Atmospheric pressure
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Define atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted by the atmosphere on the surface in contact with it
Atmospheric pressure and weather
Changes in pressure are linked to changes in weather. Low pressure brings clouds, rain and wind, while high pressure tends to bring dry, clear and calm conditions
Unit for pressure
N/m² = pascal (Pa)
Different units for pressure
Average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 101,325 pascals (Pa)
1hPa=100Pa
Millibars (mb) same as hPa. 1013.25mb=1013.25hPa
Inches of mercury (inHg)
1013.25hPa/1013.25mb = 29.92inHg
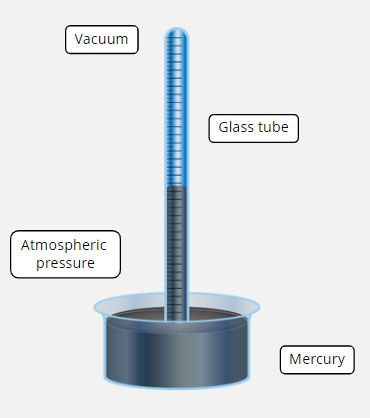
How does the mercury barometer work?
As atmospheric pressure increases, mercury is forced up inside the vacuum tube
As atmospheric pressure decreases, the mercury in the tube drops
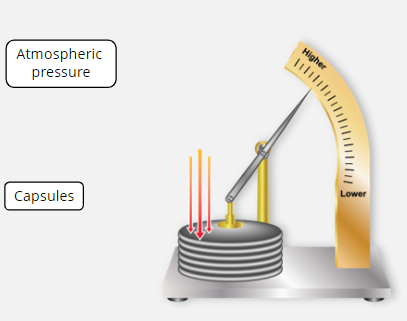
How does the aneroid barometer work?
It is a series of partially evacuated capsules. The higher number of capsules the higher the accuracy. As pressure increases, the capsules squeeze which moves the needle upwards
How does the altimeter work?
An altimeter is a barometer that shows an increase with height with a decrease in pressure and vice versa.

Relationship of pressure and height
As height increases, pressure decreases as there’s less mass above you
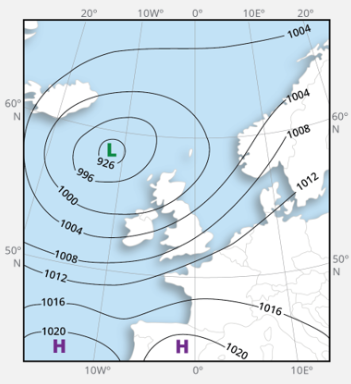
What are isobars?
These are lines showing the same atmospheric pressure on a surface pressure chart
when isobars are closer together, there’s a high pressure gradient, so strong winds (as wind is just air equalising the high and low pressure)
when further apart, there a low pressure gradient, so winds are weaker
Pressure and altitude relationship
High altitude low pressure
Low altitude high pressure
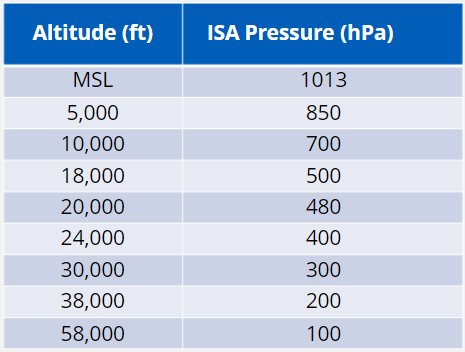
What are the ISA pressure values (hPa)?
MSL - 1013
5,000ft - 850
10,000ft - 700
18,000ft - 500
20,000ft - 480
24,000ft - 400
30,000ft - 300
38,000ft - 200
58,000ft - 100
What are the pressure lapse rate?
MSL - 27ft/hPa
20,000ft - 50ft/hPa
40,000ft - 100ft/hPa
How does temperature affect pressure?
Warm air
expands pressure levels
pressure falls slowly with height (because the atmosphere is less dense and expanded vertical so it’s gradual)
Cold air
compacts pressure levels
pressure falls rapidly with height (because the atmosphere is more dense and compact so it’s more quick)
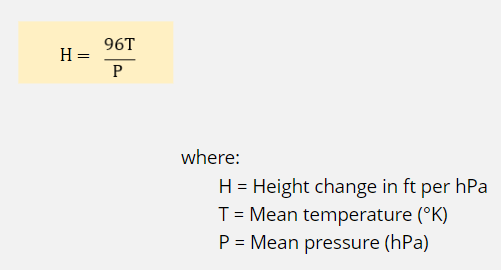
Calculating temperature lapse rate?
H = 96T/P