cells and body systems
4.8(6)
4.8(6)
New
Card Sorting
1/38
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
cell
* cells make up organisms.
* They are the most basic and **smallest unit** of all living things.
* They are made up of **organelles**.
* They are the most basic and **smallest unit** of all living things.
* They are made up of **organelles**.
2
New cards
Organelle
* Found inside of a cell
* Each organelle has a special job.
* Animal and plant cells have some organelles that are the same and some that are different.
* Each organelle has a special job.
* Animal and plant cells have some organelles that are the same and some that are different.
3
New cards
7 organelles found in cells
1. Cell membrane- gate
2. Nucleus- DNA
3. Mitochondria- Energy
4. Cytoplasm- jelly
5. Ribosome- protein
6. Chloroplast- only found in plants
7. Cell wall - only found in plants
4
New cards
***Cell membrane***
* ”Skin” of the cell, forming a barrier around the cell
* Acts like a gatekeeper, letting things in and out
* Acts like a gatekeeper, letting things in and out
5
New cards
***Cytoplasm***
* Jelly-like fluid that holds the organelles
* Contains nutrients and waste products
* Contains nutrients and waste products
6
New cards
***Nucleus***
* Contains DNA (*deoxyribonucleic acid)*
* DNA contains the instructions for every job the cell needs to do
* It is passed down through generations
* Your DNA is from your parents, half from each
* DNA contains the instructions for every job the cell needs to do
* It is passed down through generations
* Your DNA is from your parents, half from each
7
New cards
mitochondria
* Where energy is produced
* they release energy from food
* they release energy from food
8
New cards
chloroplast
* only found in plants
* the green part of plants
* plants make their own food from water and carbon dioxide using energy from the sun
* this is called photosynthesis and takes place in the chloroplast
* the green part of plants
* plants make their own food from water and carbon dioxide using energy from the sun
* this is called photosynthesis and takes place in the chloroplast
9
New cards
ribosome
Microscopic factories that produce the proteins used by the body for growth and repair.
10
New cards
cell wall
Plants don’t have a skeleton, so they need something else to keep them upright and in shape
The cell wall is OUTSIDE the cell membrane
The cell wall is OUTSIDE the cell membrane
11
New cards
similarities and differences between animal and plant cells
Animal cells:
* Small vacuole
* Blob shape
Both:
* Nucleus
* Mitochondria
* Ribosome
* Cell membrane
* Cytoplasm
* Vacuole
Plant cells:
* Large vacuole
* cell wall
* Chloroplasts
* Rectangular shape
* Small vacuole
* Blob shape
Both:
* Nucleus
* Mitochondria
* Ribosome
* Cell membrane
* Cytoplasm
* Vacuole
Plant cells:
* Large vacuole
* cell wall
* Chloroplasts
* Rectangular shape
12
New cards
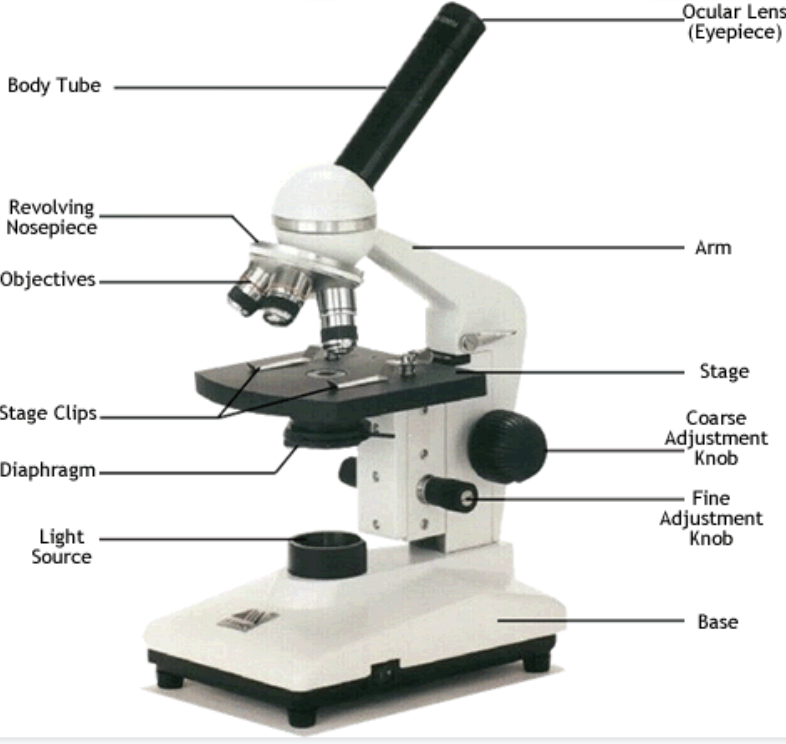
main parts of a microscope
* Ocular Lens (Eyepiece)
* Body Tube
* Arm
* Revolving
Nosepiece
* Objectives
* Stage
* Stage Clips
* Coarse
Adjustment
Knob
* Fine
Adjustment
Knob
* Diaphragm
* Light
Source
* base
* Body Tube
* Arm
* Revolving
Nosepiece
* Objectives
* Stage
* Stage Clips
* Coarse
Adjustment
Knob
* Fine
Adjustment
Knob
* Diaphragm
* Light
Source
* base

13
New cards
setting up a microscope
1. place the slide on the stage, securing it with the stage clips
2. bring the stage as close as possible to the objective lens using the coarse focus knob
3. while looking through the ocular lens, adjust the stage, using the coarse focus knob
4. use the fine focus knob to make it clearer
14
New cards
Unicellular
Simple organisms made up of only one cell
15
New cards
Multicellular
* Made of more than one cell
* Cells work together, but do not have the same function - they are ***specialised***
* More complex organisms
* Cells work together, but do not have the same function - they are ***specialised***
* More complex organisms
16
New cards
Tissue
* Groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
17
New cards
Organ
* A group of tissues that work together to perform a particular function
18
New cards
Organ system
* Groups of two or more organs which work together to perform a specific function
19
New cards
8 Organ systems
Excretory system, Nervous system, Digestive System, Circulatory system, Reproductive System, Respiratory System, Muscle system, Skeletal system
20
New cards
How are cells, tissues and organs arranged to make organ systems?
\
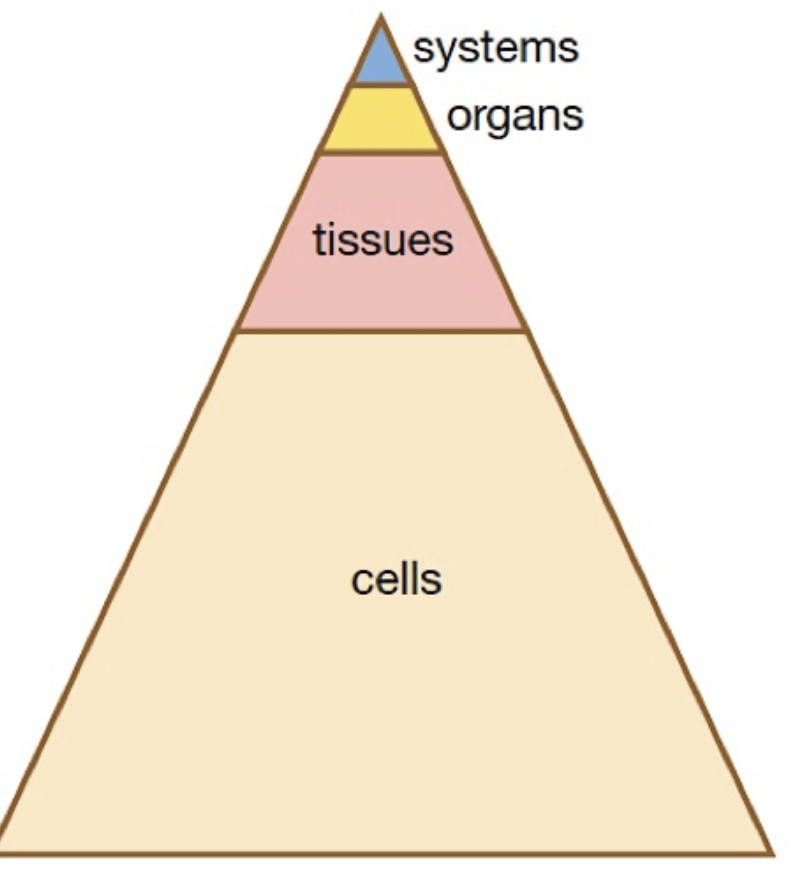
21
New cards
five vital organs
Brain, Heart, Lungs, Liver, Kidney
22
New cards
Brain
* controls all the body's functions
* Part of nervous system
* Part of nervous system
23
New cards
Heart
* Collect blood from the lungs (high in oxygen) and pumps it out to the body
* Part of Circulatory system
* Part of Circulatory system
24
New cards
Lungs
* to allow oxygen in the air to be taken into the body
* Part of Respiratory System
* Part of Respiratory System
25
New cards
Liver
* cleans your blood, produces bile, stores energy in the form of a sugar called glycogen
* part of Excretory system
* part of Excretory system
26
New cards
kidneys
* filters the blood and takes out all the waste in the blood
* sends the waste onto the bladder in the form of urine
* part of the Excretory system
* sends the waste onto the bladder in the form of urine
* part of the Excretory system
27
New cards
Role of the organ systems that contain the 5 main organs
1. Nervous system
* Controls everything you do, including, breathing, walking, thinking and feeling
2. Circulatory system
* carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells, and removes waste products, like carbon dioxide
3. Respiratory System
* allows oxygen in the air to be taken into the body, while also letting the body get rid of carbon dioxide
4. Excretory system
* filters your blood to remove wastes that could be harmful to your body
\
28
New cards
6 organs in the digestive system
1. oesophagus
2. stomach
3. large intestine
4. small intestine
5. rectum
6. anus
29
New cards
main function of the oesophagus
* transfers food from the mouth to the stomach.
30
New cards
main function of the stomach
* stores the food you've eaten.
* breaks down the food into a liquidy mixture.
* Slowly emptys that liquidy mixture into the small intestine.
* breaks down the food into a liquidy mixture.
* Slowly emptys that liquidy mixture into the small intestine.
31
New cards
main function of the small intestine
* absorbing almost all of the nutrients you get from foods into your bloodstream
32
New cards
main function of the large intestine
* to **absorb water and salts from the material that has not been digested as food**
* **get rid of any waste products left over**
* **get rid of any waste products left over**
33
New cards
main function of the rectum
* The rectum acts as a **storage facility** that stretches to hold **faeces** – the **undigested material**
34
New cards
main function of the anus
* When the rectum has stretched sufficiently, it moves the faeces out of the body through the **anus.**
35
New cards
5 organs in the excretory system
1. liver
2. lungs
3. skin
4. kidneys
5. urinary system- ureters, bladder and urethra
36
New cards
main function of the skin
* covers and protects everything inside your body
* The sweat glands help cool the body.
* Heat escapes through millions of pores on the skin’s surface.
* Perspiration (evaporative cooling) is 99% water, mineral salts, and urea.
* The sweat glands help cool the body.
* Heat escapes through millions of pores on the skin’s surface.
* Perspiration (evaporative cooling) is 99% water, mineral salts, and urea.
37
New cards
main function of the Ureters
* connects the kidney to the bladder
38
New cards
main function of the bladder
* The ***bladder*** is a muscular sac that stores urine. It expands when it is filled.
39
New cards
main function of the Urethra
* a tube leading from the bladder allowing urine to be released from the body.
\
\