MODULE 7
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Which of the following is not true regarding osmosis?
Osmosis is involved in blood pressure.
Patients with congestive heart failure should increase their water intake to decrease the rate of osmosis to the interstitial fluid.
Electrolytes play an essential role in the process of osmosis.
Osmosis describes the direction of water as it moves through a membrane.
Patients with congestive heart failure should increase their water intake to decrease the rate of osmosis to the interstitial fluid.
What best describes the role of sodium (Na+) in human health?
A high sodium diet helps to maintain a low blood pressure.
We need a lot of sodium to maintain an isotonic environment.
A low sodium diet can cause edemas (swelling of extremities).
Sodium regulates both fluid and pH balance in the body.
Sodium regulates both fluid and pH balance in the body.
What best describes the term Hypernatremia?
Abnormally high Sodium levels which can cause high blood pressure
Electrolytes that are positively charged:
Na, K, Mg, Ca
Electrolytes that are negatively charged:
Cl, P
What is the standard diet recommendation for patients with hypertension?
A reduction of sodium in the diet.
T/F: A cell immersed in a hypertonic solution would shrink
true
Which of the following is true regarding electrolytes?
Electrolytes are confined to the intracellular space.
Electrolytes regulate the fluid distribution in our body.
Electrolytes are vitamins that maintain osmosis.
Electrolytes are confined to the extracellular space.
Electrolytes regulate the fluid distribution in our body.
Which of the following is true regarding Potassium (K+)?
Potassium is actively pumped out of the cell.
Potassium is an electrolyte.
Potassium is only found in the intracellular fluid.
Potatoes and bananas are food sources with low potassium levels.
Potassium is an electrolyte.
T/F: Most of the body's fluids are found outside of cells in the extracellular fluid.
False
Which of the following is TRUE regarding water and water consumption - choose all that apply
Both dehydration and water intoxication (excess intake) can have serious side effects
Food is a significant source of water
It is generally most beneficial to only consume distilled water without minerals
Body fluids are composed of water and electrolytes
Both dehydration and water intoxication (excess intake) can have serious side effects
Food is a significant source of water
Body fluids are composed of water and electrolytes
T/F: For most adults with hypertension, there is no known cause. Roughly half of the patients with hypertension can help symptoms by reducing sodium in the diet.
True
T/F: The amount of salt in a solution does not affect its tonicity.
False
Which of the following correctly describes a function of sodium?
Sodium reduces the likelihood of the formation of edemas (swelling in extremities).
Sodium transports glucose into cells when it moves down its concentration gradient.
High sodium levels are essential for moving fluid out of capillaries and into the interstitial fluid.
Because sodium is negatively charged, it reduces the pH of the blood.
Sodium transports glucose into cells when it moves down its concentration gradient.
Which of the following is true regarding electrolytes?
Electrolytes are always found at higher concentrations in the extracellular fluid.
The cell cannot regulate the concentration of electrolytes across its plasma membrane.
The kidneys are responsible for maintaining electrolyte balance.
Electrolytes are always negatively charged
The kidneys are responsible for maintaining electrolyte balance.
T/F: If the solute concentration is higher in the intracellular space compared to the extracellular space, then water will have an increased net movement to the extracellular space.
False
Which of the following is true regarding hyperkalemia?
Hyperkalemia can be caused by liver disease, and it can lead to insomnia.
Hyperkalemia can be caused by pancreatic cancer, and it can lead to migraines.
Hyperkalemia can be caused by cardiac disease, and it can lead to diarrhea.
Hyperkalemia can be caused by kidney disease, and it can lead to cardiac arrest.
Hyperkalemia can be caused by kidney disease, and it can lead to cardiac arrest.
Electrolytes located Intracellularly include:
K, P, Mg
Electrolytes located Extracellularly include:
Ca, Cl, Na
The __________ is the term for the substance that is dissolved in the _____________.
solute; solvent
What best describes the term Hyperkalemia?
Abnormally high Potassium levels which can cause abnormal heart rhythm
Abnormally low Potassium levels which can cause low blood pressure
Abnormally low Sodium levels which can cause low blood pressure
Abnormally high Sodium levels which can cause cardiac arrest
Abnormally high Potassium levels which can cause abnormal heart rhythm
The most common cause of electrolyte imbalance is:
pregnancy
cancer
overconsumption of dairy foods
kidney disease
kidney disease
What is true regarding Sodium and Potassium? Choose all that apply
Potassium (K) is the major positively charged intracellular cation
Potassium (K) is the major positively charged extracellular cation
Sodium (Na) is the major positively charged extracellular cation
Sodium (Na) is the major positively charged intracellular cation
Potassium (K) is the major positively charged intracellular cation.
Sodium (Na) is the major positively charged extracellular cation
same solute concentration
Isotonic solution
higher solute concentration; cell shrinks
Hypertonic solution
lower solute concentration; cell swells
Hypotonic solution
T/F: A cell immersed in a hypotonic solution would increase in volume.
True
What best describes the term electrolytes?
Charged minerals dissolved in water which regulate fluid distribution
Which of the following is false regarding water consumption? Choose all that apply.
A sign of dehydration is lighter colored urine
Food is a major source of water
Water makes up 25% of a person's body weight
Water is one of the components of body fluids
A sign of dehydration is lighter colored urine
Water makes up 25% of a person's body weight
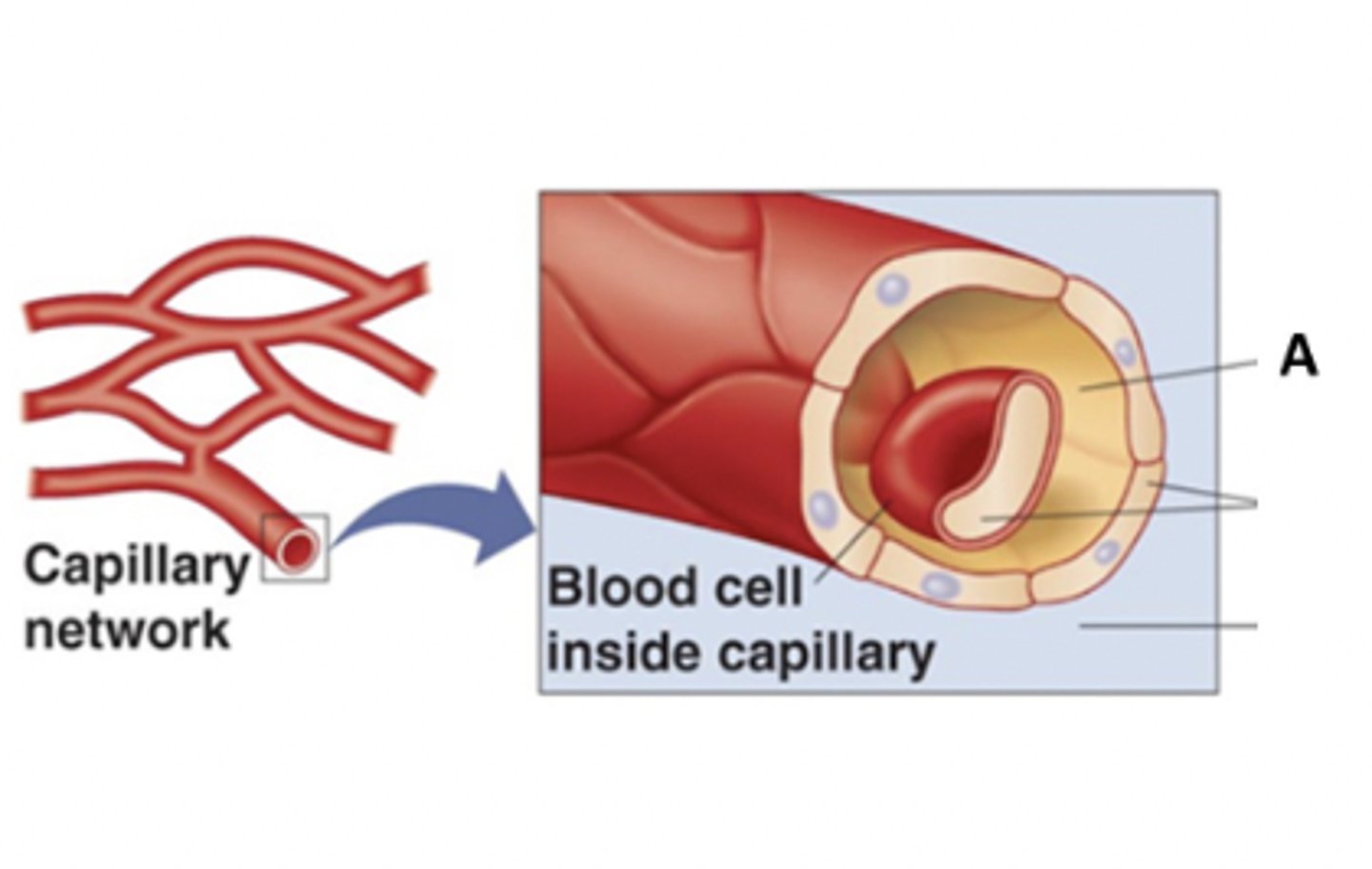
A region which has a relatively high sodium (Na+) concentration
With regard to electrolyte concentrations, the letter "A" depicts (points to):
A region which has a relatively high Magnesium (Mg+) concentration
A region which has a relatively high Phosphorus (P+) concentration
A region which has a relatively high Potassium (K+) concentration
A region which has a relatively high sodium (Na+) concentration
Which of the following best describes osmosis?
Osmosis is the movement of water toward an area of lower solute concentration.
Osmosis is the movement of water toward an area of higher solute concentration.
Osmosis is the movement of solutes down the concentration gradient.
Osmosis is the movement of solutes up the concentration gradient.
Osmosis is the movement of water toward an area of higher solute concentration.
T/F: Osmosis refers to the movement of water across a membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
True
T/F: Electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, have no impact on blood pH regulation.
False
T/F: Hyperkalemia refers to low potassium levels in the blood.
False (Hyperkalemia refers to high potassium levels)
T/F: Water always moves from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution.
True (Water moves to the area with higher solute concentration, which is the hypertonic side)
T/F: Chloride is the most abundant electrolyte in intracellular fluid.
False (Chloride is most abundant in extracellular fluid)
The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane is called __________.
osmosis
Potassium is the major positively charged electrolyte found in __________ fluid, while sodium is the major positively charged electrolyte found in __________ fluid.
Intracellular; Extracellular
If a solution is __________, water will move into the cell, causing it to expand.
Hypotonic
The kidneys help regulate blood pH by filtering out excess __________ and reabsorbing bicarbonate.
Hydrogen ions (H⁺)
__________ is the electrolyte most commonly involved in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
Sodium
Which of the following is true about osmosis?
A) Water moves from a hypertonic solution to a hypotonic solution.
B) Water moves from an area of high solute concentration to low solute concentration.
C) Water moves from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration.
D) Osmosis only occurs in plant cells.
Water moves from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration.
What happens when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution?
A) Water moves into the cell, and the cell swells.
B) Water moves out of the cell, and the cell shrinks.
C) There is no change in the cell's volume.
D) The cell's volume stays the same, but its shape changes.
Water moves out of the cell, and the cell shrinks.
Which of the following is the most common cause of hypernatremia?
A) Dehydration
B) Excessive potassium intake
C) Increased sodium intake from processed foods
D) Kidney failure
Dehydration
Which of the following electrolytes plays a critical role in muscle contractions and nerve impulses?
A) Potassium
B) Calcium
C) Sodium
D) All of the above
All of the above
Which electrolyte imbalance is most commonly associated with kidney disease?
A) Hyperkalemia
B) Hypernatremia
C) Hypocalcemia
D) Hyperchloremia
Hyperkalemia (Kidneys are responsible for regulating potassium, and kidney dysfunction often results in hyperkalemia.)
Which of the following is an example of how the body compensates for an acidic blood pH?
A) Increased retention of bicarbonate by the kidneys
B) Increased hydrogen ion secretion by the kidneys
C) Decreased bicarbonate production
D) Increased potassium release
Increased retention of bicarbonate by the kidneys (To neutralize excess acid, the kidneys retain bicarbonate.)
In a solution with a higher concentration of Na+ (sodium) outside the cell compared to inside, what would happen to the water in the cell?
A) Water would move into the cell, causing it to swell.
B) Water would move out of the cell, causing it to shrink.
C) There would be no movement of water.
D) The cell would maintain its volume, but its shape would change.
Water would move out of the cell, causing it to shrink. (This describes a hypertonic solution where water moves toward the higher solute concentration.)
A patient is diagnosed with hyperkalemia. Which of the following would be a priority in managing this condition?
A) Decreasing sodium intake
B) Monitoring blood pressure closely
C) Administering calcium gluconate or sodium bicarbonate
D) Restricting calcium and phosphorus intake
Administering calcium gluconate or sodium bicarbonate (to help stabilize the cardiac membrane in cases of hyperkalemia)
A patient with dehydration is admitted to the hospital. You are concerned that the dehydration might cause which electrolyte imbalance?
Select all that apply.
A) Hypernatremia
B) Hypokalemia
C) Hypercalcemia
D) Hyponatremia
A) Hypernatremia, D) Hyponatremia (Dehydration can lead to either depending on the electrolyte content lost in fluids, but hypernatremia is more common)
A patient is receiving potassium supplementation due to hypokalemia. Which of the following would be the most concerning sign of hyperkalemia?
A) Muscle weakness and cramps
B) Increased urine output
C) Slow, irregular heart rhythm
D) Increased blood pressure
Slow, irregular heart rhythm (Hyperkalemia can disrupt the electrical conduction of the heart, leading to arrhythmias)
In a patient with kidney disease, the kidneys' ability to excrete excess electrolytes is impaired. What electrolyte imbalance would you expect to find most frequently in this patient?
A) Hypercalcemia
B) Hyperkalemia
C) Hypophosphatemia
D) Hypermagnesemia
Hyperkalemia (Due to impaired renal function, potassium cannot be excreted efficiently, leading to an accumulation in the blood)
Which of the following electrolyte imbalances can lead to a condition where the blood pH becomes too acidic (acidosis)?
A) Hypernatremia
B) Hyperkalemia
C) Hyperchloremia
D) Hypocalcemia
Hyperchloremia (Excess chloride can lead to a decrease in blood pH, causing acidosis)
If a patient is experiencing prolonged vomiting, which electrolyte imbalance would you be most concerned about?
Select all that apply.
A) Hyponatremia
B) Hypokalemia
C) Hyperkalemia
D) Hypercalcemia
A) Hyponatremia, B) Hypokalemia (Vomiting causes loss of both sodium and potassium, leading to hyponatremia and hypokalemia)
The body compensates for respiratory acidosis by increasing the retention of which electrolyte to neutralize the acid?
A) Sodium
B) Potassium
C) Bicarbonate
D) Calcium
Bicarbonate (In respiratory acidosis, the kidneys retain bicarbonate to buffer the excess hydrogen ions and help normalize pH)
What is the primary role of sodium in nerve impulse transmission?
A) Sodium creates the action potential by moving into the cell.
B) Sodium helps stabilize the resting membrane potential.
C) Sodium assists in transporting potassium out of the cell.
D) Sodium blocks calcium entry into the cell.
Sodium creates the action potential by moving into the cell (When sodium enters the nerve cell, it depolarizes the membrane, allowing the action potential to propagate)