Informatics Chapter 6 Computer Networks
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Semester test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
telecommunications
The electronic transmission of signals for communications; enables
organizations to carry out their processes and tasks through effective computer networks.
synchronous communication
the receiver gets the message almost instantaneously, when it is sent such as a phone call, virtual classroom, Zoom meetings
asynchronous communication (such as e-mail)
there is a measurable delay between the sending and receiving of the message, sometimes hours or even days.
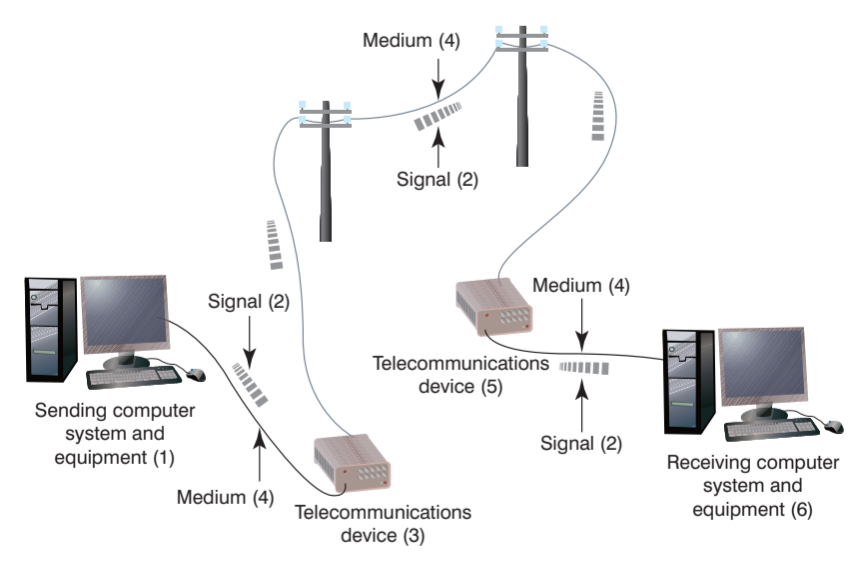
Elements of a Telecommunications System
The model starts with a sending unit (1), such as a person, a computer system, a terminal or another device, that originates the message. The sending unit transmits a signal (2) to a telecommunications device (3). The telecommunications device – a hardware component that facilitates electronic communication performs many tasks, which can include converting the signal into a different form or from one type to another. The telecommunications device then sends the signal through a medium (4). A telecommunications medium is any material substance that carries an electronic signal to support communications between a sending and receiving device. Another telecommunications device (5) connected to the receiving computer (6) receives the signal. The process can be reversed, and the receiving unit (6) can send another message to the original sending unit (1).
Channel bandwidth
The rate (speed) at which data is exchanged over a communications channel, usually measured in bits per second (bps).
broadband communications
A telecommunications system in which a very high rate of data exchange is possible.
narrowband communications
A telecommunications system that supports a much lower rate of data exchange than broadband.
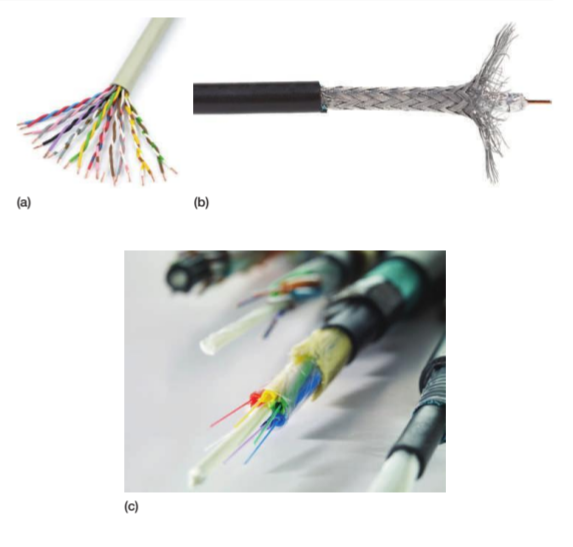
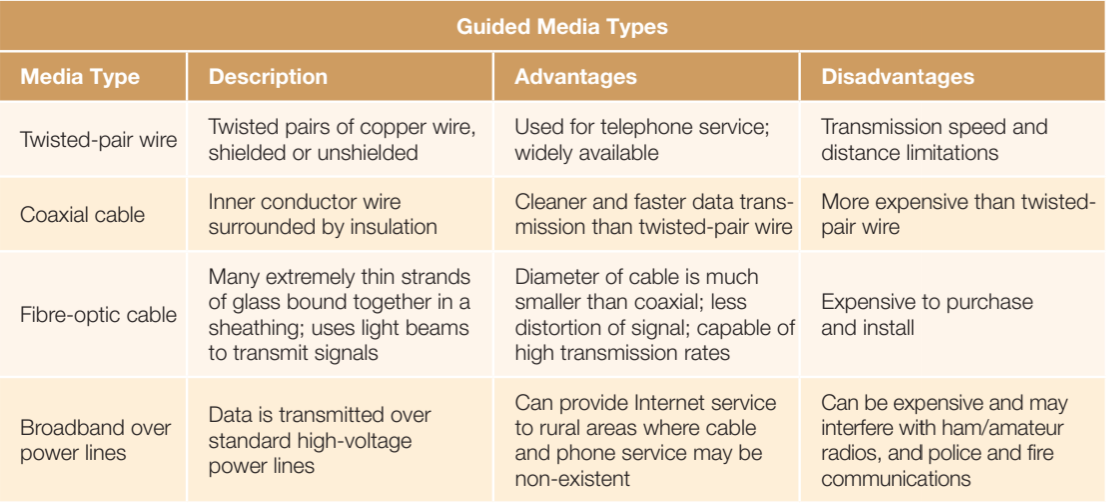
Guided transmission (using a solid medium):
• Twisted-pair wire
• Coaxial cable
• Fiber-optic cable
• Broadband over power lines
Wireless transmission: Microwave Transmission
Microwave is a high frequency (300 MHz–300 GHz) signal sent through the air.
Terrestrial (Earthbound) microwaves are transmitted by line of sight devices, so that the line of sight between the transmitter and receiver must be unobstructed.
The satellite receives the signal from the Earth station, amplifies the relatively weak signal and then rebroadcasts it at a different frequency. The advantage of satellite communications is that it can receive and broadcast over large geographic regions.
Wireless communication generations (1G to 5G)
represent the evolution of mobile network technology, from the first analog systems to the latest high-speed digital networks.

wi-fi (Wireless Fidelity)
A medium-range wireless telecommunications technology brand owned by the
Wi-Fi Alliance.
is a technology that allows devices to connect to a local area network (LAN) or the internet wirelessly using radio waves.
near field communication (NFC)
A very short-range wireless connectivity technology designed for consumer electronics, smartphones and credit cards.
Once two NFCenabled devices are in close proximity (touching or a few centimetres apart), they exchange the necessary communications
Bluetooth
A wireless communications specification that describes how smartphones, computers, printers and other electronic devices can be interconnected over distances of a few metres at a rate or about 2 Mbps.
ultra wideband (UWB)
A form of short-range communication that employs extremely short electromagnetic pulses lasting 50 to 1,000 picoseconds that are transmitted across a broad range of radio frequencies or several gigahertz.
is a wireless communication technology that transmits data over a very wide frequency spectrum with very low power.
Infrared Transmission
sends signals through the air via light waves at a frequency of 300 GHz and above.
modems
A telecommunications hardware device that converts (modulates and demodulates) communications signals so they can be transmitted over the communication media.
is a device that converts digital signals from a computer into analog signals for transmission over telephone lines or other analog media, and vice versa.
multiplexer.
A device that encodes data from two or more data sources onto a single communications channel, thus reducing the number of communications channels needed and therefore lowering telecommunications costs
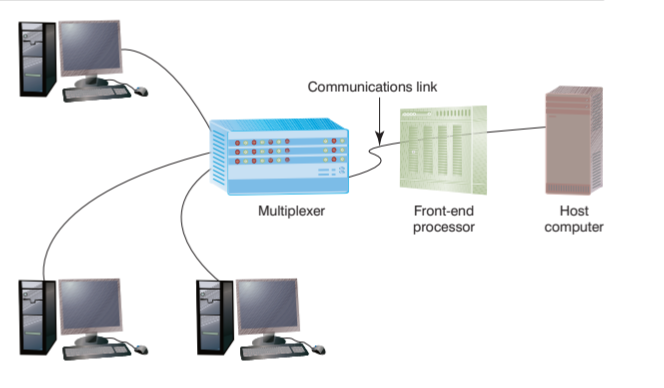
front-end processors
A special purpose computer that manages communications to and from a computer system serving hundreds or even thousands of users.
private branch exchange (PBX)
is a telephone switching exchange that serves a single organization. It enables users to share a certain number of outside lines (trunk lines) to make telephone calls to people outside the organization.
switch
A telecommunications device that uses the physical device address in each incoming message on the network to determine to which output port it should forward the message to reach another device on the same network.
bridge
A telecommunications device that connects one LAN to another LAN that uses the same telecommunications protocol.
router
is a networking device that connects multiple networks together and directs data packets between them.
gateway
A telecommunications device that serves as an entrance to another network.
computer network
consists of communications media, devices and software needed to connect two or more computer systems or devices.
The computers and devices on the networks are called network nodes
▪ Nodes can share data, information, and processing jobs
▪ Networks enable geographically separated workgroups to share information, which fosters teamwork, innovative ideas, and new business strategies
personal area network (PAN)
A network that supports the interconnection of information technology within a range of ten metres or so.
Local Area Networks
A network that connects computer systems and devices within a small area, such as an office, home or several floors in a building
metropolitan area network (MAN)
A telecommunications network that connects users and their devices in a geographical area that spans a campus or city.
wide area network (WAN)
A telecommunications network that ties together large geographic regions.
Mesh networking
is a network topology in which each device (node) is connected to multiple other nodes, allowing data to be routed dynamically through multiple paths.
Centralized processing
all processing occurs in a single location or facility. This approach offers the highest degree of control because a single centrally managed computer performs all data processing
Decentralized processing
processing devices are placed at various remote locations. Each computer system is isolated and does not communicate with another system. Suitable for companies that have independent operating divisions.
client/server
An architecture in which multiple computer platforms are dedicated to special functions such as database management, printing, communications and program execution.
The Client/Server model is a computing architecture where:
The client = requests services or resources (e.g., a web browser).
The server = provides services, processes requests, and sends responses (e.g., a web server).
network operating system (NOS)
Systems software that controls the computer systems and devices on a network and allows them to communicate with each other.
network-management software
Software that enables a manager on a networked desktop to monitor the use of individual computers and shared hardware (such as printers), scan for viruses and ensure compliance with software licences.
Software-Defined Networking
is an emerging approach to networking that allows network administrators to manage a network via a controller that does not require physical access to all the network devices.
encryption
The process of converting an original message into a form that can be understood only by the intended receiver.
encryption key A variable value that is applied (using an algorithm) to a set of unencrypted text to produce encrypted text or to decrypt encrypted text.
virtual private network (VPN)
A private network that uses a public network (usually the Internet) to connect multiple remote locations.
A VPN provides network connectivity over a potentially long physical distance and thus can be considered a form of wide area network.
ARPANET
A project started by the US Department of Defense (DoD) in 1969 as both an experiment in reliable networking and a means to link DoD and military research contractors, including many universities doing military-funded research.
Internet Protocol (IP)
A communication standard that enables traffic to be routed from one network to another as needed
is a set of rules that defines how data is addressed, routed, and delivered across networks (like the Internet).
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
The widely used transport layer protocol that most Internet applications use with IP.
backbone
One of the Internet’s high-speed, long-distance communications links.
uniform resource locator (URL)
An assigned address on the Internet for each computer.
Internet service provider (ISP)
Any company that provides people or organizations with access to the Internet.
World Wide Web (WWW or W3)
A collection of tens of thousands of independently owned computers that work together as one in an Internet service.
home page A cover page for a website that has graphics, titles and text.
hypertext Text used to connect web pages, allowing users to access information in whatever order they wish.
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) The standard page description language for web pages.
HTML tags Codes that let the web browser know how to format text – as a heading, as a list, or as body text – and whether images, sound or other elements should be inserted.
Extensible Markup Language (XML) The markup language for web documents containing structured information, including words, pictures and other
elements.
web browser
translates HTML so you can read it. It provides a graphical interface to the web. The menu consists of graphics, titles and text with hypertext links.
is used to access and read Web pages which are usually written in Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML)
hypermedia
An extension of hypertext where the data, including text, images, video and other media, on web pages is connected allowing users to access information in whatever order they wish.
search engines
A web search tool
Web Programming Languages
Java An object-oriented programming language from Sun Microsystems based on C++ that allows small programs (applets) to be embedded within an HTML document.
applets a small program embedded in web pages
Web services
consist of standards and tools that streamline and simplify communication among websites, promising to revolutionize the way we develop and use the web for business and personal purposes.
Telnet
is a terminal emulation protocol that enables you to log on to other computers on the Internet to gain access to their publicly available files.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
A protocol that describes a file transfer process between a host and a remote computer and allows users to copy files from one computer to another.
Cloud computing
A computing environment where software and storage are provided as an Internet service and are accessed via a web browser.
Internet
a global network of interconnected computer networks that communicate using the TCP/IP protocols.
intranet
is an internal company network built using Internet and World Wide Web standards and products.
Employees of an organization use it to gain access to company information.
creates connections inside an organization.
Extranet
is a network that links selected resources of the intranet of a company with its customers, suppliers or other business partners.
creates connections beyond (outside) an organization
The Internet of Things (IoT)
is a network of physical objects or ‘things’ embedded with sensors, processors, software and network connectivity to enable them to exchange data with the manufacturer of the device, device operators and other connected devices.