Energy Profile Diagrams & Catalysts
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
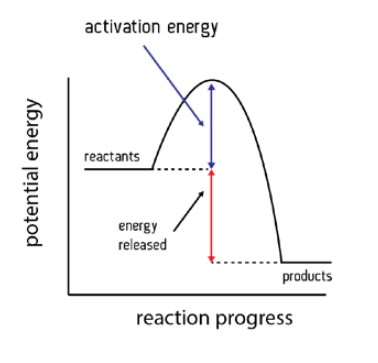
Explain the energy profile diagram for an exothermic reaction.
In an exothermic reaction, the reactants lose energy and heat is given out to the surroundings.
The enthalpy of the reactants is greater than the enthalpy of the products ∴ ΔH is negative.
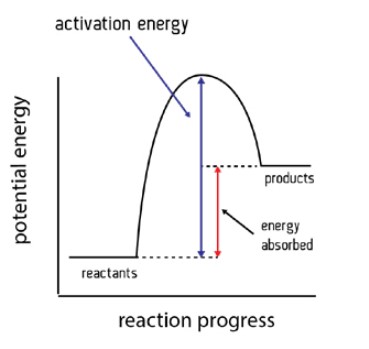
Explain the energy profile diagram for an endothermic reaction.
For an endothermic reaction, heat is taken in from the surroundings.
The enthalpy of the products is greater than the enthalpy of the reactants ∴ ΔH is positive.
What is a catalyst?
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the process.
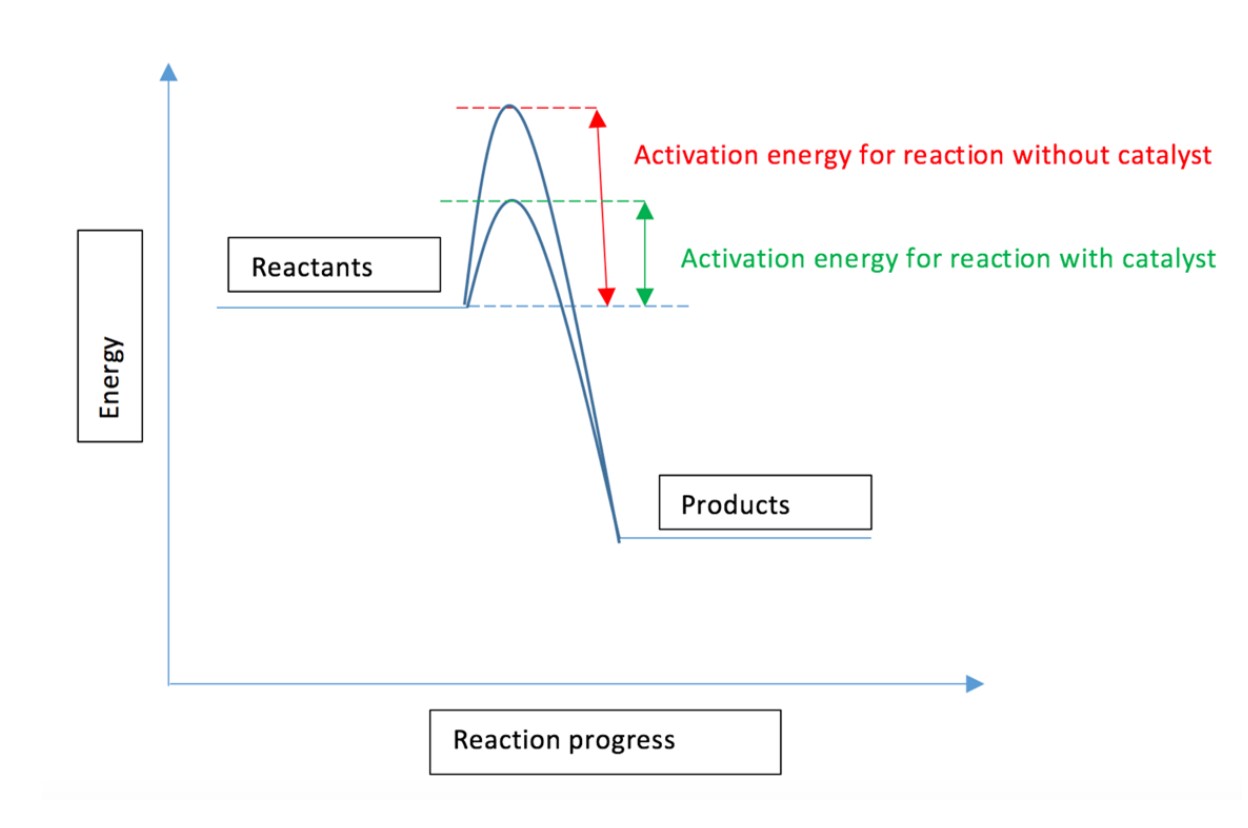
How does a catalyst affect the rate of a reaction?
A catalyst provides an alternative route for lower activation energy.
If the activation energy is lower, more particles will have that activation energy, so that the reaction will be faster.
State the 2 types of catalysts.
Heterogenous catalysts.
Homogenous catalysts.
What is a heterogenous catalyst?
A catalyst that has a different physical state (phase) to the reactants.
How does a heterogenous catalyst work?
Usually, reactant molecules are in the gaseous phase and the catalyst is in the solid phase (many are transition metals).
Gases are adsorbed onto the metal surface of the catalyst and the reaction takes place.
Products are desorbed (released) from the surface of the catalyst.
What is a homogenous catalyst?
A catalyst that has the same physical state (phase) to the reactants.
How does a homogenous catalyst work?
The catalyst reacts with the reactants to form an intermediate.
The intermediate reacts again and the catalyst is regenerated.
Outline the economic benefits of using catalysts in industrial processes.
Catalyst use lowers production costs:
Allows for the reaction to take place at a lower temperature and pressures, which decreases energy demands.
Allows more product to be formed in less time.
Outline the environmental benefits of using catalysts in industrial processes.
Catalyst use makes industrial processes more sustainable:
If industrial processes can operate at lower temperatures and pressures, less fossil fuels have to be burned and CO2 emissions are reduced.
Catalyst use reduces waste production:
Using catalysts improves the atom economy of the reaction hence producing less unwanted by-products.