Lecture #14: Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
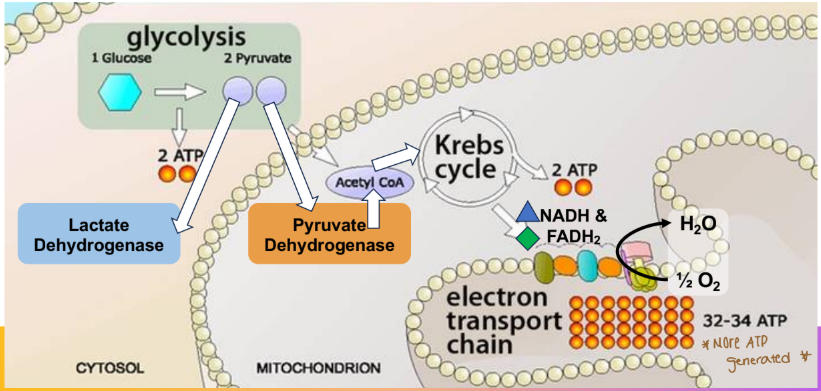
What is the terminal electron acceptor in the electron transport chain
(where we can get WAY more ATP than using glycolysis alone)
Oxygen
Where is glucose derived from?
Glycogenolysis
Gluconeogenesis
Diet
What is used for the initial oxidation to pyruvate via glycolysis?
Glucose is used for the initial oxidation
Glucose
Derived from glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, or the diet
Initial oxidation to pyruvate via glycolysis
Reduction to lactate (low oxygen, cytosol) OR oxidation to acetyl-CoA (normal oxygen, mitochondria)
Many oxidation steps in TCA
What do we do with NADH/FADH2?
Send them hoes to the electron transport chain (ETC)
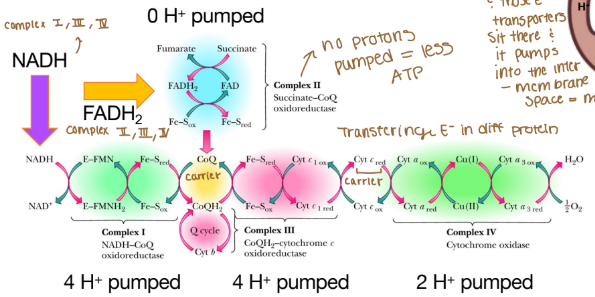
What does ETC complexes turn chemical bonds into?
Electrochemical potential
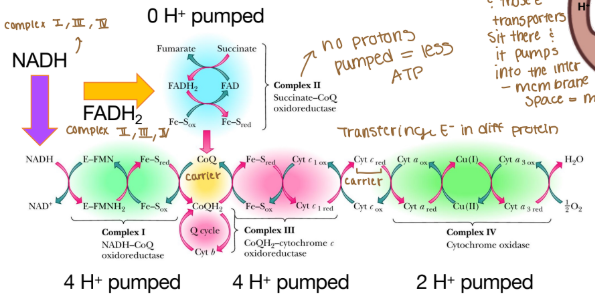
Electrons are passed from REs:
NADH at complex I (purple arrow)
FADH2 at complex II (yellow arrow)
Coenzyme Q at complex III
Cytochrome c at complex IV
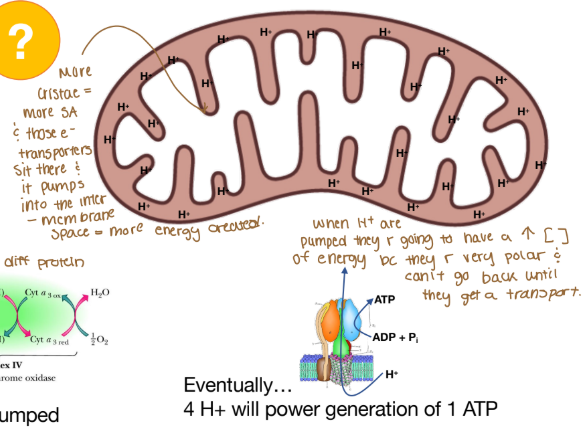
Where are protons passed through?
Intermembrane space (mitochondria)
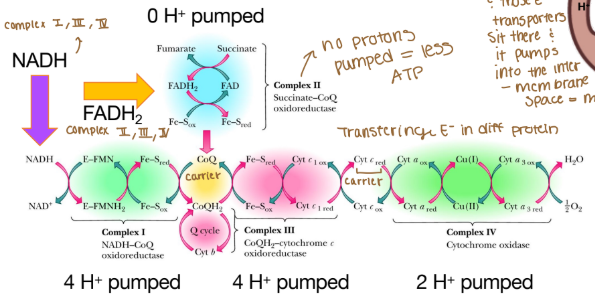
The order of complexes if it is NADH?
Complex I: 4 H pumped
Complex III: 4 H pumped
Complex IV: 2 H pumped
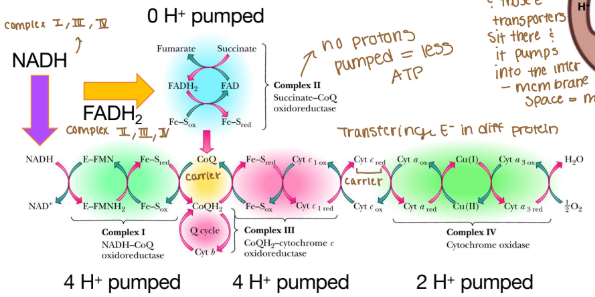
Are any protons (H) pumped into complex II?
None because that creates less ATP
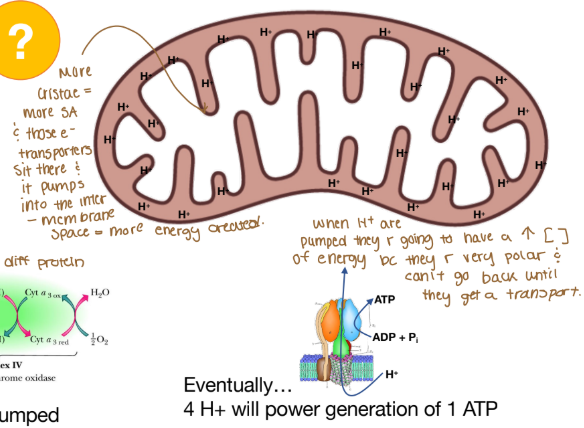
Why is there a high concentration of energy when H+ are pumped into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria?
The H+ is very polar and can’t go back until they get a transporter.
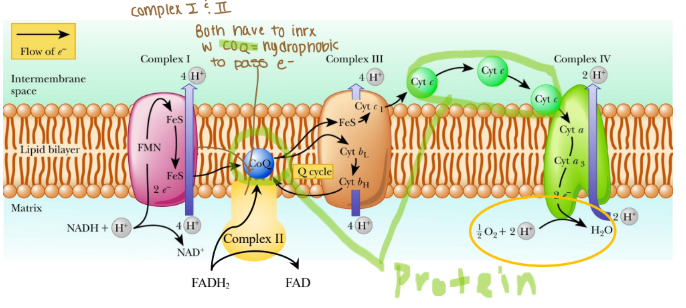
ETC complexes span the inner mitochondrial membrane
Solubility at work!
Complexes are integral, hydrophobic proteins
Coenzyme Q is hydrophobic protein
Cytochrome c is hydrophilic
Complexes associate in lipid rafts
Protons cannot cross membrane w/o transporter!
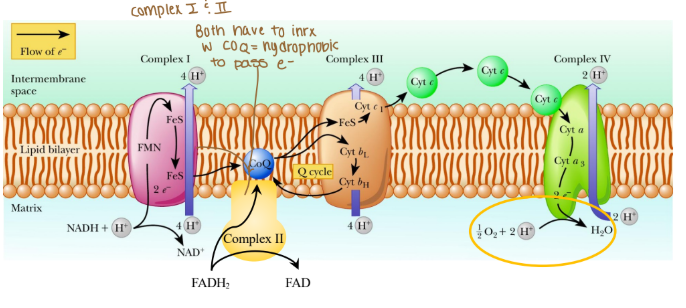
How are the complexes in the ETC placed?
They are integral, hydrophobic proteins
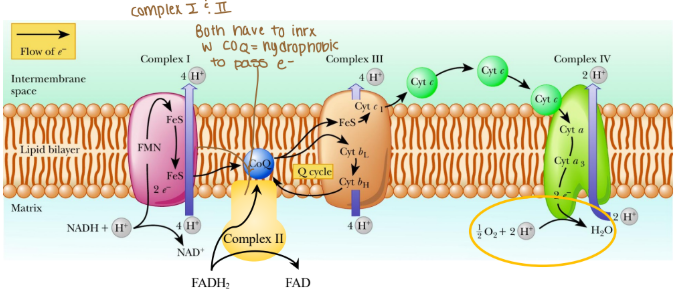
Which coenzyme is a hydrophobic protein in the ETC?
Coenzyme Q
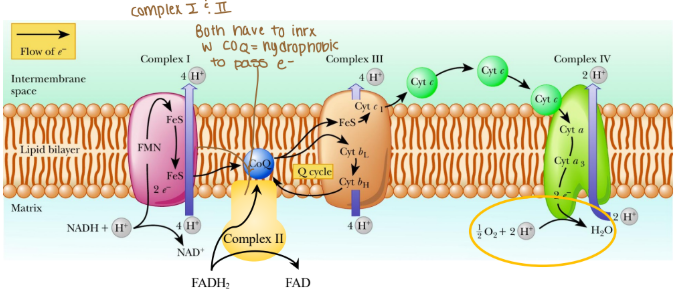
Is cytochrome c hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophilic
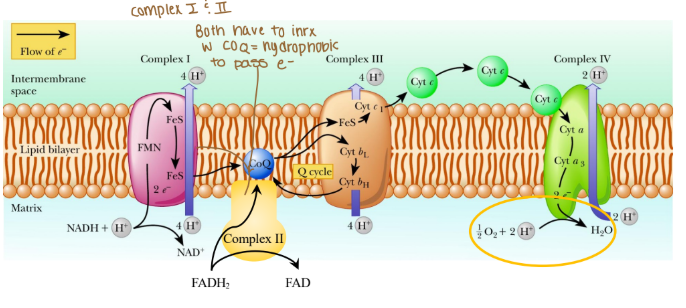
What are the complexes in the ETC associated in with?
Associated in lipid rafts
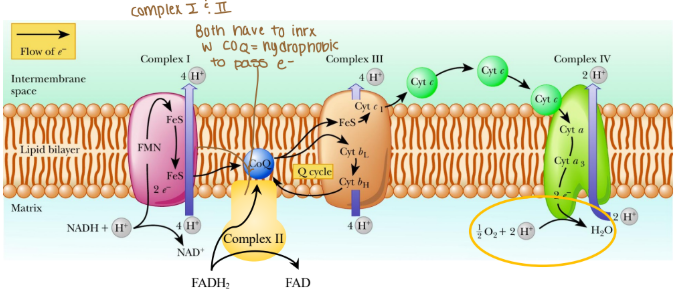
True/False: Can protons cross the ETC w/o a transporter?
False: bc protons are hydrophobics and need to be hydrophilic so they do need a transporter.
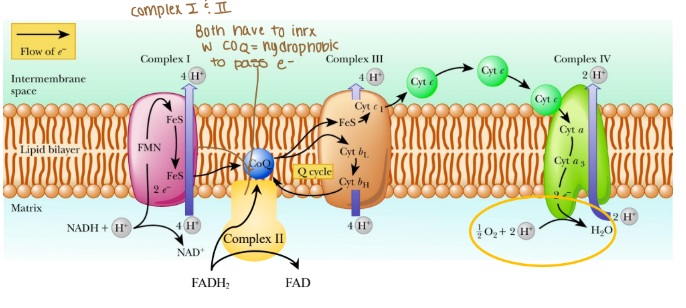
How does oxygen status regulate which metabolic pathway is utilized?
Oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor which forms water and that is how it regulates which metabolic pathway is used.
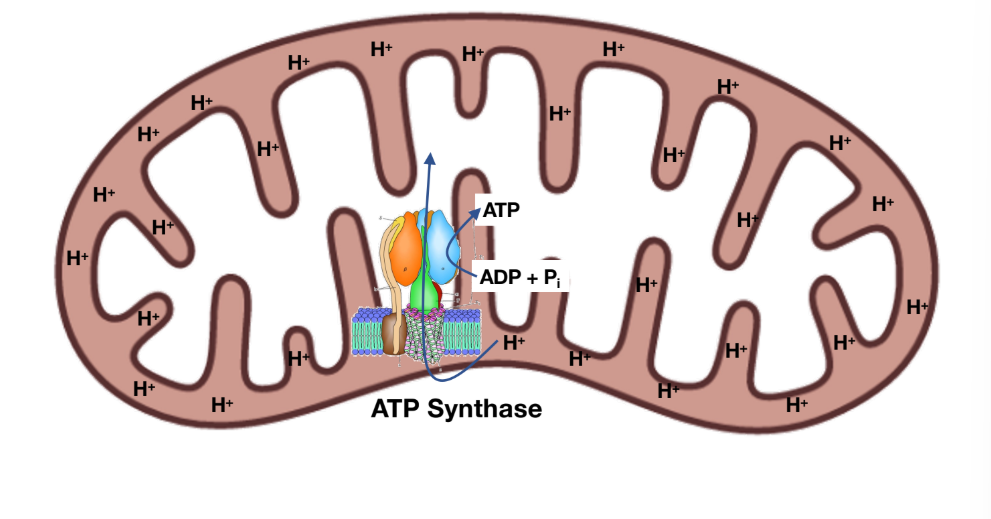
ATP synthase converts electrochemical potential to chemical energy
Chemiosmotic coupling = process by which chemical gradient becomes chemical E
Oxidative phosphorylation: for every 4 protons transported, 1 ATP generated!
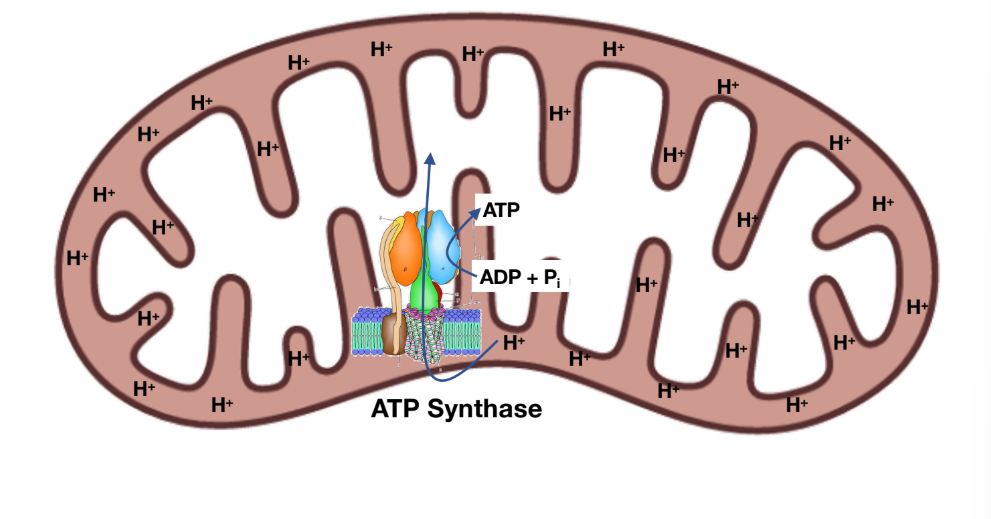
Chemiosmotic coupling
The processes which the chemical gradient becomes chemical energy
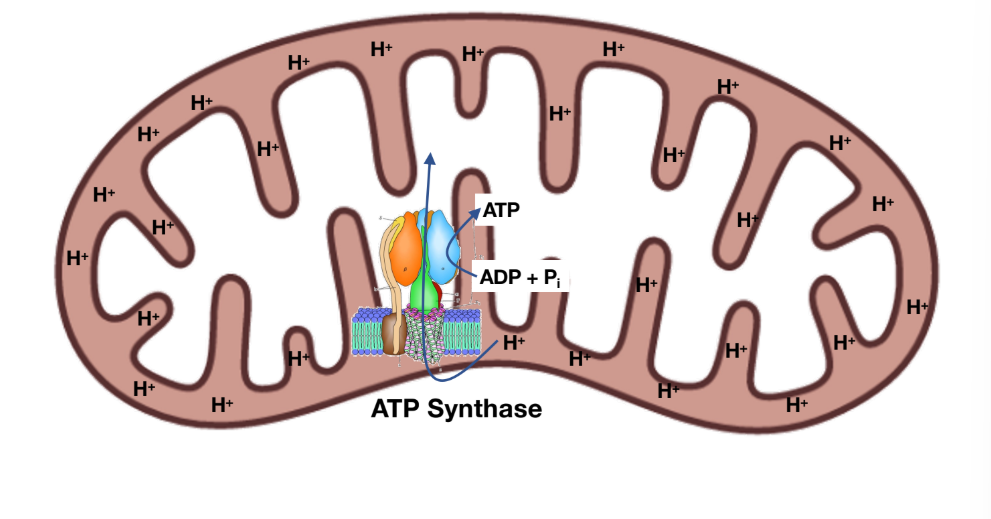
Oxidative phosphorylation
For every 4 protons that are transported, 1 ATP is generated
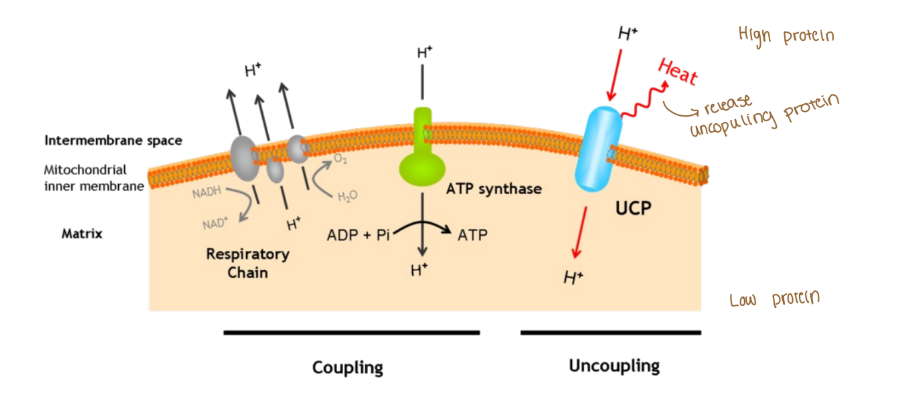
Why does not-all proton pumping leads to ATP synthesis?
Uncoupling
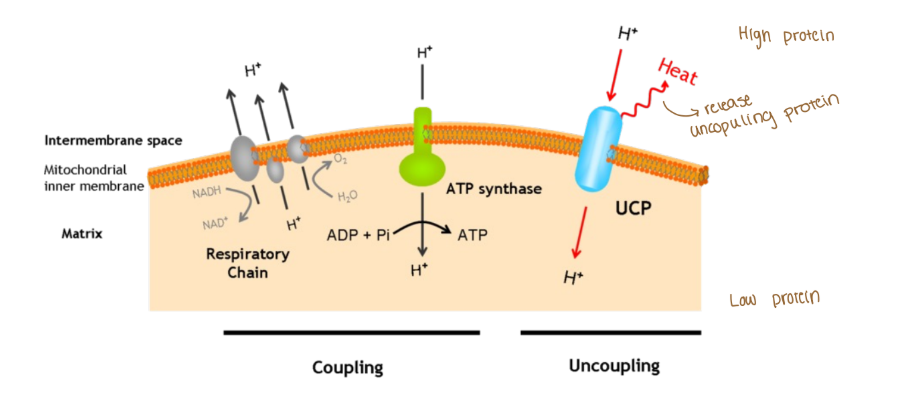
Uncoupling
Disconnect btwn the ETC and ATP synthase (uncoupling protein: UCP)
In order for ATP synthase to create ATP there needs to be that H+ (proton) gradients in the intermembrane space of the mitochondria
2,4-dinitrophenol (lipogenic) stops that H+ gradient in the intermembrane space which then it makes the ATP synthase unable to be active to make ATP
When no atp is created then a byproduct is heat
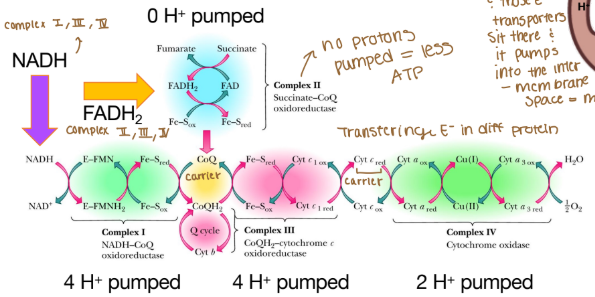
Which molecules carry electrons to the ETC?
NADH
FADH2
Which proteins shuttle electrons between ETC complexes?
Coenzyme Q
Cytochrome c
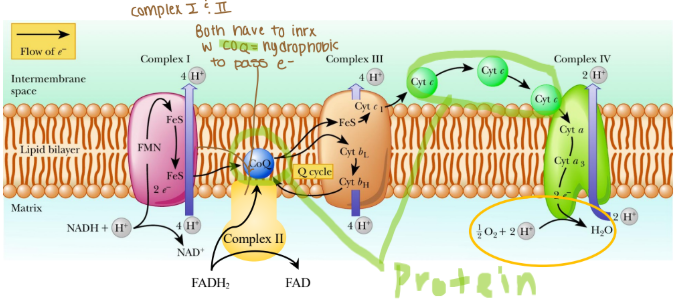
Why can’t complex II pump protons?
It lacks the necessary components to do so and the energy released from its reaction is insufficient to drive proton translocation across the mitochondrial membrane. Instead of pumping protons, it transfers electrons from FADH₂ to ubiquinone (Coenzyme Q), which then carries the electrons to Complex III.
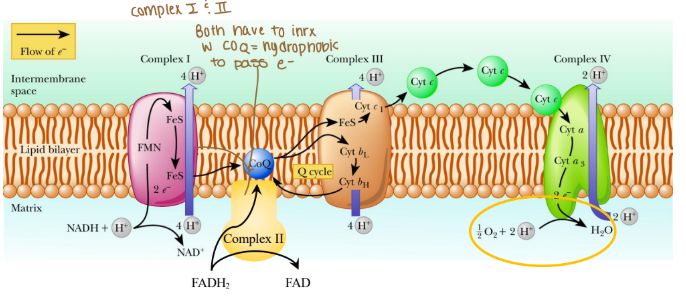
Why would coenzyme Q need to be hydrophobic?
Coenzyme Q needs to be hydrophobic because it is embedded in the lipid bilayer of membranes, particularly in the inner mitochondrial membrane where it functions as an electron carried in the ETC.

If a molecule of glucose enters glycolysis, then pyruvate dehydrogenase, then tricarboxylic acid cycle, and all of the reducing equivalents complete the electron transport chain (assume any NADH formed in the cytosol utilizes the malate-
aspartate shuttle), how many molecules of ATP will be produced?
32 ATP will be produced