THE STRUCTURAL LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION AND MAJOR DIVISIONS OF THE BODY
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Anatomy
Study of the structure of body parts and their relationship to one another
Physiology
Study of the function of body parts; how they work to carry out life-sustaining activities
Gross/macroscopic anatomy
The study of large, visible structures. Ex. kidney, brain, heart
Regional anatomy
Looks at all structures in a particular area of the body
System anatomy
Looks at just one system. Ex. Nervous, cardiovascular
Surface anatomy
Looks at internal structures as they relate to overlaying skin (what’s under the skin)
Microscopic anatomy
Structures too small to be seen by the naked eye (need a microscope)
Developmental anatomy
Studies anatomical and physiological development throughout life. Ex, bones changing as you grow
Chemical level
Atoms, molecules and organelles (most basic form of life)
Cellular level
Single cell
Tissue level
Groups of similar cells
Organ level
Two or more types of tissues
Organ system level
Organs that work together
Organismal level
All organ systems combined to make the whole organism
Body has 5 survival needs
Nutrients
Oxygen
Water
Normal body temperature
Atmospheric pressure
Homeostasis
Is the maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions despite continuous changes in the environment
Receptor(sensor)
Monitors environment
Respond to stimuli (things that cause changes in controlled variables)
Control center
determines set point at which variable is maintained
Receives input from receptors
Determines appropriate response
Effector
Receives output from control center
Provides the means to respond
Response either reduces stimulus(negative feedback) or enhances stimulus(positive feedback)
Negative feedback
most used feedback mechanisms
Reduces or shuts off original stimulus
Ex. Regulating body temperature
Positive feedback
Enhances or exaggerates the original stimulus
Ex. Enhancement of labor contractions
Anatomical position
Standing straight, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward with thumbs pointing away
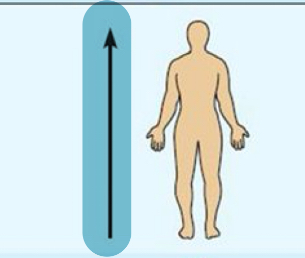
Superior(cranial)
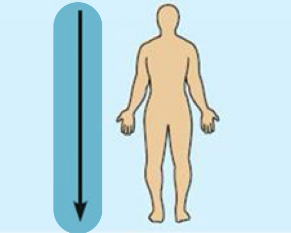
Inferior(caudal)
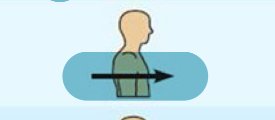
Anterior(Ventral)
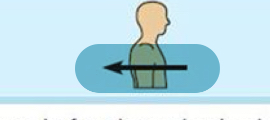
Posterior(dorsal)
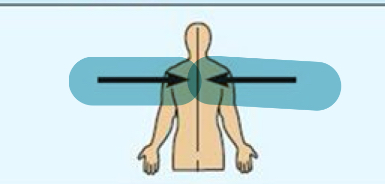
Medial
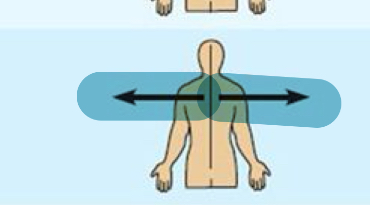
Lateral
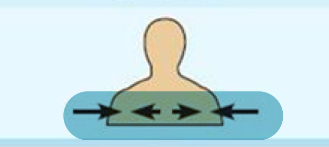
Intermediate
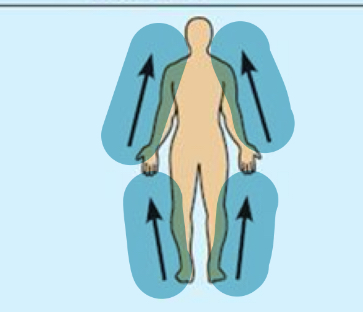
Proximal
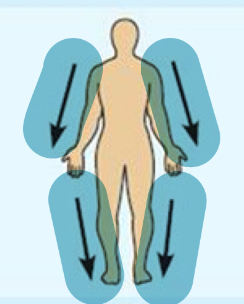
Distal
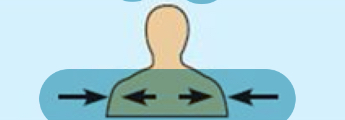
Towards or at body surface
Superficial(external)
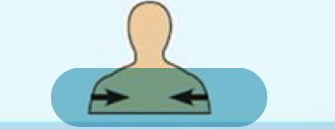
Away from the body surface;more internal
Deep(internal)
Axial
Head, neck, and trunk
Appendicular
Limbs
Sagittal plane
Divides body into left and right parts
Midsagittal (median) plane
Straight through the middle on midline
Parasagittal plane
Cut was off-center, not on midline
Frontal (coronal) plane
Decides body vertically into anterior and posterior parts (front and back)
Transverse (horizontal) plane
Divides into superior and inferior parts
Dorsal body cavity
Protects brain and spinal cord. Two subdivisions, cranial and vertebral cavities
Cranial cavity
Encase brain
Vertebral cavity
Encases spinal cord
Ventral body cavity
Houses the internal organs (collectively called viscera). Two subdivisions separated by diaphragm
Thoracic cavity
Two pleural cavities, one for each lung
Mediastinum
Contains pericardial(enclose heart) cavity. Surrounds other thoracic organs, like esophagus, trachea, etc
Abdominopelvic cavity
Abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
Abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver
Pelvic cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
Serosa (serous membrane)
Thin, double layered membrane that covers surfaces in ventral body cavity
Parietal serosa
On the outside. Lines internal body cavity walls
Visceral serosa
Inside, touching. Covers internal organs (viscera).
Serous fluid
Fluid secreted by both layers of membrane
Right upper quadrant
Gallbladder, liver, etc.
Left upper quadrant
Stomach, spleen, pancreas, etc.
Right lower quadrant
Appendix, cecum, etc.
Left lower quadrant
Part of small and large intestine, etc