Gametogenesis – Key Vocabulary
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of vocabulary flashcards covering the essential cells, structures, hormones, and processes involved in human gametogenesis, including both oogenesis and spermatogenesis.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Primordial Germ Cells (PGCs)
Pluripotent cells formed in the epiblast during week 2 that migrate to the developing gonads and give rise to all gametes.
Gametogenesis
The maturation process in which germ cells undergo meiosis and cytodifferentiation to become mature spermatozoa or oocytes.
Fertilization
Union of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete (oocyte) to form a diploid zygote.
Mitosis
Somatic cell division producing two genetically identical diploid daughter cells.
Meiosis
Germ-cell division consisting of meiosis I and II that reduces chromosome number from diploid (46) to haploid (23).
Diploid
A cell containing two complete sets of chromosomes (46 in humans).
Haploid
A cell containing one set of chromosomes (23 in humans), characteristic of gametes.
Homologous Chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes—one maternal, one paternal—that carry the same genes and pair during meiosis I.
Crossover (Recombination)
Exchange of chromatid segments between homologous chromosomes during meiosis I, increasing genetic variability.
Polar Body
Small cell with minimal cytoplasm produced during female meiotic divisions that usually degenerates.
Oogenesis
Process by which oogonia develop into mature secondary oocytes ready for fertilization.
Oogonium
Diploid female germ cell derived from PGCs that performs mitosis before entering meiosis.
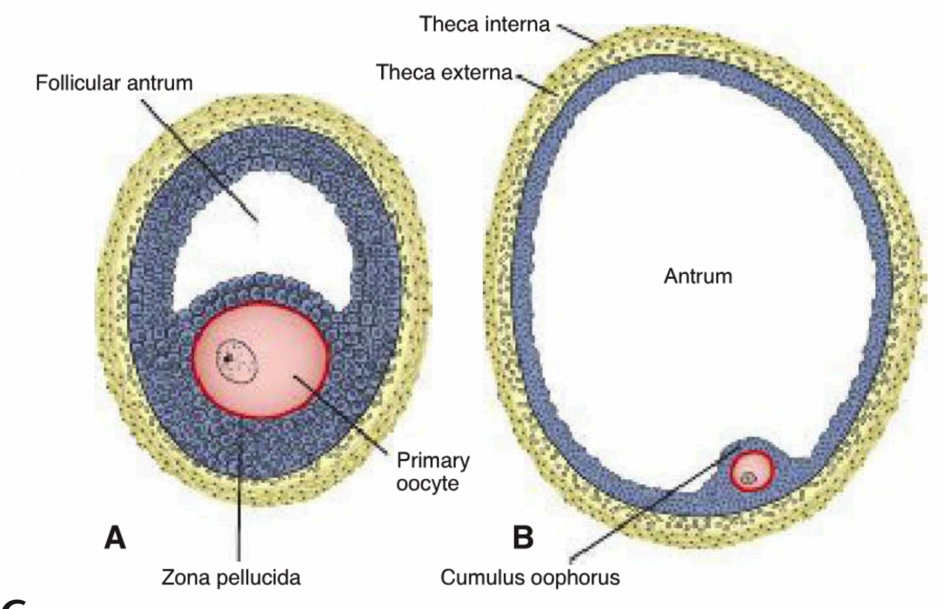
Primary Oocyte
Oogonium that has entered prophase of meiosis I and remains arrested until puberty.
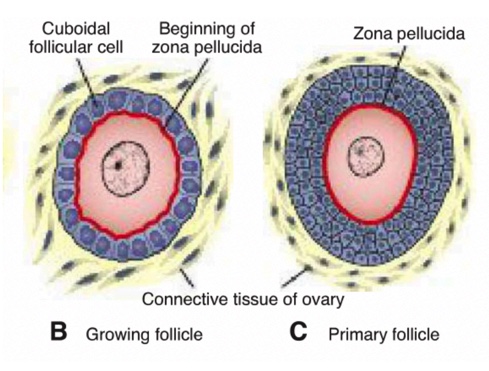
Primordial Follicle
Primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of flat follicular epithelial cells.
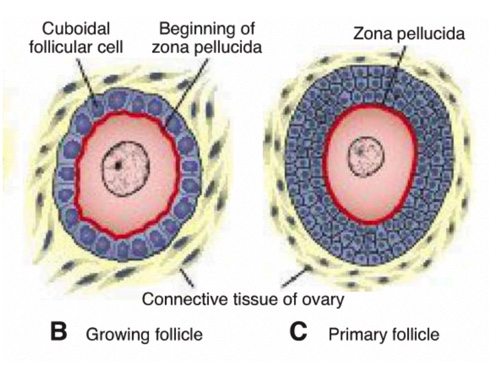
Zona Pellucida
Glycoprotein layer secreted by the oocyte and granulosa cells that surrounds the oocyte.
Diplotene Stage
Resting phase of prophase I where primary oocytes remain arrested until puberty.
Oocyte Maturation Inhibitor (OMI)
Substance produced by follicular cells that maintains meiotic arrest of the primary oocyte.
Primary Follicle
Follicle in which flat cells become cuboidal granulosa cells forming a stratified epithelium around the oocyte.
Antrum
Fluid-filled cavity forming among granulosa cells; its presence designates an antral or vesicular follicle.
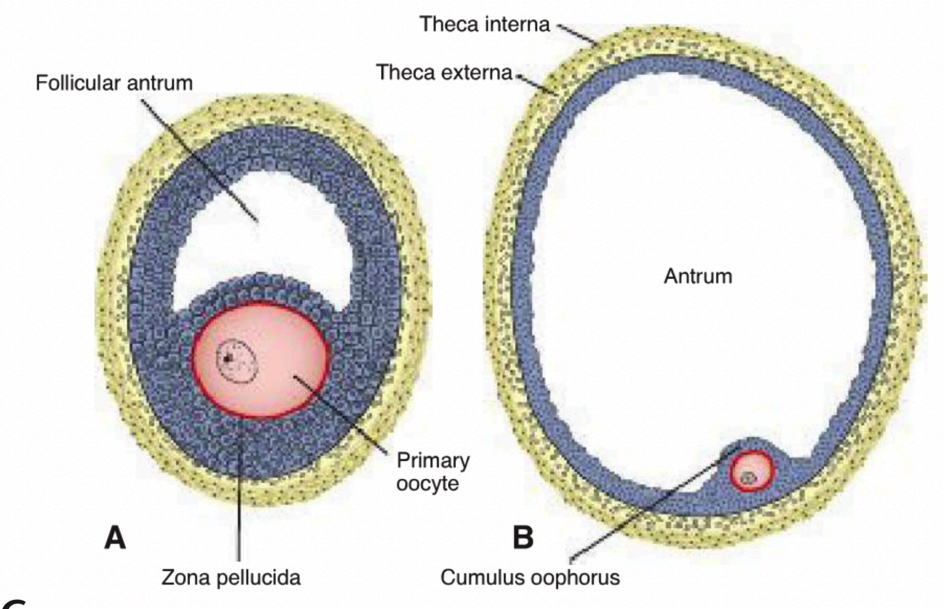
Vesicular (Graafian) Follicle
Fully mature antral follicle, ~25 mm in diameter, ready for ovulation.
Theca Interna
Inner vascular, steroid-secreting layer of the follicle wall.
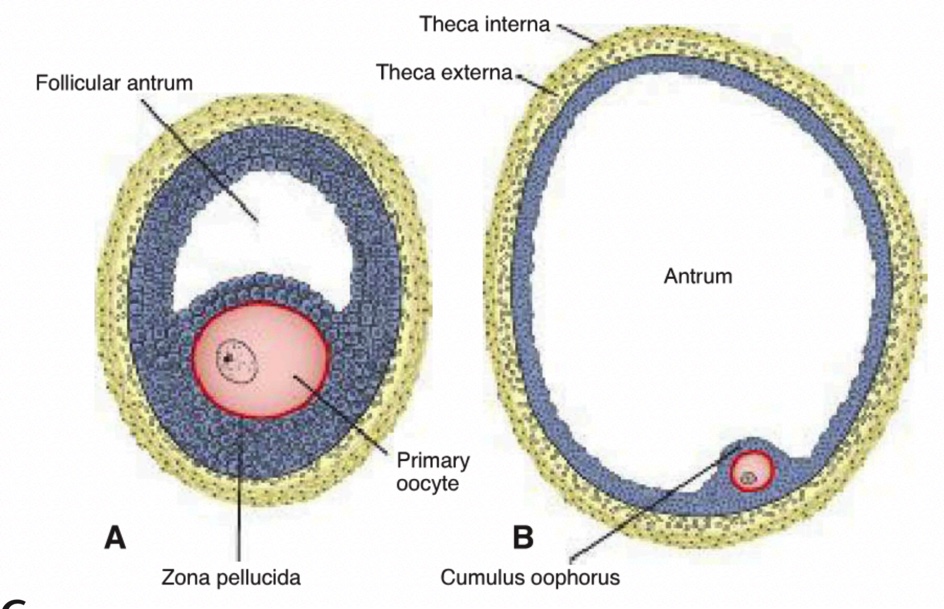
Theca Externa
Outer fibrous connective-tissue capsule of the follicle.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Pituitary hormone whose surge triggers completion of meiosis I and ovulation in females; stimulates Leydig cells in males.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Pituitary hormone that stimulates granulosa cells in females and Sertoli cells in males; essential for gametogenesis.
Secondary Oocyte
Cell formed after completion of meiosis I; enters meiosis II and arrests in metaphase until fertilization.
Perivitelline Space
Gap between the secondary oocyte membrane and the zona pellucida containing the first polar body.
Spermatogenesis
Series of events in which spermatogonia become mature spermatozoa.
Spermatogonium
Diploid male germ cell residing on the basal lamina of seminiferous tubules; includes Type A (stem) and Type B (differentiating) cells.
Primary Spermatocyte
Type B spermatogonium that enters meiosis I; possesses 46 duplicated chromosomes.
Secondary Spermatocyte
Product of meiosis I containing 23 duplicated chromosomes; quickly enters meiosis II.
Spermatid
Haploid cell produced by meiosis II that will undergo spermiogenesis.
Sertoli Cell
Supporting cell of the seminiferous epithelium that nourishes developing germ cells and mediates FSH and testosterone actions.
Leydig Cell
Interstitial testicular cell stimulated by LH to produce testosterone.
Spermiogenesis
Morphologic transformation of spermatids into motile spermatozoa.
Acrosome
Cap-like vesicle covering the anterior half of the sperm nucleus containing enzymes for oocyte penetration.
Residual Bodies
Cytoplasmic fragments shed by spermatids during spermiogenesis; phagocytosed by Sertoli cells.
Seminiferous Tubules
Highly coiled testicular tubules where spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis occur.
Epididymis
Duct where sperm acquire motility and are stored prior to ejaculation.
Teratoma
Tumor derived from pluripotent cells (PGCs or epiblast) containing tissues from all three germ layers.
Abnormal Spermatozoa
Sperm with structural defects (head, tail, size) often lacking motility and fertility potential.