week 6: vision
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Prevalence and conditions with high prevalence of visual impairment
Globally, 2.2 billion people have vision impairment or blindness (WHO, 2022)
• Globally, majority of people with vision impairment over age of 50 yrs (WHO, 2022)
The role of occupational therapy
• Evaluation for visual impairment
• Identify the limitation(s)
• Link the performance limitation to impairment
• Determine treatment
• Refer to specialists
• Optometrists, ophthalmologists, vision rehabilitation therapists, certified low vision
therapists
• Identify most appropriate Intervention
Functional vision screening
Visual screening falls within the domain of OT practice
Safety
occupational performance
participation
How we see
• Light reflects off object hitting curve of the lens of the eye
• Light rays bend and converge at the focal point
• Image formed by the convex lens is upside down & is reversed left to right
• Light passes through lens and vitreous humor to the retina to excite
photoreceptors
• Electrical impulses transmitted to optic nerve

Visual processing
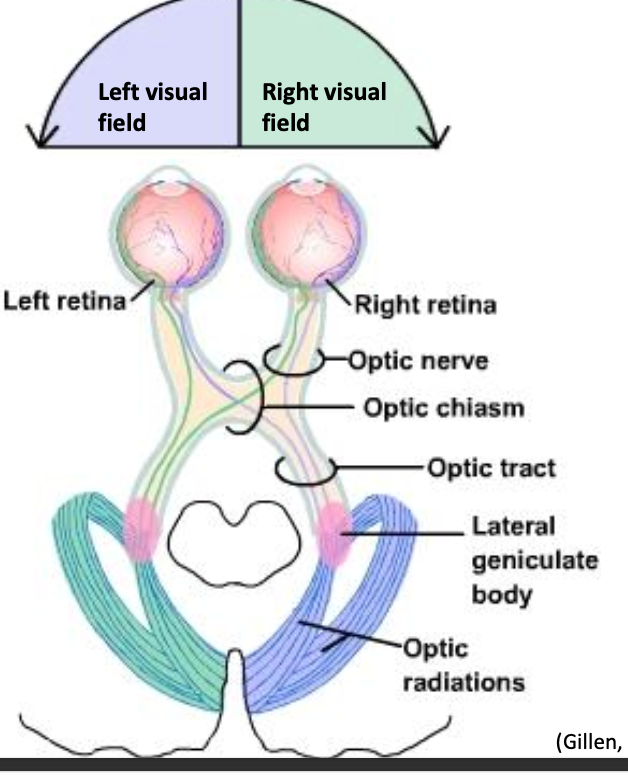
Processing in the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe
• Processing in the visual association cortex
• Object recognition -- color, shape, size
• Visual spatial perception and movement
Mary Warren’s Visual Perceptual Hierarchy
Adaptation
through vision
Visuocognition
Visual memory
Pattern recognition
Scanning
Attention = alert and attending
Oculomotor control, visual fields, visual acuity
Pupillary response
Pupil’s ability to respond to changes in light may affect:
• The process of accommodation… affecting near acuity
• The ability to adjust/respond to changes in illumination
• Screen for pupil size, symmetry, and response to light stimulation using a pen
light
Near acuity:
• Clearly seeing, identifying and understanding objects within arm's length
• Distance acuity:
• Clearly seeing, identifying and understanding objects at a distance
Peripheral Field
• Recognition of “Where”
• Monitoring and interpreting what
is happening in the surrounding
field of vision
• Alerts the CNS to presence of
objects
• Precursor to recognition of “what”
• Central Field
• Recognition of “What”
• Requires more precise visual info
Contrast sensitivity acuity
• High contrast acuity
• Near
• Far
• Low contrast acuity (contrast sensitivity function)
Possible Clinical Observations
Blurriness
• Squinting
• Unable to read near and/or far
• Needs increased light
• Bumps into objects
• Difficulty recognizing faces or distinguishing colors
• Light sensitivity
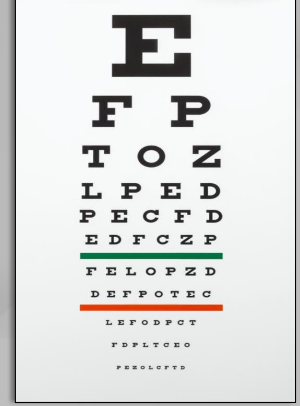
Evaluation of acuity examples
• Snellen Chart
• biVABA
Oculomotor Function
• Ability to move the eyes together, coordinated
Eye movement
• Controlled by CN 3 (oculomotor), CN4 (trochlear), CN6 (abducens)
Extraocular muscles:
• Lateral, medial, superior, inferior rectus muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles
Smooth Pursuits:
• The ability of the eye to move smoothly across a printed page or while following a moving object
• Convergence:
• Bringing the eyes together… a reflexive response elicited when attending to a target moving closer
• Saccades:
• Quick, simultaneous movement of both eyes between two or more phases of fixation in the same direction
Evaluation of oculomotor function
➢Observe behavior during functional activities
➢Use biVABA to assess
• Alignment
• Eye movements
Diplopia
• Double vision
Functional Implications:
• Judging distances
• Overreaching/under reaching
• Head turn/ tilt
• “Spaced out” appearance
• Avoidance of near tasks
• Blurred vision
• Balance and vestibular deficits
• Nausea
• Reading deficits
• Visual motor deficits
Diplopia – oculomotor assessments
• Scanning assessments – convergence and ocular range of motion/ mobility
• biVABA
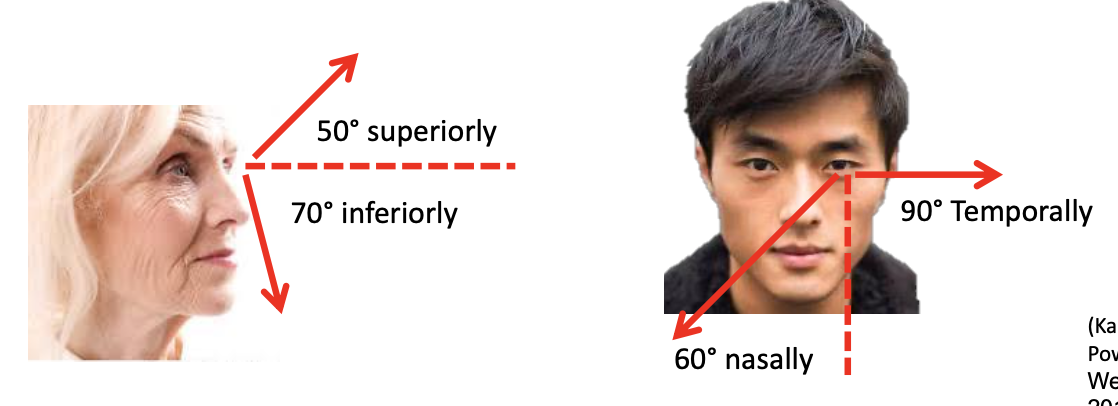
Visual fields
• Ensures the presence of vision or that all of the environment is represented in the visual picture
• Binocular (both eyes combined) horizontal field = 180º
• Monocular (one eye) visual field -> see below…
Field Cut / Hemianopia prevalence and definition
• Visual field deficits common with acquired brain injury
• Most common visual disturbance associated with stroke
• TBI loss is often in superior fields
• Hemianopia – affects half of the visual field
• Homonymous hemianopia involves both eyes
Field Cut / Hemianopia
1. blindness of R eye d/t lesion of optic nerve;
2. bitemporal hemianopia d/t chiasmal lesions;
3. L homonymous hemianopia d/t lesion of right parietal or temporal
lobes w/ pressure on R optic nerve
4. L upper contralateral quadrantic anopsia;
5. 5 & 6 = partial lesions of the visual cortex, leading to partial lesions of
the opposite side.
Visual Field Cut (Only)
awareness of left field
attempts to actively compensate
confined to visual system (ex: should not see signs of personal neglect)
Attentional demands should not change performance
hemi-inattention
Decreased awareness of one side
Not sure where left side is
May be observed across sensorimotor functions (motor, auditory, tactile etc.)
Symptoms predictably change with increased selective attentional demands and demands for sustained attention
Visual field deficits and occupations
• Can significantly impact ability to complete ADLs
• Can significantly impact safe interaction with the environment
• Impair ability to locate and search
Limits scope and speed of scanning
Decreases visual details
• Usually unaware of VFD at first
• With increased awareness, perceptual completion may occur
• Adopt adaptive protective strategies
• Inaccurate saccades
Saccades are less regular/ less accurate/ too small for organized scanning and reading
• Disorganized scanning
• Require longer visual search times
• Omit relevant objects in the environment
Hemianopia – additional impairments
Focus on their intact hemi-field
inaccurate saccades
disorganized scanning
Potential functional changes with visual field loss
• Reading Difficulties
• Writing Difficulties
• Difficulty with ADLs
• Problems with functional Mobility
Emotional impact of visual field deficits
• Increased anxiety
• Decreased self confidence
• Increased passivity
• Social isolation
Evaluation of visual field deficits
• Observation: Look for functional changes
Standardized clinical testing:
• Automated perimetry test
• Scanning tests
• Confrontation testing
Certified Orientation Mobility Specialists
(O & M Specialist)
• Work with people who are blind or have low vision
• Train/instruct clients in the use of remaining senses to determine position in the environment
• Teach techniques for safe movement from one place to another
• Community based
• Goal Develop: independent travel skills
Certified Vision Rehabilitation Therapist
(CVRT)
• Provide instruction guidance in adaptive independent living skills
• Basic ADL’s, household management, Communication, education, leisure, &
orientation and movement in indoor environments
Optometrists - (FCOVD)
• Board Certification in Vision Development and Vision Therapy (FCOVD)
• Optometrists who successfully complete their certification process are board certified and are designated Fellows of COVD (College of Optometrists in Vision development)
• State-of-the-art clinical services in behavioral and developmental vision care,
optometric vision therapy and vision rehabilitation.
Ophthalmologist
• Complete a medical degree which is followed by a 1-year internship & a 3-
year residency in ophthalmology at an accredited program
• Specialize in the treatment of diseases & conditions of the eye & visual system
• Focus: diagnosing & medically managing conditions through surgery,
pharmaceuticals, or optic devices
Visual screening lab
✓ Pupillary Size
✓ Pupillary response to light
✓ Accommodation
✓ Responsiveness of pupils to accommodation
✓ Visual pursuit/tracking
✓ Saccades
✓ Convergence
✓ 1-Person confrontation
✓ 2-Person confrontation