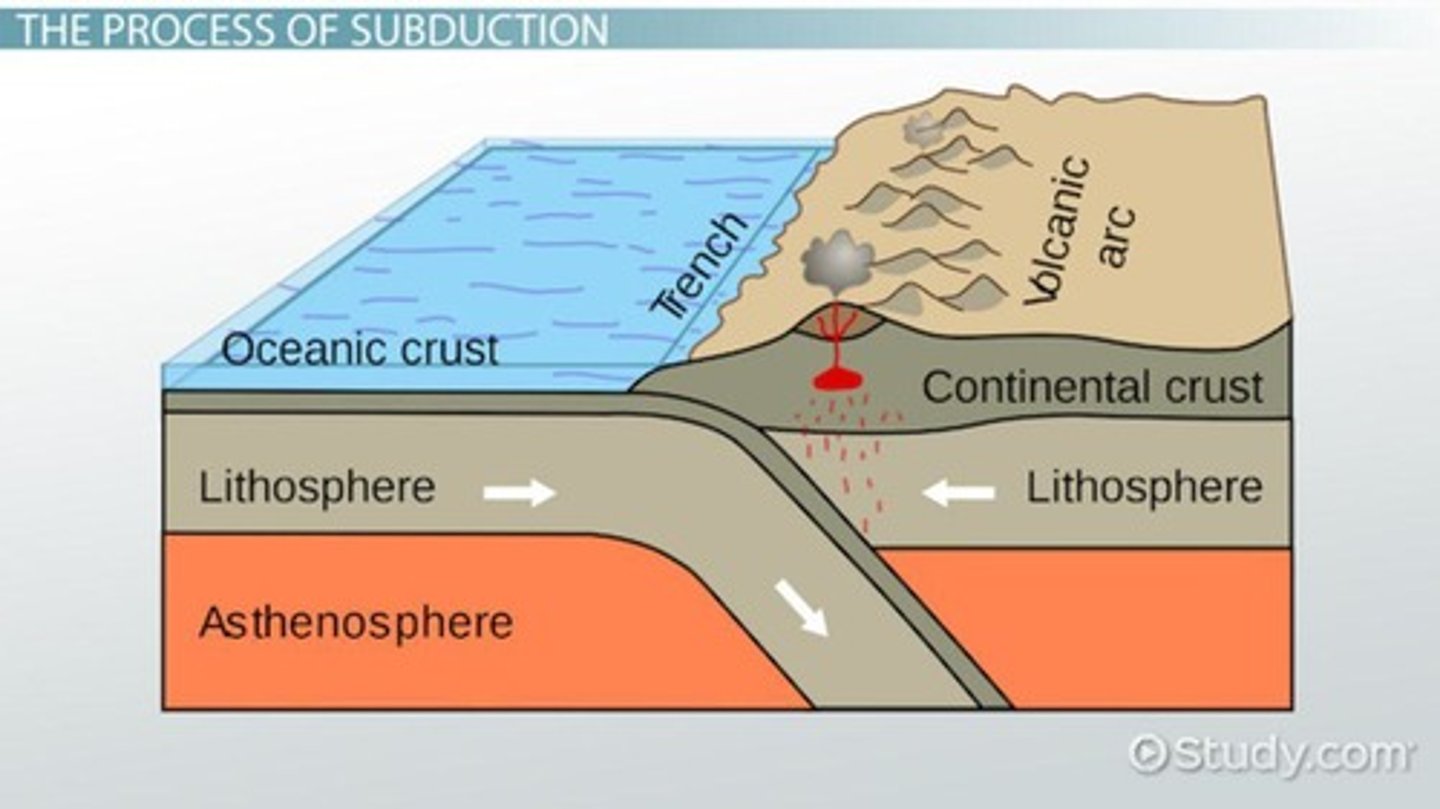
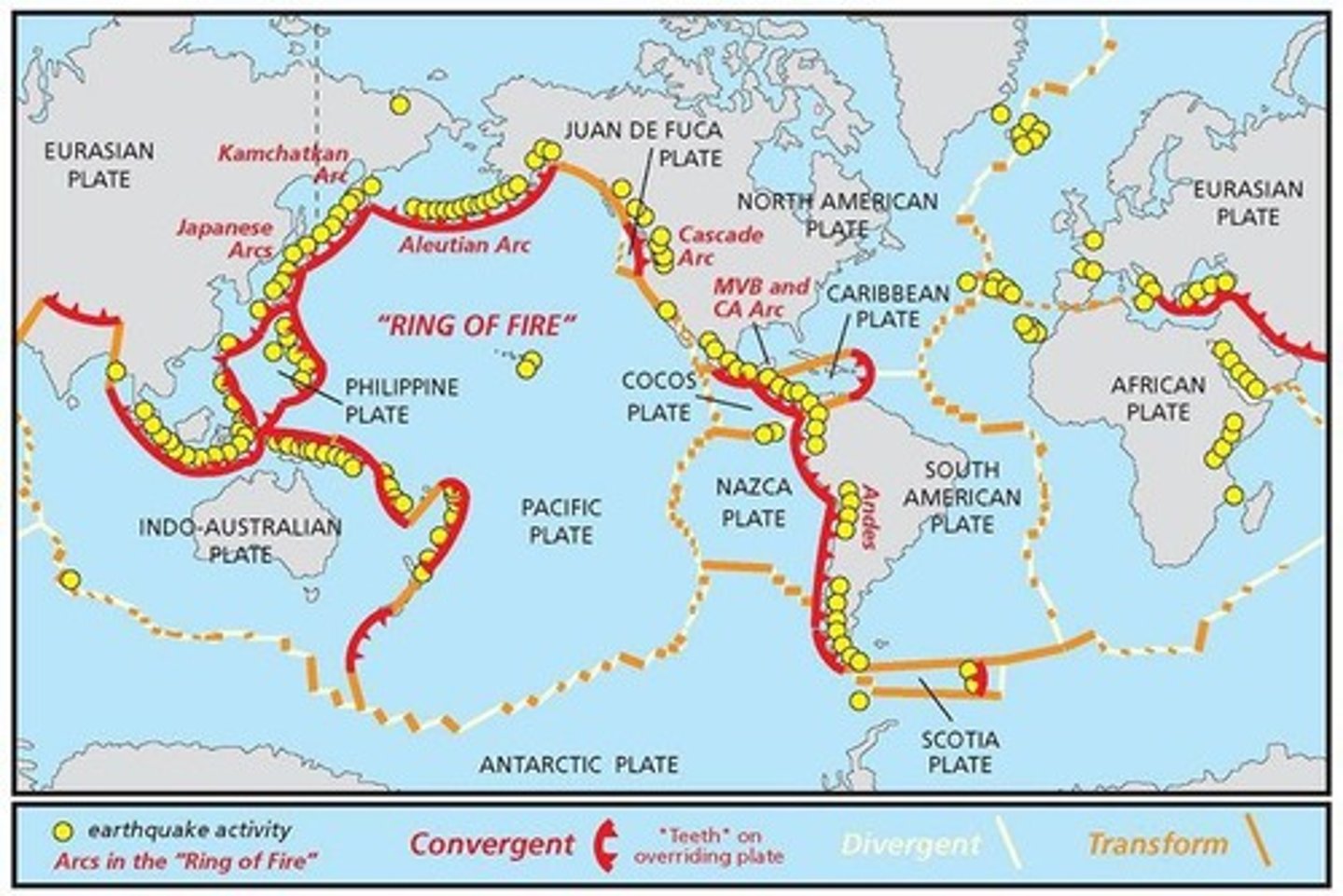
What is the Ring of Fire?
A pattern of volcanoes and earthquake zones around the Pacific Plate
What is soil composed of?
A mix of geologic (rock) and organic (living) components
What is humus?
The main organic part of soil, consisting of broken down biomass
What is weathering?
The breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces
What is erosion?
The transport of weathered rock fragments by wind and rain
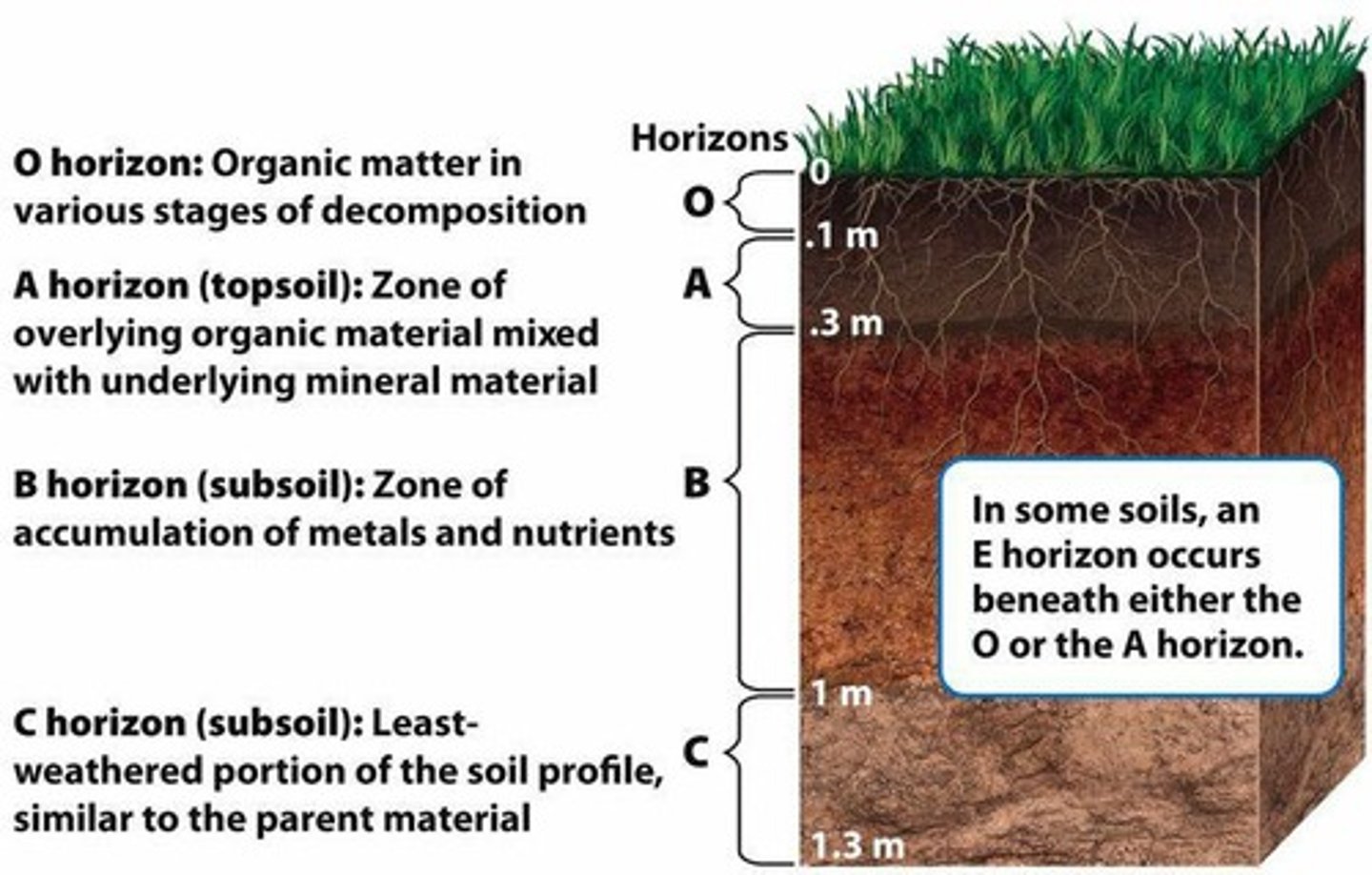
What are the soil horizons?
Layers of soil including O-Horizon (organic matter), A-Horizon (topsoil), B-Horizon (subsoil), and C-Horizon (parent material)
What is soil degradation?
The loss of the ability of soil to support plant growth
What factors contribute to soil fertility?
Nutrients, water retention, and soil texture
What is the ideal soil texture for plant growth?
Loam, which balances porosity and water holding capacity
What happens to soil that is too sandy?
It drains water too quickly, drying out the roots
What is permeability in soil?
How easily water drains through a soil
What is the relationship between permeability and water holding capacity?
More permeable soils have lower water holding capacity
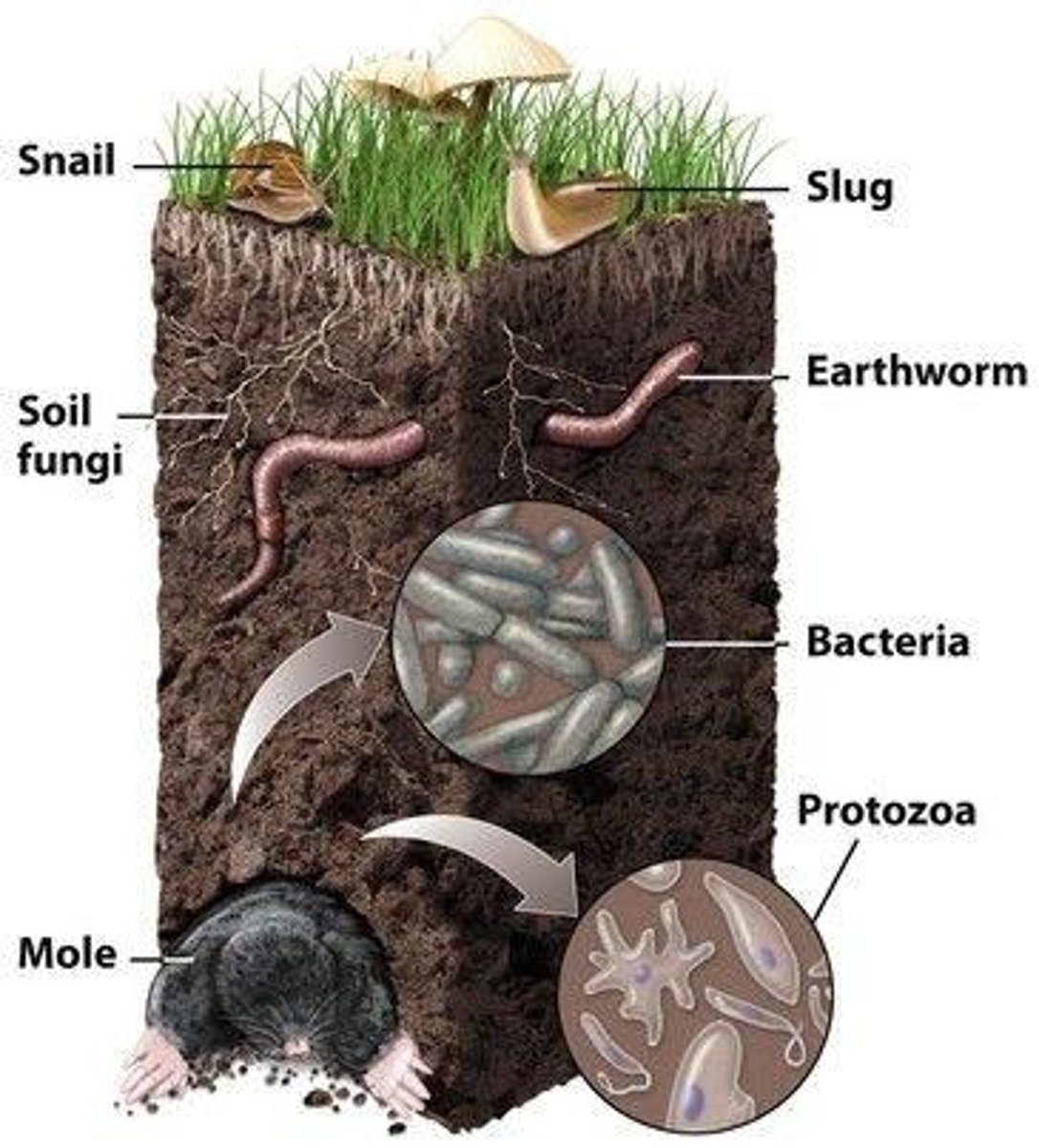
What role do decomposers play in soil?
They break down dead organic matter and return nutrients to the soil
What is nutrient recycling in soil?
The process of returning nutrients to the soil through decomposition
What is the effect of climate on soil formation?
Warmer climates lead to faster breakdown of organic matter and increased weathering
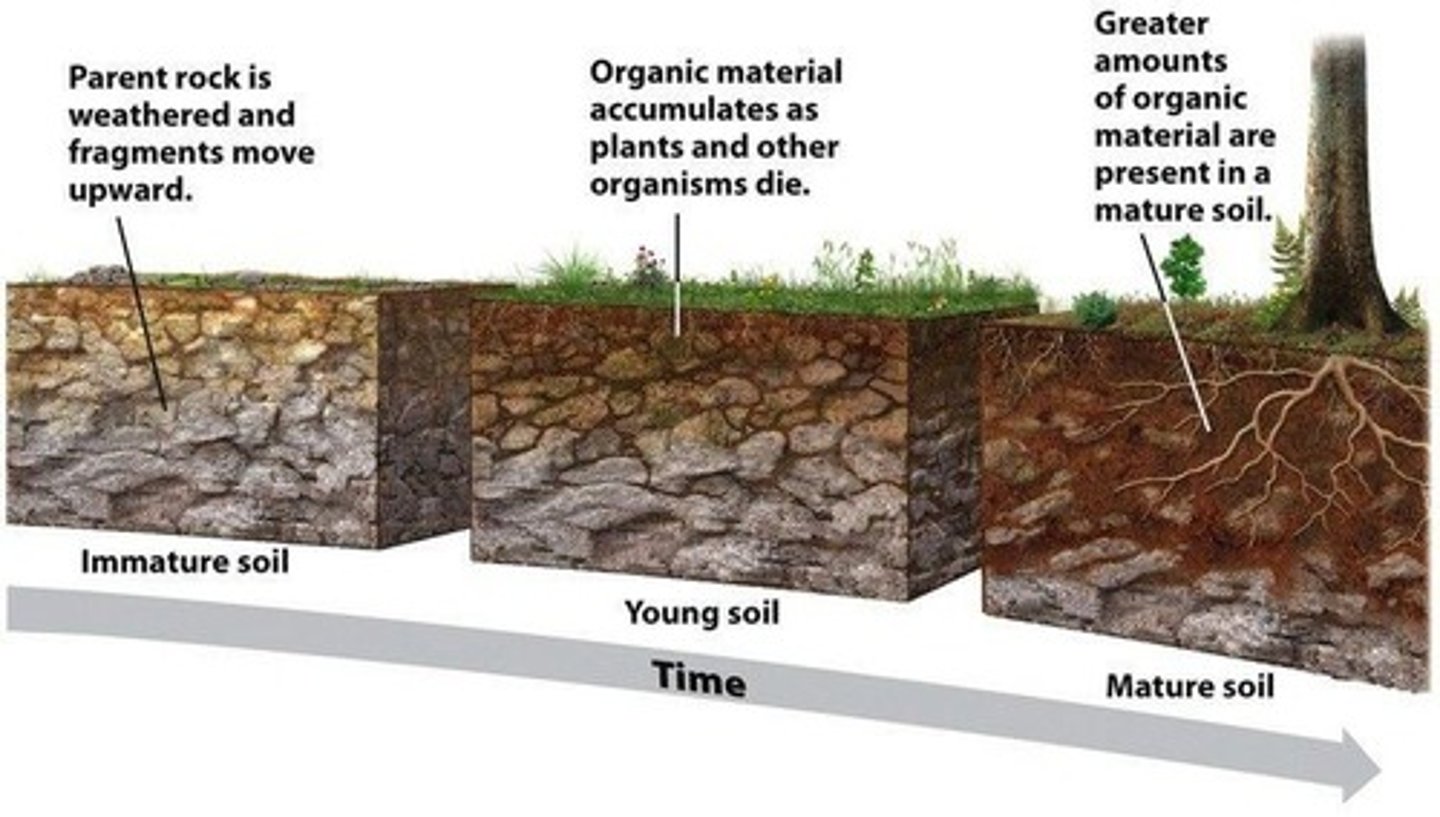
What is the impact of compaction on soil?
It reduces the soil's ability to hold moisture and support plant growth

What is the significance of parent material in soil formation?
It affects soil pH and nutrient content
What are the main nutrients needed for plant growth?
Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), Magnesium (Mg), and Calcium (Ca)
What is permeability in soil science?
Permeability is how easily water drains through a soil.
What factors increase soil permeability?
Larger, connected pore spaces.
What is H2O holding capacity?
H2O holding capacity refers to how well water is retained, or held by a soil.
What is the relationship between permeability and H2O holding capacity?
More permeable soils have a lower H2O holding capacity.
What is soil fertility?
Soil fertility is the ability of soil to support plant growth.
Which nutrients are essential for soil fertility?
N, P, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Na+.
What factors increase H2O holding capacity in soil?
Aerated soil, compost/humus/organic matter, clay content, and root structure.
What factors decrease H2O holding capacity in soil?
Compacted soil, topsoil erosion, sand, and root loss.
What factors increase soil nutrients?
Organic matter, humus, decomposer activity, clay, and bases like calcium carbonate.
What factors decrease soil nutrients?
Acids leach positively charged nutrients, excessive irrigation, excessive farming, and topsoil erosion.
How can soil texture be tested?
By letting soil settle in a jar of water and measuring the three layers that form (sand, silt, clay).
What does the permeability test measure?
The time for water to drain through a column of soil.
What does pH testing indicate about soil?
It indicates how acidic or basic/alkaline the soil is.
What does soil color indicate?
Darker soil indicates more humus, nutrients, and moisture.

How is nutrient level in soil measured?
By measuring ammonium, nitrate, or phosphate levels.
What is the composition of Earth's atmosphere?
Nitrogen ~ 78%, Oxygen ~ 21%, Water Vapor ~ 0-4%, Argon ~ 0.93%, CO2 ~ 0.04%.
What is the role of oxygen in the atmosphere?
Produced by photosynthesis and needed for human/animal respiration.
What is the significance of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
It is the most important greenhouse gas and leads to global warming.
What characterizes the exosphere?
It is the outermost layer where the atmosphere merges with space.
What occurs in the thermosphere?
It is the hottest layer, absorbing harmful X-rays and UV radiation.
What is the stratosphere known for?
It contains the thickest ozone layer, which absorbs UV-B and UV-C rays.
What happens in the troposphere?
Weather occurs here, and it contains most of the atmosphere's gas molecules and water vapor.
What is the temperature gradient in the thermosphere?
Temperature increases due to absorption of solar radiation.
What is the temperature gradient in the mesosphere?
Temperature decreases because density decreases.
What causes global wind patterns?
Energy from sunlight, density properties of air, and the rotation of the Earth (Coriolis effect).
What is the Coriolis effect?
The apparent deflection of objects traveling through the atmosphere due to the Earth's spin.
What is insolation?
Insolation is the amount of solar radiation reaching an area, measured in Watts/m2.
What causes the seasons on Earth?
The orbit of Earth around the sun and the tilt of its axis changes the angle of the sun's rays.
What is the significance of the equinoxes and solstices?
They mark the times when the Northern or Southern hemisphere is maximally tilted toward or away from the sun.
What is a watershed?
All of the land that drains into a specific body of water (river, lake, bay, etc.)
What determines the boundaries of a watershed?
Ridges of land that divide watersheds and determine runoff directions.
How does vegetation affect watershed drainage?
More vegetation leads to more infiltration and groundwater recharge.
What is the impact of slope on watershed runoff?
Greater slope results in faster velocity of runoff and increased soil erosion.
What role does soil permeability play in watersheds?
Soil permeability determines the rates of runoff versus infiltration.
How do human activities impact water quality in watersheds?
Activities like agriculture, clearcutting, urbanization, dams, and mining can degrade water quality.
What is the Chesapeake Bay Watershed?
A six-state region that drains into a series of streams/rivers and eventually into Chesapeake Bay.
What makes estuary habitats in Chesapeake Bay productive?
The mix of fresh and salt water along with nutrients in sediment.
List some ecosystem services provided by estuaries and wetlands.
Tourism revenue, water filtration, habitats for food sources, and storm protection.
What causes eutrophication in Chesapeake Bay?
Nutrient pollution (nitrogen and phosphorus) leading to algae blooms.
What are the major sources of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution?
Discharge from sewage treatment plants, animal waste from CAFOs, and synthetic fertilizers.
What is the effect of clearcutting on soil erosion?
Loss of stabilizing root structure leads to increased soil erosion and sediment deposits in streams.
How does clearcutting affect water temperature in streams?
Loss of tree shade increases soil and stream temperatures.
What is albedo?
The proportion of light that is reflected by a surface.
How does albedo affect surface temperature?
Surfaces with lower albedo absorb more heat, while those with higher albedo reflect more light.
What is the urban heat island effect?
Urban areas are hotter than surrounding rural areas due to low albedo of surfaces like blacktop.
How do mountains affect regional precipitation?
Mountains disrupt wind patterns and create rain shadow effects.
What is the role of upwelling zones in ocean currents?
They bring oxygen and nutrients to the surface, supporting productive fisheries.
What is the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO)?
A pattern of shifting atmospheric pressure and ocean currents in the Pacific Ocean affecting global weather.
What are the effects of El Niño on fisheries?
Suppressed upwelling leads to less productive fisheries in South America.
What are the effects of La Niña on weather patterns?
Stronger upwelling and better fisheries in South America, along with cooler, drier conditions in Australia and Southeast Asia.
How does human activity increase metal contaminants in streams?
Through industrial discharge and urban runoff that introduces pollutants into water bodies.
What is hypoxia and how is it related to eutrophication?
Hypoxia is low oxygen levels in water caused by bacteria decomposing dead plants, leading to dead zones.
What is the impact of sediment pollution on aquatic habitats?
Increases turbidity, reduces photosynthesis, and covers rocky streambed habitats.
How does deforestation affect water quality in streams?
It can lead to increased sedimentation, higher temperatures, and reduced organic matter.
What is thermohaline circulation?
A global ocean circulation pattern that mixes salt, nutrients, and temperature throughout the world's oceans.
What are the consequences of urbanization on watersheds?
Increased runoff, reduced infiltration, and potential degradation of water quality.
What is the relationship between albedo and polar bear habitats?
Changing albedo affects heat absorption, impacting polar bear habitats as ice melts.