BI380: Chapter 7 - Ocean Chemistry
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Key Concept 1
Water is a powerful solvent. The concentration of dissolved inorganic solids in water is its salinity.
Key Concept 2
Though salinity may vary with location, the ratio of dissolved solids and seawater is constant
Key Concept 3
Gases dissolve in seawater. Cold water can hold more gas in solution than warm water (why colder water is more nutrient rich)
Key Concept 4
The ocean is a vast reservoir of carbon. The dynamics of carbon exchange between ocean at atmosphere affect Earth's climate
Key Concept 5
The ocean's acid-base (pH) balance varies with depth and dissolved components. Carbonate chemistry serves to serves to moderate (buffer) wide swings in oceanic pH.
hydrologic cycle
The cycle through which water in the hydrosphere moves; includes such processes as evaporation, precipitation, and surface and groundwater runoff
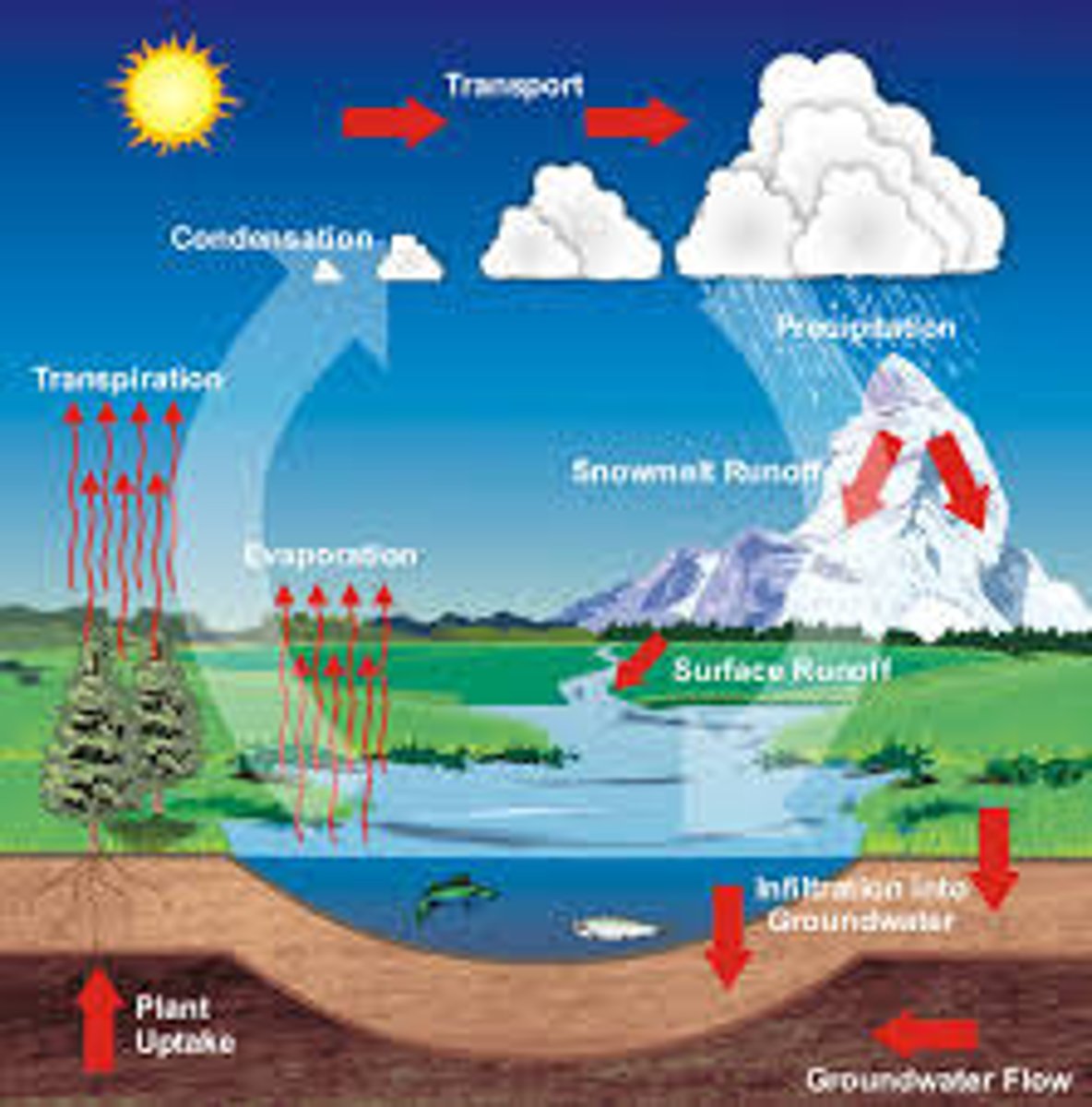
Vast majority of the Earth's water is where?
On the Earth's surface (97.5% in the ocean)
solution
made of two components: the solvent and solute
solvent
usually a liquid and more abundant than constituent
solute
usually a dissolved solid or gas (less abundant)
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined (like sand and water)
ion
at atom or small group of atoms that has an unbalanced electrical charge
Salinity
The total amount of dissolved salts in a water sample. (ocean's salinity varies from 3.3% to 3.7%)
Heat capacity of water decreases with increasing salinity
(less heat is necessary to raise the temp of seawater by 1 degree than is required to raise the temp of freshwater by the same amount)
Salinity increases
freezing point of water decreases (salt acts as an antifreeze)
Which evaporates faster, seawater or fresh water?
Fresh water. Sea water lingers longer because the dissolved salts tend to attract water molecules
colligative properties
properties of a solution that depend only on the number of particles dissolved in it, not the properties of the particles themselves. The main ones are boiling point elevation and freezing point depression.

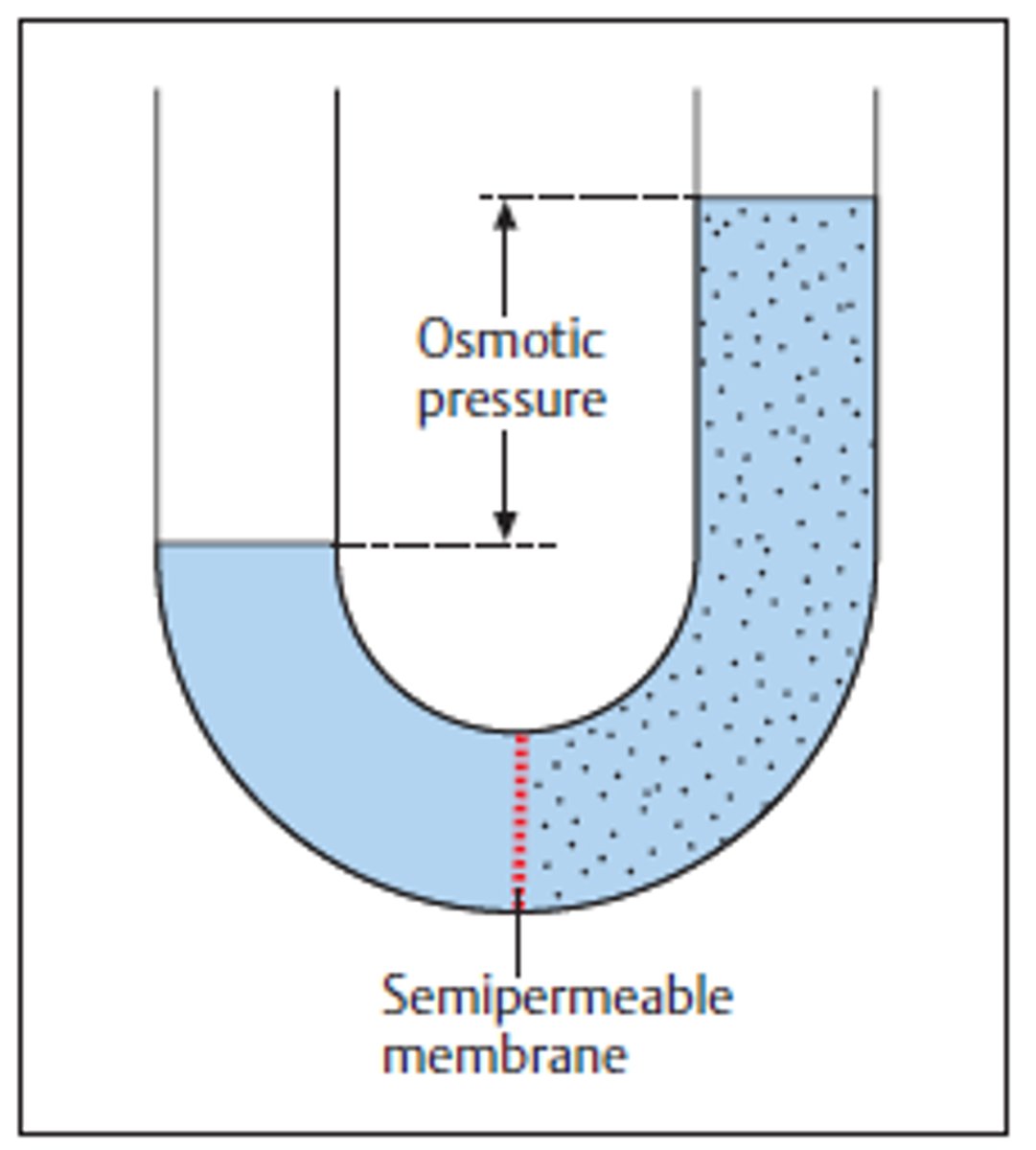
osmotic pressure
the pressure exerted on a biological membrane when the salinity of the environment is different from that within cells, rises with increasing salinity
trace elements
elements present in amounts less than 0.001 (1 ppm)
excess volatiles
components of ocean water whose proportions are not accounted for by the weathering of surface rocks
Deeply trapped volatile substances escape to the exterior by
the movement of tectonic plates, outgassing through volcanoes and rift vents
What are some examples of excess volatiles?
carbon dioxide, chlorine , sulfur, hydrogen, fluorine, nitrogen and water vapor
Forchhammer's Principle
The constant proportion of solids or salts in seawater, aka principle of constant proportions
Salinity is calculated by seawater's
conductivity (measure of the water's ability for electrical currents to pass through)
What are some elements present in the ocean?
Bicarbonate, calcium, sulfate, sodium, magnesium, chloride, Hydrogen, carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid
salinometer
An electronic device that determines salinity by measuring the electrical conductivity of a seawater sample.
residence time
average length of time an atom of an element spends in the ocean
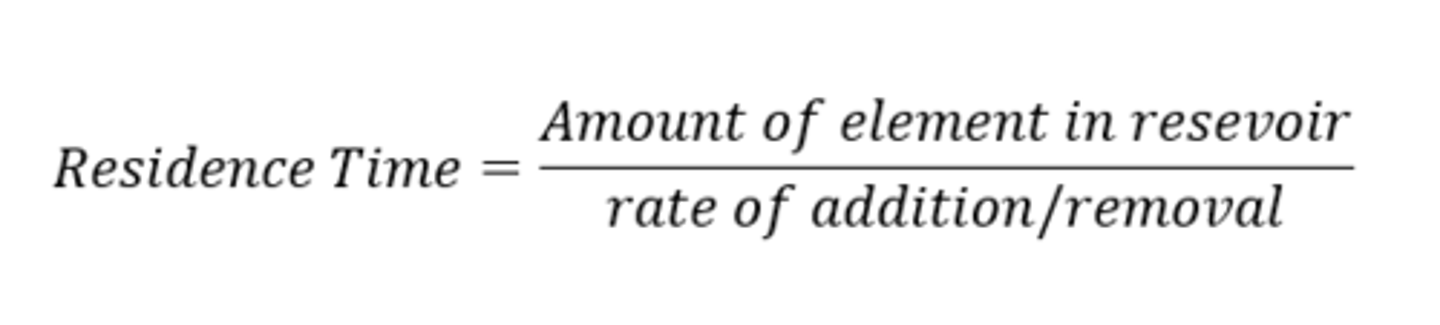
conservative constituents
seawater constituents that occur in constant proportion or change very slowly through time, long residence times
nonconservative constituents
substances dissolved in seawater that are ties to biological or seasonal cycles or to very short geological cycles (short residence times)
ex. dissolved oxygen, co2, silica and calcium compounds
What is the most abundant gas dissolved in sea water?
Nitrogen (48% of dissolved gas in seawater in nitrogen)
What do living organisms use nitrogen for?
use it to build proteins and other important chemicals
How much oxygen is dissolved in the ocean?
36%
The ocean is a vast carbon reservoir
CO2 combines chemically with water to form a weak acid; water can hold a thousands times more co2 than either nitrogen or oxygen
Gas concentration vary with depth
As oxygen decreases in water, CO2 increases and vice versa
Acid
substance that releases a hydrogen ion in solution
base
substance that combines with a hydrogen ion in a solution
alkaline solution
solution containing a base
pH scale
measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
Buffer
compound that prevents sharp, sudden changes in pH;
rivers and lakes have a much smaller buffering capacity
What is the average pH of seawater
8, with bicarbonate ion being most prevalent
The ocean serves as a natural sink for excess CO2
about 25% of the CO2 emitted by human activity in 2000-2006 was taken up by the ocean
Increasing acidity decreases the concentration of calcium carbonate in the water
this makes it hard for construction of some hard parts (shells, skeletons, rigid coverings)
What would be affected by the loss of coral reefs?
loss of species diversity; people; infrastrcuture; lagoon and marine ecosystems; mangrove forests; fisheries; aquaculture operations; tourism and many more