Exercise & Mechanisms Human Disease (Chapter 1 - Quiz 1 study guide)
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
Write at least two sentences about the contributions Claude Bernard made to science.
Claude Bernard introduced the concept of the internal environment, which later became the foundation of the concept of homeostasis. He was the first to clearly explain that living organisms survive by keeping their internal conditions stable, regardless of external changes.
Define Health in three words
Physical, mental, and social well-being
Give an example of how the definition of health could be criticized.
This definition can be criticized because different aspects of an individual's life, such as an individual being blind, may contradict this definition. Even though their overall health is completely fine and it’s just their site that is impacted. And an injury may create temporary problems in a specific area, but even so, their overall health is fine.
What is the definition of DISEASE?
Deviation from the normal state of homeostasis
Give an example of how the definition of disease could be criticized.
Because not every deviation means someone has a disease. Factors such as blood pressure and body temperature may fluctuate, but it doesn’t necessarily mean they have a disease. For example, someone who is pregnant may experience clear deviation from her previous state, such as lots of hormonal changes, but that does not mean she has a disease.
Student A says: “People should drink roughly 8 cups of water every day.”
Student B says: “People should consume an amount of water that is equivalent to roughly 8 cups per day.”
Reconcile the TWO STATEMENTS
Student A is suggesting that an individual should obtain their 8 cups of water through liquid water. While Student B is suggesting that roughly 8 cups of water can also be achieved through a combination of food and water.
Describe possible continuations of the conversation. You may want to re-read the section on normal limits (p. 2), and refer to the handy tables at the end of the textbook:
A physiologist was speaking with her mother’s nurse about lab results. The lab results indicate a blood sugar level of 145 mg/dL. The nurse says, “That’s a little high.” The physiologist says, “Maybe it’s not that simple.”
The physiologist may be referring to different factors that can interfere with this individual’s blood sugar levels. For example, this mother may be an older woman, and age can play a role in increased blood sugar even in healthy adults. Even though throughout the day older individuals can experience fluctuation in their blood sugar while doing exercises, body positions, and even emotions. Meaning, because several factors can establish an increase in blood sugar levels, this may not be too high for this specific individual.
What is hematocrit?
Hematocrit (HCT) indicates the percentage of erythrocytes in a specific volume of blood. The number of white blood cells (WBCs) is not significant in measuring the cell volume. Hematocrit can indicate fluid imbalance or anemia.
There are 7 steps to health. Name the first TWO (1 & 2)
Be a nonsmoker and avoid secondhand smoke
Eat 5 to 10 servings of vegetables and fruit a day. Choose high-fiber, lower-fat foods. Limit alcohol intake.
There are 7 steps to health. Name the NEXT TWO (3 & 4)
Be a nonsmoker and avoid secondhand smoke
Eat 5 to 10 servings of vegetables and fruit a day. Choose high-fiber, lower-fat foods. Limit alcohol intake.
PA on a regular basis
Protection from the sun
There are 7 steps to health. Name the NEXT TWO (5 & 6)
Be a nonsmoker and avoid secondhand smoke
Eat 5 to 10 servings of vegetables and fruit a day. Choose high-fiber, lower-fat foods. Limit alcohol intake.
PA on a regular basis
Protection from the sun
Follow cancer screening guidelines
Visit a doctor or dentist if there any changes in the normal state of health
There are 7 steps to health. Name the LAST ONE (#7)
Be a nonsmoker and avoid secondhand smoke
Eat 5 to 10 servings of vegetables and fruit a day. Choose high-fiber, lower-fat foods. Limit alcohol intake.
PA on a regular basis
Protection from the sun
Follow cancer screening guidelines
Visit a doctor or dentist if any changes in the normal state of health
Follow health and safety guidelines at home and at work when using, storing, and disposing of hazardous materials
PREVENTION can involve what four things?
Maintaining routine vaccination programs
Participation in screening programs
Community health programs
Regular routine doctor visits
DEFINE PREVENTION and use the word intervention in the definition (my definition)
The act of stopping something from happening or arising, often through early intervention or proactive measures designed to reduce risk or eliminate potential problems before they occur
What are the THREE levels of prevention?
Primary Prevention
Secondary Prevention
Tertiary Prevention
What happens in the first level of Prevention?: Primary Prevention
intervening before health effects occur, through measures such as vaccinations, altering risky behaviors and banning substances known to be associated with a disease or health condition
Give TWO examples of risky behaviors that will have to be eliminated during/practicing Primary Prevention
poor eating habits
tobacco use
What happens in the second level of Prevention?: Secondary Prevention
screening to identify diseases in the earliest stages, before the onset of signs and symptoms, through measures such as mammography and regular blood pressure testing.
What happens in the third level of Prevention?: Tertiary Prevention
Managing disease post-diagnosis to slow or stop disease progression through measures such as chemotherapy, rehabilitation, and screening for complications.
Define Iatrogenic
Slideshow definition: Error/ treatment/ procedure may cause the disease
Book definition: a treatment, a procedure, or an error may cause a disease, which is described as an iatrogenic
HINT:
Iatrogenic
I-am-in trouble
Genic- caused by
How would u describe iatrogenic disease to a friend or relative?
Iatrogenic means a health problem or complication is caused by medical treatment or a procedure
Give an example of a dose-response effect?
Alcohol:
Having a small dose of alcohol may make someone feel relaxed
A moderate dose can slow reaction time and impair judgment
A large dose can cause loss of coordination and unconsciousness
Dose-response effect: when something increases, it makes another thing increase
graph will go here (alcohol) for dose-response effect
where is the independent and dependent located on the Y and X axis
Dose-response effect: when something increases, it makes another thing increase
Contrast Primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention.
Primary Prevention: The goal is to protect healthy people from developing a disease or experiencing an injury in the first place
slide definition: intervening before health effects occur, through
measures such as vaccinations, altering risky behaviors (poor eating
habits, tobacco use) and banning substances known to be associated with a disease or health condition.
Secondary Prevention: Happens after an illness or serious risk factors have already been diagnosed. The goal is to halt or slow the progress of the disease (if possible) in its earliest stages
Slide definition: screening to identify diseases in the earliest
stages, before the onset of signs and symptoms, through measures such as mammography and regular blood pressure testing
Tertiary Prevention: managing disease post-diagnosis to slow or stop disease progression through measures such as chemotherapy, rehabilitation, and screening for complications.
Slide definition: This phase focuses on helping people manage complicated, long-term health problems such as diabetes, heart disease, cancer, and chronic musculoskeletal pain. The goals include preventing further physical deterioration and maximizing quality of life.
Fill in the blank:
Research findings that are determined to have merit after the lengthy three-stage research process are often referred to as ______
“evidence-based research findings”
A medical history includes questions on what?
Current and prior illnesses
Allergies
Hospitalizations
Treatment
Specific difficulties
Any type of therapy or drugs
- Prescription
- Nonprescription
- Herbal items, including food supplements
Current health status is particularly important and should include what?
Current symptoms
Recent illnesses
ongoing treatments
current medications
Changes in health and well-being
Define Epidemiology
The science of tracking the pattern occurrence of disease
Slide definition:
Tracking the pattern or occurrence of disease
Major data collection centers: WHO and CDC
Incidence versus prevalence
Hint:
Epi- epidemic
demos- people
ology- the study of
epidemiology= Study of disease patters in people
Define Etiology
Causative factors in a particular disease
Book definition: concerns the causative factors in a particular disease
Hint:
Etio= Cause
ology= The study of
etiology = the study of the cause
Etiology
What could these Causative factors be, name four.
• Inherited or genetic disorders
• Microorganisms
• Immunologic dysfunctions
• Metabolic, nutritional problems
What is the difference between Epidemiology and Etiology?
Epidemiology is the science of tracking the pattern occurrence of disease and Etiology is the Causative factors in a particular disease
Define Pathogenesis
Slide definition: The development of the disease
_________________________________________
Book definition: Refers to the development of the disease or the sequence of events involved in the tissue changes related to the specific disease process
Hint:
Patho- disease
genesis- the beginning or development of
What are the characteristics of the onset of a disease? (name 2)
Slide definition:
Sudden/acute
Insidious: gradual, vague or mild signs
______________________________________
Book definition (goes more in depth):
The onset of a disease may be sudden and obvious or acute (e.g., gastroenteritis, with vomiting, cramps, and diarrhea) or it may be insidious, best described as a gradual progression with only vague or very mild signs. Hepatitis may manifest quietly in this way. There may be several stages in the development of a single disease
What are the characteristics of an acute disease? (2)
Slide definition:
Short-term, develops quickly
High fever or severe pain
_____________________________
Book definition (more in-depth):
Indicates a short-term illness that develops quickly with marked signs such as high fever or severe pain (e.g., acute appendicitis)
What are the characteristics of a chronic disease?(2)
Slide definition:
Develops gradually
Milder symptoms, often intermitted with acute episodes
__________________________________________
Book definition (more in-depth): Often a milder condition that develops gradually but that persists for a long time and usually causes more permanent tissue damage, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Often a chronic disease is marked by intermittent acute episodes
What are the characteristics of the sub clinical state?
Exists in some conditions in which pathologic changes occur, but the patient exhibits no obvious manifestations (symptoms) perhaps because of the great reserve capacity of some organs. For example, kidney damage may progress to an advanced stage of renal failure before symptoms are manifested (symptoms).
HINT:
Pathologic changes: how your body physically responds to disease
The disease is present but silent. The person feels healthy and does not know anything is wrong. The disease is not yet severe enough to show outward symptoms
Characteristics of an initial latent or “silent” stage
In which no clinical signs are evident characterizes some diseases. In infectious diseases, this stage may be referred to as the incubation period, Which is the time between exposure to the micro organisms and the onset of signs or symptoms it may last for a day or so or maybe prolonged perhaps for days or weeks often the disease agent may be communicable during the incubation Period.
Hint:
INitial = INcubation
Easier definition:
The incubation period, which is the time between exposure to a pathogen (microorganisms) and the onset of signs & symptoms
What are the characteristics of the prodromal period?
Comprises the time in the early development of a disease when one is aware of a change in the body, but the signs are non-specific (e.g., fatigue, loss of appetite, or headache). A sense of feeling threatened often develops in the early stage of infections. Laboratory tests are negative during the prodromal period; thus, it is difficult to confirm a diagnosis.
HINT:
Pro- before
Drome- symptoms
ProDromal = Development
Easier definition:
The early development of a disease when a person notices vague symptoms. but the signs are non-specific and are hard to diagnose (LAB TESTS ARE NEGATIVE IN THIS STAGE)
What are the characteristics of the manifestations of a disease?
Are the clinical evidence or effects, the signs and symptoms, of disease. These manifestations, such as redness and swelling, may be local, found at the site of the problem. Or signs and symptoms may be systemic meaning they are general indicators of illness, such as fever.
Define SIGNS FOR DISEASES. (1)
Slide definition:
Objective indicators of disease
____________________________
Book definition (more in-depth):
Objective indicators of disease that are obvious to someone other than the affected individual. Signs can be either local, found at the site of the problem (such as a skin rash); or systemic, which are general indicators (such as a fever)
Define symptoms FOR A DISEASE? (1)
Slide definition:
Subjective feelings
____________________________________
Book definition (more in-depth):
Subjective feelings, such as pain or nausea both signs and symptoms are significant in diagnosing a particular problems
Define what a lesion is? (define) (1)
Slide definition:
Specific local change in the tissue
_____________________________
Book definition (more in-depth):Used to describe a specific local change in the tissue. Such a change may be microscopic, such as when liver cells are examined for pathologic change, or highly visible, such as a blister or pimple observed on the skin.
What is the definition of a syndrome (define)? (1)
Slide definition:
A collection of signs and symptoms
_______________________________________
Book definition (more in-depth): A collection of signs and symptoms often affecting more than one organ that usually occur together in response to a certain condition
What are diagnostic tests? (2)
Slide definition:
Various laboratory tests
Appropriate to manifestations and medical history
_________________________________________________
Book definition (more in-depth):Laboratory tests that assist in the diagnosis of a specific disease. The appropriate test are ordered based on the patient manifestations and medical history, the clinical examination, and the patients answers to specific questions. These test may also be used for monitoring the response to treatment or the progress of the disease. Such test may involve chemical analysis of body fluids, such as blood, examination of tissues and cells from specimens (e.g., biopsies or body secretions), identification of microorganisms in body, fluids, or tissue specimens, or radiologic examination of the body. It is important that medical laboratories have a quality assurance program in place to ensure accurate test results.
Characteristics of REMISSIONS and EXACERBATIONS.
May mark the course of progress of a disease. A remission is a period or condition in which the manifestations of the disease subside, either permanently or temporarily. An exacerbation is a worsening in the severity of the disease or in it signs/symptoms.
Define precipitating Factor (1)
Slide definition:
Condition that triggers an acute episode
____________________________________
Book definition (more in-depth): A condition that triggers an acute episode such as a seizure in an individual with a seizure disorder.
Define Predisposing Factor (1)
Slide definition:
Age, gender, inherited factors, environment, etc…
____________________________________________
Book definition (more in-depth):
Encompass the tendencies that promote development of a disease in an individual. And indicates a high risk for the disease but not certain development.
What is the difference between the precipitating factor and the predisposing factor? (contrast)
My personal CONTRAST:
Predisposing factor makes someone more likely to develop the condition over time (e.g., having a family history of Diabetes). And precipitating factor is the event or trigger that brings on the condition (e.g., experiencing extreme stress triggering a diabetic crisis)
Book definition (more in-depth):
Note that a precipitating factor differs from a pre-disposing factor for example of patient may be predisposed to a coronary artery disease and angina because of high cholesterol diet and angina attack can be precipitated by shoveling snow on a very cold day.
Define Complications
new secondary or additional problems
Define therapy or therapeutic interventions (what are they?)
treatment measures used to promote recovery or slow the progress of a disease. These measures may include surgery, drugs, physiotherapy, alternative therapy, or behavior modifications.
What is a sequelae?
The potential unwanted outcomes of the primary condition such as paralysis following recovery from a stroke
_______________________________________
Another defintion: long term, permanent outcomes, or after effects that result from a disease, injury or infection
What is CONVALESCENCE (con-vuh-lah-sense) or REHABILITATION?
The period of recovery and return to the normal healthy state it may last for several days or months
define MORBIDITY
→
←
Slide definition:
Disease rates within a group
_____________________________
Book definition (more in-depth):
Indicates the disease rates within a group. This term is sometimes used to indicate the functional impairment that certain conditions such as a stroke caused within a population.
HINT:
Morbid = illness or disease
ity= state or condition
Morbidity= d = disease
How many people are sick
Define MORTALITY
Slide definition:
Relative number of deaths resulting from the disease
__________________________________________
Book definition (more in-depth):
Indicate the relative number of deaths resulting from a particular disease
HINT: mortality → Eternity
(No one lives for eternity = death)
define PROGNOSIS
My definition:
The predicted future of a patient’s condition, including the likelihood of recovery, potential complications, and overall outlook for health
____________________________________________________
Book definition (more in-depth):
Defined the probability or likelihood for recovery or other outcomes the probability figures used and prognosis are based on average outcomes, and there may be considerable variation among affected individuals. It is important to consider the basis of the statistics used to form such conclusions.
Define Epidemics?
Slide definition:
a sudden increase in the number of cases of a disease above what is normally expected in a specific population or area
__________________________________________
Book definition (more in-depth): Occur when there are higher than expected number of cases of an infectious disease within a given area, whereas pandemics involve higher numbers of cases of many regions of the globe influenza may occur sporadically, as well as in epidemic or pandemic outbreaks.
Define Prevalence
The TOTAL NUMBER of cases (both old and existing) of a disease or condition in a specific population at a given time
Hint: Prevalence = Present + Past = TOTAL
existing cases + old cases= TOTAL
Define Incidence
The number of new cases of a disease or condition that develops in a specific population during a specific time period
Hint: new cases only
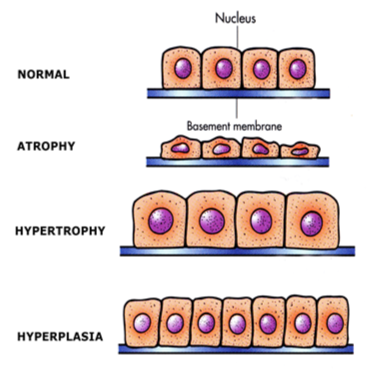
Cellular Adaptations:
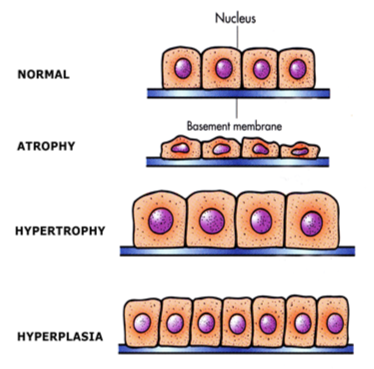
Define Atrophy (2)
Decrease in the size of cells
Results in reduced tissue mass
_____________
Hint: Atrophy - A decrease
Cellular Adaptations:
Define Hypertrophy (2)
Increase in cell size
results in enlarged tissue mass
_____________________
Hint:
Hypertrophy = Hyper = Alot = BIGGER
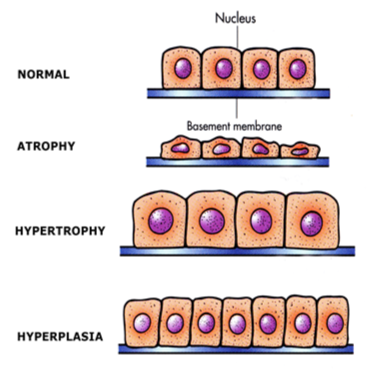
Cellular Adaptations:
Define Hyperplasia (2)
Increased number of cells
results in enlarged tissue mass
_______________________
Hint:
Hyperplasia
Hyper = A lot= BIGGER
Plasia = Plenty = Plenty number of cells
Cell damage:
Define Apoptosis (2)
Refers to programmed cell death
Normal occurrence in the body
Hint:
Apoptosis= programmed
Cell damage:
Define Ischemia (1)
Deficit of oxygen in the cells
Hint:
Ischemia = Ish-can’t-breathe-ia
cells are starving for oxygen and can’t breathe properly
Cell damage:
Define Hypoxia (2)
Reduced oxygen in tissues
Nutritional deficits
Hint:
Hypo=low
oxia=oxygen
Cell damage:
Define Pyroptosis (1)
Results in lysis causing nearby inflammation
_________________________________
Hint:
Pyro= fiery → inflammation
Necrosis:
Define Necrosis (1)
Dying cells cause further cell damage due to cellular disintegration
Hint:
Necro = Death
NeCrosis= Cells
Necrosis:
Define Liquefaction Necrosis (1)
Dead cells liquefy because of release of cell enzymes
Necrosis:
Define Coagulative Necrosis (1)
Cell proteins are altered or denatured — coagulation
Necrosis:
Define Infarction (1)
Area of dead cells as a result of oxygen deprivation
___________________________
Hint:
Infarction = area of dead cells
Necrosis:
Define Gangrene (1)
Area of necrotic tissue that has been invaded by bacteria
Define AUTOPSY or POSTMORTEM EXAMINATION
Examination of the body and organs after death
_________________________________________
May be performed after death to determine the exact cause of death or the course of the illness and effectiveness of treatment. An autopsy is an examination of all or part of the body by a pathologist. It includes gross and microscopic examination of tissues, organs, and fluids, and can include a variety of tests depending on individual circumstances
Characteristics of the occurrence of a disease (how to track it)?
Tracked by recording two factors: the incidence and the prevalence. The incidence of a disease indicates the number of new cases in a given population noted with an estimate of time. A significant increase or decrease in incidence of a specific disease may be analyzed to determine the responsible factors. Prevalence refers to the number of new or old existing cases with a specific population and time period
HINT:
Incidence sounds like “incident” → something just happened
incidents = incoming cases with an estimated time
Prevalence = Irrelevant
based on old cases and some new too
Define COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
Are infections that can be spread from one person to another. Some of these must be reported to health authorities.
Hint;
communicable=communicate = talk to one another aka can spread to one another
Characteristics of notifiable or reportable diseases
Must be reported by the physician to certain designated authorities. The authority varies with the local jurisdiction. The specific diseases required to be reported may change overtime. The requirement of reporting is intended to prevent further spread of the disease and maintain public health. Infections such as measles, severe acute respiratory syndrome, and human immunodeficiency virus may be included in some jurisdictions
How many STAGES ARE IN THE RESEARCH PROCESS?
Three (3)
What is (Stage 1) of the research process?
“Basic science” and following the scientific method
Identification of technology to be used
Work done in the laboratory
Might require animal or cell/tissue cultures
What is (stage 2) of the research process?
Small number of human subjects
What is (stage 3) of the research process? (2)
Clinical trials —- a large number of patients with the disease or risk of the disease
“Double-blind studies”
What does “evidence based” mean?
means using the best proof from research and facts to make decisions, instead of just guessing or doing things because “that’s how it’s always been done.”
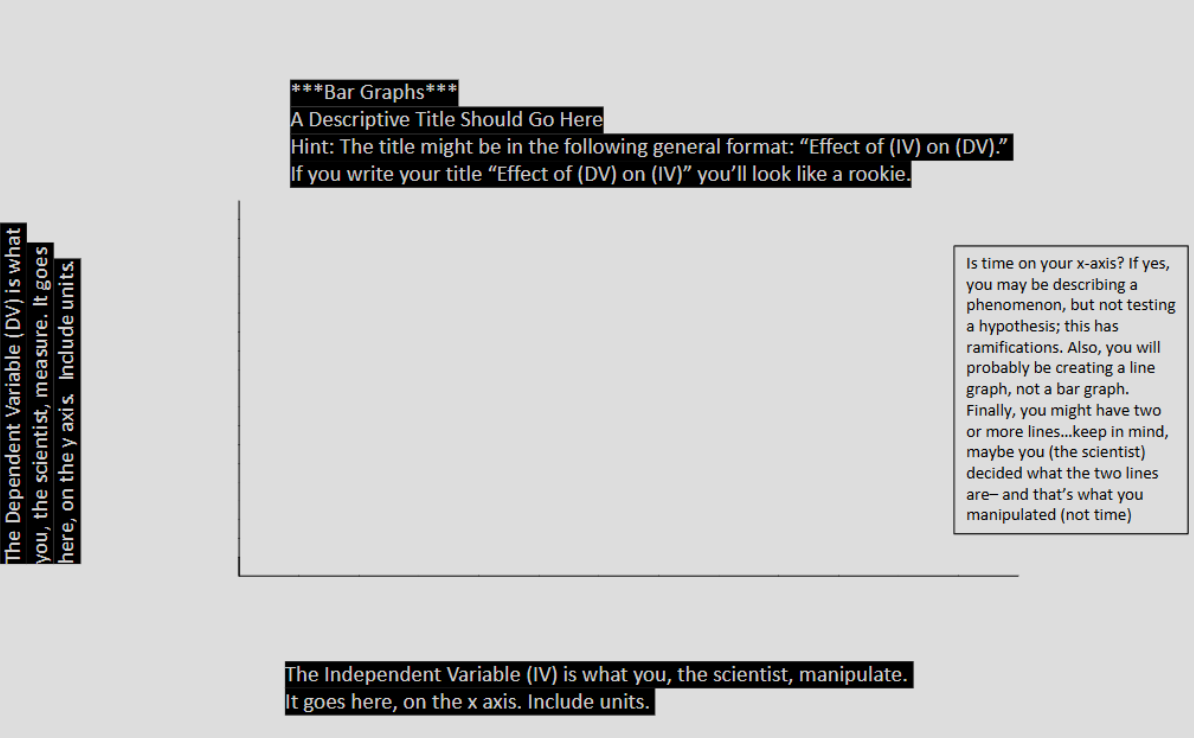
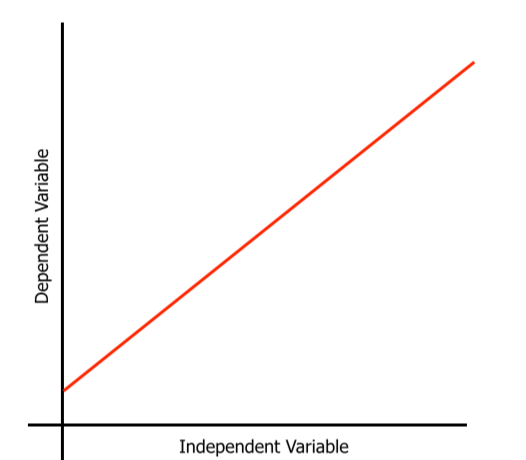
Experiment: Distance from Light Source vs. Plant Group
Explain what the independent and dependent variables would be
If it would go up or down
Explain how this experiment would go and the units involved
Independent variable: Distance from light source (e.g., 5cm, 10cm, 20cm, 25cm)
Dependent variable: Average plant height (cm) after 10 days (e.g., 12.5cm, 10.2cm, 8.1cm, 6.0cm, 4.3cm)
CHAPTER 2
Almost there! KEEP GOING!
What is the major component of the body?
WATER
Where is water found in the body?
Found within and outside the cells
Define Fluid intake
Ingestion of solid food or fluids
Name 4 types of Fluid loss
Urine, feces, perspiration, exhaled air
Name FIVE things that the water is responsible for.
From slide:
Essential to homeostasis
Place for metabolic reactions
Transportation system for the body
Essential for cell survival
Facilitates movements of body parts
____________________________________
From Book (just more in-depth):
Essential to homeostasis, which is the maintenance of a relatively constant and favorable environment for cells
The medium within which metabolic reactions and other processes take place
Transportation system for the body (H2O carries nutrients into cell, removes wastes, transports enzymes in digestive secretions, and moves blood cells around the body)
Essential for cell survival (without adequate fluid, cells can not properly function → death)
Facilitates movement of body parts (e.g., joints & lungs)
What is the Percentage (%) of body water (total) for males, women, elderly women, and infants
Male - 60% (healthy adult male)
Women - 50%
Elderly women- 45% (due to fat/low reserves)
Infant - 70%
Define Intracellular compartment aka intracellular fluid (ICF)
Fluid inside the cells
What percentage (%) of intracellular fluid(ICF) does males, females, and infants have?
Female - 33%
Male - 40%
Infant - 40%
Define Extracellular compartment aka Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Fluid outside of the cell
What percentage (%) of Extracellular fluid(ECF) does males, females, and infants have?
Female- 17%
Male- 20%
Infant- 30%
What FOUR substances does Extracellular Fluid (ECF) include?
Intravascular fluid (IVF)
Interstitial fluid (ISF)
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) (suh-re-brul-spinal)
Transcellular fluids (e.g., synovial fluid)
What’s another word for……
Intravascular fluid and interstitial fluid
Intravascular fluid = BLOOD
Interstitial fluid = INTERCELLULAR FLUID
Transcellular fluids present in various secretions, such as what? (2)
such as those in the….
Pericardial (heart) cavity
Synovial cavities of the joints
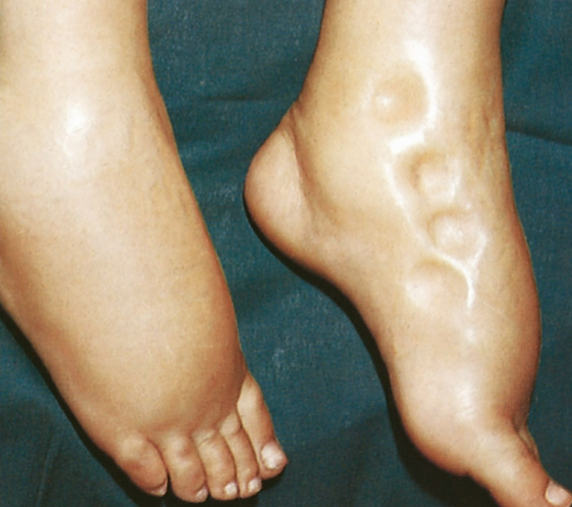
Edema refers to an excessive amount of fluid that occurs in what fluid compartment?
Interstitial Compartment
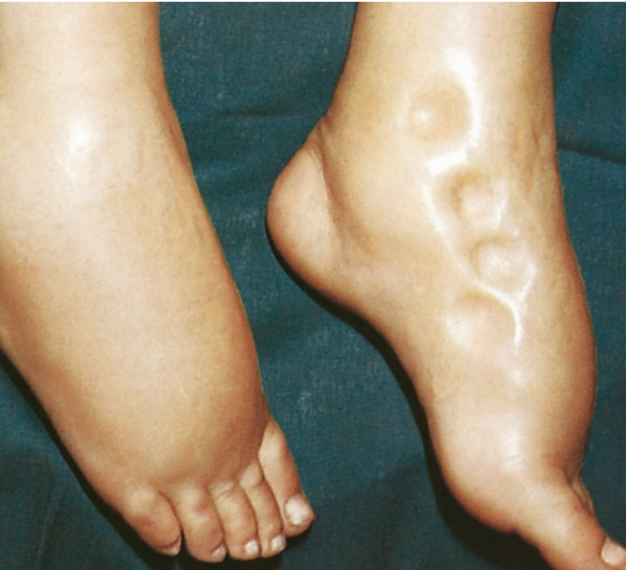
Name FOUR things that Edema does to the body.
Causes swelling or enlargement of tissue
May be localized or throughout the body
May impair tissue perfusion
May trap drugs in the interstitial fluid (ISF)
Even though edema may trap drugs in the interstitial fluid (ISF), do we want drugs in the ISF?
YES, because that where most body cells are located and where it can reach its target receptors!
What are the FOUR general causes of EDEMA?
Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
loss of plasma proteins (albumin)
Obstruction of the lymphatic circulation
Increased capillary permeability
Edema
What is caused by “increased capillary hydrostatic pressure?” (3)
Caused by higher blood pressure or increased blood volume
Forces increased fluid out of capillaries into interstitial fluid (ISF) of tissue
Can cause pulmonary edema
What are the THREE effects of EDEMA?
Swelling - local area
Pitting edema
Inc. in body weight