L30 Introduction to Immunology and the Immune System
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts from the Introduction to Immunology and the Immune System lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Immunology
The study of an organism’s immune system in health and disease.
Immune System
An organised system of organs, cells and molecules that interact together to defend the body against disease (pathogens)
Disease examples
Infectious= HIV, influenza, malraia. Inflammatory= Alergy, lupus, diabetes. Cancer.
Microbes
Viruses, Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoa. Some are pathogens.
Primary and secondary lymphoid organs
Primary: production of white blood cells (lymphocytes); Secondary: sites where immune responses are initiated
Primary lymphoid organs
Thymus, bone marrow.
Thymus
‘School’ for white blood cells called T cells; developing T cells learn not to react to self. As we age this disapears because autoimmune system.
Bone marrow
Source of stem cells that develop into cells of the innate and adaptive immune responses
Secondary lymphoid organs
Spleen, lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes
Located along lymphatic vessels; Lymph fluid from blood and tissue is filtered; Site of initiation of immune responses
Spleen
Site of initiation for immune responses against blood-borne pathogens (filters blood).
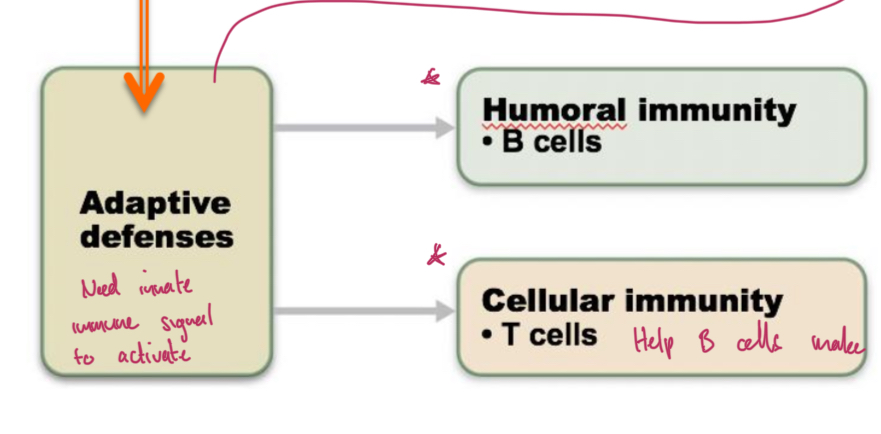
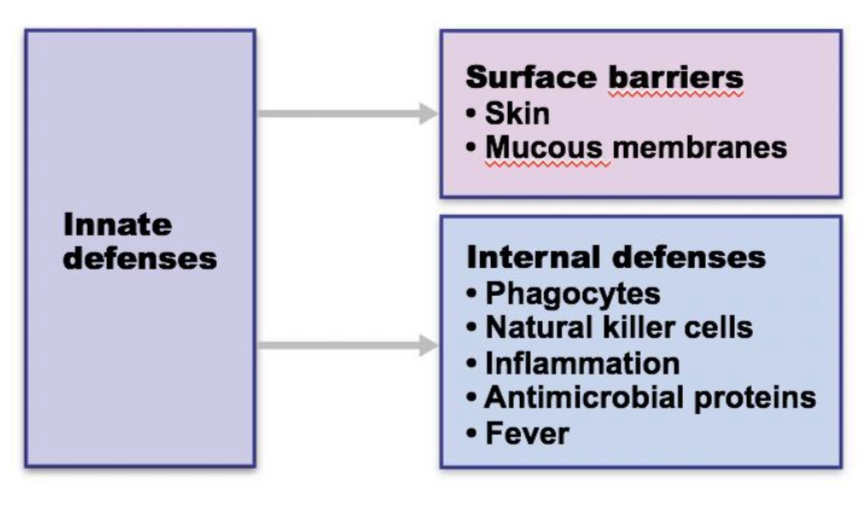
3 layers of defense
chemical and physical barriers, innate, and adaptive.
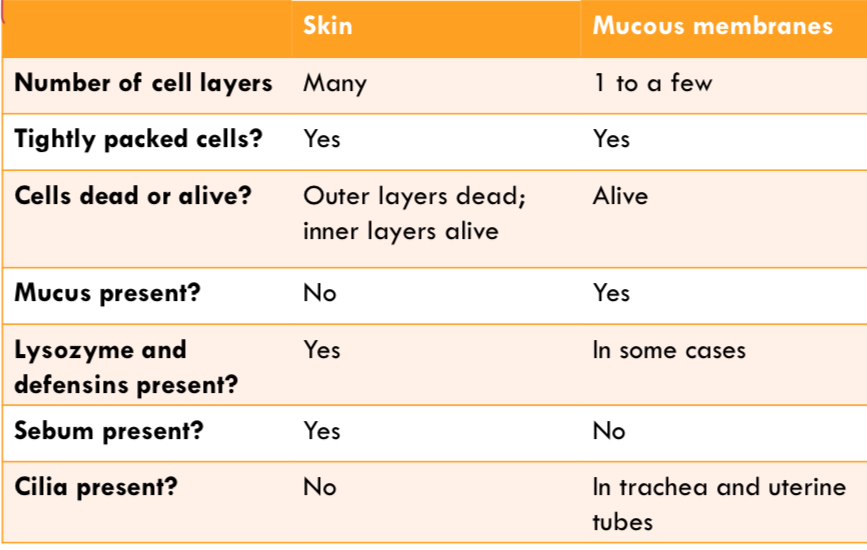
Epidermis
Dead cells, keratin and phagocytic immune cells (thin outer layer).
Dermis
Thick layer of connective tissue, collagen and blood vessels and phagocytic immune cells
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) or skins defensins
Forms pores in microbial cell membranes. Lysozyme (breaks down bacterial cell walls= cell death). Sebum (low pH), Salt (hypertonic). Making a hostile environment for pathogen.
Mucosal membranes
Line inside of body exposed to outside, 1-2 layers.
The mucociliary escelator
Cilia line epithelium, and move in tandem to move mucus containing microbe before it does harm. Thats why we cough up mucus.
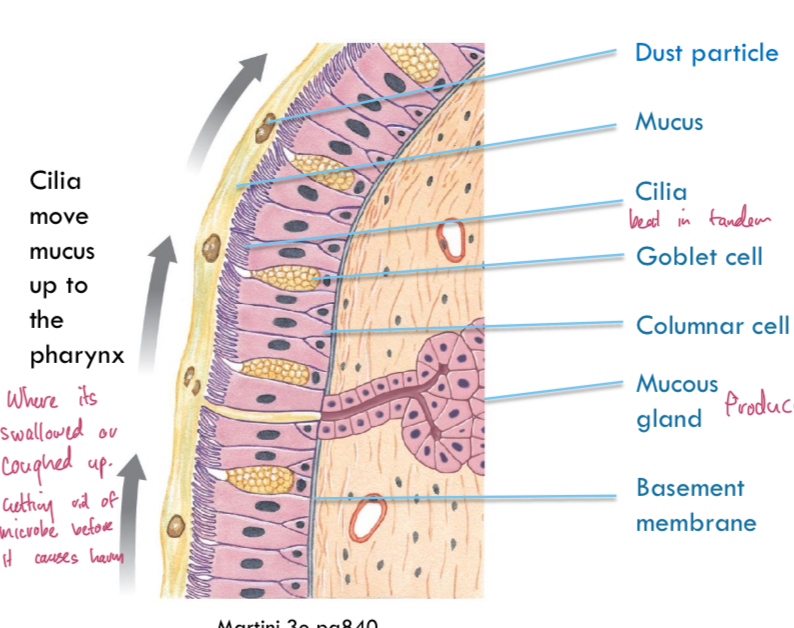
Epithelium
Tightly packed live cells, constantly renewed, mucus-producing goblet cells
Chemical defensins of mucosal surfaces
Stomach- low pH, gall bladder- bile, intestine- digestive enzymes (break down microbes), mucus (contains defensins and lysozymes), (tears, urine) flush out.
Skin vs mucous membranes
Innate immunity
Already in place, Rapid (hours), Fixed, Limited specificities, Has no specific memory
Adaptive immunity
Improves during the response, Slow (days to weeks), Variable, Highly specific, Has long-term specific memory