B2.2 Organelles and compartmentalization
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are organelles?
Organelles are subunits of cells that perform specific functions. They can be solid structures or membrane bound sacs
What is compartmentalization?
It is when membrane-bound organelles act as barriers between aqueous solution. The membrane around an organelle creates a compartment with controlled conditions inside
What are advantages of compartmentalization?
-it allows for the development of structures such as chloroplasts and mitochondria
-enzymes and metabolites can be concentrated in a small space, increasing the chance of collision
-substances that can damage cells can be isolation/trapped within a membrane
-conditions such as pH can be maintained at an optimal value for a particular reaction
Where can organelles be found?
In prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Where are membrane-bound organelles found?
Only in eukaryotic cells, as the organelles in prokaryotic cells are much simpler
Give an example of an organelle that benefits from compartmentalization. Why?
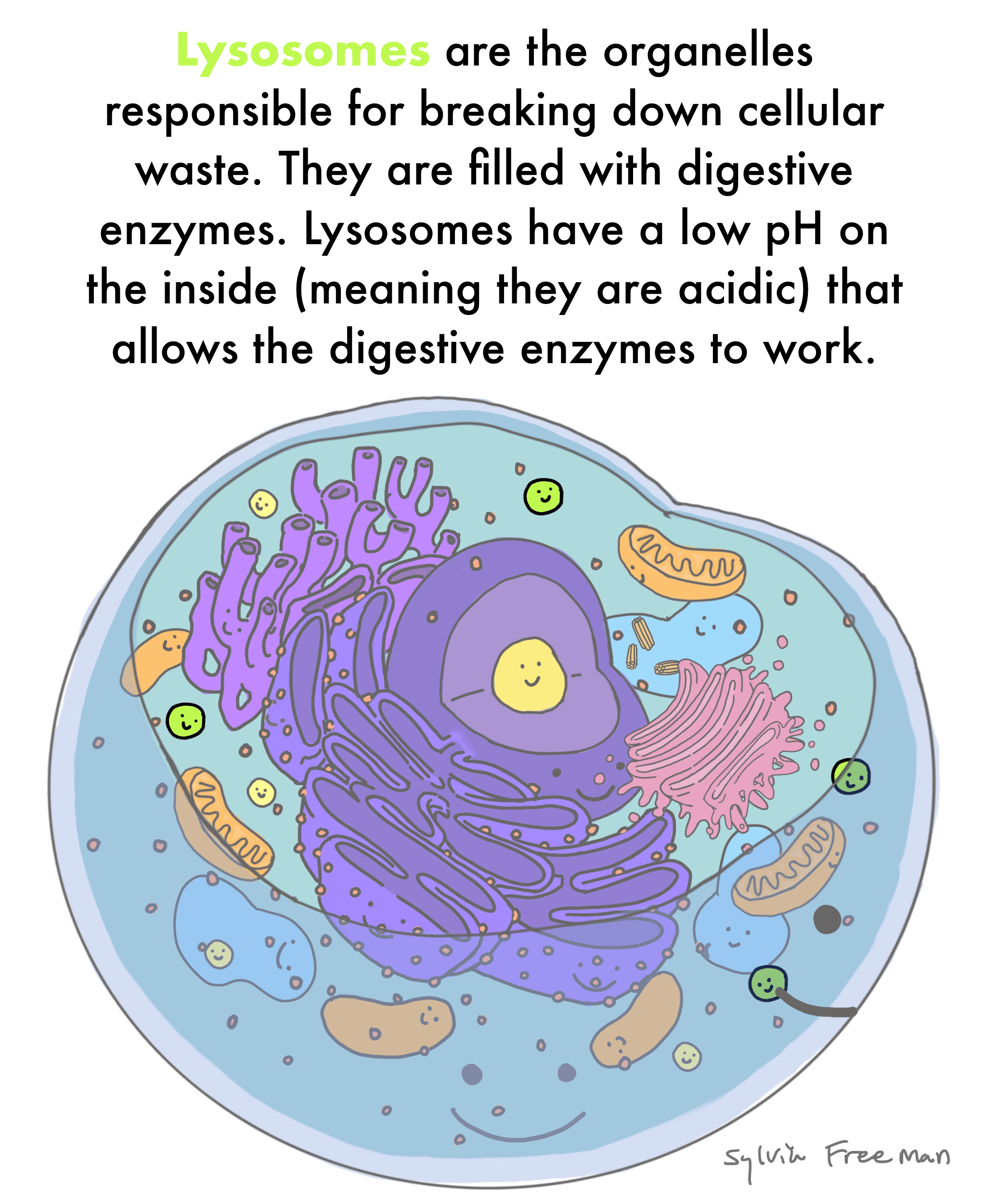
Lysosomes are organelles responsible for breaking down cellular waste. This requires digestive enzymes which could be harmful to other parts of the cell. Isolating the enzymes protects the rest of the cell
What does it mean when an organelle does not have a membrane?
This means it is not enclosed by a phospholipid bilayer, and the solid structures are located within the cytoplasm.
Give some examples of organelles that don’t have a membrane
Ribosomes, cell wall, cytoskeleton
(Ribosomes don’t have a membrane so that they can easily carry out translation)
What does it mean when an organelle is single membrane bound?
They are sacs enclosed by a single phospholipid bilayer
Give some examples of single membrane bound organelles?
rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes
What does it mean when an organelle is double membrane bound?
They are structures enclosed by two phospholipid bilayers
Give some examples of double membrane bound organelles?
nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts
What is transcription?
The process where DNA is copied into RNA. This occurs in the nucleus where the DNA is located. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosomes where protein synthesis occurs
Why does transcription occur?
Because DNA can’t leave the nucleus, so mRNA is made, so it leaves the nucleus to travel to the ribosomes where protein synthesis occurs
What is protein synthesis?
It is the entire process where DNA is copied into RNA, which then travels out of the nucleus. It includes when amino acids are assembled into proteins in ribosomes, due to the genetic code from mRNA. Peptide bonds form between these amino acids, which forms a polypeptide sequence
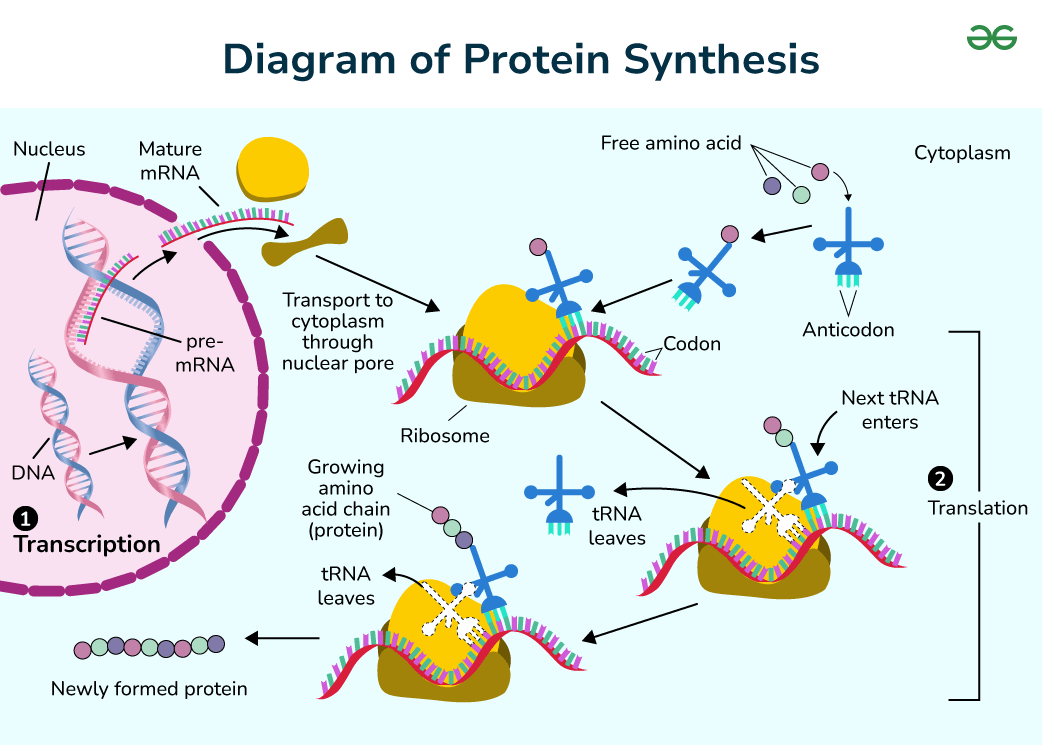
What is translation?
Where RNA is coded into amino acids, forming proteins. This occurs in the ribosome. The RNA has to leave the nucleus first in eukaryotic cells
Where does transcription and translation occur in prokaryotic cells?
In the cytoplasm, as there is no nucleus. This means that the protein is produced right after the mRNA is finished. It does not have to leave the nucleus first
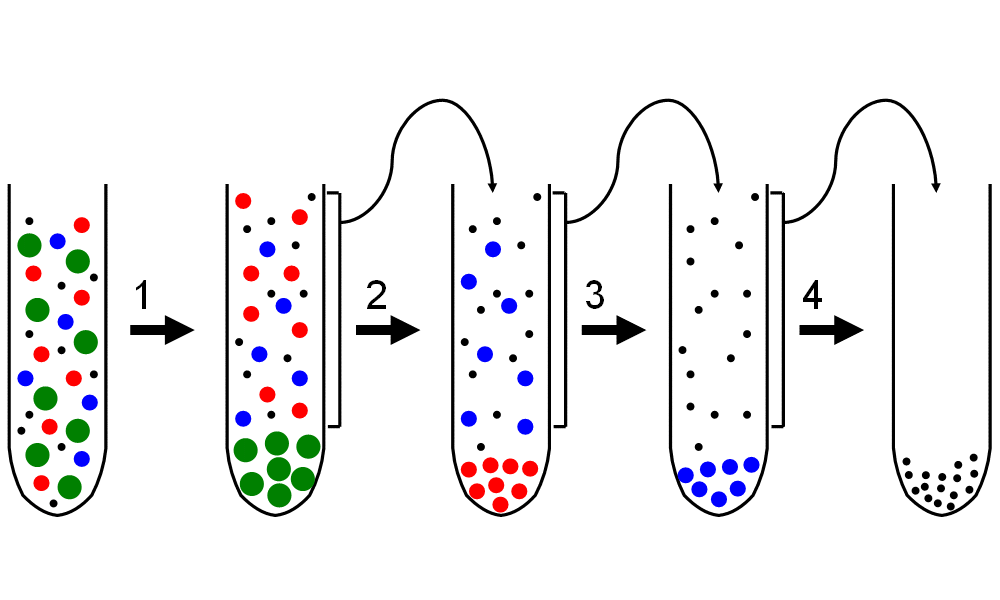
What is differential centrifugation?
It is a procedure used to separate organelles, based on their sedimentation rate
How does differential centrifugation work?
Cells are disrupted in a homogenizer by a high centrifugal force. The denser material will form a solid pellet at the base of the tube. The remaining liquid can undergo repeated centrifugation at higher speeds to fractionate cells into their components. Eventually, these will also form solid pellets
What is the cytoskeleton?
A network made up of protein filaments that provides structural support of the cell, helping to maintain the cell shape. It is the “skeleton” of the cell
What are ribosomes?
The site where protein synthesis occurs. They have a small and a large subunit
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
It is lined with ribosomes, and is involved in protein synthesis
What is the Golgi apparatus?
It modifies and packages proteins and lipids for delivery to other organelles
What are the mitochondria?
It is the powerhouse of the cell, as it provides energy through cellular respiration
What are lysosomes?
They break down waste materials with digestive enzymes. (when lysosomes are absent from plant cells, the vacuole takes on its role)
What are chloroplasts?
They convert sunlight into energy during photosynthesis, with chlorophyll
What is a flagella?
A long-thin tail attatched to bacteria to allow it to move
What are centrioles and where are they found?
Centrioles are found in animal cells, and not plant cells. They release microtubeles which split the cell during cell division
What is the difference between the rough and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is lined with ribosomes, whereas the smooth endoplasmic reticulum isn’t
What types of ribosomes are in eukaryotic cells?
80S ribosomes
What types of ribosomes are in prokaryotic cells?
70S