unit 8 market failure, gov intervention
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
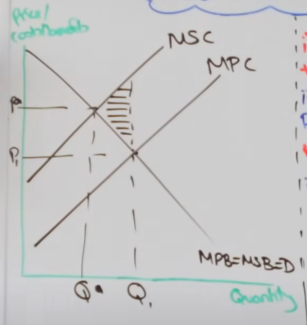
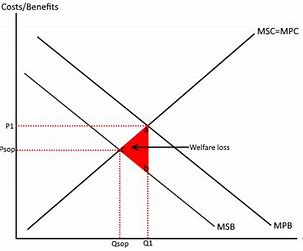
negative production externalities
social costs on third parties as a result of a separate agent
air pollution
waste
MSC > MPC (sc = pc + ec)
analysis
market allocates resources at the private optimum (Q1, P1)
self interest
over production
price is too low
encourages more consumption
misallocation of recourses
allocative inefficiency
resulting in a welfare loss
allocative efficiency = P* Q* - social optimum
externality def
a consequence of an economic activity that is experienced by unrelated third parties
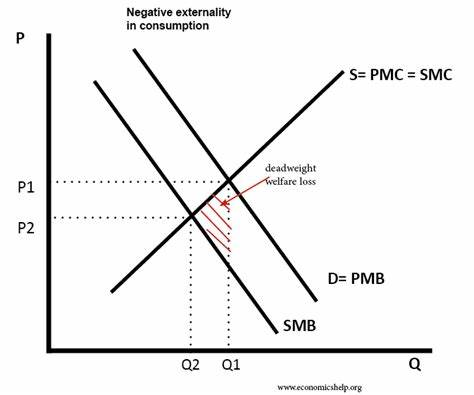
negative consumption externalities
cost to a third parties as a result of actions of consumers
MPB > MSB
smoking
alcohol
analysis
self interest - consumers ignoring social costs
misallocation of resources at Q1 P1
overconsumption and overproduction
allocative inefficiency
allocative efficiency = P* Q*
welfare loss to society
sb = pb + eb
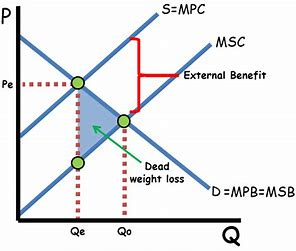
positive consumption externality
benefit to third parties as a result of consumers action
healthcare
education
MSB > MBP
sb = pb + eb
greater external benefit
by not producing at q*, society is losing out on potential social benefit
analysis
self interest - consumers ignoring social benefit
under consumption
misallocation of resources
too few resources being allocated to this market
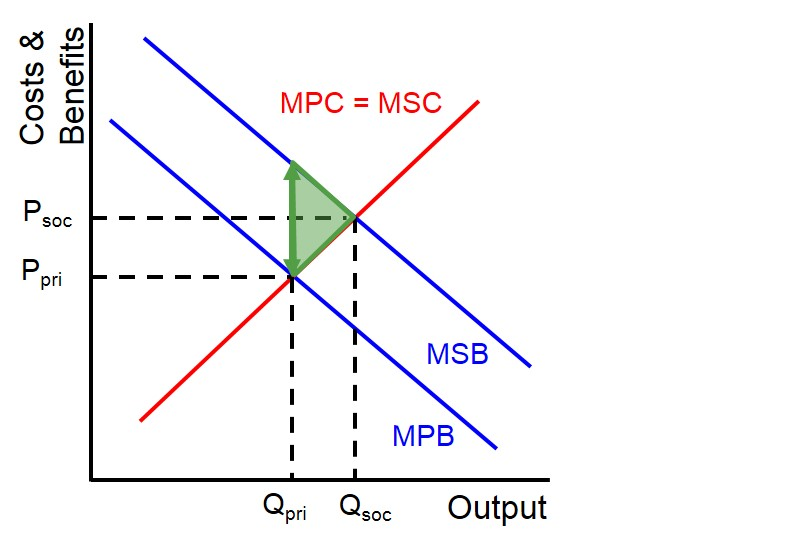
positive production externality
benefit to third parties as a result of actions of producers
training
R and D
MPC > MSC
by not producing the extra units (Q1 to Q*) society is losing out on welfare
analysis
producers only consider private costs - self interest
under production
resources are allocated at the private optimum not the social optimum
misallocation of resources
allocative inefficiency
welfare loss
merit good def
goods that are more beneficial to consumers than they realise - generate positive consumption externalities
healthcare
education
reasons for this
imperfect information
information failure - consumers don’t understand the benefit
asymmetric information
imperfect information
one party do not have complete or accurate information to make informed decisions, leading to suboptimal choices
asymmetric information
one party has more information that another
moral hazard
a situation where one party takes risks because they do not bear the consequences
insurance is an example where the insured party may engage in riskier behaviour, knowing that they are protected from the costs of that risk
adverse selection
buyers or sellers of a product are able to use their private knowledge of the risk factors involved in the transaction to maximize their outcomes, at the expense of the other parties to the transaction
de merit goods
goods deemed more harmful to consumers than they realise
why
information failure - information is ignored / not presented
asymmetric information - producers have full information but don’t share it with consumers
generates negative consumption externalities
alcohol
gambling
overconsumed / overproduced
irrational decisions
merit goods diagram
underconsumption (P1 Q1) causes welfare loss
too many resources being allocated
allocative inefficiency
due to information failure
irrational decisions made by consumers
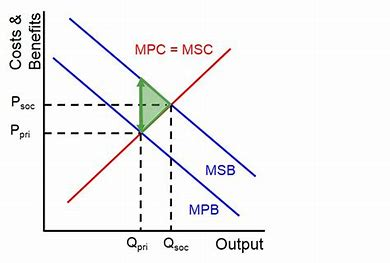
demerit goods diagram
too many resources being allocated
allocative inefficiency
overconsumed
welfare loss
pure public good
non excludable
no price can be charged for a public good
the benefits of consuming a public good cant be confined to an individual who has paid for it
no cost efficient price
non rivalrous
quality of the good doesn’t diminish upon consumption
road signs
street lights
free rider problem
when individuals benefit from resources or services without paying for them, leading to under provision of public goods
missing market
a market does not supply a good or service
due to
lack of demand
improper incentives
free rider problem
leading to inefficient allocation of resources
quasi public good
mix of a public and private good
roads can be excludable - toll roads, can be rivalrous
beaches - can be excludable, rivalrous during peak times
tragedy of the commons
a situation in which individuals acting in their own self-interest deplete shared resources, leading to environmental market failure and long-term damage to the resource
common access resources
natural resources over which no private ownership has been established
air
forests
how lack of private ownership causes tragedy of the commons
producers act in self interest and exploit common access resources
depreciation of resource because of profit motive
even if a producer stops because of concerns, other producers will take all the resources, meaning only the producers that has stopped will lose out
income inequality
those on lower incomes are unable to consume
underconsumption
allocative inefficiency
factor immobility
refers to the inability of factors of production to move easily from one industry to another, leading to unemployment and inefficiency in the economy
occupational immobility of labour
inability of workers to change jobs or industries due to lack of skills, training, or experience needed
geographical immobility of labour
workers who cannot move to different locations for employment due to factors such as housing constraints, family ties, or lack of information about job opportunities
effect of unemployment in micro
FOP not being fully utilised
allocative inefficiency
economy is inside PPF
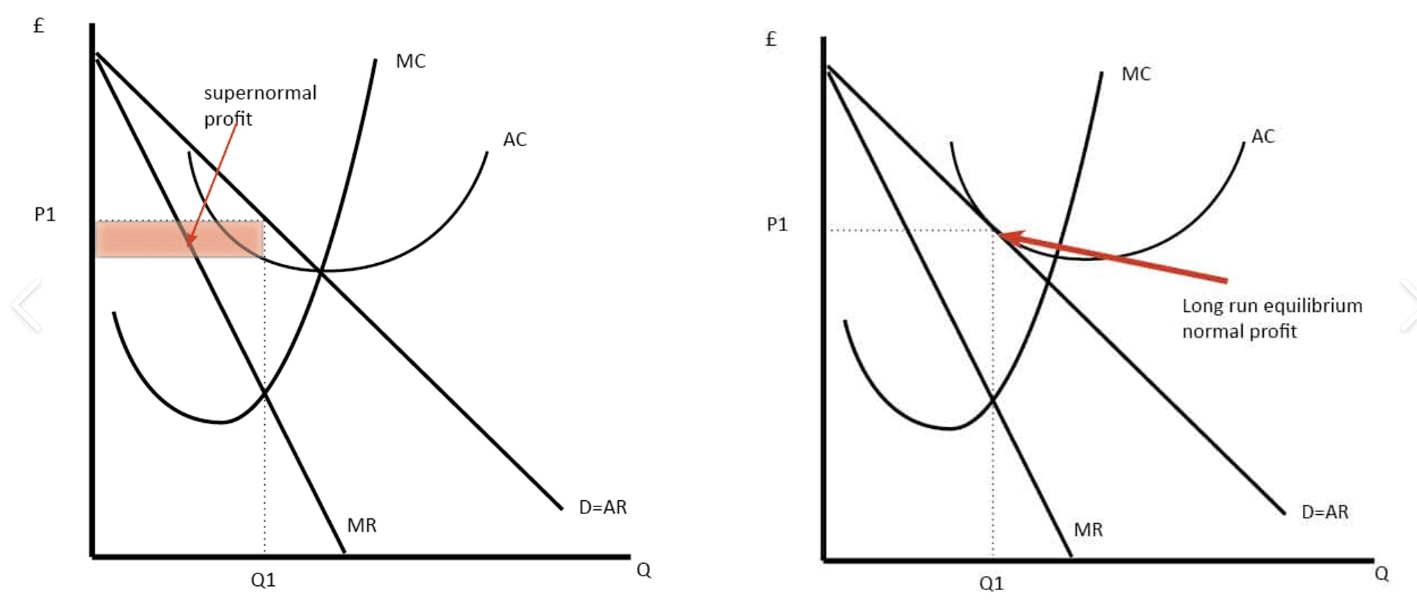
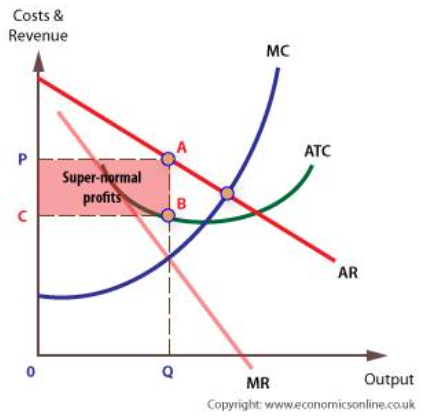
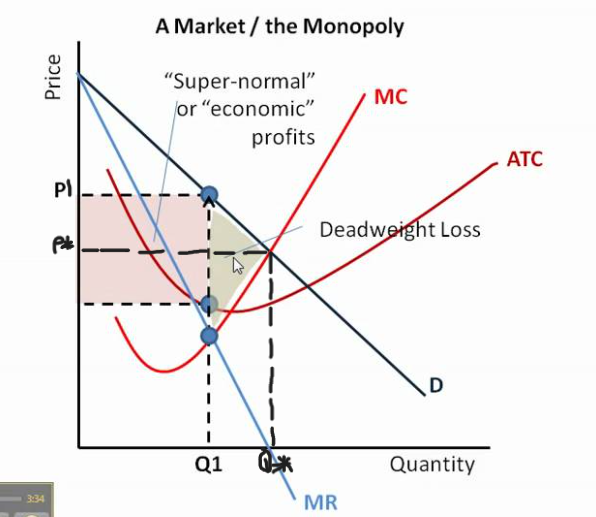
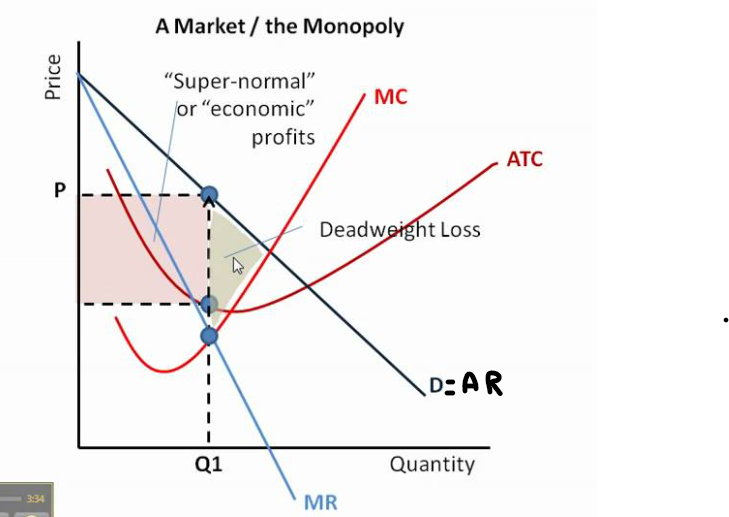
monopoly cuases market failure
as a monopoly is profit maximising, price is set to MR = MC
restricts output as some consumers are priced out the market
underconsumption of the good
misallocation of resources
lower consumer surplus
allocative inefficiency
also x inefficient - no incentive to lower costs or reduce waste - no competition
are able to charge a price below AC to force new entrants out the market
once rivals leave, price increases
characteristics of a monopoly
profit maximisers (MR = MC)
price makers
unique goods
supernormal profit
high barriers to entry
absence of property rights - market failure
def - legal right to control and benefit from a resources, e.g. land
production
factory pollutes a river - no one owns the river
costs of polluting the river are dumped on society
negative production externality
consumption
if people overconsume a public park, it becomes overcrowded and degraded
each person gets a MPB
but the cost of wear and tear is on everyone else
negative consumption externality
tragedy of the commons
complete market failure
market is unable to allocate resources efficiently, leading to a total lack of supply for a good or service
partial market failure
market produces the wrong quantity, leading to inefficient allocation of resources
fails to deliver socially optimum outcome
government intervention
the actions taken by a government to correct market failures, regulate markets, or provide public goods and services
subsidies
tax
regulation
information provision
price controls / pollution permits
state provision
indirect tax
uses
correct market failure
raise government revenue
def - expenditure tax, an extra charge when goods and services are sold
increase costs of production for firms
can be passed onto consumers in the form of higher prices
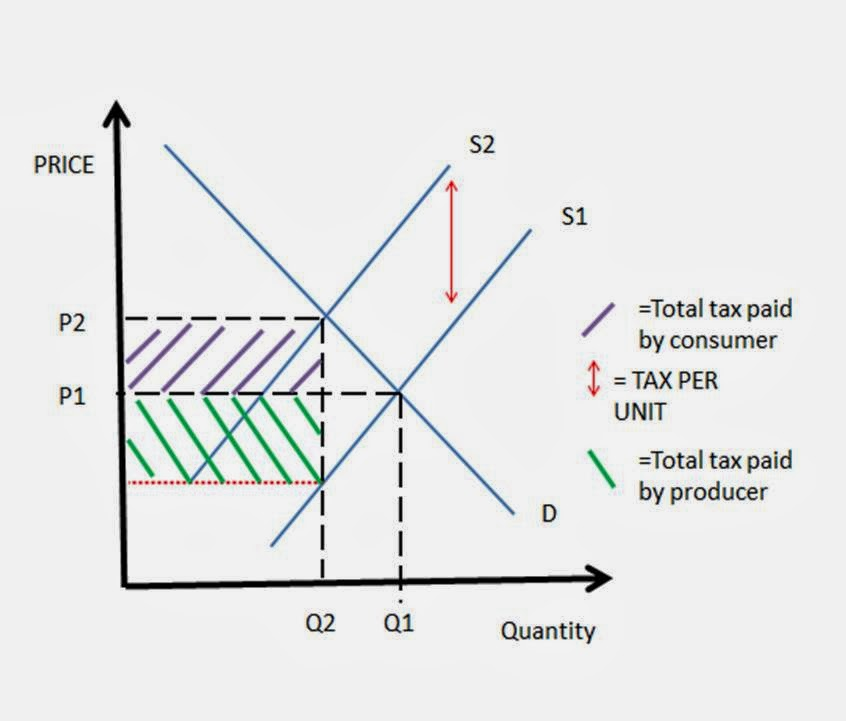
specific unit tax
tax placed on each item regardless of price
increase cost of production
solves overconsumption/production
promotes allocative efficiency whilst generating government revenue
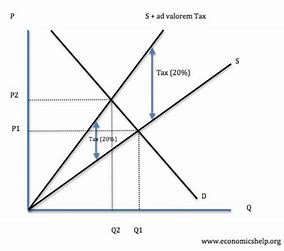
ad valorem tax
percentage tax on top of price
increase cost of production
solves overconsumption/production
promotes allocative efficiency whilst generating government revenue
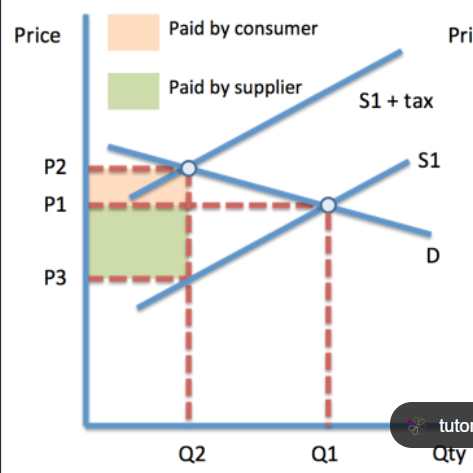
price elastic indirect tax
consumer burden - lower
producer burden = higher
tax revenue = lower
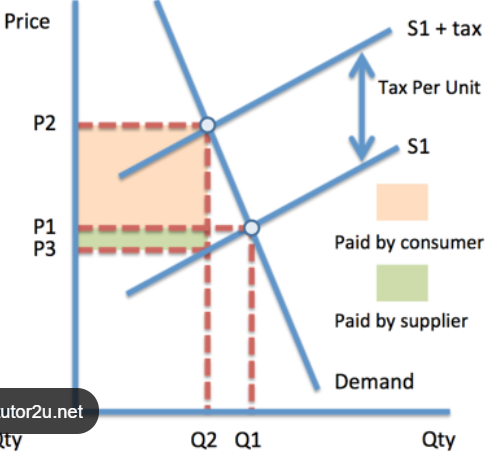
price inelastic indirect tax
consumer burden = higher
producer burden = lower
tax revenue = higher
indirect tax evaluation
effectiveness at reducing consumption depends on PED
if demand is price inelastic - quantity demand wont fall
if gov have imperfect information, tax rate could be too hight
consumers avoid tax
black market
smuggling
firms shut down / leave country
unemployment
lost tax revenue
regressive tax promotes income inequality
subsidies
money grant to firms by the government to reduce costs of production and encourage an increase in output
uses
solve market failure
increase affordability - necessity’s, under consumed goods
consumer + producer incidence = gov spend
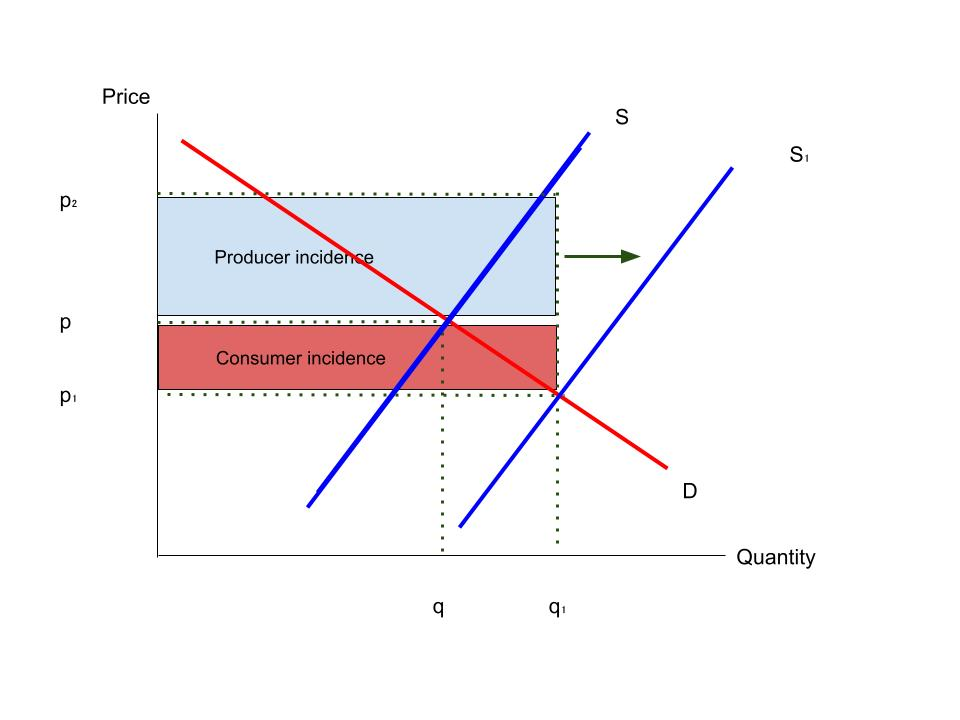
price elastic subsidy
producer benefit increase
consumer benefit decrease
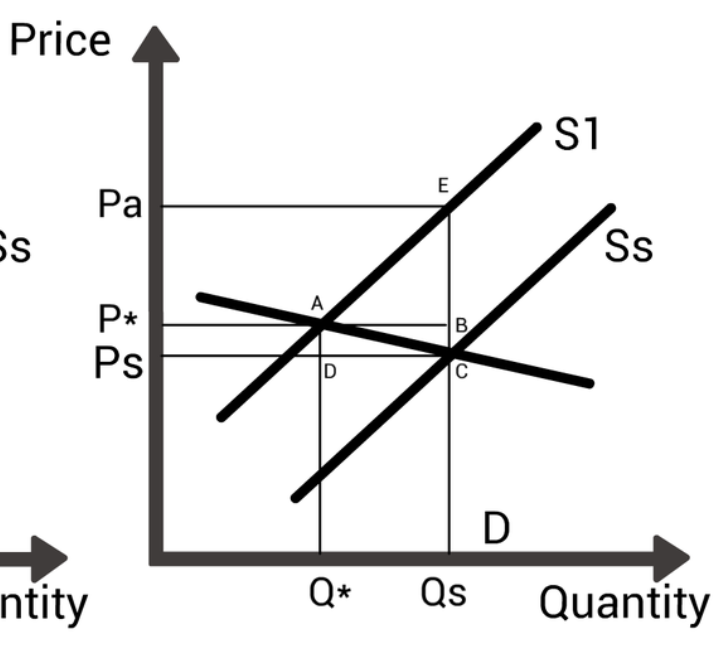
price inelastic subsidy
producer benefit decrease
consumer benefit increase
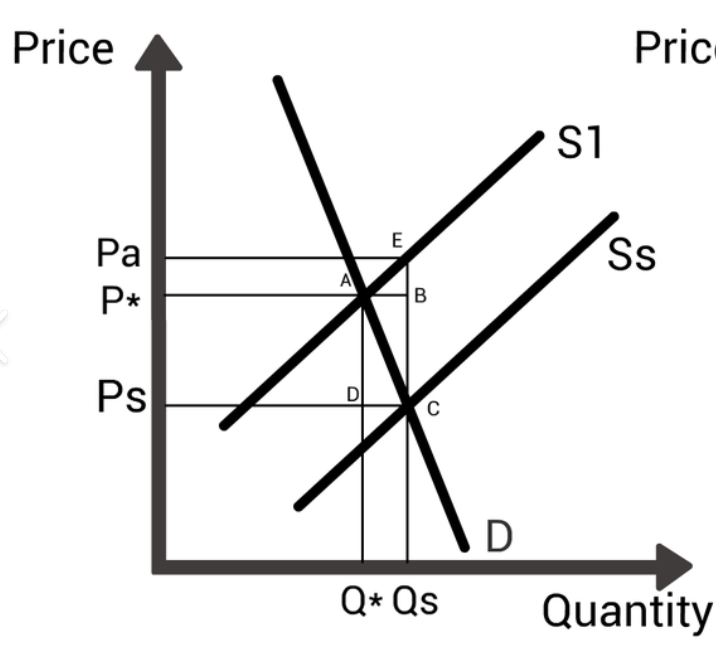
benefits of subsidies
encourage production of merit goods
benefit society
lower price encourages competition
supports unestablished industries
solves underconsumption/production
allocatively efficient
welfare gain
subsidies evaluation
firms may become reliant of subsidies which can lead to inefficiencies
opportunity cost of subsidy - cuts to healthcare spending
is government acting with perfect info - could be a higher cost to government
effectives depends on elasticity
needs to be price elastic demand to solve market failure
minimum price / price floor
a fixed price enacted by the government usually set above the equilibrium price\
why
protect producers from price volatility
solve market failure - discourage consumption of demerit goods
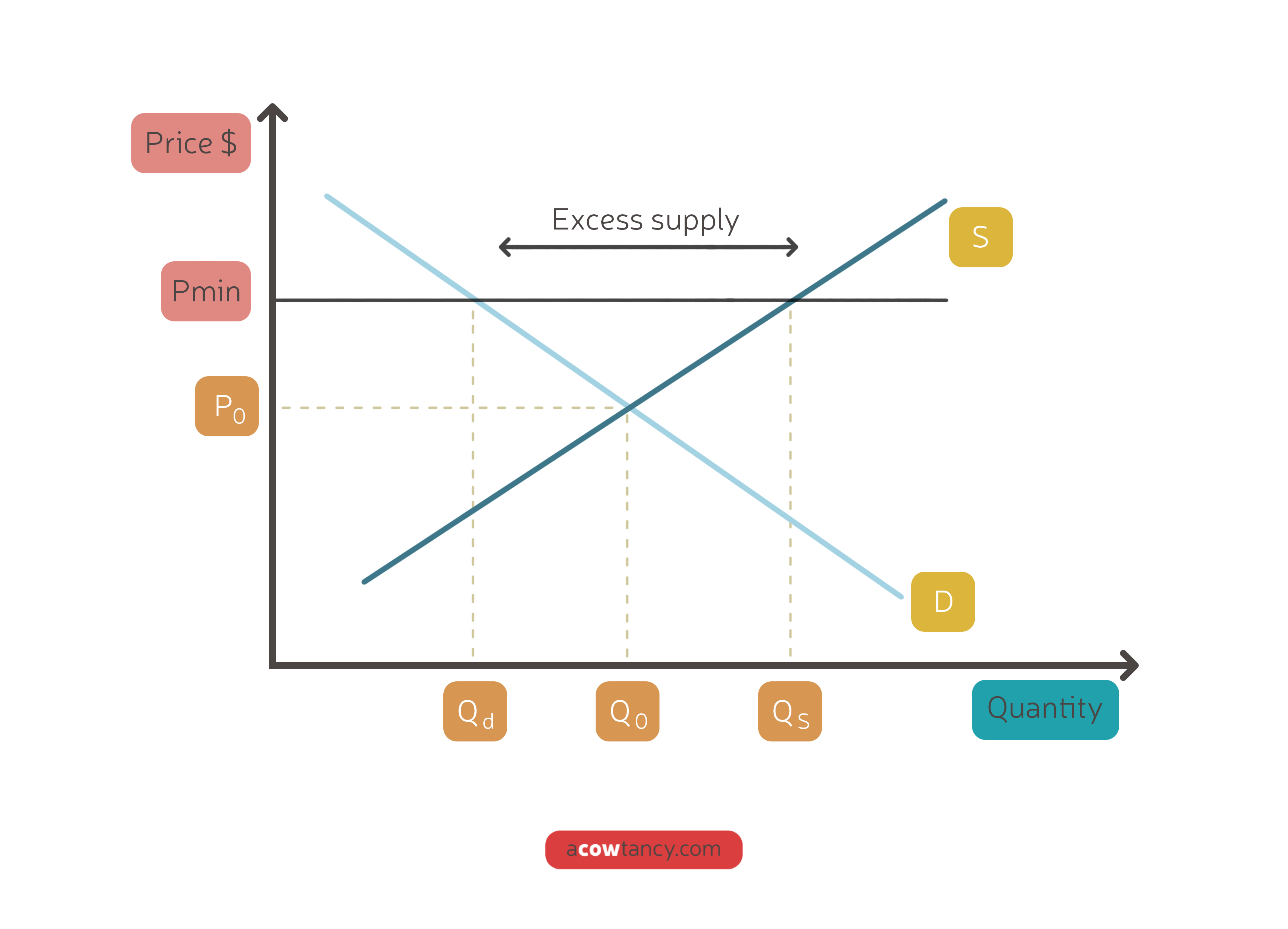
ADV minimum price
producers have guaranteed minimum income
encourage investment and dynamic efficiency
stockpiles can be used when supply is reduced
discourages consumption of demerit goods, increasing society welfare
DIS minimum price
consumers pay more - less consumer surplus, less PP
producer revenue depends on if the government are intervention buying
if PED is inelastic it may not solve market failure - but consumers revenue will increase
can incentivise black markets or find alternatives
recourses used to producer excess supply could be used elsewhere - opportunity cost, allocative inefficiency
dumping excess supply - worsen international relations
maximum price / price ceiling
a fixed price enacted by the government usually set below the equilibrium market price
uses
improve affordability of necessity’s
doesn’t exclude those on lower incomes
extension in QD
contraction in supply
producers are less willing and able to supply
producers cant satisfy demand
lower producer revenue - dynamically inefficient
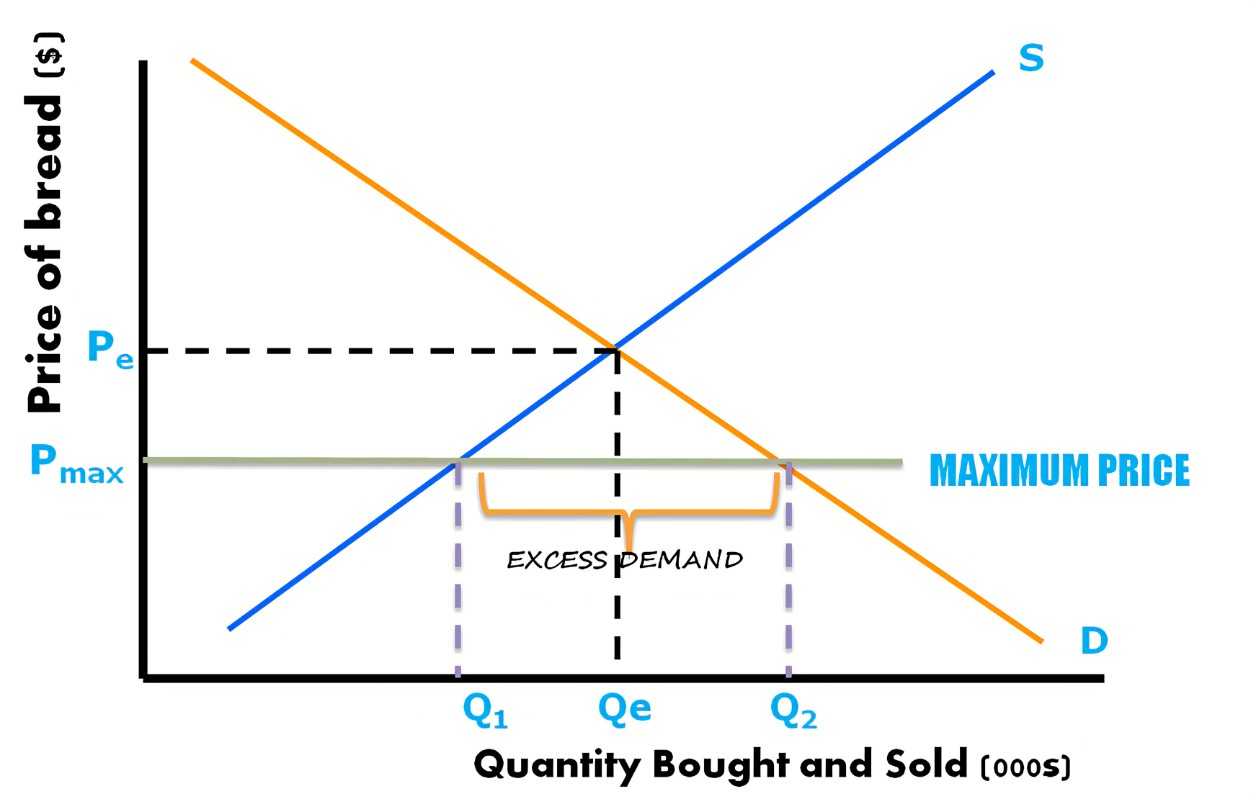
ADV maximum price
affordability increases
DIS maximum price
some consumers cant access the good due to excess demand - shortage
may be forced to alternative supply
smuggling, black markets
fall in producer revenue and surplus
unintended consequences - black markets
may have to intervene with subsidy to meet demand
enforcement costs - high admin costs
state provision
direct provision of goods and services by the government free at the point of consumption
why
free market fails to produce at the right quantity
merit goods are under consumed and underproduced
public goods, missing market
inequitable distribution of income
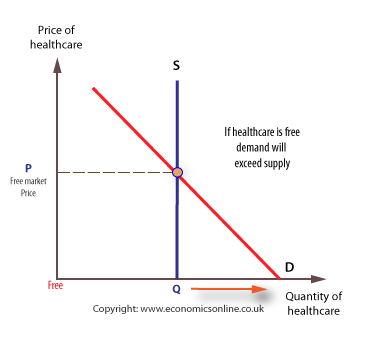
DIS state provision
cost to taxpayer
may lack information about price and quantity
gov may lack dynamic, productive and X efficiency as they are not profit maximisers
excess demand
regulation
rule / law enacted by the government that must be followed by economic agents to encourage a change in behaviour
aim
reduce negative externalities
change monopoly / oligopoly behaviour
improve inequitable distribution of income
can be restrictive or prohibitive
DIS regulation
cost - regulators (administration)
fines for breaking rules may not be enough of a deterrent
unintended consequences - high regulation causes firms to shut down or leave the country
lots of regulation may reduce productive efficiency (red tape)
pollution permits
giving firms a legal right to pollute a certain amount
if a firm pollutes less it can sell its pollution permits to other firms
if a firm pollutes more a firm has to buy more from the government
promotes long run incentives to invest in green technology
increase profits through selling pollution permits
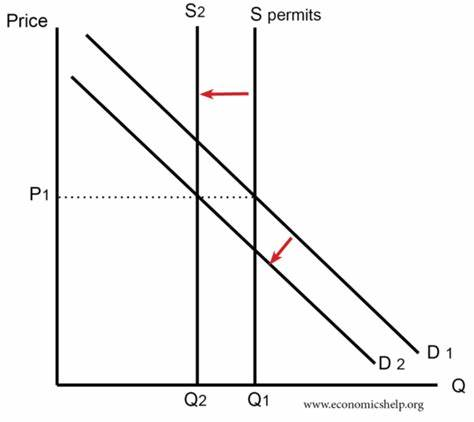
DIS pollution permits
enforcement costs - opportunity cost
gov may have imperfect information - cap may be set at the wrong level
unintended consequences - increases cost of production for firms - may shut down - or pass on costs to consumers
information provision
government funded information provision to encourage or discourage consumption through advertising or education
information provision with merit goods
there is under consumption and production
demand shift as consumers make rational decisions
with info provision, MPB will move right to MSB ( MSB = MPB + provision) at the socially optimum level
allocative efficiency and more welfare
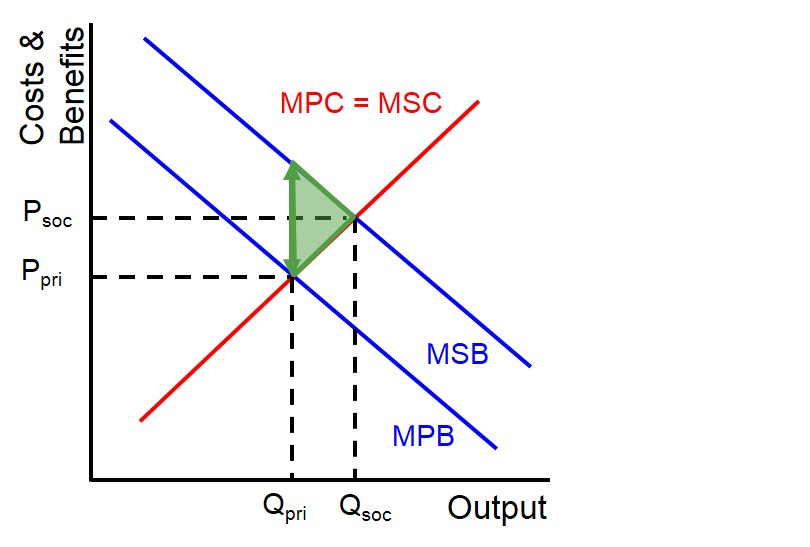
information provision with demerit goods
there is over consumption and production
demand shift as consumers make rational decisions
with info provision, MPB will shift left to MSB (MSB = MPB + provision) at the socially optimum
allocative efficiency and more welfare
DIS information provision
expensive - opportunity cost
no guarantee of success
only effective in the long run
gov may not have perfect information
property rights
incentive not to exploit common access resources
negative externality internalised to producer / owner of land
if enforced, will reduce quantity to socially optimum level
DIS property rights
can they be efficiently distributed
enforcement needed - cost
equity - who gets rights
government failure
occurs when the government intervenes in a failing market but fail to improve the allocation of resources
costs of intervening outweigh the benefits
may make existing market failure worse or create whole new market failure
less social welfare
distortion of the price signal - gov failure
refers to government intervention that alters the natural information conveyed by prices, leading to inefficient resource allocation
information failure - gov failure
government may not have full / correct information to enable them to make an effective decision about the best ay to allocate resources - not at Q*
excessive administration costs - gov failure
correcting market failure can come with high militance and enforcement costs
regulation
subsidies
state provision
price controls - excess supply / demand cost
opportunity cost
unintended consequences - gov failure
intervention leads to am unexpected / unintended effect
black markets
negative impacts that aren’t part of the policy
poor - min price, taxation, less PP
impact on firms - subsidies can make them wasteful - X inefficient
employment
regulatory capture - gov failure
interests of society are overlooked for the interests of firms
because firms influence regulators
political self interest - gov failure
pursuit of self interest amongst politicians and government officials can lead to a misallocation of resources
policy myopia - gov failure
short-sightedness in policy-making that focuses on immediate benefits rather than long-term effects, often leading to negative outcomes
free market
any place where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods and services, free from government intervention
ADV free markets
allocative efficiency
encourage competition
dynamic efficiency - investment
job creation, economic growth
no risk of government failure
DIS free markets
markets can fail - monopoly / oligopoly
inequity given inequality - may exclude consumers
creative destruction - cost cutting in dangerous areas like safety
price volatility
price volatility
the tendency for prices to fluctuate significantly over short periods due to market instability or changes in supply and demand
why are primary commodities volatile
demand and supply are inelastic
lack of substitutes
production lag
hard to store'
regular shifts in demand and supply
supply - weather
demand - global growth
consequences of price volatility
less tax revenue
less revenue for firms
recessions
lower investment
UK competition body
competition policy is government regulation which aims to make markets more competitive
the competition market authority (CMA) in the government agency responsible for overseeing competition policy
ADV competition policy
lower prices for consumers
more choice
improved efficiency
innovation is encouraged
DIS competition policy
enforcement costs
regulatory failure
reduced EOS
compliance costs for firms
example of competition policy
competition markets authority blocked Microsoft from acquiring Activision in 2022 but then it was allowed later with approved conditions
competition policy 3 focuses
monopolies
mergers
restrictive trading practices
monopoly busting
compulsory breakup of monopolistic firms to promote competition in the market
ADV monopoly busting
encourages competition
prevents abuse of monopoly power - reduces chance of price fixing or limiting supply
benefits consumers - lower prices more choice
supports smaller businesses
DIS monopoly busting
high implementation costs
disruption of EOS - could incr3ease costs and prices
windfall taxes
a levy imposed by the government on firms that have benefitted from something they where not responsible for
ADV windfall taxes
revenue generation for government
redistribution of wealth
DIS windfall taxes
disincentive to invest - firms may resist investing in markets prone to windfall taxes
complexity and fairness
potential for pass-through costs - firms may pass on the tax burden to consumers
ADV price control promoting competition
protects consumer - ensures affordability for consumers
prevents exploitation - stops dominant firms charging high prices
economic stability - helps manage inflation
DIS price control promoting competition
market distortions - lead to shortage if firms cant cover their costs
disincentive for investment
black markets
administrative burden
promoting competition and contestability
enhance growth of small businesses
give training and grants to entrepreneurs
tax incentives or subsidies
lowing barriers to entry
deregulation
monopoly to monopolistic competition
lower prices
better quality
innovation
less waste - x efficiency
more choice
privatisation
the transfer of ownership from the public sector to the private sector
ADV privatisation - x efficiency
in the private sector firms have stronger incentive to minimise costs and reduce waste to maximise their profits for shareholders
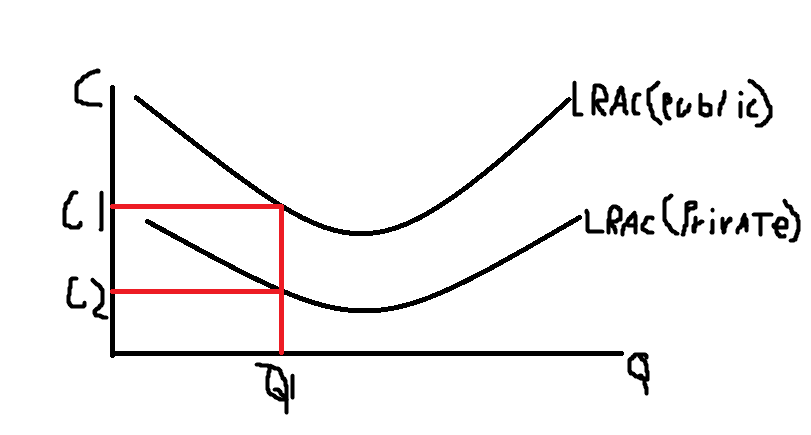
ADV privatisation - dynamic efficiency
the public sector may lack supernormal profits to innovate as they have pressure to produce at the allocatively efficient point (P=MC) rather than the profit maximising point (MR=MC)
other ADV of privitisation
raises one off revenue for government
reduces public spending
increased tax revenue
improved resource allocation as private firms respond to signal of demand and supply
DIS privatisation - productive inefficiency
if the market becomes dominated by a single firm, it may reduce productive efficiency
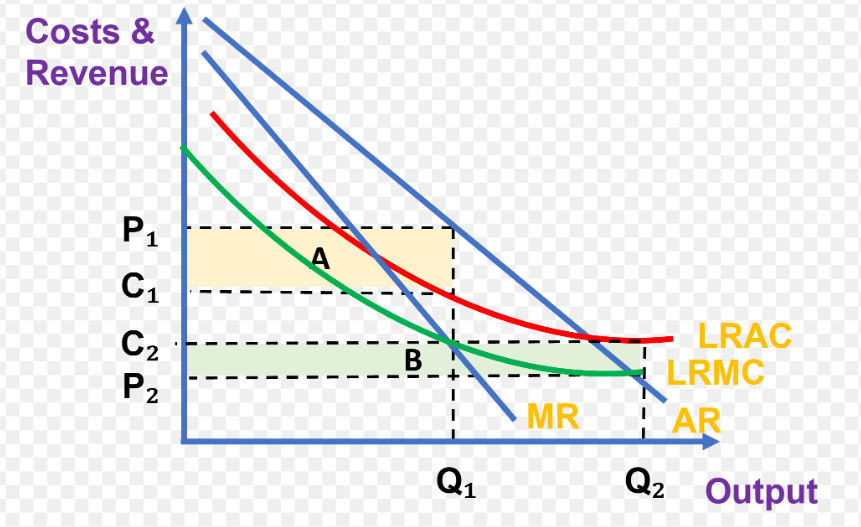
a natural monopoly sauch as the railway network may involve high fixed costs and EOS that make competition wasteful - wasteful duplication of resources
so privatisation may result in higher prices without improving quality
DIS privatisation - x inefficiency
without the discipline of the market, nationalised firms may become complacent
leading to higher costs and more waste
DIS privatisation - allocative inefficiency
if there is limited competition firms don’t need to produce at the highest quality
may charge higher prices than necessary, resulting in a misallocation of resources and reduced consumer welfare
DIS privatisation - income inequality
privatisation may disproportionally affect low income groups
when essential services like public transport are privatised, higher prices can exclude poorer households, leading to increased income inequality and reduced welfare due to allocative inefficiency
income inequality
misallocation of resources
other DIS privitisation
a privatised public monopoly needs regulation - cost
may be in danger to short term profits - dividends to shareholders
may sell the firm too cheaply
privatisation eval
costs - natural monopoly
quality of regulation and cost
types of good
externalities generated
depends of level of competition - monopolies, oligopolies
nationalisation
taking a privately owned industry into government hands
operated for the benefit of consumers not private shareholders, prices can fall and output can rise
used to achieve social objectives, address market failure and manage essential services