RADT 1030 - Humerus and Shoulder Girdle
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
An injury of the anteroinferior aspect of the glenoid labrum often caused by anterior dislocation of the proximal humerus. Repeated dislocation may result in small avulsion fracture of the glenoid rim.
Bankart lesion
projection at the lateral end of the scapular spine
acromion
thickened posterior border of the scapular spine
crest of the spine
projection that results in a lateral view of the head and neck of the humerus and demonstrates the relationship of the humerus and glenoid cavity
inferosuperior (axiolateral) projection
projection of the humerus - epicondyles perpendicular to the IR
internal rotation
projection of the humerus - epicondyles parallel to IR
external rotation
projection of the humerus - epicondyles oblique to IR
neutral rotation
kVp w/o grid and with grid for analog and digital
analog:
without grid: 65-70 kVp
with grid: 70-80 kVp
digital:
+ 5-10 kVp
Impingement of the greater tuberosity and soft tissues on the coracoacromial ligamentous and osseous arch, generally during abduction of the arm
impingement syndrome
most common Bankart lesion exams
AP internal rotation, Scapular Y and Grashey
subacromial spurs appear in what pathology
impingement syndrome
compression fracture of the articular surface of the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head associated with anterior of humeral head dislocation
Hill- Sachs defect
another name for the anterior surface of the scapiula
costal surface
the angels of the scapula
superior
inferior
lateral (head)
borders of the scapula
superior border
medial (vertebral) border
lateral (axillary) border
most common exams for shoulder disloaction
scapular Y
transthoracic lateral
Garth Method
Upper scapular margin location
T2 (2nd posterior rib)
which tubercle is on lateral aspect of the humerus?
greater tubercle
which tubercle is on medial aspect of the humerus?
lesser tubercle
CR location on AP shoulder?
1" inferior to coracoid process
what does the NEER method demonstrate?
coracoacromial arch for supraspinatus outlet region for possible shoulder impingement
common exams for impingement syndrome?
Scapular Y
Neer method
most common exams for Hill - Sachs defect?
AP internal rotation
exaggerated external rotation
axillary lateral
Description for lateral scapula - ERECT
-patient faces IR
-to demonstrate the body of the scapula, have the patient grab opposite shoulder.
-to demonstrate acromion and coracoid process, drop affected arm and flex elbow and place arm behind back.
-CR to mid vertebral border of scapula
Description for lateral scapula - RECUMBENT
-supine position with arm across chest, bend knee to maintain oblique
-CR to midscapular lateral border
AP radiograph with what rotation places the humerus in true AP or frontal position?
AP with external rotation
Shoulder girdle consists of what bones?
scapula
clavicle
most fractured neck of the humerus?
surgical neck
where does the deltoid attach?
deltoid tuberosity
AP position that has the greater tubercle in profile?
AP with external rotation
humeral condyles 45 degree angle from IR
natural humerus
What position is AP humerus with lesser tubercle in profile, greater tubercle mid and humeral epicondyles perpendicular to IR?
AP humerus w/ internal rotation
what is the only articulation between the upper limb and axial skeleton?
SC joints
Parts of the clavicle
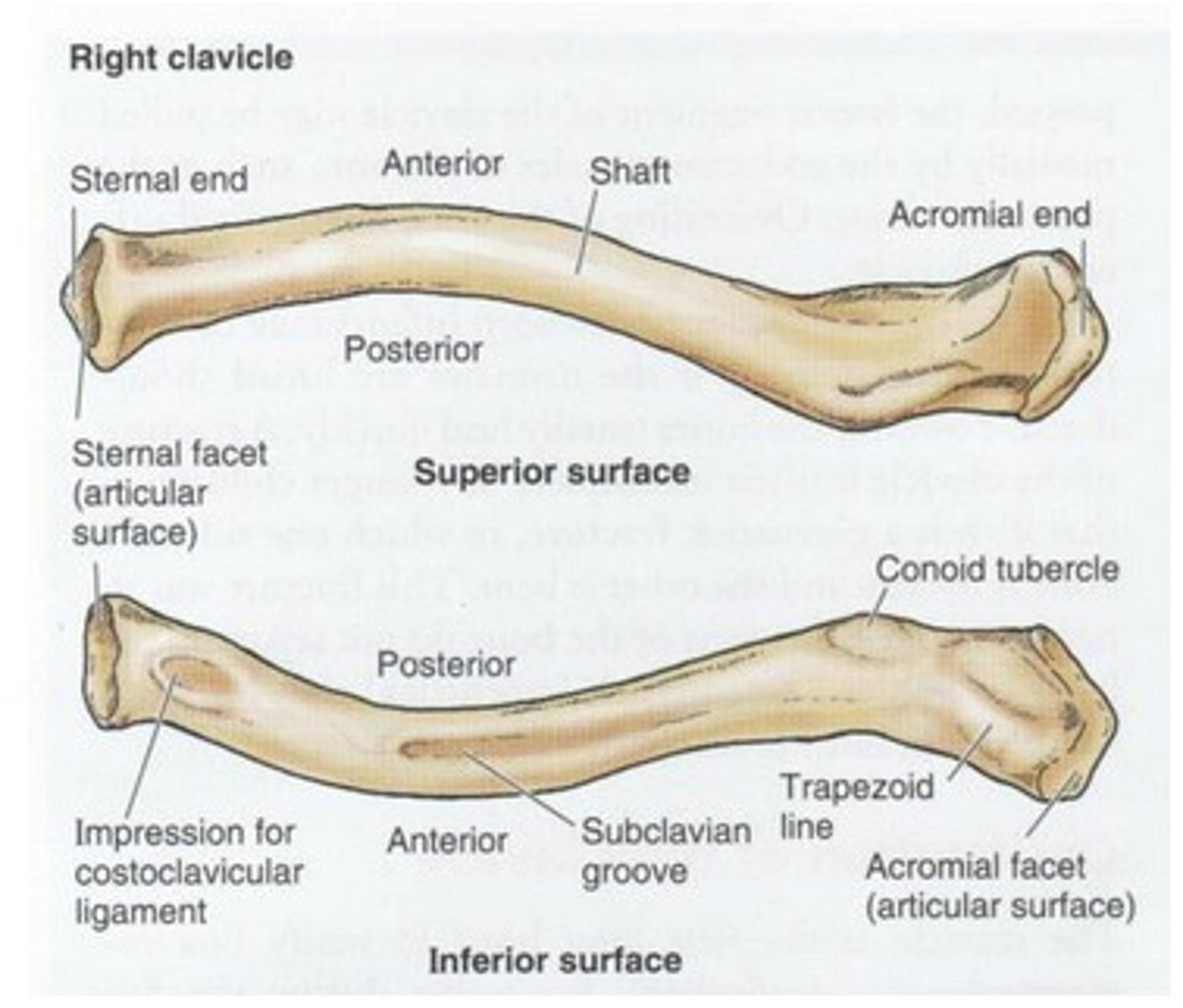
articulation of the clavicle and sternum
sternoclavicular joint (SC joint)
Clavicles are usually shorter and less curved in which gender?
female
prominent structure on the dorsal (posterior) surface of the scapula
spine of the scapula
the 3 shoulder girdle joints are classified as what type of joint?
synovial
the mobility types of the 3 shoulder girdle joints
diarthrodial
movement type of the scapulohumeral (glenohumeral) joint
spheroidal (ball and socket)
Movement type of the sternoclavicular joint
plane/gliding
Movement type of the acromioclavicular joint
plane/gliding
injury in which the distal clavicle is displaced superiorly, usually caused by a fall?
AC dislocation
rotator cuff muscles
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
subscapularis
teres minor
For Humerus/Shoulder:
Grid or no grid?
What AEC cell is used?
What is shielded if possible?
higher or lower mA and exposure time?
- grid (wall or table bucky)
- center cell AEC
- shield breast, thyroid, lungs gonads
- higher mA, lower exposure time
Trauma projections of the humerus
transthoracic lateral
horizontal beam lateral
breathing instructions given for AP humerus?
deep breath in an hold
SID for humerus
40 inch SID
most common exams for bursitis, idiopathic chronic adhesive capsulitis, osteoarthritis, RA and osteoporosis?
AP and Lateral shoulder
Most common AC joint exams for dislocation?
Bilateral AP erect AC w/o weights
Most common AC joint exams for separation?
Bilateral AP with and without weights
____________% of shoulder dislocations are_______________.
95%
anterior
Chronic systemic disease characterized by inflammatory changes that occur throughout the connective tissues of the body
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Osteoarthritis generally occurs in what groups of people?
people ages 50+
chronically obese
atheletes
noninflammatory joint disease characterized by gradual deterioration of articular cartilage w/ hypertonic bone formation
osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease (DJD))
another name for osteoarthritis?
Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
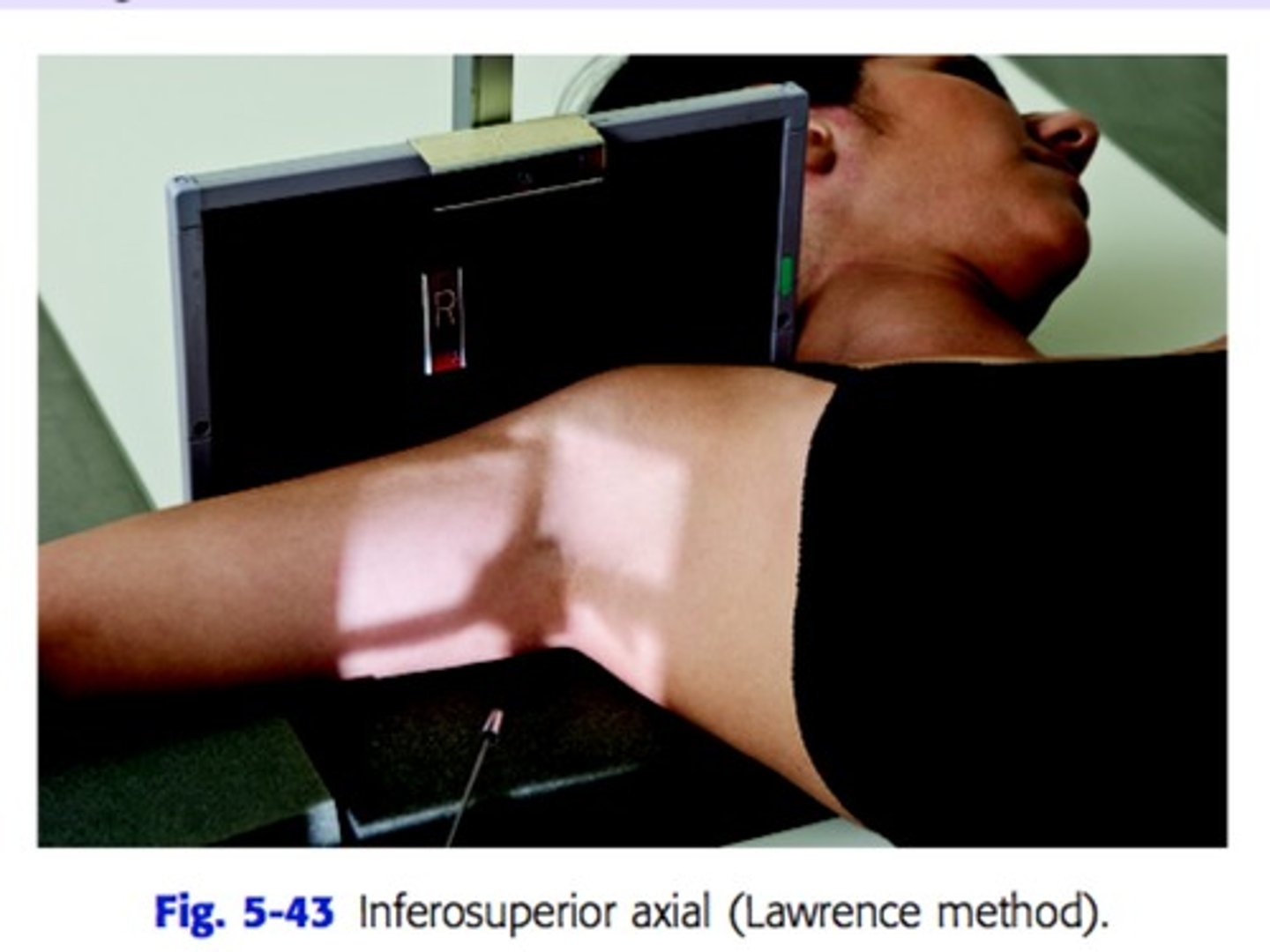
another name for inferosuperior axial projection : shoulder
Clements modification
another name for inferosuperior axial projection: shoulder and what is it used for?
(non trauma)
Lawerence method
- used for degenerative conditions and Hill-Sachs defect
How do you position the patient and tube for non trauma Lawrence method?
Patient is supine with should raised about 2 inches from table top using a sponge. Place cart at edge of table to support forearm. IR at top of shoulder, patient head turned .
CR - 25-30 degree into axilla
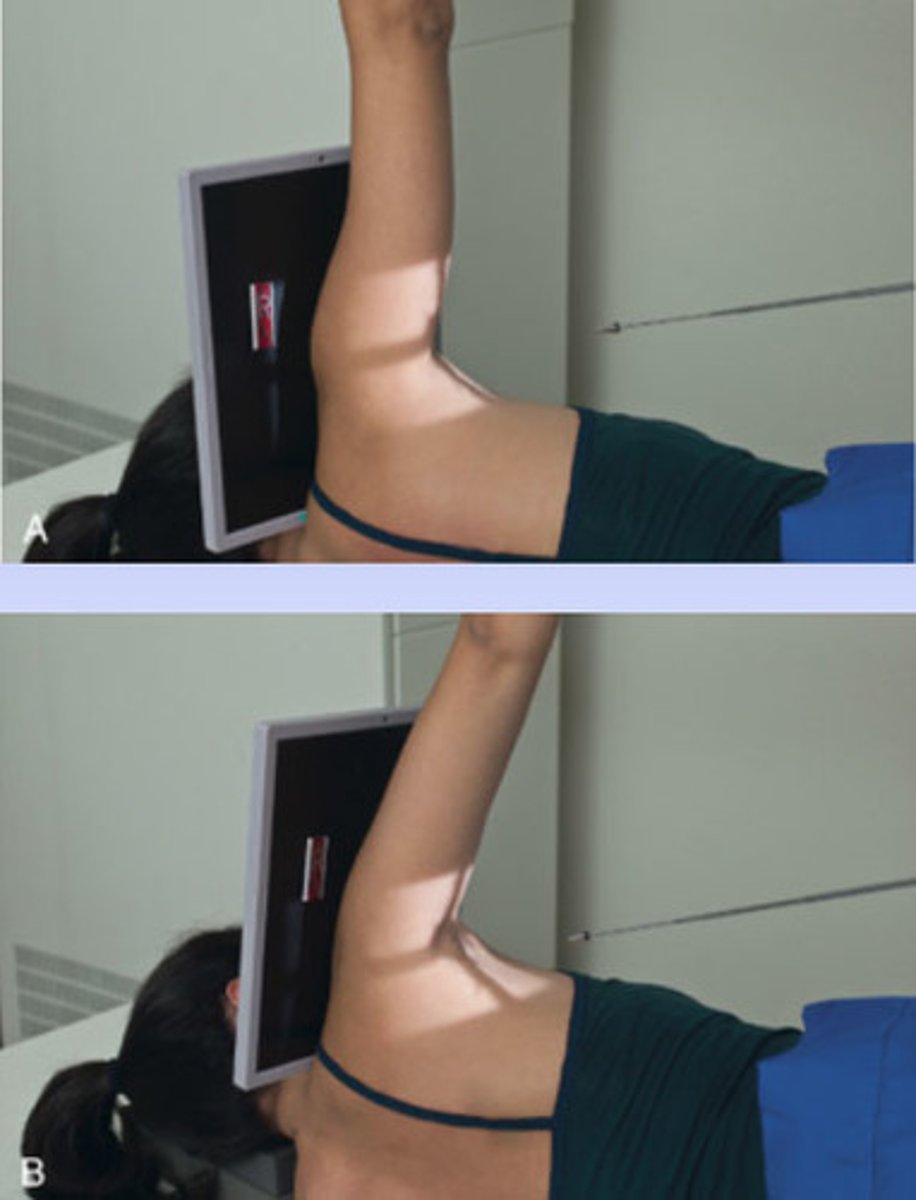
another name for transaxillary projection of the shoulder?
Hobbs modification
patient position and CR direction for Hobbs method?
-Patient is erect or leaning over the end of the table with arm of interest raised as high as possible. The patient is positioned in a slight 5 to 10 degree anterior oblique.
-CR is directed perpendicular to the axilla and the humeral head to pass through the glenohumeral joint.
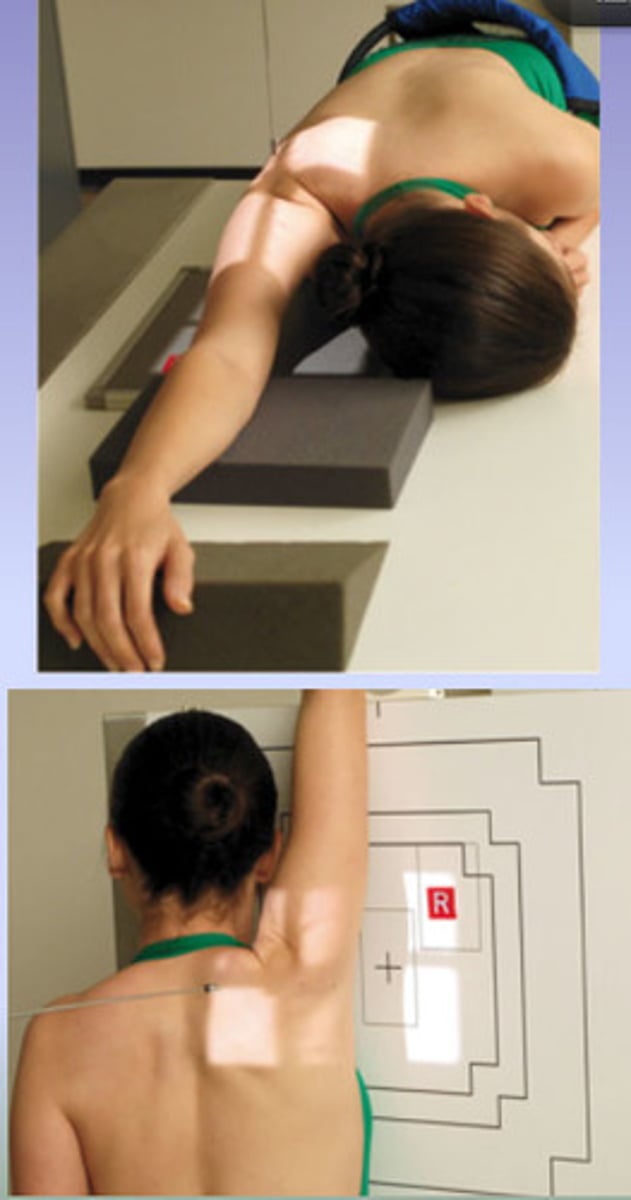
another name for the posterior oblique position - Glenoid Cavity : Shoulder
Grashey method
Patient and CR position on Grashey method?
patient is rotated 35-45 degrees from the IR toward affected side.
CR - centered to scapulohumeral joint

Method name of the tangential projection - intertubercular Groove: shoulder?
Fisk Method
Patient and CR location for Fisk method?
ERECT - patient is bent over end of table with elbow flexed holding IR in supinated hand, leaning forward 10-15 degrees from vertical
SUPINE- Arm at side with hand supinated. Cassette against top of shoulder, head turned away from cassette. CR 10-15 degrees cephalad @ mid humeral head.
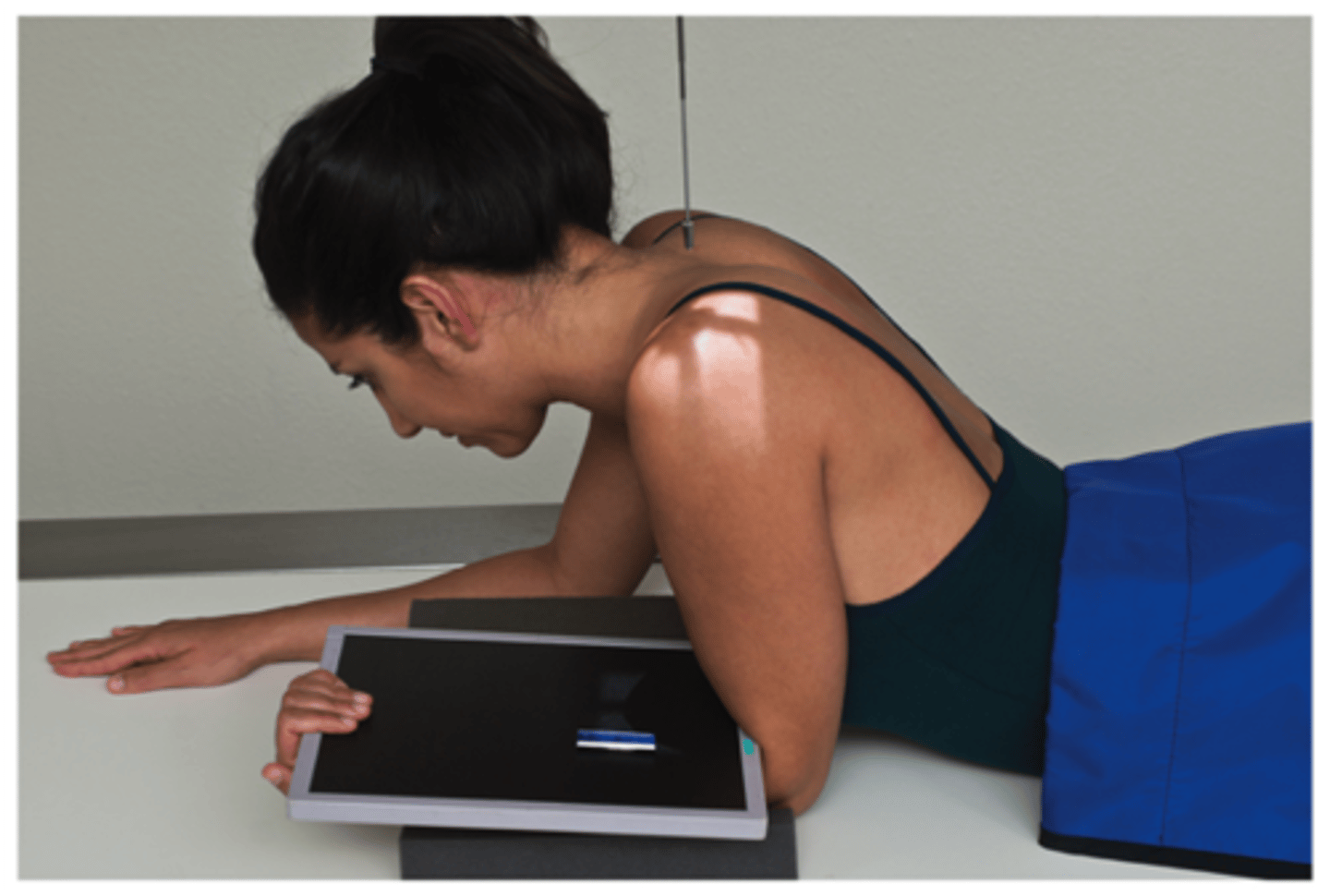
AP Neutral rotation shoulder, TRAUMA CR location
CR is directed at mid scapulohumeral joint
What is the CR difference in the Transthoracic lateral humerus and the Lawerence method Trauma?
The transthoracic lateral humerus & CR is a mid- diaphysis. The lawrence trauma visualizes the proximal humerus with CR at surgical neck of humerus.
Guidelines to be followed when using digital imaging systems?
collimation
accurate centering
exposure factors
post processing evaluation of exposure factors
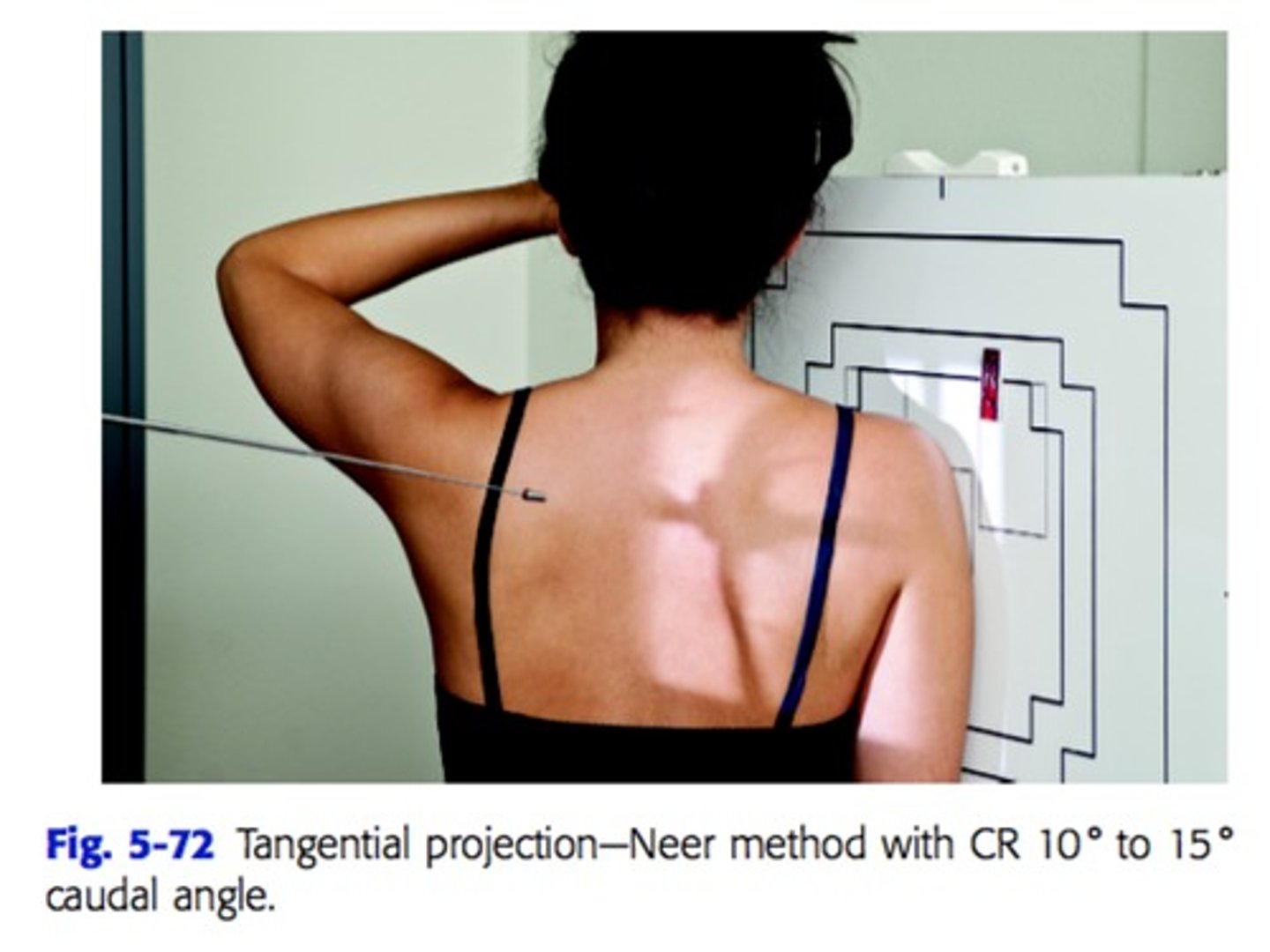
Tangential projection - Supraspinatus Outlet: Shoulder (TRAUMA) -
whats the name for this method?
NEER method

Patient and CR location of an AP scapular Y lateral oblique position
rotate patient into anterior oblique position, to 45-60 degrees, the line between the superior angle of the scapula and the AC joint should be perpendicular to IR>. CR is directed at the scapulohumeral joinh.
What is the trauma Lawrence method and the non trauma Lawrence method
Trauma - transthoracic proximal humerus
Nontrauma - inferosuperior axial projection of the shoulder
Patient position and CR location of NEER method
patient is at 45-60 degree anterior oblique position
CR 10-15 degree caudal angle centered at superior margin of humeral head
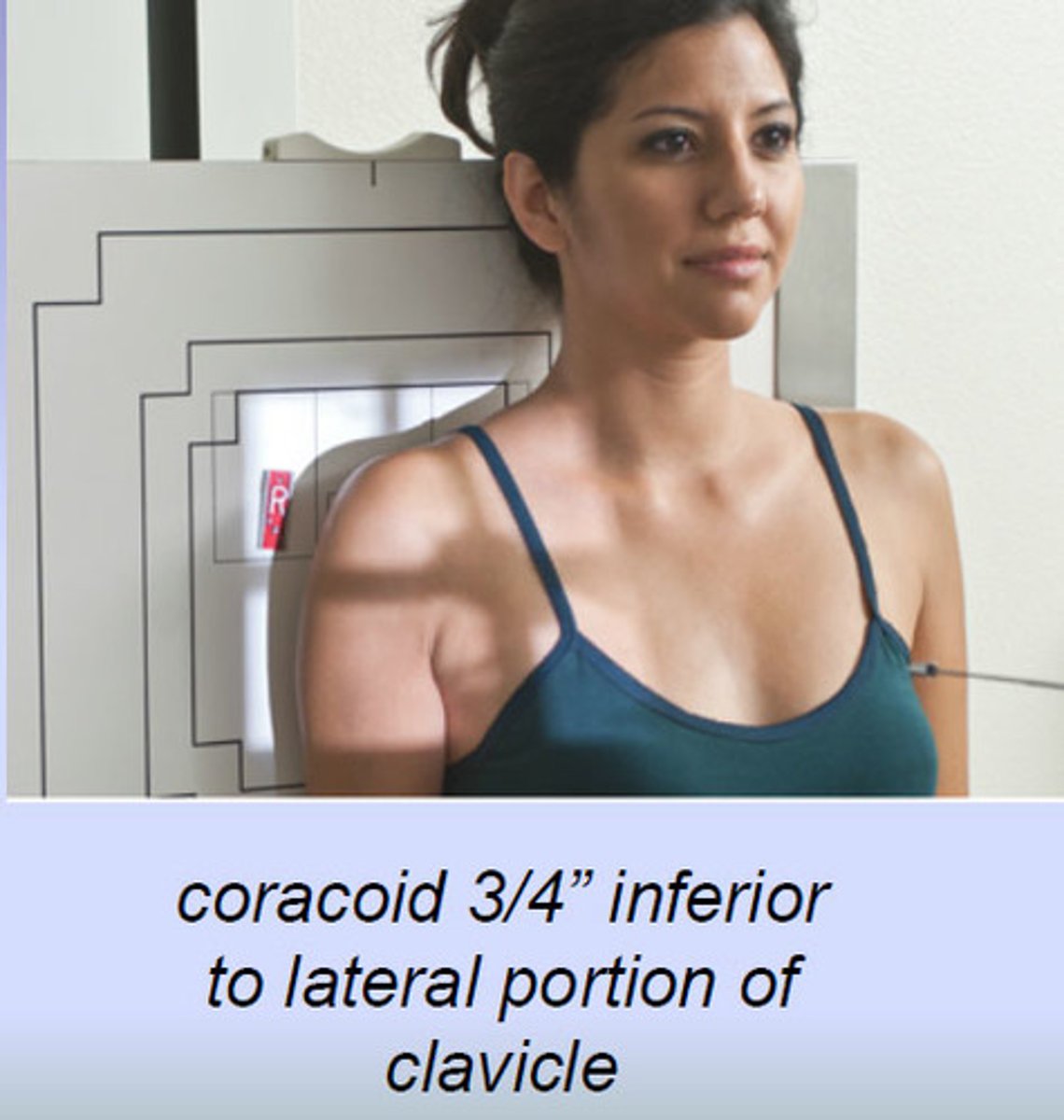
another name for the AP apical oblique axial projection : Shoulder (trauma)
Garth method
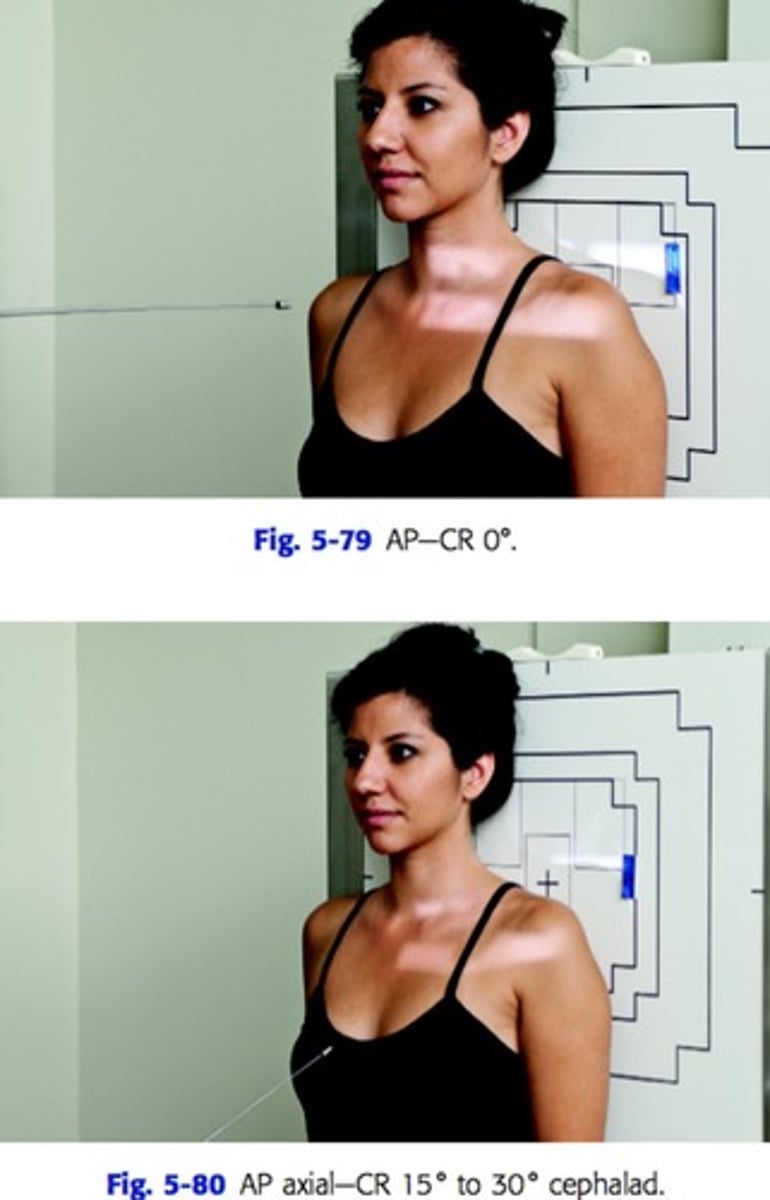
patient position and CR position for AP projection of clavicle
patient standing with back to IR
CR perpendicular to IR and centered at mid clavicle
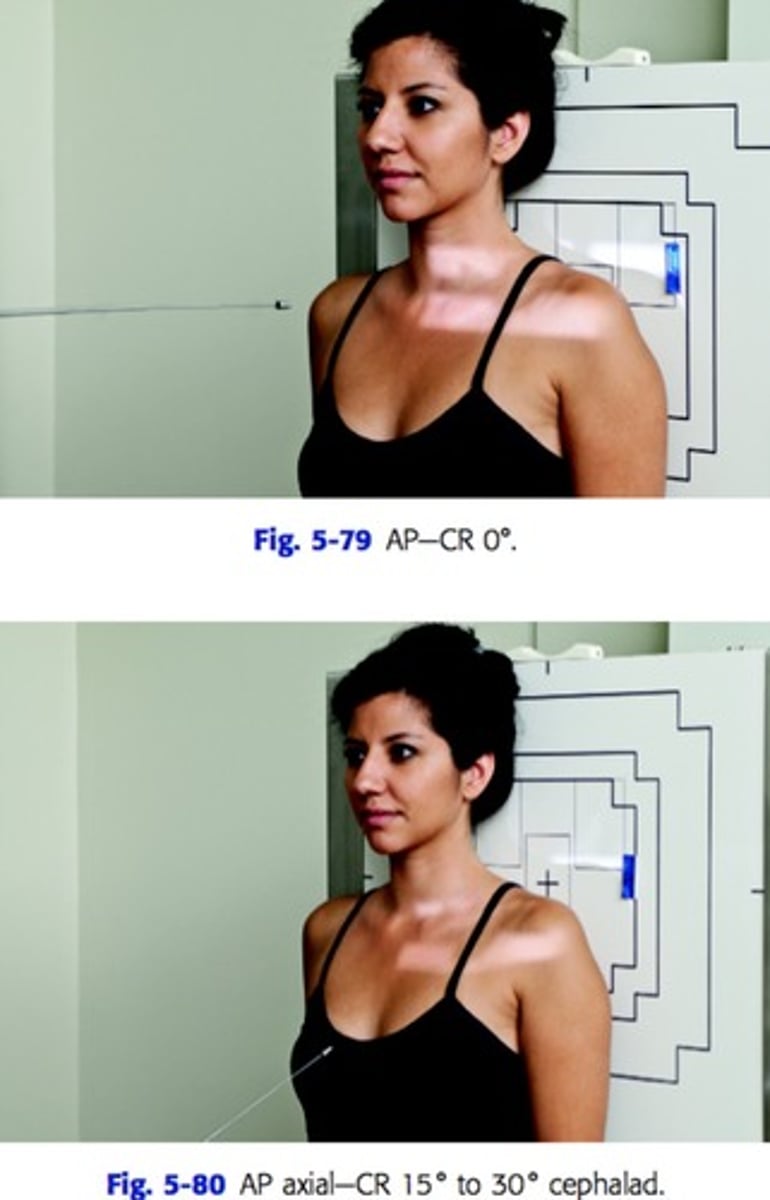
patient position and CR position for AP Axial projection of clavicle
patient standing with back to IR
CR at 15-30 degree cephalad angle and centered mid clavicle
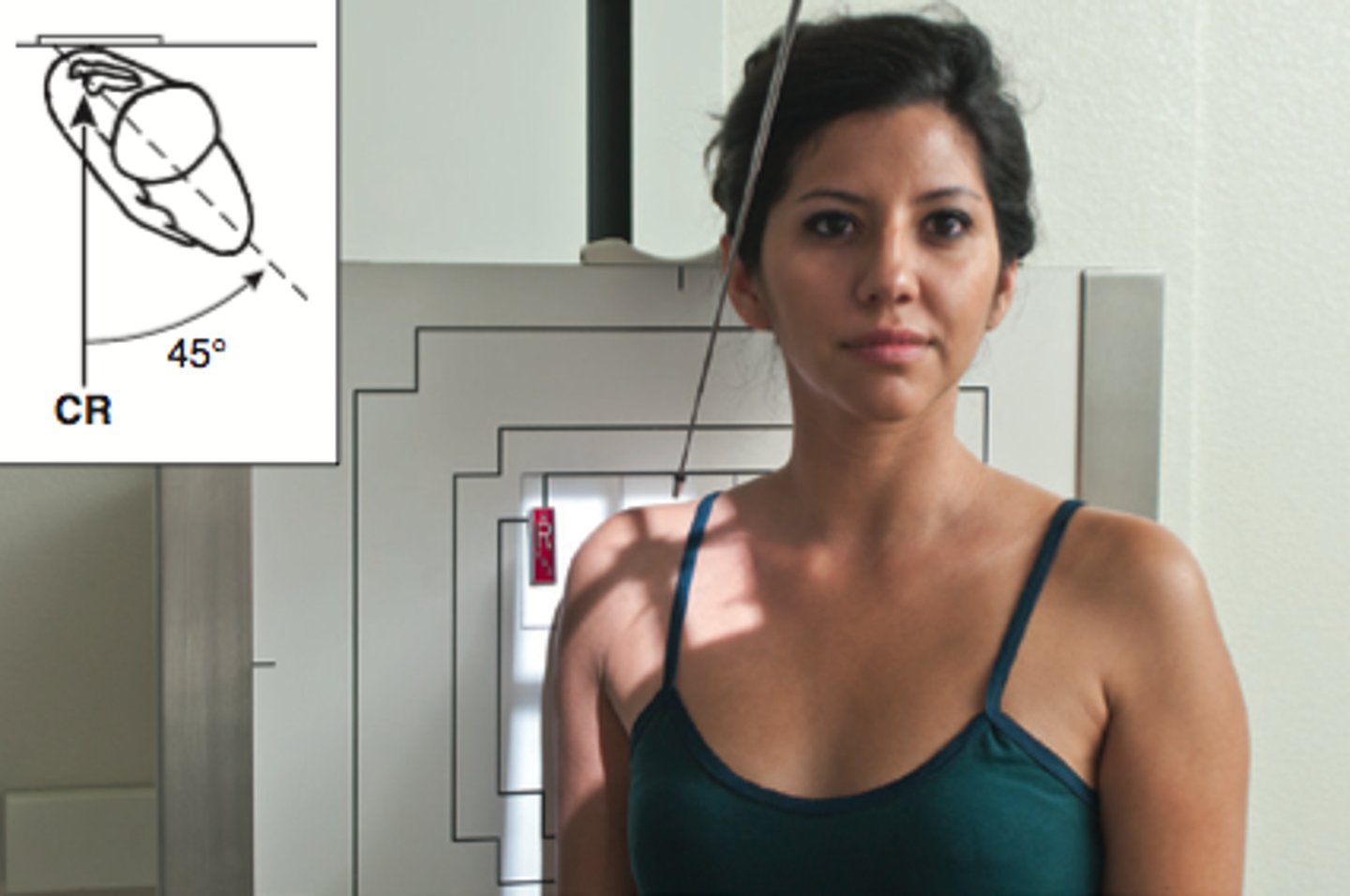
patient and cr position for Garth method
patient erect or supine at 45 degrees toward affected side
CR at 45 degree caudad angle and centered at scapulohumeral joint
What is the Alexander method?
AP axial projection of AC joints
CR is 15 degrees cephalic angle centered at the level of the AC joints
How are AC joints projections positioned?
bilateral
with and without weights
72 in SID
CR is 1 " inch above jugular notch
How to position patient and CR fo AP scapula?
Patient with back to IR, abduct arm 90 degrees and supinate hand (fainting look)
CR at level of axilla and 2 inches medial from lateral side of patient
How to position the patient and CR for AP scapula?
Patient with back of IR, abduct arm 90 degrees and supinate hand (fainting look).
CR @ level of Axilla and 2 inches medial from lateral side of patient
