Unit 3: DNA (Molecular Biology)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Nucleotide
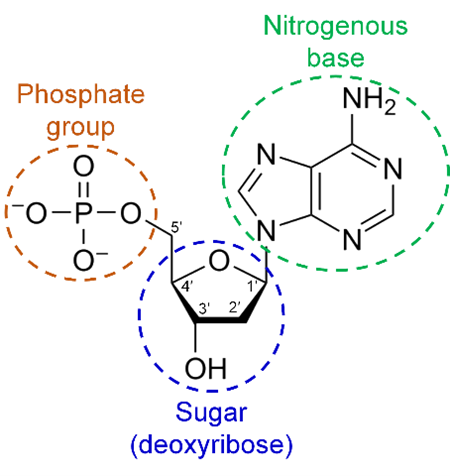
Monomer of nucleic acids which consist of a sugar, phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
DNA
A molecule in double helix shaped, composed of two strands of nucleotides. A goes with T, and C goes with G
Transcription
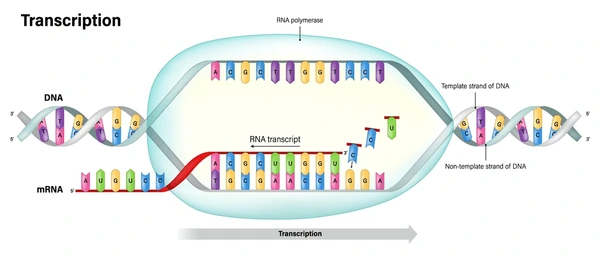
Occurs in nucleus
RNA polymerase unravels DNA, and reads the template strand from the TATA box (3’) to terminator region(5’),
DNA template strand into a complimentary strand of RNA → A with U
Spiceosome ill them remove INTRONS and keeps EXONS in the mRNA strand
Finally 5’ cap is added to 5’ end and a poly-A tail to the 3’ end, for protection of exonuclease
Translation
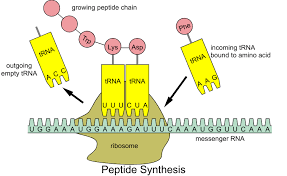
Initiation
Ribosome binds to the mRNA (5’→3)
Ribosome reads mRNA in groups of 3
Matching tRNA binds to the start of codon at the A site, bringing a anti-codon
Elongation
Codon in A site moves to P site, and is attached to tRNA
Then moves to E site ith its tRNA, but the amino acid is left at the E site
The steps repeat and start build a polypeptide chain
Termination
Ribosome will reach a stop codon and let go
Differentiated cells
Cell that has potential to become a cell in need
Methylated DNA
Tightly packed DNA and is prevented from binding to mRNA, meaning cell produces less proteins
Acetylated DNA
Uncoiled DNA which allows binding to mRNA, meaning cell produces more proteins
Transcription Factors
Helps RNA polymerase attach or detach to mRNA
Controls how much or how little a protein gets expressed
Base substitution
A single nucleotide gets replaced with another
Insertion
Nucleotide is added into DNA
Deletion
Nucleotide is deleted from DNA
Silent
Though the codon changed, it still codes for the same amino acid
Nonsense
Changes the codon into a stop codon, leading for the mRNA to stop early
Missense
Codon changes to code another amino acid
Hydrogen bonds
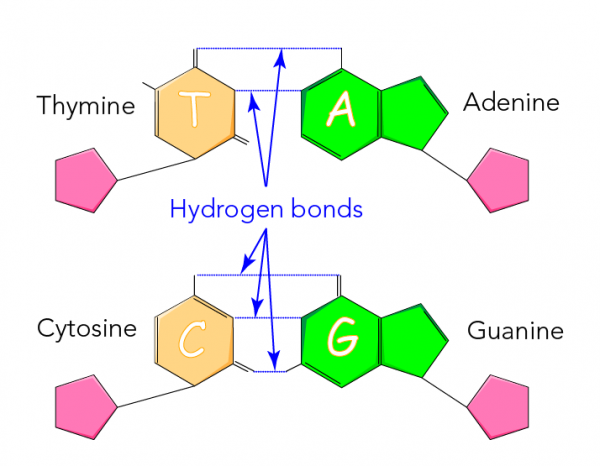
Formed between different nucleotide bases
Covalent bonds
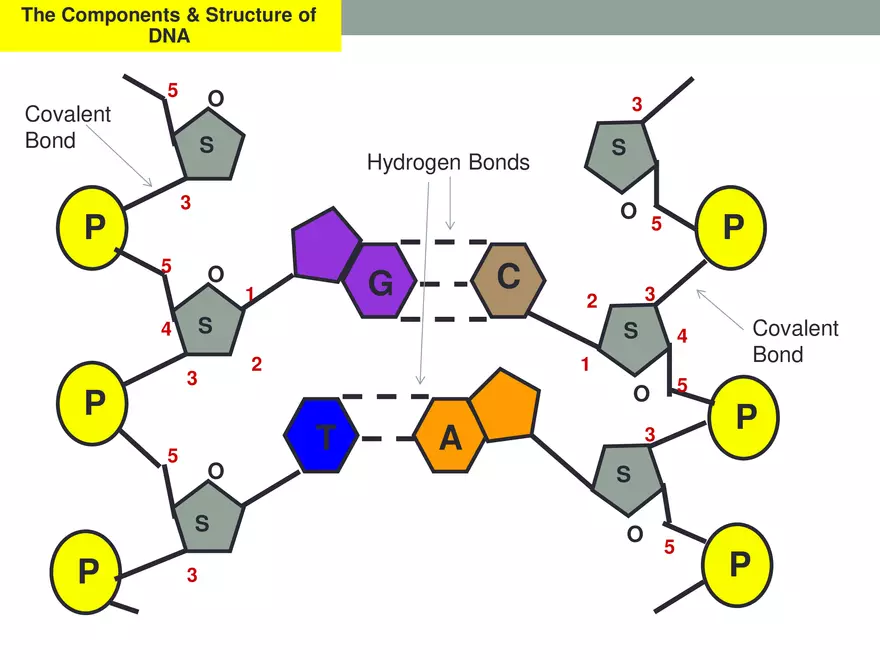
Covalent bonds in DNA connect the sugar to the phosphate
Adenine and Thymine
2 hydrogen bonds
Guanine and Cytosine
3 hydrogen bonds